vedo.shapes
Submodule to generate simple and complex geometric shapes
1#!/usr/bin/env python3 2# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3import os 4from typing import List, Union, Any 5from functools import lru_cache 6from weakref import ref as weak_ref_to 7 8import numpy as np 9import vedo.vtkclasses as vtki 10 11import vedo 12from vedo import settings 13from vedo.transformations import LinearTransform, pol2cart, cart2spher, spher2cart 14from vedo.colors import cmaps_names, get_color, printc 15from vedo import utils 16from vedo.pointcloud import Points, merge 17from vedo.mesh import Mesh 18from vedo.image import Image 19 20__docformat__ = "google" 21 22__doc__ = """ 23Submodule to generate simple and complex geometric shapes 24 25 26""" 27 28__all__ = [ 29 "Marker", 30 "Line", 31 "DashedLine", 32 "RoundedLine", 33 "Tube", 34 "Tubes", 35 "ThickTube", 36 "Lines", 37 "Spline", 38 "KSpline", 39 "CSpline", 40 "Bezier", 41 "Brace", 42 "NormalLines", 43 "Ribbon", 44 "Arrow", 45 "Arrows", 46 "Arrow2D", 47 "Arrows2D", 48 "FlatArrow", 49 "Polygon", 50 "Triangle", 51 "Rectangle", 52 "Disc", 53 "Circle", 54 "GeoCircle", 55 "Arc", 56 "Star", 57 "Star3D", 58 "Cross3D", 59 "IcoSphere", 60 "Sphere", 61 "Spheres", 62 "Earth", 63 "Ellipsoid", 64 "Grid", 65 "TessellatedBox", 66 "Plane", 67 "Box", 68 "Cube", 69 "Spring", 70 "Cylinder", 71 "Cone", 72 "Pyramid", 73 "Torus", 74 "Paraboloid", 75 "Hyperboloid", 76 "TextBase", 77 "Text3D", 78 "Text2D", 79 "CornerAnnotation", 80 "Latex", 81 "Glyph", 82 "Tensors", 83 "ParametricShape", 84 "ConvexHull", 85 "VedoLogo", 86] 87 88############################################## 89_reps = ( 90 (":nabla", "∇"), 91 (":inf", "∞"), 92 (":rightarrow", "→"), 93 (":leftarrow", "←"), 94 (":partial", "∂"), 95 (":sqrt", "√"), 96 (":approx", "≈"), 97 (":neq", "≠"), 98 (":leq", "≤"), 99 (":geq", "≥"), 100 (":foreach", "∀"), 101 (":permille", "‰"), 102 (":euro", "€"), 103 (":dot", "·"), 104 (":int", "∫"), 105 (":pm", "±"), 106 (":times", "×"), 107 (":Gamma", "Γ"), 108 (":Delta", "Δ"), 109 (":Theta", "Θ"), 110 (":Lambda", "Λ"), 111 (":Pi", "Π"), 112 (":Sigma", "Σ"), 113 (":Phi", "Φ"), 114 (":Chi", "X"), 115 (":Xi", "Ξ"), 116 (":Psi", "Ψ"), 117 (":Omega", "Ω"), 118 (":alpha", "α"), 119 (":beta", "β"), 120 (":gamma", "γ"), 121 (":delta", "δ"), 122 (":epsilon", "ε"), 123 (":zeta", "ζ"), 124 (":eta", "η"), 125 (":theta", "θ"), 126 (":kappa", "κ"), 127 (":lambda", "λ"), 128 (":mu", "μ"), 129 (":lowerxi", "ξ"), 130 (":nu", "ν"), 131 (":pi", "π"), 132 (":rho", "ρ"), 133 (":sigma", "σ"), 134 (":tau", "τ"), 135 (":varphi", "φ"), 136 (":phi", "φ"), 137 (":chi", "χ"), 138 (":psi", "ψ"), 139 (":omega", "ω"), 140 (":circ", "°"), 141 (":onehalf", "½"), 142 (":onefourth", "¼"), 143 (":threefourths", "¾"), 144 (":^1", "¹"), 145 (":^2", "²"), 146 (":^3", "³"), 147 (":,", "~"), 148) 149 150 151######################################################################## 152class Glyph(Mesh): 153 """ 154 At each vertex of a mesh, another mesh, i.e. a "glyph", is shown with 155 various orientation options and coloring. 156 157 The input can also be a simple list of 2D or 3D coordinates. 158 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the orientation 159 vectors in `orientation_array`. 160 """ 161 162 def __init__( 163 self, 164 mesh, 165 glyph, 166 orientation_array=None, 167 scale_by_scalar=False, 168 scale_by_vector_size=False, 169 scale_by_vector_components=False, 170 color_by_scalar=False, 171 color_by_vector_size=False, 172 c="k8", 173 alpha=1.0, 174 ) -> None: 175 """ 176 Arguments: 177 orientation_array: (list, str, vtkArray) 178 list of vectors, `vtkArray` or name of an already existing pointdata array 179 scale_by_scalar : (bool) 180 glyph mesh is scaled by the active scalars 181 scale_by_vector_size : (bool) 182 glyph mesh is scaled by the size of the vectors 183 scale_by_vector_components : (bool) 184 glyph mesh is scaled by the 3 vectors components 185 color_by_scalar : (bool) 186 glyph mesh is colored based on the scalar value 187 color_by_vector_size : (bool) 188 glyph mesh is colored based on the vector size 189 190 Examples: 191 - [glyphs1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs1.py) 192 - [glyphs2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs2.py) 193 194  195 """ 196 if utils.is_sequence(mesh): 197 # create a cloud of points 198 poly = utils.buildPolyData(mesh) 199 else: 200 poly = mesh.dataset 201 202 cmap = "" 203 if isinstance(c, str) and c in cmaps_names: 204 cmap = c 205 c = None 206 elif utils.is_sequence(c): # user passing an array of point colors 207 ucols = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 208 ucols.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 209 ucols.SetName("GlyphRGB") 210 for col in c: 211 cl = get_color(col) 212 ucols.InsertNextTuple3(cl[0] * 255, cl[1] * 255, cl[2] * 255) 213 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(ucols) 214 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("GlyphRGB") 215 c = None 216 217 gly = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 218 gly.GeneratePointIdsOn() 219 gly.SetInputData(poly) 220 try: 221 gly.SetSourceData(glyph) 222 except TypeError: 223 gly.SetSourceData(glyph.dataset) 224 225 if scale_by_scalar: 226 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByScalar() 227 elif scale_by_vector_size: 228 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByVector() 229 elif scale_by_vector_components: 230 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByVectorComponents() 231 else: 232 gly.SetScaleModeToDataScalingOff() 233 234 if color_by_vector_size: 235 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 236 gly.SetColorModeToColorByVector() 237 elif color_by_scalar: 238 gly.SetColorModeToColorByScalar() 239 else: 240 gly.SetColorModeToColorByScale() 241 242 if orientation_array is not None: 243 gly.OrientOn() 244 if isinstance(orientation_array, str): 245 if orientation_array.lower() == "normals": 246 gly.SetVectorModeToUseNormal() 247 else: # passing a name 248 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveVectors(orientation_array) 249 gly.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, 0, orientation_array) 250 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 251 elif utils.is_sequence(orientation_array): # passing a list 252 varr = vtki.vtkFloatArray() 253 varr.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 254 varr.SetName("glyph_vectors") 255 for v in orientation_array: 256 varr.InsertNextTuple(v) 257 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 258 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveVectors("glyph_vectors") 259 gly.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, 0, "glyph_vectors") 260 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 261 262 gly.Update() 263 264 super().__init__(gly.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 265 self.flat() 266 267 if cmap: 268 self.cmap(cmap, "VectorMagnitude") 269 elif c is None: 270 self.pointdata.select("GlyphRGB") 271 272 self.name = "Glyph" 273 274 275class Tensors(Mesh): 276 """ 277 Geometric representation of tensors defined on a domain or set of points. 278 Tensors can be scaled and/or rotated according to the source at each input point. 279 Scaling and rotation is controlled by the eigenvalues/eigenvectors of the 280 symmetrical part of the tensor as follows: 281 282 For each tensor, the eigenvalues (and associated eigenvectors) are sorted 283 to determine the major, medium, and minor eigenvalues/eigenvectors. 284 The eigenvalue decomposition only makes sense for symmetric tensors, 285 hence the need to only consider the symmetric part of the tensor, 286 which is `1/2*(T+T.transposed())`. 287 """ 288 289 def __init__( 290 self, 291 domain, 292 source="ellipsoid", 293 use_eigenvalues=True, 294 is_symmetric=True, 295 three_axes=False, 296 scale=1.0, 297 max_scale=None, 298 length=None, 299 res=24, 300 c=None, 301 alpha=1.0, 302 ) -> None: 303 """ 304 Arguments: 305 source : (str, Mesh) 306 preset types of source shapes is "ellipsoid", "cylinder", "cube" or a `Mesh` object. 307 use_eigenvalues : (bool) 308 color source glyph using the eigenvalues or by scalars 309 three_axes : (bool) 310 if `False` scale the source in the x-direction, 311 the medium in the y-direction, and the minor in the z-direction. 312 Then, the source is rotated so that the glyph's local x-axis lies 313 along the major eigenvector, y-axis along the medium eigenvector, 314 and z-axis along the minor. 315 316 If `True` three sources are produced, each of them oriented along an eigenvector 317 and scaled according to the corresponding eigenvector. 318 is_symmetric : (bool) 319 If `True` each source glyph is mirrored (2 or 6 glyphs will be produced). 320 The x-axis of the source glyph will correspond to the eigenvector on output. 321 length : (float) 322 distance from the origin to the tip of the source glyph along the x-axis 323 scale : (float) 324 scaling factor of the source glyph. 325 max_scale : (float) 326 clamp scaling at this factor. 327 328 Examples: 329 - [tensors.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/volumetric/tensors.py) 330 - [tensor_grid1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/tensor_grid1.py) 331 - [tensor_grid2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/tensor_grid2.py) 332 333  334 """ 335 if isinstance(source, Points): 336 src = source.dataset 337 else: # is string 338 if "ellip" in source: 339 src = vtki.new("SphereSource") 340 src.SetPhiResolution(res) 341 src.SetThetaResolution(res*2) 342 elif "cyl" in source: 343 src = vtki.new("CylinderSource") 344 src.SetResolution(res) 345 src.CappingOn() 346 elif source == "cube": 347 src = vtki.new("CubeSource") 348 else: 349 vedo.logger.error(f"Unknown source type {source}") 350 raise ValueError() 351 src.Update() 352 src = src.GetOutput() 353 354 tg = vtki.new("TensorGlyph") 355 if isinstance(domain, vtki.vtkPolyData): 356 tg.SetInputData(domain) 357 else: 358 tg.SetInputData(domain.dataset) 359 tg.SetSourceData(src) 360 361 if c is None: 362 tg.ColorGlyphsOn() 363 else: 364 tg.ColorGlyphsOff() 365 366 tg.SetSymmetric(int(is_symmetric)) 367 368 if length is not None: 369 tg.SetLength(length) 370 if use_eigenvalues: 371 tg.ExtractEigenvaluesOn() 372 tg.SetColorModeToEigenvalues() 373 else: 374 tg.SetColorModeToScalars() 375 376 tg.SetThreeGlyphs(three_axes) 377 tg.ScalingOn() 378 tg.SetScaleFactor(scale) 379 if max_scale is None: 380 tg.ClampScalingOn() 381 max_scale = scale * 10 382 tg.SetMaxScaleFactor(max_scale) 383 384 tg.Update() 385 tgn = vtki.new("PolyDataNormals") 386 tgn.ComputeCellNormalsOff() 387 tgn.SetInputData(tg.GetOutput()) 388 tgn.Update() 389 390 super().__init__(tgn.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 391 self.name = "Tensors" 392 393 394class Line(Mesh): 395 """ 396 Build the line segment between point `p0` and point `p1`. 397 398 If `p0` is already a list of points, return the line connecting them. 399 400 A 2D set of coords can also be passed as `p0=[x..], p1=[y..]`. 401 """ 402 403 def __init__(self, p0, p1=None, closed=False, res=2, lw=1, c="k1", alpha=1.0) -> None: 404 """ 405 Arguments: 406 closed : (bool) 407 join last to first point 408 res : (int) 409 resolution, number of points along the line 410 (only relevant if only 2 points are specified) 411 lw : (int) 412 line width in pixel units 413 """ 414 415 if isinstance(p1, Points): 416 p1 = p1.pos() 417 if isinstance(p0, Points): 418 p0 = p0.pos() 419 try: 420 p0 = p0.dataset 421 except AttributeError: 422 pass 423 424 if isinstance(p0, vtki.vtkPolyData): 425 poly = p0 426 top = np.array([0,0,1]) 427 base = np.array([0,0,0]) 428 429 elif utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): # detect if user is passing a list of points 430 431 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 432 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 433 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(np.asarray(p0), dtype=np.float32)) 434 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 435 npt = len(p0) 436 if closed: 437 lines.InsertNextCell(npt + 1) 438 else: 439 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 440 for i in range(npt): 441 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 442 if closed: 443 lines.InsertCellPoint(0) 444 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 445 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 446 poly.SetLines(lines) 447 top = p0[-1] 448 base = p0[0] 449 if res != 2: 450 printc(f"Warning: calling Line(res={res}), try remove []?", c='y') 451 res = 2 452 453 else: # or just 2 points to link 454 455 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 456 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 457 p1 = utils.make3d(p1) 458 line_source.SetPoint1(p0) 459 line_source.SetPoint2(p1) 460 line_source.SetResolution(res - 1) 461 line_source.Update() 462 poly = line_source.GetOutput() 463 top = np.asarray(p1, dtype=float) 464 base = np.asarray(p0, dtype=float) 465 466 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 467 468 self.slope: List[float] = [] # populated by analysis.fit_line 469 self.center: List[float] = [] 470 self.variances: List[float] = [] 471 472 self.coefficients: List[float] = [] # populated by pyplot.fit() 473 self.covariance_matrix: List[float] = [] 474 self.coefficient_errors: List[float] = [] 475 self.monte_carlo_coefficients: List[float] = [] 476 self.reduced_chi2 = -1 477 self.ndof = 0 478 self.data_sigma = 0 479 self.error_lines: List[Any] = [] 480 self.error_band = None 481 self.res = res 482 self.is_closed = closed 483 484 self.lw(lw) 485 self.properties.LightingOff() 486 self.actor.PickableOff() 487 self.actor.DragableOff() 488 self.base = base 489 self.top = top 490 self.name = "Line" 491 492 def clone(self, deep=True) -> "Line": 493 """ 494 Return a copy of the ``Line`` object. 495 496 Example: 497 ```python 498 from vedo import * 499 ln1 = Line([1,1,1], [2,2,2], lw=3).print() 500 ln2 = ln1.clone().shift(0,0,1).c('red').print() 501 show(ln1, ln2, axes=1, viewup='z').close() 502 ``` 503  504 """ 505 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 506 if deep: 507 poly.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 508 else: 509 poly.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 510 ln = Line(poly) 511 ln.copy_properties_from(self) 512 ln.transform = self.transform.clone() 513 ln.name = self.name 514 ln.base = self.base 515 ln.top = self.top 516 ln.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 517 "clone", parents=[self], shape="diamond", c="#edede9") 518 return ln 519 520 def linecolor(self, lc=None) -> "Line": 521 """Assign a color to the line""" 522 # overrides mesh.linecolor which would have no effect here 523 return self.color(lc) 524 525 def eval(self, x: float) -> np.ndarray: 526 """ 527 Calculate the position of an intermediate point 528 as a fraction of the length of the line, 529 being x=0 the first point and x=1 the last point. 530 This corresponds to an imaginary point that travels along the line 531 at constant speed. 532 533 Can be used in conjunction with `lin_interpolate()` 534 to map any range to the [0,1] range. 535 """ 536 distance1 = 0.0 537 length = self.length() 538 pts = self.coordinates 539 if self.is_closed: 540 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 541 542 for i in range(1, len(pts)): 543 p0 = pts[i - 1] 544 p1 = pts[i] 545 seg = p1 - p0 546 distance0 = distance1 547 distance1 += np.linalg.norm(seg) 548 w1 = distance1 / length 549 if w1 >= x: 550 break 551 w0 = distance0 / length 552 v = p0 + seg * (x - w0) / (w1 - w0) 553 return v 554 555 def eval2d(self, x: float) -> np.ndarray: 556 """ 557 Calculate the position of an intermediate point 558 at the specified value of x in absolute units. 559 Assume the line is in the xy-plane. 560 """ 561 xcoords, ycoords, _ = self.coordinates.T 562 # find the segment where x is located 563 idx = np.where((xcoords[:-1] <= x) & (xcoords[1:] >= x))[0] 564 if len(idx) > 0: 565 i = idx[0] 566 return np.array([x, np.interp(x, xcoords[i:i+2], ycoords[i:i+2])]) 567 return np.array([x, 0.0]) 568 569 def find_index_at_position(self, p) -> float: 570 """ 571 Find the index of the line vertex that is closest to the point `p`. 572 Note that the returned index is fractional as `p` may not be exactly 573 one of the vertices of the line. 574 """ 575 tf = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 576 tf.SetPassLines(True) 577 tf.SetPassVerts(False) 578 tf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 579 tf.Update() 580 polyline = tf.GetOutput() 581 582 if not self.cell_locator: 583 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("StaticCellLocator") 584 self.cell_locator.SetDataSet(polyline) 585 self.cell_locator.BuildLocator() 586 587 q = [0, 0, 0] 588 cid = vtki.mutable(0) 589 dist2 = vtki.mutable(0) 590 subid = vtki.mutable(0) 591 self.cell_locator.FindClosestPoint(p, q, cid, subid, dist2) 592 593 # find the 2 points 594 a = polyline.GetCell(cid).GetPointId(0) 595 b = polyline.GetCell(cid).GetPointId(1) 596 597 pts = self.coordinates 598 if self.is_closed: 599 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 600 d = np.linalg.norm(pts[a] - pts[b]) 601 t = a + np.linalg.norm(pts[a] - q) / d 602 return t 603 604 def pattern(self, stipple, repeats=10) -> "Line": 605 """ 606 Define a stipple pattern for dashing the line. 607 Pass the stipple pattern as a string like `'- - -'`. 608 Repeats controls the number of times the pattern repeats in a single segment. 609 610 Examples are: `'- -', '-- - --'`, etc. 611 612 The resolution of the line (nr of points) can affect how pattern will show up. 613 614 Example: 615 ```python 616 from vedo import Line 617 pts = [[1, 0, 0], [5, 2, 0], [3, 3, 1]] 618 ln = Line(pts, c='r', lw=5).pattern('- -', repeats=10) 619 ln.show(axes=1).close() 620 ``` 621  622 """ 623 stipple = str(stipple) * int(2 * repeats) 624 dimension = len(stipple) 625 626 image = vtki.vtkImageData() 627 image.SetDimensions(dimension, 1, 1) 628 image.AllocateScalars(vtki.VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR, 4) 629 image.SetExtent(0, dimension - 1, 0, 0, 0, 0) 630 i_dim = 0 631 while i_dim < dimension: 632 for i in range(dimension): 633 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 0, 255) 634 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 1, 255) 635 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 2, 255) 636 if stipple[i] == " ": 637 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 3, 0) 638 else: 639 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 3, 255) 640 i_dim += 1 641 642 poly = self.dataset 643 644 # Create texture coordinates 645 tcoords = vtki.vtkDoubleArray() 646 tcoords.SetName("TCoordsStippledLine") 647 tcoords.SetNumberOfComponents(1) 648 tcoords.SetNumberOfTuples(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()) 649 for i in range(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()): 650 tcoords.SetTypedTuple(i, [i / 2]) 651 poly.GetPointData().SetTCoords(tcoords) 652 poly.GetPointData().Modified() 653 texture = vtki.vtkTexture() 654 texture.SetInputData(image) 655 texture.InterpolateOff() 656 texture.RepeatOn() 657 self.actor.SetTexture(texture) 658 return self 659 660 def length(self) -> float: 661 """Calculate length of the line.""" 662 pts = self.coordinates 663 if self.is_closed: 664 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 665 distance = 0.0 666 for i in range(1, len(pts)): 667 distance += np.linalg.norm(pts[i] - pts[i - 1]) 668 return distance 669 670 def tangents(self) -> np.ndarray: 671 """ 672 Compute the tangents of a line in space. 673 674 Example: 675 ```python 676 from vedo import * 677 shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[58] 678 pts = shape.rotate_x(30).coordinates 679 tangents = Line(pts).tangents() 680 arrs = Arrows(pts, pts+tangents, c='blue9') 681 show(shape.c('red5').lw(5), arrs, bg='bb', axes=1).close() 682 ``` 683  684 """ 685 v = np.gradient(self.coordinates)[0] 686 ds_dt = np.linalg.norm(v, axis=1) 687 tangent = np.array([1 / ds_dt] * 3).transpose() * v 688 return tangent 689 690 def curvature(self) -> np.ndarray: 691 """ 692 Compute the signed curvature of a line in space. 693 The signed is computed assuming the line is about coplanar to the xy plane. 694 695 Example: 696 ```python 697 from vedo import * 698 from vedo.pyplot import plot 699 shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[55] 700 curvs = Line(shape.coordinates).curvature() 701 shape.cmap('coolwarm', curvs, vmin=-2,vmax=2).add_scalarbar3d(c='w') 702 shape.render_lines_as_tubes().lw(12) 703 pp = plot(curvs, ac='white', lc='yellow5') 704 show(shape, pp, N=2, bg='bb', sharecam=False).close() 705 ``` 706  707 """ 708 v = np.gradient(self.coordinates)[0] 709 a = np.gradient(v)[0] 710 av = np.cross(a, v) 711 mav = np.linalg.norm(av, axis=1) 712 mv = utils.mag2(v) 713 val = mav * np.sign(av[:, 2]) / np.power(mv, 1.5) 714 val[0] = val[1] 715 val[-1] = val[-2] 716 return val 717 718 def compute_curvature(self, method=0) -> "Line": 719 """ 720 Add a pointdata array named 'Curvatures' which contains 721 the curvature value at each point. 722 723 NB: keyword `method` is overridden in Mesh and has no effect here. 724 """ 725 # overrides mesh.compute_curvature 726 curvs = self.curvature() 727 vmin, vmax = np.min(curvs), np.max(curvs) 728 if vmin < 0 and vmax > 0: 729 v = max(-vmin, vmax) 730 self.cmap("coolwarm", curvs, vmin=-v, vmax=v, name="Curvature") 731 else: 732 self.cmap("coolwarm", curvs, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, name="Curvature") 733 return self 734 735 def plot_scalar( 736 self, 737 radius=0.0, 738 height=1.1, 739 normal=(), 740 camera=None, 741 ) -> "Line": 742 """ 743 Generate a new `Line` which plots the active scalar along the line. 744 745 Arguments: 746 radius : (float) 747 distance radius to the line 748 height: (float) 749 height of the plot 750 normal: (list) 751 normal vector to the plane of the plot 752 camera: (vtkCamera) 753 camera object to use for the plot orientation 754 755 Example: 756 ```python 757 from vedo import * 758 circle = Circle(res=360).rotate_y(20) 759 pts = circle.coordinates 760 bore = Line(pts).lw(5) 761 values = np.arctan2(pts[:,1], pts[:,0]) 762 bore.pointdata["scalars"] = values + np.random.randn(360)/5 763 vap = bore.plot_scalar(radius=0, height=1) 764 show(bore, vap, axes=1, viewup='z').close() 765 ``` 766  767 """ 768 ap = vtki.new("ArcPlotter") 769 ap.SetInputData(self.dataset) 770 ap.SetCamera(camera) 771 ap.SetRadius(radius) 772 ap.SetHeight(height) 773 if len(normal)>0: 774 ap.UseDefaultNormalOn() 775 ap.SetDefaultNormal(normal) 776 ap.Update() 777 vap = Line(ap.GetOutput()) 778 vap.linewidth(3).lighting('off') 779 vap.name = "ArcPlot" 780 return vap 781 782 def sweep(self, direction=(1, 0, 0), res=1) -> "Mesh": 783 """ 784 Sweep the `Line` along the specified vector direction. 785 786 Returns a `Mesh` surface. 787 Line position is updated to allow for additional sweepings. 788 789 Example: 790 ```python 791 from vedo import Line, show 792 aline = Line([(0,0,0),(1,3,0),(2,4,0)]) 793 surf1 = aline.sweep((1,0.2,0), res=3) 794 surf2 = aline.sweep((0.2,0,1)).alpha(0.5) 795 aline.color('r').linewidth(4) 796 show(surf1, surf2, aline, axes=1).close() 797 ``` 798  799 """ 800 line = self.dataset 801 rows = line.GetNumberOfPoints() 802 803 spacing = 1 / res 804 surface = vtki.vtkPolyData() 805 806 res += 1 807 npts = rows * res 808 npolys = (rows - 1) * (res - 1) 809 points = vtki.vtkPoints() 810 points.Allocate(npts) 811 812 cnt = 0 813 x = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0] 814 for row in range(rows): 815 for col in range(res): 816 p = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0] 817 line.GetPoint(row, p) 818 x[0] = p[0] + direction[0] * col * spacing 819 x[1] = p[1] + direction[1] * col * spacing 820 x[2] = p[2] + direction[2] * col * spacing 821 points.InsertPoint(cnt, x) 822 cnt += 1 823 824 # Generate the quads 825 polys = vtki.vtkCellArray() 826 polys.Allocate(npolys * 4) 827 pts = [0, 0, 0, 0] 828 for row in range(rows - 1): 829 for col in range(res - 1): 830 pts[0] = col + row * res 831 pts[1] = pts[0] + 1 832 pts[2] = pts[0] + res + 1 833 pts[3] = pts[0] + res 834 polys.InsertNextCell(4, pts) 835 surface.SetPoints(points) 836 surface.SetPolys(polys) 837 asurface = Mesh(surface) 838 asurface.copy_properties_from(self) 839 asurface.lighting("default") 840 self.coordinates = self.coordinates + direction 841 return asurface 842 843 def reverse(self): 844 """Reverse the points sequence order.""" 845 pts = np.flip(self.coordinates, axis=0) 846 self.coordinates = pts 847 return self 848 849 850class DashedLine(Mesh): 851 """ 852 Consider using `Line.pattern()` instead. 853 854 Build a dashed line segment between points `p0` and `p1`. 855 If `p0` is a list of points returns the line connecting them. 856 A 2D set of coords can also be passed as `p0=[x..], p1=[y..]`. 857 """ 858 859 def __init__(self, p0, p1=None, spacing=0.1, closed=False, lw=2, c="k5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 860 """ 861 Arguments: 862 closed : (bool) 863 join last to first point 864 spacing : (float) 865 relative size of the dash 866 lw : (int) 867 line width in pixels 868 """ 869 if isinstance(p1, vtki.vtkActor): 870 p1 = p1.GetPosition() 871 if isinstance(p0, vtki.vtkActor): 872 p0 = p0.GetPosition() 873 if isinstance(p0, Points): 874 p0 = p0.coordinates 875 876 # detect if user is passing a 2D list of points as p0=xlist, p1=ylist: 877 if len(p0) > 3: 878 if not utils.is_sequence(p0[0]) and not utils.is_sequence(p1[0]) and len(p0) == len(p1): 879 # assume input is 2D xlist, ylist 880 p0 = np.stack((p0, p1), axis=1) 881 p1 = None 882 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 883 if closed: 884 p0 = np.append(p0, [p0[0]], axis=0) 885 886 if p1 is not None: # assume passing p0=[x,y] 887 if len(p0) == 2 and not utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): 888 p0 = (p0[0], p0[1], 0) 889 if len(p1) == 2 and not utils.is_sequence(p1[0]): 890 p1 = (p1[0], p1[1], 0) 891 892 # detect if user is passing a list of points: 893 if utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): 894 listp = p0 895 else: # or just 2 points to link 896 listp = [p0, p1] 897 898 listp = np.array(listp) 899 if listp.shape[1] == 2: 900 listp = np.c_[listp, np.zeros(listp.shape[0])] 901 902 xmn = np.min(listp, axis=0) 903 xmx = np.max(listp, axis=0) 904 dlen = np.linalg.norm(xmx - xmn) * np.clip(spacing, 0.01, 1.0) / 10 905 if not dlen: 906 super().__init__(vtki.vtkPolyData(), c, alpha) 907 self.name = "DashedLine (void)" 908 return 909 910 qs = [] 911 for ipt in range(len(listp) - 1): 912 p0 = listp[ipt] 913 p1 = listp[ipt + 1] 914 v = p1 - p0 915 vdist = np.linalg.norm(v) 916 n1 = int(vdist / dlen) 917 if not n1: 918 continue 919 920 res = 0.0 921 for i in range(n1 + 2): 922 ist = (i - 0.5) / n1 923 ist = max(ist, 0) 924 qi = p0 + v * (ist - res / vdist) 925 if ist > 1: 926 qi = p1 927 res = np.linalg.norm(qi - p1) 928 qs.append(qi) 929 break 930 qs.append(qi) 931 932 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 933 for i, q1 in enumerate(qs): 934 if not i % 2: 935 continue 936 q0 = qs[i - 1] 937 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 938 line_source.SetPoint1(q0) 939 line_source.SetPoint2(q1) 940 line_source.Update() 941 polylns.AddInputData(line_source.GetOutput()) 942 polylns.Update() 943 944 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 945 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 946 self.base = listp[0] 947 if closed: 948 self.top = listp[-2] 949 else: 950 self.top = listp[-1] 951 self.name = "DashedLine" 952 953 954class RoundedLine(Mesh): 955 """ 956 Create a 2D line of specified thickness (in absolute units) passing through 957 a list of input points. Borders of the line are rounded. 958 """ 959 960 def __init__(self, pts, lw, res=10, c="gray4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 961 """ 962 Arguments: 963 pts : (list) 964 a list of points in 2D or 3D (z will be ignored). 965 lw : (float) 966 thickness of the line. 967 res : (int) 968 resolution of the rounded regions 969 970 Example: 971 ```python 972 from vedo import * 973 pts = [(-4,-3),(1,1),(2,4),(4,1),(3,-1),(2,-5),(9,-3)] 974 ln = Line(pts).z(0.01) 975 ln.color("red5").linewidth(2) 976 rl = RoundedLine(pts, 0.6) 977 show(Points(pts), ln, rl, axes=1).close() 978 ``` 979 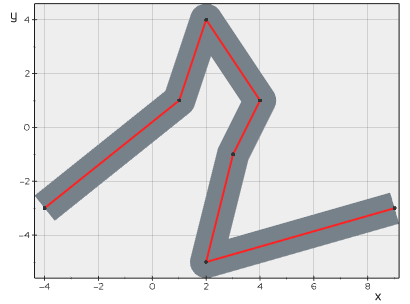 980 """ 981 pts = utils.make3d(pts) 982 983 def _getpts(pts, revd=False): 984 985 if revd: 986 pts = list(reversed(pts)) 987 988 if len(pts) == 2: 989 p0, p1 = pts 990 v = p1 - p0 991 dv = np.linalg.norm(v) 992 nv = np.cross(v, (0, 0, -1)) 993 nv = nv / np.linalg.norm(nv) * lw 994 return [p0 + nv, p1 + nv] 995 996 ptsnew = [] 997 for k in range(len(pts) - 2): 998 p0 = pts[k] 999 p1 = pts[k + 1] 1000 p2 = pts[k + 2] 1001 v = p1 - p0 1002 u = p2 - p1 1003 du = np.linalg.norm(u) 1004 dv = np.linalg.norm(v) 1005 nv = np.cross(v, (0, 0, -1)) 1006 nv = nv / np.linalg.norm(nv) * lw 1007 nu = np.cross(u, (0, 0, -1)) 1008 nu = nu / np.linalg.norm(nu) * lw 1009 uv = np.cross(u, v) 1010 if k == 0: 1011 ptsnew.append(p0 + nv) 1012 if uv[2] <= 0: 1013 # the following computation can return a value 1014 # ever so slightly > 1.0 causing arccos to fail. 1015 uv_arg = np.dot(u, v) / du / dv 1016 if uv_arg > 1.0: 1017 # since the argument to arcos is 1, simply 1018 # assign alpha to 0.0 without calculating the 1019 # arccos 1020 alpha = 0.0 1021 else: 1022 alpha = np.arccos(uv_arg) 1023 db = lw * np.tan(alpha / 2) 1024 p1new = p1 + nv - v / dv * db 1025 ptsnew.append(p1new) 1026 else: 1027 p1a = p1 + nv 1028 p1b = p1 + nu 1029 for i in range(0, res + 1): 1030 pab = p1a * (res - i) / res + p1b * i / res 1031 vpab = pab - p1 1032 vpab = vpab / np.linalg.norm(vpab) * lw 1033 ptsnew.append(p1 + vpab) 1034 if k == len(pts) - 3: 1035 ptsnew.append(p2 + nu) 1036 if revd: 1037 ptsnew.append(p2 - nu) 1038 return ptsnew 1039 1040 ptsnew = _getpts(pts) + _getpts(pts, revd=True) 1041 1042 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 1043 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(np.asarray(ptsnew), dtype=np.float32)) 1044 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1045 npt = len(ptsnew) 1046 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 1047 for i in range(npt): 1048 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 1049 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1050 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 1051 poly.SetLines(lines) 1052 vct = vtki.new("ContourTriangulator") 1053 vct.SetInputData(poly) 1054 vct.Update() 1055 1056 super().__init__(vct.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1057 self.flat() 1058 self.properties.LightingOff() 1059 self.name = "RoundedLine" 1060 self.base = ptsnew[0] 1061 self.top = ptsnew[-1] 1062 1063 1064class Lines(Mesh): 1065 """ 1066 Build the line segments between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 1067 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 1068 """ 1069 1070 def __init__( 1071 self, start_pts, end_pts=None, dotted=False, res=1, scale=1.0, lw=1, c="k4", alpha=1.0 1072 ) -> None: 1073 """ 1074 Arguments: 1075 scale : (float) 1076 apply a rescaling factor to the lengths. 1077 c : (color, int, str, list) 1078 color name, number, or list of [R,G,B] colors 1079 alpha : (float) 1080 opacity in range [0,1] 1081 lw : (int) 1082 line width in pixel units 1083 dotted : (bool) 1084 draw a dotted line 1085 res : (int) 1086 resolution, number of points along the line 1087 (only relevant if only 2 points are specified) 1088 1089 Examples: 1090 - [fitspheres2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/fitspheres2.py) 1091 1092 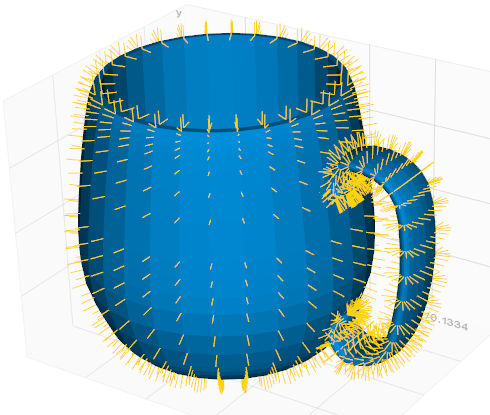 1093 """ 1094 1095 if isinstance(start_pts, vtki.vtkPolyData):######## 1096 super().__init__(start_pts, c, alpha) 1097 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1098 self.name = "Lines" 1099 return ######################################## 1100 1101 if utils.is_sequence(start_pts) and len(start_pts)>1 and isinstance(start_pts[0], Line): 1102 # passing a list of Line, see tests/issues/issue_950.py 1103 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1104 for ln in start_pts: 1105 polylns.AddInputData(ln.dataset) 1106 polylns.Update() 1107 1108 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1109 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1110 if dotted: 1111 self.properties.SetLineStipplePattern(0xF0F0) 1112 self.properties.SetLineStippleRepeatFactor(1) 1113 self.name = "Lines" 1114 return ######################################## 1115 1116 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 1117 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 1118 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 1119 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 1120 1121 if end_pts is not None: 1122 start_pts = np.stack((start_pts, end_pts), axis=1) 1123 1124 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1125 1126 if not utils.is_ragged(start_pts): 1127 1128 for twopts in start_pts: 1129 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 1130 line_source.SetResolution(res) 1131 if len(twopts[0]) == 2: 1132 line_source.SetPoint1(twopts[0][0], twopts[0][1], 0.0) 1133 else: 1134 line_source.SetPoint1(twopts[0]) 1135 1136 if scale == 1: 1137 pt2 = twopts[1] 1138 else: 1139 vers = (np.array(twopts[1]) - twopts[0]) * scale 1140 pt2 = np.array(twopts[0]) + vers 1141 1142 if len(pt2) == 2: 1143 line_source.SetPoint2(pt2[0], pt2[1], 0.0) 1144 else: 1145 line_source.SetPoint2(pt2) 1146 polylns.AddInputConnection(line_source.GetOutputPort()) 1147 1148 else: 1149 1150 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1151 for t in start_pts: 1152 t = utils.make3d(t) 1153 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 1154 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(t, dtype=np.float32)) 1155 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1156 npt = len(t) 1157 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 1158 for i in range(npt): 1159 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 1160 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1161 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 1162 poly.SetLines(lines) 1163 polylns.AddInputData(poly) 1164 1165 polylns.Update() 1166 1167 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1168 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1169 if dotted: 1170 self.properties.SetLineStipplePattern(0xF0F0) 1171 self.properties.SetLineStippleRepeatFactor(1) 1172 1173 self.name = "Lines" 1174 1175 1176class Arc(Line): 1177 """ 1178 Build a 2D circular arc between 2 points. 1179 """ 1180 1181 def __init__( 1182 self, 1183 center=None, 1184 point1=None, 1185 point2=None, 1186 normal=None, 1187 angle=None, 1188 invert=False, 1189 res=60, 1190 c="k3", 1191 alpha=1.0, 1192 ) -> None: 1193 """ 1194 Build a 2D circular arc between 2 points. 1195 Two modes are available: 1196 1. [center, point1, point2] are specified 1197 1198 2. [point1, normal, angle] are specified. 1199 1200 In the first case it creates an arc defined by two endpoints and a center. 1201 In the second the arc spans the shortest angular sector defined by 1202 a starting point, a normal and a spanning angle. 1203 if `invert=True`, then the opposite happens. 1204 1205 Example 1: 1206 ```python 1207 from vedo import * 1208 center = [0,1,0] 1209 p1 = [1,2,0.4] 1210 p2 = [0.5,3,-1] 1211 arc = Arc(center, p1, p2).lw(5).c("purple5") 1212 line2 = Line(center, p2) 1213 pts = Points([center, p1,p2], r=9, c='r') 1214 show(pts, line2, arc, f"length={arc.length()}", axes=1).close() 1215 ``` 1216 1217 Example 2: 1218 ```python 1219 from vedo import * 1220 arc = Arc(point1=[0,1,0], normal=[0,0,1], angle=270) 1221 arc.lw(5).c("purple5") 1222 origin = Point([0,0,0], r=9, c='r') 1223 show(origin, arc, arc.labels2d(), axes=1).close() 1224 ``` 1225 """ 1226 ar = vtki.new("ArcSource") 1227 if point2 is not None: 1228 center = utils.make3d(center) 1229 point1 = utils.make3d(point1) 1230 point2 = utils.make3d(point2) 1231 ar.UseNormalAndAngleOff() 1232 ar.SetPoint1(point1-center) 1233 ar.SetPoint2(point2-center) 1234 elif normal is not None and angle and point1 is not None: 1235 normal = utils.make3d(normal) 1236 point1 = utils.make3d(point1) 1237 ar.UseNormalAndAngleOn() 1238 ar.SetAngle(angle) 1239 ar.SetPolarVector(point1) 1240 ar.SetNormal(normal) 1241 self.top = normal 1242 else: 1243 vedo.logger.error("in Arc(), incorrect input combination.") 1244 raise TypeError 1245 ar.SetNegative(invert) 1246 ar.SetResolution(res) 1247 ar.Update() 1248 1249 super().__init__(ar.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1250 self.lw(2).lighting("off") 1251 if point2 is not None: # nb: not center 1252 self.pos(center) 1253 self.name = "Arc" 1254 1255 1256class Spline(Line): 1257 """ 1258 Find the B-Spline curve through a set of points. This curve does not necessarily 1259 pass exactly through all the input points. Needs to import `scipy`. 1260 """ 1261 1262 def __init__(self, points, smooth=0.0, degree=2, closed=False, res=None, easing="") -> None: 1263 """ 1264 Arguments: 1265 smooth : (float) 1266 smoothing factor. 1267 - 0 = interpolate points exactly [default]. 1268 - 1 = average point positions. 1269 degree : (int) 1270 degree of the spline (between 1 and 5). 1271 easing : (str) 1272 control sensity of points along the spline. 1273 Available options are 1274 `[InSine, OutSine, Sine, InQuad, OutQuad, InCubic, OutCubic, InQuart, OutQuart, InCirc, OutCirc].` 1275 Can be used to create animations (move objects at varying speed). 1276 See e.g.: https://easings.net 1277 res : (int) 1278 number of points on the spline 1279 1280 See also: `CSpline` and `KSpline`. 1281 1282 Examples: 1283 - [spline_ease.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/spline_ease.py) 1284 1285 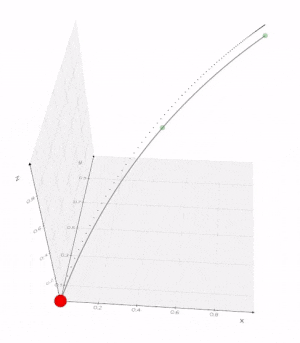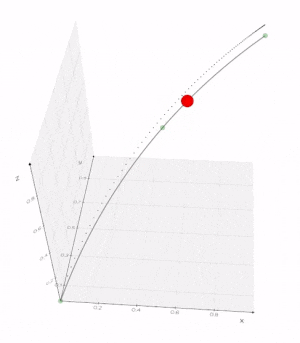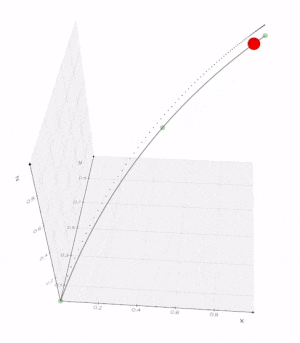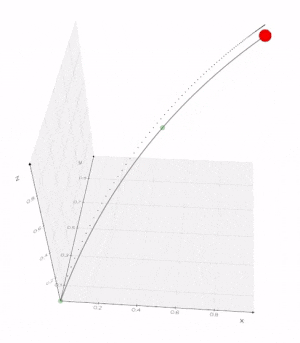 1286 """ 1287 from scipy.interpolate import splprep, splev 1288 1289 if isinstance(points, Points): 1290 points = points.coordinates 1291 1292 points = utils.make3d(points) 1293 1294 per = 0 1295 if closed: 1296 points = np.append(points, [points[0]], axis=0) 1297 per = 1 1298 1299 if res is None: 1300 res = len(points) * 10 1301 1302 points = np.array(points, dtype=float) 1303 1304 minx, miny, minz = np.min(points, axis=0) 1305 maxx, maxy, maxz = np.max(points, axis=0) 1306 maxb = max(maxx - minx, maxy - miny, maxz - minz) 1307 smooth *= maxb / 2 # must be in absolute units 1308 1309 x = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, res) 1310 if easing: 1311 if easing == "InSine": 1312 x = 1.0 - np.cos((x * np.pi) / 2) 1313 elif easing == "OutSine": 1314 x = np.sin((x * np.pi) / 2) 1315 elif easing == "Sine": 1316 x = -(np.cos(np.pi * x) - 1) / 2 1317 elif easing == "InQuad": 1318 x = x * x 1319 elif easing == "OutQuad": 1320 x = 1.0 - (1 - x) * (1 - x) 1321 elif easing == "InCubic": 1322 x = x * x 1323 elif easing == "OutCubic": 1324 x = 1.0 - np.power(1 - x, 3) 1325 elif easing == "InQuart": 1326 x = x * x * x * x 1327 elif easing == "OutQuart": 1328 x = 1.0 - np.power(1 - x, 4) 1329 elif easing == "InCirc": 1330 x = 1.0 - np.sqrt(1 - np.power(x, 2)) 1331 elif easing == "OutCirc": 1332 x = np.sqrt(1.0 - np.power(x - 1, 2)) 1333 else: 1334 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown ease mode {easing}") 1335 1336 # find the knots 1337 tckp, _ = splprep(points.T, task=0, s=smooth, k=degree, per=per) 1338 # evaluate spLine, including interpolated points: 1339 xnew, ynew, znew = splev(x, tckp) 1340 1341 super().__init__(np.c_[xnew, ynew, znew], lw=2) 1342 self.name = "Spline" 1343 1344 1345class KSpline(Line): 1346 """ 1347 Return a [Kochanek spline](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kochanek%E2%80%93Bartels_spline) 1348 which runs exactly through all the input points. 1349 """ 1350 1351 def __init__(self, points, 1352 continuity=0.0, tension=0.0, bias=0.0, closed=False, res=None) -> None: 1353 """ 1354 Arguments: 1355 continuity : (float) 1356 changes the sharpness in change between tangents 1357 tension : (float) 1358 changes the length of the tangent vector 1359 bias : (float) 1360 changes the direction of the tangent vector 1361 closed : (bool) 1362 join last to first point to produce a closed curve 1363 res : (int) 1364 approximate resolution of the output line. 1365 Default is 20 times the number of input points. 1366 1367 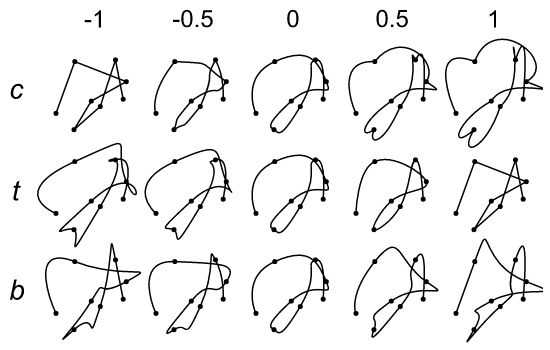 1368 1369 Warning: 1370 This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points 1371 as requested by `res`. Some points may be concident and removed. 1372 1373 See also: `Spline` and `CSpline`. 1374 """ 1375 if isinstance(points, Points): 1376 points = points.coordinates 1377 1378 if not res: 1379 res = len(points) * 20 1380 1381 points = utils.make3d(points).astype(float) 1382 1383 vtkKochanekSpline = vtki.get_class("KochanekSpline") 1384 xspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1385 yspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1386 zspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1387 for s in [xspline, yspline, zspline]: 1388 if bias: 1389 s.SetDefaultBias(bias) 1390 if tension: 1391 s.SetDefaultTension(tension) 1392 if continuity: 1393 s.SetDefaultContinuity(continuity) 1394 s.SetClosed(closed) 1395 1396 lenp = len(points[0]) > 2 1397 1398 for i, p in enumerate(points): 1399 xspline.AddPoint(i, p[0]) 1400 yspline.AddPoint(i, p[1]) 1401 if lenp: 1402 zspline.AddPoint(i, p[2]) 1403 1404 ln = [] 1405 for pos in np.linspace(0, len(points), res): 1406 x = xspline.Evaluate(pos) 1407 y = yspline.Evaluate(pos) 1408 z = 0 1409 if lenp: 1410 z = zspline.Evaluate(pos) 1411 ln.append((x, y, z)) 1412 1413 super().__init__(ln, lw=2) 1414 self.clean() 1415 self.lighting("off") 1416 self.name = "KSpline" 1417 self.base = np.array(points[0], dtype=float) 1418 self.top = np.array(points[-1], dtype=float) 1419 1420 1421class CSpline(Line): 1422 """ 1423 Return a Cardinal spline which runs exactly through all the input points. 1424 """ 1425 1426 def __init__(self, points, closed=False, res=None) -> None: 1427 """ 1428 Arguments: 1429 closed : (bool) 1430 join last to first point to produce a closed curve 1431 res : (int) 1432 approximate resolution of the output line. 1433 Default is 20 times the number of input points. 1434 1435 Warning: 1436 This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points 1437 as requested by `res`. Some points may be concident and removed. 1438 1439 See also: `Spline` and `KSpline`. 1440 """ 1441 1442 if isinstance(points, Points): 1443 points = points.coordinates 1444 1445 if not res: 1446 res = len(points) * 20 1447 1448 points = utils.make3d(points).astype(float) 1449 1450 vtkCardinalSpline = vtki.get_class("CardinalSpline") 1451 xspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1452 yspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1453 zspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1454 for s in [xspline, yspline, zspline]: 1455 s.SetClosed(closed) 1456 1457 lenp = len(points[0]) > 2 1458 1459 for i, p in enumerate(points): 1460 xspline.AddPoint(i, p[0]) 1461 yspline.AddPoint(i, p[1]) 1462 if lenp: 1463 zspline.AddPoint(i, p[2]) 1464 1465 ln = [] 1466 for pos in np.linspace(0, len(points), res): 1467 x = xspline.Evaluate(pos) 1468 y = yspline.Evaluate(pos) 1469 z = 0 1470 if lenp: 1471 z = zspline.Evaluate(pos) 1472 ln.append((x, y, z)) 1473 1474 super().__init__(ln, lw=2) 1475 self.clean() 1476 self.lighting("off") 1477 self.name = "CSpline" 1478 self.base = points[0] 1479 self.top = points[-1] 1480 1481 1482class Bezier(Line): 1483 """ 1484 Generate the Bezier line that links the first to the last point. 1485 """ 1486 1487 def __init__(self, points, res=None) -> None: 1488 """ 1489 Example: 1490 ```python 1491 from vedo import * 1492 import numpy as np 1493 pts = np.random.randn(25,3) 1494 for i,p in enumerate(pts): 1495 p += [5*i, 15*sin(i/2), i*i*i/200] 1496 show(Points(pts), Bezier(pts), axes=1).close() 1497 ``` 1498 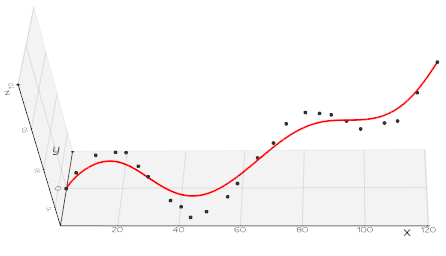 1499 """ 1500 N = len(points) 1501 if res is None: 1502 res = 10 * N 1503 t = np.linspace(0, 1, num=res) 1504 bcurve = np.zeros((res, len(points[0]))) 1505 1506 def binom(n, k): 1507 b = 1 1508 for t in range(1, min(k, n - k) + 1): 1509 b *= n / t 1510 n -= 1 1511 return b 1512 1513 def bernstein(n, k): 1514 coeff = binom(n, k) 1515 1516 def _bpoly(x): 1517 return coeff * x ** k * (1 - x) ** (n - k) 1518 1519 return _bpoly 1520 1521 for ii in range(N): 1522 b = bernstein(N - 1, ii)(t) 1523 bcurve += np.outer(b, points[ii]) 1524 super().__init__(bcurve, lw=2) 1525 self.name = "BezierLine" 1526 1527 1528class NormalLines(Mesh): 1529 """ 1530 Build an `Glyph` to show the normals at cell centers or at mesh vertices. 1531 1532 Arguments: 1533 ratio : (int) 1534 show 1 normal every `ratio` cells. 1535 on : (str) 1536 either "cells" or "points". 1537 scale : (float) 1538 scale factor to control size. 1539 """ 1540 1541 def __init__(self, msh, ratio=1, on="cells", scale=1.0) -> None: 1542 1543 poly = msh.clone().dataset 1544 1545 if "cell" in on: 1546 centers = vtki.new("CellCenters") 1547 centers.SetInputData(poly) 1548 centers.Update() 1549 poly = centers.GetOutput() 1550 1551 mask_pts = vtki.new("MaskPoints") 1552 mask_pts.SetInputData(poly) 1553 mask_pts.SetOnRatio(ratio) 1554 mask_pts.RandomModeOff() 1555 mask_pts.Update() 1556 1557 ln = vtki.new("LineSource") 1558 ln.SetPoint1(0, 0, 0) 1559 ln.SetPoint2(1, 0, 0) 1560 ln.Update() 1561 glyph = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 1562 glyph.SetSourceData(ln.GetOutput()) 1563 glyph.SetInputData(mask_pts.GetOutput()) 1564 glyph.SetVectorModeToUseNormal() 1565 1566 b = poly.GetBounds() 1567 f = max([b[1] - b[0], b[3] - b[2], b[5] - b[4]]) / 50 * scale 1568 glyph.SetScaleFactor(f) 1569 glyph.OrientOn() 1570 glyph.Update() 1571 1572 super().__init__(glyph.GetOutput()) 1573 1574 self.actor.PickableOff() 1575 prop = vtki.vtkProperty() 1576 prop.DeepCopy(msh.properties) 1577 self.actor.SetProperty(prop) 1578 self.properties = prop 1579 self.properties.LightingOff() 1580 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 1581 self.name = "NormalLines" 1582 1583 1584class Tube(Mesh): 1585 """ 1586 Build a tube along the line defined by a set of points. 1587 """ 1588 1589 def __init__(self, points, r=1.0, cap=True, res=12, c=None, alpha=1.0) -> None: 1590 """ 1591 Arguments: 1592 r : (float, list) 1593 constant radius or list of radii. 1594 res : (int) 1595 resolution, number of the sides of the tube 1596 c : (color) 1597 constant color or list of colors for each point. 1598 1599 Example: 1600 Create a tube along a line, with data associated to each point: 1601 1602 ```python 1603 from vedo import * 1604 line = Line([(0,0,0), (1,1,1), (2,0,1), (3,1,0)]).lw(5) 1605 scalars = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3]) 1606 line.pointdata["myscalars"] = scalars 1607 tube = Tube(line, r=0.1).lw(1) 1608 tube.cmap('viridis', "myscalars").add_scalarbar3d() 1609 show(line, tube, axes=1).close() 1610 ``` 1611 1612 Examples: 1613 - [ribbon.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/ribbon.py) 1614 - [tube_radii.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/tube_radii.py) 1615 1616 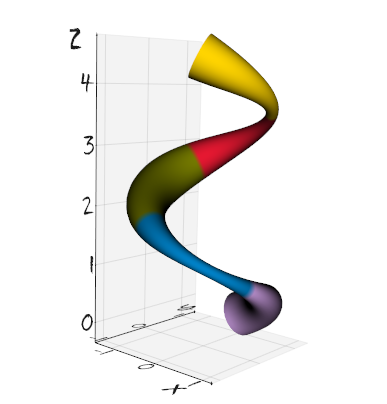 1617 """ 1618 if utils.is_sequence(points): 1619 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 1620 idx = len(points) 1621 for p in points: 1622 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 1623 line = vtki.new("PolyLine") 1624 line.GetPointIds().SetNumberOfIds(idx) 1625 for i in range(idx): 1626 line.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i) 1627 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1628 lines.InsertNextCell(line) 1629 polyln = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1630 polyln.SetPoints(vpoints) 1631 polyln.SetLines(lines) 1632 self.base = np.asarray(points[0], dtype=float) 1633 self.top = np.asarray(points[-1], dtype=float) 1634 1635 elif isinstance(points, Mesh): 1636 polyln = points.dataset 1637 n = polyln.GetNumberOfPoints() 1638 self.base = np.array(polyln.GetPoint(0)) 1639 self.top = np.array(polyln.GetPoint(n - 1)) 1640 1641 # from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersCore import vtkTubeBender 1642 # bender = vtkTubeBender() 1643 # bender.SetInputData(polyln) 1644 # bender.SetRadius(r) 1645 # bender.Update() 1646 # polyln = bender.GetOutput() 1647 1648 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 1649 tuf.SetCapping(cap) 1650 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(res) 1651 tuf.SetInputData(polyln) 1652 if utils.is_sequence(r): 1653 arr = utils.numpy2vtk(r, dtype=float) 1654 arr.SetName("TubeRadius") 1655 polyln.GetPointData().AddArray(arr) 1656 polyln.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("TubeRadius") 1657 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByAbsoluteScalar() 1658 else: 1659 tuf.SetRadius(r) 1660 1661 usingColScals = False 1662 if utils.is_sequence(c): 1663 usingColScals = True 1664 cc = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 1665 cc.SetName("TubeColors") 1666 cc.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 1667 cc.SetNumberOfTuples(len(c)) 1668 for i, ic in enumerate(c): 1669 r, g, b = get_color(ic) 1670 cc.InsertTuple3(i, int(255 * r), int(255 * g), int(255 * b)) 1671 polyln.GetPointData().AddArray(cc) 1672 c = None 1673 tuf.Update() 1674 1675 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1676 self.phong() 1677 if usingColScals: 1678 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointFieldData() 1679 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1680 self.mapper.SelectColorArray("TubeColors") 1681 self.mapper.Modified() 1682 self.name = "Tube" 1683 1684 1685def ThickTube(pts, r1, r2, res=12, c=None, alpha=1.0) -> Union["Mesh", None]: 1686 """ 1687 Create a tube with a thickness along a line of points. 1688 1689 Example: 1690 ```python 1691 from vedo import * 1692 pts = [[sin(x), cos(x), x/3] for x in np.arange(0.1, 3, 0.3)] 1693 vline = Line(pts, lw=5, c='red5') 1694 thick_tube = ThickTube(vline, r1=0.2, r2=0.3).lw(1) 1695 show(vline, thick_tube, axes=1).close() 1696 ``` 1697 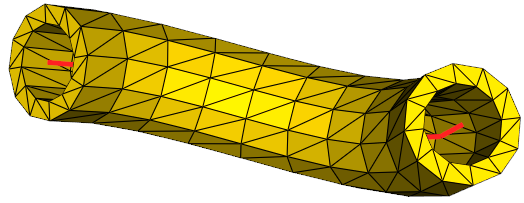 1698 """ 1699 1700 def make_cap(t1, t2): 1701 newpoints = t1.coordinates.tolist() + t2.coordinates.tolist() 1702 newfaces = [] 1703 for i in range(n - 1): 1704 newfaces.append([i, i + 1, i + n]) 1705 newfaces.append([i + n, i + 1, i + n + 1]) 1706 newfaces.append([2 * n - 1, 0, n]) 1707 newfaces.append([2 * n - 1, n - 1, 0]) 1708 capm = utils.buildPolyData(newpoints, newfaces) 1709 return capm 1710 1711 assert r1 < r2 1712 1713 t1 = Tube(pts, r=r1, cap=False, res=res) 1714 t2 = Tube(pts, r=r2, cap=False, res=res) 1715 1716 tc1a, tc1b = t1.boundaries().split() 1717 tc2a, tc2b = t2.boundaries().split() 1718 n = tc1b.npoints 1719 1720 tc1b.join(reset=True).clean() # needed because indices are flipped 1721 tc2b.join(reset=True).clean() 1722 1723 capa = make_cap(tc1a, tc2a) 1724 capb = make_cap(tc1b, tc2b) 1725 1726 thick_tube = merge(t1, t2, capa, capb) 1727 if thick_tube: 1728 thick_tube.c(c).alpha(alpha) 1729 thick_tube.base = t1.base 1730 thick_tube.top = t1.top 1731 thick_tube.name = "ThickTube" 1732 return thick_tube 1733 return None 1734 1735 1736class Tubes(Mesh): 1737 """ 1738 Build tubes around a `Lines` object. 1739 """ 1740 def __init__( 1741 self, 1742 lines, 1743 r=1, 1744 vary_radius_by_scalar=False, 1745 vary_radius_by_vector=False, 1746 vary_radius_by_vector_norm=False, 1747 vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar=False, 1748 max_radius_factor=100, 1749 cap=True, 1750 res=12 1751 ) -> None: 1752 """ 1753 Wrap tubes around the input `Lines` object. 1754 1755 Arguments: 1756 lines : (Lines) 1757 input Lines object. 1758 r : (float) 1759 constant radius 1760 vary_radius_by_scalar : (bool) 1761 use scalar array to control radius 1762 vary_radius_by_vector : (bool) 1763 use vector array to control radius 1764 vary_radius_by_vector_norm : (bool) 1765 use vector norm to control radius 1766 vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar : (bool) 1767 use absolute scalar value to control radius 1768 max_radius_factor : (float) 1769 max tube radius as a multiple of the min radius 1770 cap : (bool) 1771 capping of the tube 1772 res : (int) 1773 resolution, number of the sides of the tube 1774 c : (color) 1775 constant color or list of colors for each point. 1776 1777 Examples: 1778 - [streamlines1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/streamlines1.py) 1779 """ 1780 plines = lines.dataset 1781 if plines.GetNumberOfLines() == 0: 1782 vedo.logger.warning("Tubes(): input Lines is empty.") 1783 1784 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 1785 if vary_radius_by_scalar: 1786 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByScalar() 1787 elif vary_radius_by_vector: 1788 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByVector() 1789 elif vary_radius_by_vector_norm: 1790 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByVectorNorm() 1791 elif vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar: 1792 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByAbsoluteScalar() 1793 tuf.SetRadius(r) 1794 tuf.SetCapping(cap) 1795 tuf.SetGenerateTCoords(0) 1796 tuf.SetSidesShareVertices(1) 1797 tuf.SetRadiusFactor(max_radius_factor) 1798 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(res) 1799 tuf.SetInputData(plines) 1800 tuf.Update() 1801 1802 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput()) 1803 self.name = "Tubes" 1804 1805 1806class Ribbon(Mesh): 1807 """ 1808 Connect two lines to generate the surface inbetween. 1809 Set the mode by which to create the ruled surface. 1810 1811 It also works with a single line in input. In this case the ribbon 1812 is formed by following the local plane of the line in space. 1813 """ 1814 1815 def __init__( 1816 self, 1817 line1, 1818 line2=None, 1819 mode=0, 1820 closed=False, 1821 width=None, 1822 res=(200, 5), 1823 c="indigo3", 1824 alpha=1.0, 1825 ) -> None: 1826 """ 1827 Arguments: 1828 mode : (int) 1829 If mode=0, resample evenly the input lines (based on length) 1830 and generates triangle strips. 1831 1832 If mode=1, use the existing points and walks around the 1833 polyline using existing points. 1834 1835 closed : (bool) 1836 if True, join the last point with the first to form a closed surface 1837 1838 res : (list) 1839 ribbon resolutions along the line and perpendicularly to it. 1840 1841 Examples: 1842 - [ribbon.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/ribbon.py) 1843 1844 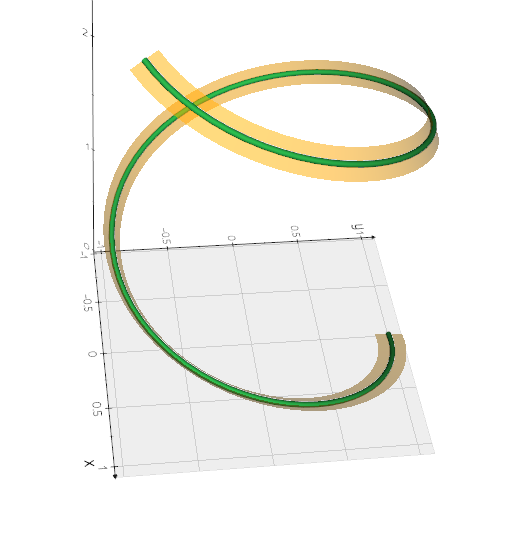 1845 """ 1846 1847 if isinstance(line1, Points): 1848 line1 = line1.coordinates 1849 1850 if isinstance(line2, Points): 1851 line2 = line2.coordinates 1852 1853 elif line2 is None: 1854 ############################################# 1855 ribbon_filter = vtki.new("RibbonFilter") 1856 aline = Line(line1) 1857 ribbon_filter.SetInputData(aline.dataset) 1858 if width is None: 1859 width = aline.diagonal_size() / 20.0 1860 ribbon_filter.SetWidth(width) 1861 ribbon_filter.Update() 1862 # convert triangle strips to polygons 1863 tris = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 1864 tris.SetInputData(ribbon_filter.GetOutput()) 1865 tris.Update() 1866 1867 super().__init__(tris.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1868 self.name = "Ribbon" 1869 ############################################## 1870 return ###################################### 1871 ############################################## 1872 1873 line1 = np.asarray(line1) 1874 line2 = np.asarray(line2) 1875 1876 if closed: 1877 line1 = line1.tolist() 1878 line1 += [line1[0]] 1879 line2 = line2.tolist() 1880 line2 += [line2[0]] 1881 line1 = np.array(line1) 1882 line2 = np.array(line2) 1883 1884 if len(line1[0]) == 2: 1885 line1 = np.c_[line1, np.zeros(len(line1))] 1886 if len(line2[0]) == 2: 1887 line2 = np.c_[line2, np.zeros(len(line2))] 1888 1889 ppoints1 = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline1 1890 ppoints1.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(line1, dtype=np.float32)) 1891 lines1 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1892 lines1.InsertNextCell(len(line1)) 1893 for i in range(len(line1)): 1894 lines1.InsertCellPoint(i) 1895 poly1 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1896 poly1.SetPoints(ppoints1) 1897 poly1.SetLines(lines1) 1898 1899 ppoints2 = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline2 1900 ppoints2.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(line2, dtype=np.float32)) 1901 lines2 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1902 lines2.InsertNextCell(len(line2)) 1903 for i in range(len(line2)): 1904 lines2.InsertCellPoint(i) 1905 poly2 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1906 poly2.SetPoints(ppoints2) 1907 poly2.SetLines(lines2) 1908 1909 # build the lines 1910 lines1 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1911 lines1.InsertNextCell(poly1.GetNumberOfPoints()) 1912 for i in range(poly1.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1913 lines1.InsertCellPoint(i) 1914 1915 polygon1 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1916 polygon1.SetPoints(ppoints1) 1917 polygon1.SetLines(lines1) 1918 1919 lines2 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1920 lines2.InsertNextCell(poly2.GetNumberOfPoints()) 1921 for i in range(poly2.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1922 lines2.InsertCellPoint(i) 1923 1924 polygon2 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1925 polygon2.SetPoints(ppoints2) 1926 polygon2.SetLines(lines2) 1927 1928 merged_pd = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1929 merged_pd.AddInputData(polygon1) 1930 merged_pd.AddInputData(polygon2) 1931 merged_pd.Update() 1932 1933 rsf = vtki.new("RuledSurfaceFilter") 1934 rsf.CloseSurfaceOff() 1935 rsf.SetRuledMode(mode) 1936 rsf.SetResolution(res[0], res[1]) 1937 rsf.SetInputData(merged_pd.GetOutput()) 1938 rsf.Update() 1939 # convert triangle strips to polygons 1940 tris = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 1941 tris.SetInputData(rsf.GetOutput()) 1942 tris.Update() 1943 out = tris.GetOutput() 1944 1945 super().__init__(out, c, alpha) 1946 1947 self.name = "Ribbon" 1948 1949 1950class Arrow(Mesh): 1951 """ 1952 Build a 3D arrow from `start_pt` to `end_pt` of section size `s`, 1953 expressed as the fraction of the window size. 1954 """ 1955 1956 def __init__( 1957 self, 1958 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 1959 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 1960 s=None, 1961 shaft_radius=None, 1962 head_radius=None, 1963 head_length=None, 1964 res=12, 1965 c="r4", 1966 alpha=1.0, 1967 ) -> None: 1968 """ 1969 If `c` is a `float` less than 1, the arrow is rendered as a in a color scale 1970 from white to red. 1971 1972 .. note:: If `s=None` the arrow is scaled proportionally to its length 1973 1974  1975 """ 1976 # in case user is passing meshs 1977 if isinstance(start_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 1978 start_pt = start_pt.GetPosition() 1979 if isinstance(end_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 1980 end_pt = end_pt.GetPosition() 1981 1982 axis = np.asarray(end_pt) - np.asarray(start_pt) 1983 length = float(np.linalg.norm(axis)) 1984 if length: 1985 axis = axis / length 1986 if len(axis) < 3: # its 2d 1987 theta = np.pi / 2 1988 start_pt = [start_pt[0], start_pt[1], 0.0] 1989 end_pt = [end_pt[0], end_pt[1], 0.0] 1990 else: 1991 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 1992 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 1993 self.source = vtki.new("ArrowSource") 1994 self.source.SetShaftResolution(res) 1995 self.source.SetTipResolution(res) 1996 1997 if s: 1998 sz = 0.02 1999 self.source.SetTipRadius(sz) 2000 self.source.SetShaftRadius(sz / 1.75) 2001 self.source.SetTipLength(sz * 15) 2002 2003 if head_length: 2004 self.source.SetTipLength(head_length) 2005 if head_radius: 2006 self.source.SetTipRadius(head_radius) 2007 if shaft_radius: 2008 self.source.SetShaftRadius(shaft_radius) 2009 2010 self.source.Update() 2011 2012 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 2013 t.Translate(start_pt) 2014 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 2015 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 2016 t.RotateY(-90) # put it along Z 2017 if s: 2018 sz = 800 * s 2019 t.Scale(length, sz, sz) 2020 else: 2021 t.Scale(length, length, length) 2022 2023 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 2024 tf.SetInputData(self.source.GetOutput()) 2025 tf.SetTransform(t) 2026 tf.Update() 2027 2028 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2029 2030 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(start_pt) 2031 2032 self.phong().lighting("plastic") 2033 self.actor.PickableOff() 2034 self.actor.DragableOff() 2035 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2036 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2037 self.top_index = self.source.GetTipResolution() * 4 2038 self.fill = True # used by pyplot.__iadd__() 2039 self.s = s if s is not None else 1 # used by pyplot.__iadd__() 2040 self.name = "Arrow" 2041 2042 def top_point(self): 2043 """Return the current coordinates of the tip of the Arrow.""" 2044 return self.transform.transform_point(self.top) 2045 2046 def base_point(self): 2047 """Return the current coordinates of the base of the Arrow.""" 2048 return self.transform.transform_point(self.base) 2049 2050class Arrows(Glyph): 2051 """ 2052 Build arrows between two lists of points. 2053 """ 2054 2055 def __init__( 2056 self, 2057 start_pts, 2058 end_pts=None, 2059 s=None, 2060 shaft_radius=None, 2061 head_radius=None, 2062 head_length=None, 2063 thickness=1.0, 2064 res=6, 2065 c='k3', 2066 alpha=1.0, 2067 ) -> None: 2068 """ 2069 Build arrows between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 2070 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 2071 2072 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows. 2073 2074 Arguments: 2075 s : (float) 2076 fix aspect-ratio of the arrow and scale its cross section 2077 c : (color) 2078 color or color map name 2079 alpha : (float) 2080 set object opacity 2081 res : (int) 2082 set arrow resolution 2083 2084 Examples: 2085 - [glyphs2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs2.py) 2086 2087 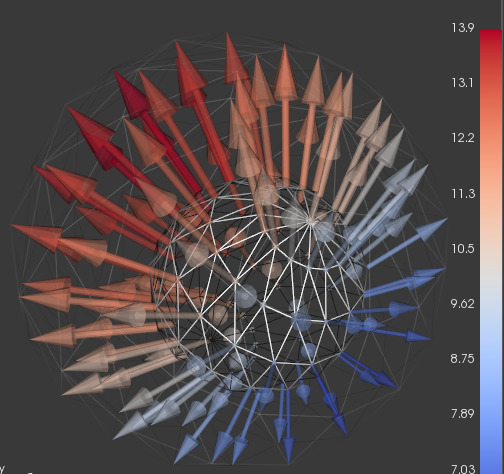 2088 """ 2089 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 2090 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 2091 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 2092 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 2093 2094 start_pts = np.asarray(start_pts) 2095 if end_pts is None: 2096 strt = start_pts[:, 0] 2097 end_pts = start_pts[:, 1] 2098 start_pts = strt 2099 else: 2100 end_pts = np.asarray(end_pts) 2101 2102 start_pts = utils.make3d(start_pts) 2103 end_pts = utils.make3d(end_pts) 2104 2105 arr = vtki.new("ArrowSource") 2106 arr.SetShaftResolution(res) 2107 arr.SetTipResolution(res) 2108 2109 if s: 2110 sz = 0.02 * s 2111 arr.SetTipRadius(sz * 2) 2112 arr.SetShaftRadius(sz * thickness) 2113 arr.SetTipLength(sz * 10) 2114 2115 if head_radius: 2116 arr.SetTipRadius(head_radius) 2117 if shaft_radius: 2118 arr.SetShaftRadius(shaft_radius) 2119 if head_length: 2120 arr.SetTipLength(head_length) 2121 2122 arr.Update() 2123 out = arr.GetOutput() 2124 2125 orients = end_pts - start_pts 2126 2127 color_by_vector_size = utils.is_sequence(c) or c in cmaps_names 2128 2129 super().__init__( 2130 start_pts, 2131 out, 2132 orientation_array=orients, 2133 scale_by_vector_size=True, 2134 color_by_vector_size=color_by_vector_size, 2135 c=c, 2136 alpha=alpha, 2137 ) 2138 self.lighting("off") 2139 if color_by_vector_size: 2140 vals = np.linalg.norm(orients, axis=1) 2141 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(vals.min(), vals.max()) 2142 else: 2143 self.c(c) 2144 self.name = "Arrows" 2145 2146 2147class Arrow2D(Mesh): 2148 """ 2149 Build a 2D arrow. 2150 """ 2151 2152 def __init__( 2153 self, 2154 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 2155 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 2156 s=1, 2157 rotation=0.0, 2158 shaft_length=0.85, 2159 shaft_width=0.055, 2160 head_length=0.175, 2161 head_width=0.175, 2162 fill=True, 2163 c="red4", 2164 alpha=1.0, 2165 ) -> None: 2166 """ 2167 Build a 2D arrow from `start_pt` to `end_pt`. 2168 2169 Arguments: 2170 s : (float) 2171 a global multiplicative convenience factor controlling the arrow size 2172 shaft_length : (float) 2173 fractional shaft length 2174 shaft_width : (float) 2175 fractional shaft width 2176 head_length : (float) 2177 fractional head length 2178 head_width : (float) 2179 fractional head width 2180 fill : (bool) 2181 if False only generate the outline 2182 """ 2183 self.fill = fill ## needed by pyplot.__iadd() 2184 self.s = s ## needed by pyplot.__iadd() 2185 2186 if s != 1: 2187 shaft_width *= s 2188 head_width *= np.sqrt(s) 2189 2190 # in case user is passing meshs 2191 if isinstance(start_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 2192 start_pt = start_pt.GetPosition() 2193 if isinstance(end_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 2194 end_pt = end_pt.GetPosition() 2195 if len(start_pt) == 2: 2196 start_pt = [start_pt[0], start_pt[1], 0] 2197 if len(end_pt) == 2: 2198 end_pt = [end_pt[0], end_pt[1], 0] 2199 2200 headBase = 1 - head_length 2201 head_width = max(head_width, shaft_width) 2202 if head_length is None or headBase > shaft_length: 2203 headBase = shaft_length 2204 2205 verts = [] 2206 verts.append([0, -shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2207 verts.append([shaft_length, -shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2208 verts.append([headBase, -head_width / 2, 0]) 2209 verts.append([1, 0, 0]) 2210 verts.append([headBase, head_width / 2, 0]) 2211 verts.append([shaft_length, shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2212 verts.append([0, shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2213 if fill: 2214 faces = ((0, 1, 3, 5, 6), (5, 3, 4), (1, 2, 3)) 2215 poly = utils.buildPolyData(verts, faces) 2216 else: 2217 lines = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0) 2218 poly = utils.buildPolyData(verts, [], lines=lines) 2219 2220 axis = np.array(end_pt) - np.array(start_pt) 2221 length = float(np.linalg.norm(axis)) 2222 if length: 2223 axis = axis / length 2224 theta = 0 2225 if len(axis) > 2: 2226 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 2227 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 2228 2229 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 2230 t.Translate(start_pt) 2231 if phi: 2232 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 2233 if theta: 2234 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 2235 t.RotateY(-90) # put it along Z 2236 if rotation: 2237 t.RotateX(rotation) 2238 t.Scale(length, length, length) 2239 2240 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 2241 tf.SetInputData(poly) 2242 tf.SetTransform(t) 2243 tf.Update() 2244 2245 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2246 2247 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(start_pt) 2248 2249 self.lighting("off") 2250 self.actor.DragableOff() 2251 self.actor.PickableOff() 2252 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2253 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2254 self.name = "Arrow2D" 2255 2256 2257class Arrows2D(Glyph): 2258 """ 2259 Build 2D arrows between two lists of points. 2260 """ 2261 2262 def __init__( 2263 self, 2264 start_pts, 2265 end_pts=None, 2266 s=1.0, 2267 rotation=0.0, 2268 shaft_length=0.8, 2269 shaft_width=0.05, 2270 head_length=0.225, 2271 head_width=0.175, 2272 fill=True, 2273 c=None, 2274 alpha=1.0, 2275 ) -> None: 2276 """ 2277 Build 2D arrows between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 2278 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 2279 2280 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows. 2281 2282 Arguments: 2283 shaft_length : (float) 2284 fractional shaft length 2285 shaft_width : (float) 2286 fractional shaft width 2287 head_length : (float) 2288 fractional head length 2289 head_width : (float) 2290 fractional head width 2291 fill : (bool) 2292 if False only generate the outline 2293 """ 2294 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 2295 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 2296 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 2297 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 2298 2299 start_pts = np.asarray(start_pts, dtype=float) 2300 if end_pts is None: 2301 strt = start_pts[:, 0] 2302 end_pts = start_pts[:, 1] 2303 start_pts = strt 2304 else: 2305 end_pts = np.asarray(end_pts, dtype=float) 2306 2307 if head_length is None: 2308 head_length = 1 - shaft_length 2309 2310 arr = Arrow2D( 2311 (0, 0, 0), 2312 (1, 0, 0), 2313 s=s, 2314 rotation=rotation, 2315 shaft_length=shaft_length, 2316 shaft_width=shaft_width, 2317 head_length=head_length, 2318 head_width=head_width, 2319 fill=fill, 2320 ) 2321 2322 orients = end_pts - start_pts 2323 orients = utils.make3d(orients) 2324 2325 pts = Points(start_pts) 2326 super().__init__( 2327 pts, 2328 arr, 2329 orientation_array=orients, 2330 scale_by_vector_size=True, 2331 c=c, 2332 alpha=alpha, 2333 ) 2334 self.flat().lighting("off").pickable(False) 2335 if c is not None: 2336 self.color(c) 2337 self.name = "Arrows2D" 2338 2339 2340class FlatArrow(Ribbon): 2341 """ 2342 Build a 2D arrow in 3D space by joining two close lines. 2343 """ 2344 2345 def __init__(self, line1, line2, tip_size=1.0, tip_width=1.0) -> None: 2346 """ 2347 Build a 2D arrow in 3D space by joining two close lines. 2348 2349 Examples: 2350 - [flatarrow.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/flatarrow.py) 2351 2352  2353 """ 2354 if isinstance(line1, Points): 2355 line1 = line1.coordinates 2356 if isinstance(line2, Points): 2357 line2 = line2.coordinates 2358 2359 sm1, sm2 = np.array(line1[-1], dtype=float), np.array(line2[-1], dtype=float) 2360 2361 v = (sm1 - sm2) / 3 * tip_width 2362 p1 = sm1 + v 2363 p2 = sm2 - v 2364 pm1 = (sm1 + sm2) / 2 2365 pm2 = (np.array(line1[-2]) + np.array(line2[-2])) / 2 2366 pm12 = pm1 - pm2 2367 tip = pm12 / np.linalg.norm(pm12) * np.linalg.norm(v) * 3 * tip_size / tip_width + pm1 2368 2369 line1.append(p1) 2370 line1.append(tip) 2371 line2.append(p2) 2372 line2.append(tip) 2373 resm = max(100, len(line1)) 2374 2375 super().__init__(line1, line2, res=(resm, 1)) 2376 self.phong().lighting("off") 2377 self.actor.PickableOff() 2378 self.actor.DragableOff() 2379 self.name = "FlatArrow" 2380 2381 2382class Triangle(Mesh): 2383 """Create a triangle from 3 points in space.""" 2384 2385 def __init__(self, p1, p2, p3, c="green7", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2386 """Create a triangle from 3 points in space.""" 2387 super().__init__([[p1, p2, p3], [[0, 1, 2]]], c, alpha) 2388 self.properties.LightingOff() 2389 self.name = "Triangle" 2390 2391 2392class Polygon(Mesh): 2393 """ 2394 Build a polygon in the `xy` plane. 2395 """ 2396 2397 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), nsides=6, r=1.0, c="coral", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2398 """ 2399 Build a polygon in the `xy` plane of `nsides` of radius `r`. 2400 2401  2402 """ 2403 t = np.linspace(np.pi / 2, 5 / 2 * np.pi, num=nsides, endpoint=False) 2404 pts = pol2cart(np.ones_like(t) * r, t).T 2405 faces = [list(range(nsides))] 2406 # do not use: vtkRegularPolygonSource 2407 super().__init__([pts, faces], c, alpha) 2408 if len(pos) == 2: 2409 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 2410 self.pos(pos) 2411 self.properties.LightingOff() 2412 self.name = "Polygon " + str(nsides) 2413 2414 2415class Circle(Polygon): 2416 """ 2417 Build a Circle of radius `r`. 2418 """ 2419 2420 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, res=120, c="gray5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2421 """ 2422 Build a Circle of radius `r`. 2423 """ 2424 super().__init__(pos, nsides=res, r=r) 2425 2426 self.nr_of_points = 0 2427 self.va = 0 2428 self.vb = 0 2429 self.axis1: List[float] = [] 2430 self.axis2: List[float] = [] 2431 self.center: List[float] = [] # filled by pointcloud.pca_ellipse() 2432 self.pvalue = 0.0 # filled by pointcloud.pca_ellipse() 2433 self.alpha(alpha).c(c) 2434 self.name = "Circle" 2435 2436 def acircularity(self) -> float: 2437 """ 2438 Return a measure of how different an ellipse is from a circle. 2439 Values close to zero correspond to a circular object. 2440 """ 2441 a, b = self.va, self.vb 2442 value = 0.0 2443 if a+b: 2444 value = ((a-b)/(a+b))**2 2445 return value 2446 2447class GeoCircle(Polygon): 2448 """ 2449 Build a Circle of radius `r`. 2450 """ 2451 2452 def __init__(self, lat, lon, r=1.0, res=60, c="red4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2453 """ 2454 Build a Circle of radius `r` as projected on a geographic map. 2455 Circles near the poles will look very squashed. 2456 2457 See example: 2458 ```bash 2459 vedo -r earthquake 2460 ``` 2461 """ 2462 coords = [] 2463 sinr, cosr = np.sin(r), np.cos(r) 2464 sinlat, coslat = np.sin(lat), np.cos(lat) 2465 for phi in np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num=res, endpoint=False): 2466 clat = np.arcsin(sinlat * cosr + coslat * sinr * np.cos(phi)) 2467 clng = lon + np.arctan2(np.sin(phi) * sinr * coslat, cosr - sinlat * np.sin(clat)) 2468 coords.append([clng / np.pi + 1, clat * 2 / np.pi + 1, 0]) 2469 2470 super().__init__(nsides=res, c=c, alpha=alpha) 2471 self.coordinates = coords # warp polygon points to match geo projection 2472 self.name = "Circle" 2473 2474 2475class Star(Mesh): 2476 """ 2477 Build a 2D star shape. 2478 """ 2479 2480 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), n=5, r1=0.7, r2=1.0, line=False, c="blue6", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2481 """ 2482 Build a 2D star shape of `n` cusps of inner radius `r1` and outer radius `r2`. 2483 2484 If line is True then only build the outer line (no internal surface meshing). 2485 2486 Example: 2487 - [extrude.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/extrude.py) 2488 2489  2490 """ 2491 t = np.linspace(np.pi / 2, 5 / 2 * np.pi, num=n, endpoint=False) 2492 x, y = pol2cart(np.ones_like(t) * r2, t) 2493 pts = np.c_[x, y, np.zeros_like(x)] 2494 2495 apts = [] 2496 for i, p in enumerate(pts): 2497 apts.append(p) 2498 if i + 1 < n: 2499 apts.append((p + pts[i + 1]) / 2 * r1 / r2) 2500 apts.append((pts[-1] + pts[0]) / 2 * r1 / r2) 2501 2502 if line: 2503 apts.append(pts[0]) 2504 poly = utils.buildPolyData(apts, lines=list(range(len(apts)))) 2505 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 2506 self.lw(2) 2507 else: 2508 apts.append((0, 0, 0)) 2509 cells = [] 2510 for i in range(2 * n - 1): 2511 cell = [2 * n, i, i + 1] 2512 cells.append(cell) 2513 cells.append([2 * n, i + 1, 0]) 2514 super().__init__([apts, cells], c, alpha) 2515 2516 if len(pos) == 2: 2517 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 2518 2519 self.properties.LightingOff() 2520 self.name = "Star" 2521 2522 2523class Disc(Mesh): 2524 """ 2525 Build a 2D disc. 2526 """ 2527 2528 def __init__( 2529 self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r1=0.5, r2=1.0, res=(1, 120), angle_range=(), c="gray4", alpha=1.0 2530 ) -> None: 2531 """ 2532 Build a 2D disc of inner radius `r1` and outer radius `r2`. 2533 2534 Set `res` as the resolution in R and Phi (can be a list). 2535 2536 Use `angle_range` to create a disc sector between the 2 specified angles. 2537 2538  2539 """ 2540 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2541 res_r, res_phi = res 2542 else: 2543 res_r, res_phi = res, 12 * res 2544 2545 if len(angle_range) == 0: 2546 ps = vtki.new("DiskSource") 2547 else: 2548 ps = vtki.new("SectorSource") 2549 ps.SetStartAngle(angle_range[0]) 2550 ps.SetEndAngle(angle_range[1]) 2551 2552 ps.SetInnerRadius(r1) 2553 ps.SetOuterRadius(r2) 2554 ps.SetRadialResolution(res_r) 2555 ps.SetCircumferentialResolution(res_phi) 2556 ps.Update() 2557 super().__init__(ps.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2558 self.flat() 2559 self.pos(utils.make3d(pos)) 2560 self.name = "Disc" 2561 2562class IcoSphere(Mesh): 2563 """ 2564 Create a sphere made of a uniform triangle mesh. 2565 """ 2566 2567 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, subdivisions=4, c="r5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2568 """ 2569 Create a sphere made of a uniform triangle mesh 2570 (from recursive subdivision of an icosahedron). 2571 2572 Example: 2573 ```python 2574 from vedo import * 2575 icos = IcoSphere(subdivisions=3) 2576 icos.compute_quality().cmap('coolwarm') 2577 icos.show(axes=1).close() 2578 ``` 2579  2580 """ 2581 subdivisions = int(min(subdivisions, 9)) # to avoid disasters 2582 2583 t = (1.0 + np.sqrt(5.0)) / 2.0 2584 points = np.array( 2585 [ 2586 [-1, t, 0], 2587 [1, t, 0], 2588 [-1, -t, 0], 2589 [1, -t, 0], 2590 [0, -1, t], 2591 [0, 1, t], 2592 [0, -1, -t], 2593 [0, 1, -t], 2594 [t, 0, -1], 2595 [t, 0, 1], 2596 [-t, 0, -1], 2597 [-t, 0, 1], 2598 ] 2599 ) 2600 faces = [ 2601 [0, 11, 5], 2602 [0, 5, 1], 2603 [0, 1, 7], 2604 [0, 7, 10], 2605 [0, 10, 11], 2606 [1, 5, 9], 2607 [5, 11, 4], 2608 [11, 10, 2], 2609 [10, 7, 6], 2610 [7, 1, 8], 2611 [3, 9, 4], 2612 [3, 4, 2], 2613 [3, 2, 6], 2614 [3, 6, 8], 2615 [3, 8, 9], 2616 [4, 9, 5], 2617 [2, 4, 11], 2618 [6, 2, 10], 2619 [8, 6, 7], 2620 [9, 8, 1], 2621 ] 2622 super().__init__([points * r, faces], c=c, alpha=alpha) 2623 2624 for _ in range(subdivisions): 2625 self.subdivide(method=1) 2626 pts = utils.versor(self.coordinates) * r 2627 self.coordinates = pts 2628 2629 self.pos(pos) 2630 self.name = "IcoSphere" 2631 2632 2633class Sphere(Mesh): 2634 """ 2635 Build a sphere. 2636 """ 2637 2638 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, res=24, quads=False, c="r5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2639 """ 2640 Build a sphere at position `pos` of radius `r`. 2641 2642 Arguments: 2643 r : (float) 2644 sphere radius 2645 res : (int, list) 2646 resolution in phi, resolution in theta is by default `2*res` 2647 quads : (bool) 2648 sphere mesh will be made of quads instead of triangles 2649 2650 [](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/32848391/72433092-f0a31e00-3798-11ea-85f7-b2f5fcc31568.png) 2651 """ 2652 if len(pos) == 2: 2653 pos = np.asarray([pos[0], pos[1], 0]) 2654 2655 self.radius = r # used by fitSphere 2656 self.center = pos 2657 self.residue = 0 2658 2659 if quads: 2660 res = max(res, 4) 2661 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 2662 img.SetDimensions(res - 1, res - 1, res - 1) 2663 rs = 1.0 / (res - 2) 2664 img.SetSpacing(rs, rs, rs) 2665 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 2666 gf.SetInputData(img) 2667 gf.Update() 2668 super().__init__(gf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2669 self.lw(0.1) 2670 2671 cgpts = self.coordinates - (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) 2672 2673 x, y, z = cgpts.T 2674 x = x * (1 + x * x) / 2 2675 y = y * (1 + y * y) / 2 2676 z = z * (1 + z * z) / 2 2677 _, theta, phi = cart2spher(x, y, z) 2678 2679 pts = spher2cart(np.ones_like(phi) * r, theta, phi).T 2680 self.coordinates = pts 2681 2682 else: 2683 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2684 res_t, res_phi = res 2685 else: 2686 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2687 2688 ss = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2689 ss.SetRadius(r) 2690 ss.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2691 ss.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2692 ss.Update() 2693 2694 super().__init__(ss.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2695 2696 self.phong() 2697 self.pos(pos) 2698 self.name = "Sphere" 2699 2700 2701class Spheres(Mesh): 2702 """ 2703 Build a large set of spheres. 2704 """ 2705 2706 def __init__(self, centers, r=1.0, res=8, c="red5", alpha=1) -> None: 2707 """ 2708 Build a (possibly large) set of spheres at `centers` of radius `r`. 2709 2710 Either `c` or `r` can be a list of RGB colors or radii. 2711 2712 Examples: 2713 - [manyspheres.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/manyspheres.py) 2714 2715  2716 """ 2717 2718 if isinstance(centers, Points): 2719 centers = centers.coordinates 2720 centers = np.asarray(centers, dtype=float) 2721 base = centers[0] 2722 2723 cisseq = False 2724 if utils.is_sequence(c): 2725 cisseq = True 2726 2727 if cisseq: 2728 if len(centers) != len(c): 2729 vedo.logger.error(f"mismatch #centers {len(centers)} != {len(c)} #colors") 2730 raise RuntimeError() 2731 2732 risseq = False 2733 if utils.is_sequence(r): 2734 risseq = True 2735 2736 if risseq: 2737 if len(centers) != len(r): 2738 vedo.logger.error(f"mismatch #centers {len(centers)} != {len(r)} #radii") 2739 raise RuntimeError() 2740 if cisseq and risseq: 2741 vedo.logger.error("Limitation: c and r cannot be both sequences.") 2742 raise RuntimeError() 2743 2744 src = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2745 if not risseq: 2746 src.SetRadius(r) 2747 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2748 res_t, res_phi = res 2749 else: 2750 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2751 2752 src.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2753 src.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2754 src.Update() 2755 2756 psrc = vtki.new("PointSource") 2757 psrc.SetNumberOfPoints(len(centers)) 2758 psrc.Update() 2759 pd = psrc.GetOutput() 2760 vpts = pd.GetPoints() 2761 2762 glyph = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 2763 glyph.SetSourceConnection(src.GetOutputPort()) 2764 2765 if cisseq: 2766 glyph.SetColorModeToColorByScalar() 2767 ucols = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 2768 ucols.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 2769 ucols.SetName("Colors") 2770 for acol in c: 2771 cx, cy, cz = get_color(acol) 2772 ucols.InsertNextTuple3(cx * 255, cy * 255, cz * 255) 2773 pd.GetPointData().AddArray(ucols) 2774 pd.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("Colors") 2775 glyph.ScalingOff() 2776 elif risseq: 2777 glyph.SetScaleModeToScaleByScalar() 2778 urads = utils.numpy2vtk(2 * np.ascontiguousarray(r), dtype=np.float32) 2779 urads.SetName("Radii") 2780 pd.GetPointData().AddArray(urads) 2781 pd.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("Radii") 2782 2783 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(centers - base, dtype=np.float32)) 2784 2785 glyph.SetInputData(pd) 2786 glyph.Update() 2787 2788 super().__init__(glyph.GetOutput(), alpha=alpha) 2789 self.pos(base) 2790 self.phong() 2791 if cisseq: 2792 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 2793 else: 2794 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2795 self.c(c) 2796 self.name = "Spheres" 2797 2798 2799class Earth(Mesh): 2800 """ 2801 Build a textured mesh representing the Earth. 2802 """ 2803 2804 def __init__(self, style=1, r=1.0) -> None: 2805 """ 2806 Build a textured mesh representing the Earth. 2807 2808 Example: 2809 - [geodesic_curve.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/geodesic_curve.py) 2810 2811  2812 """ 2813 tss = vtki.new("TexturedSphereSource") 2814 tss.SetRadius(r) 2815 tss.SetThetaResolution(72) 2816 tss.SetPhiResolution(36) 2817 tss.Update() 2818 super().__init__(tss.GetOutput(), c="w") 2819 atext = vtki.vtkTexture() 2820 pnm_reader = vtki.new("JPEGReader") 2821 fn = vedo.file_io.download(vedo.dataurl + f"textures/earth{style}.jpg", verbose=False) 2822 pnm_reader.SetFileName(fn) 2823 atext.SetInputConnection(pnm_reader.GetOutputPort()) 2824 atext.InterpolateOn() 2825 self.texture(atext) 2826 self.name = "Earth" 2827 2828 2829class Ellipsoid(Mesh): 2830 """Build a 3D ellipsoid.""" 2831 def __init__( 2832 self, 2833 pos=(0, 0, 0), 2834 axis1=(0.5, 0, 0), 2835 axis2=(0, 1, 0), 2836 axis3=(0, 0, 1.5), 2837 res=24, 2838 c="cyan4", 2839 alpha=1.0, 2840 ) -> None: 2841 """ 2842 Build a 3D ellipsoid centered at position `pos`. 2843 2844 Arguments: 2845 axis1 : (list) 2846 First axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2847 axis2 : (list) 2848 Second axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2849 axis3 : (list) 2850 Third axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2851 """ 2852 self.center = utils.make3d(pos) 2853 2854 self.axis1 = utils.make3d(axis1) 2855 self.axis2 = utils.make3d(axis2) 2856 self.axis3 = utils.make3d(axis3) 2857 2858 self.va = np.linalg.norm(self.axis1) 2859 self.vb = np.linalg.norm(self.axis2) 2860 self.vc = np.linalg.norm(self.axis3) 2861 2862 self.va_error = 0 2863 self.vb_error = 0 2864 self.vc_error = 0 2865 2866 self.nr_of_points = 1 # used by pointcloud.pca_ellipsoid() 2867 self.pvalue = 0 # used by pointcloud.pca_ellipsoid() 2868 2869 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2870 res_t, res_phi = res 2871 else: 2872 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2873 2874 elli_source = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2875 elli_source.SetRadius(1) 2876 elli_source.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2877 elli_source.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2878 elli_source.Update() 2879 2880 super().__init__(elli_source.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2881 2882 matrix = np.c_[self.axis1, self.axis2, self.axis3] 2883 lt = LinearTransform(matrix).translate(pos) 2884 self.apply_transform(lt) 2885 self.name = "Ellipsoid" 2886 2887 def asphericity(self) -> float: 2888 """ 2889 Return a measure of how different an ellipsoid is from a sphere. 2890 Values close to zero correspond to a spheric object. 2891 """ 2892 a, b, c = self.va, self.vb, self.vc 2893 asp = ( ((a-b)/(a+b))**2 2894 + ((a-c)/(a+c))**2 2895 + ((b-c)/(b+c))**2 ) / 3. * 4. 2896 return float(asp) 2897 2898 def asphericity_error(self) -> float: 2899 """ 2900 Calculate statistical error on the asphericity value. 2901 2902 Errors on the main axes are stored in 2903 `Ellipsoid.va_error`, Ellipsoid.vb_error` and `Ellipsoid.vc_error`. 2904 """ 2905 a, b, c = self.va, self.vb, self.vc 2906 sqrtn = np.sqrt(self.nr_of_points) 2907 ea, eb, ec = a / 2 / sqrtn, b / 2 / sqrtn, b / 2 / sqrtn 2908 2909 # from sympy import * 2910 # init_printing(use_unicode=True) 2911 # a, b, c, ea, eb, ec = symbols("a b c, ea, eb,ec") 2912 # L = ( 2913 # (((a - b) / (a + b)) ** 2 + ((c - b) / (c + b)) ** 2 + ((a - c) / (a + c)) ** 2) 2914 # / 3 * 4) 2915 # dl2 = (diff(L, a) * ea) ** 2 + (diff(L, b) * eb) ** 2 + (diff(L, c) * ec) ** 2 2916 # print(dl2) 2917 # exit() 2918 2919 dL2 = ( 2920 ea ** 2 2921 * ( 2922 -8 * (a - b) ** 2 / (3 * (a + b) ** 3) 2923 - 8 * (a - c) ** 2 / (3 * (a + c) ** 3) 2924 + 4 * (2 * a - 2 * c) / (3 * (a + c) ** 2) 2925 + 4 * (2 * a - 2 * b) / (3 * (a + b) ** 2) 2926 ) ** 2 2927 + eb ** 2 2928 * ( 2929 4 * (-2 * a + 2 * b) / (3 * (a + b) ** 2) 2930 - 8 * (a - b) ** 2 / (3 * (a + b) ** 3) 2931 - 8 * (-b + c) ** 2 / (3 * (b + c) ** 3) 2932 + 4 * (2 * b - 2 * c) / (3 * (b + c) ** 2) 2933 ) ** 2 2934 + ec ** 2 2935 * ( 2936 4 * (-2 * a + 2 * c) / (3 * (a + c) ** 2) 2937 - 8 * (a - c) ** 2 / (3 * (a + c) ** 3) 2938 + 4 * (-2 * b + 2 * c) / (3 * (b + c) ** 2) 2939 - 8 * (-b + c) ** 2 / (3 * (b + c) ** 3) 2940 ) ** 2 2941 ) 2942 err = np.sqrt(dL2) 2943 self.va_error = ea 2944 self.vb_error = eb 2945 self.vc_error = ec 2946 return err 2947 2948 2949class Grid(Mesh): 2950 """ 2951 An even or uneven 2D grid. 2952 """ 2953 2954 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=(1, 1), res=(10, 10), lw=1, c="k3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2955 """ 2956 Create an even or uneven 2D grid. 2957 Can also be created from a `np.mgrid` object (see example). 2958 2959 Arguments: 2960 pos : (list, Points, Mesh) 2961 position in space, can also be passed as a bounding box [xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax]. 2962 s : (float, list) 2963 if a float is provided it is interpreted as the total size along x and y, 2964 if a list of coords is provided they are interpreted as the vertices of the grid along x and y. 2965 In this case keyword `res` is ignored (see example below). 2966 res : (list) 2967 resolutions along x and y, e.i. the number of subdivisions 2968 lw : (int) 2969 line width 2970 2971 Example: 2972 ```python 2973 from vedo import * 2974 xcoords = np.arange(0, 2, 0.2) 2975 ycoords = np.arange(0, 1, 0.2) 2976 sqrtx = sqrt(xcoords) 2977 grid = Grid(s=(sqrtx, ycoords)).lw(2) 2978 grid.show(axes=8).close() 2979 2980 # Can also create a grid from a np.mgrid: 2981 X, Y = np.mgrid[-12:12:10*1j, 200:215:10*1j] 2982 vgrid = Grid(s=(X[:,0], Y[0])) 2983 vgrid.show(axes=8).close() 2984 ``` 2985  2986 """ 2987 resx, resy = res 2988 sx, sy = s 2989 2990 try: 2991 bb = pos.bounds() 2992 pos = [(bb[0] + bb[1])/2, (bb[2] + bb[3])/2, (bb[4] + bb[5])/2] 2993 sx = bb[1] - bb[0] 2994 sy = bb[3] - bb[2] 2995 except AttributeError: 2996 pass 2997 2998 if len(pos) == 2: 2999 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3000 elif len(pos) in [4,6]: # passing a bounding box 3001 bb = pos 3002 pos = [(bb[0] + bb[1])/2, (bb[2] + bb[3])/2, 0] 3003 sx = bb[1] - bb[0] 3004 sy = bb[3] - bb[2] 3005 if len(pos)==6: 3006 pos[2] = bb[4] - bb[5] 3007 3008 if utils.is_sequence(sx) and utils.is_sequence(sy): 3009 verts = [] 3010 for y in sy: 3011 for x in sx: 3012 verts.append([x, y, 0]) 3013 faces = [] 3014 n = len(sx) 3015 m = len(sy) 3016 for j in range(m - 1): 3017 j1n = (j + 1) * n 3018 for i in range(n - 1): 3019 faces.append([i + j * n, i + 1 + j * n, i + 1 + j1n, i + j1n]) 3020 3021 super().__init__([verts, faces], c, alpha) 3022 3023 else: 3024 ps = vtki.new("PlaneSource") 3025 ps.SetResolution(resx, resy) 3026 ps.Update() 3027 3028 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3029 t.Translate(pos) 3030 t.Scale(sx, sy, 1) 3031 3032 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3033 tf.SetInputData(ps.GetOutput()) 3034 tf.SetTransform(t) 3035 tf.Update() 3036 3037 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3038 3039 self.wireframe().lw(lw) 3040 self.properties.LightingOff() 3041 self.name = "Grid" 3042 3043 3044class Plane(Mesh): 3045 """Create a plane in space.""" 3046 def __init__( 3047 self, 3048 pos=(0, 0, 0), 3049 normal=(0, 0, 1), 3050 s=(1, 1), 3051 res=(1, 1), 3052 edge_direction=(), 3053 c="gray5", 3054 alpha=1.0, 3055 ) -> None: 3056 """ 3057 Create a plane of size `s=(xsize, ysize)` oriented perpendicular 3058 to vector `normal` so that it passes through point `pos`, optionally 3059 aligning an edge with `direction`. 3060 3061 Arguments: 3062 pos : (list) 3063 position of the plane center 3064 normal : (list) 3065 normal vector to the plane 3066 s : (list) 3067 size of the plane along x and y 3068 res : (list) 3069 resolution of the plane along x and y 3070 edge_direction : (list) 3071 direction vector to align one edge of the plane 3072 """ 3073 if isinstance(pos, vtki.vtkPolyData): 3074 super().__init__(pos, c, alpha) 3075 3076 else: 3077 ps = vtki.new("PlaneSource") 3078 ps.SetResolution(res[0], res[1]) 3079 tri = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 3080 tri.SetInputConnection(ps.GetOutputPort()) 3081 tri.Update() 3082 super().__init__(tri.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3083 3084 pos = utils.make3d(pos) 3085 normal = np.asarray(normal, dtype=float) 3086 axis = normal / np.linalg.norm(normal) 3087 3088 # Calculate orientation using normal 3089 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 3090 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 3091 3092 t = LinearTransform() 3093 t.scale([s[0], s[1], 1]) 3094 3095 # Rotate to align normal 3096 t.rotate_y(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3097 t.rotate_z(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3098 3099 # Additional direction alignment 3100 if len(edge_direction) >= 2: 3101 direction = utils.make3d(edge_direction).astype(float) 3102 direction /= np.linalg.norm(direction) 3103 3104 if s[0] <= s[1]: 3105 current_direction = np.asarray([0,1,0]) 3106 else: 3107 current_direction = np.asarray([1,0,0]) 3108 3109 transformed_current_direction = t.transform_point(current_direction) 3110 n = transformed_current_direction / np.linalg.norm(transformed_current_direction) 3111 3112 if np.linalg.norm(transformed_current_direction) >= 1e-6: 3113 angle = np.arccos(np.dot(n, direction)) 3114 t.rotate(axis=axis, angle=np.rad2deg(angle)) 3115 3116 t.translate(pos) 3117 self.apply_transform(t) 3118 3119 self.lighting("off") 3120 self.name = "Plane" 3121 self.variance = 0 # used by pointcloud.fit_plane() 3122 3123 def clone(self, deep=True) -> "Plane": 3124 newplane = Plane() 3125 if deep: 3126 newplane.dataset.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 3127 else: 3128 newplane.dataset.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 3129 newplane.copy_properties_from(self) 3130 newplane.transform = self.transform.clone() 3131 newplane.variance = 0 3132 return newplane 3133 3134 @property 3135 def normal(self) -> np.ndarray: 3136 pts = self.coordinates 3137 # this is necessary because plane can have high resolution 3138 # p0, p1 = pts[0], pts[1] 3139 # AB = p1 - p0 3140 # AB /= np.linalg.norm(AB) 3141 # for pt in pts[2:]: 3142 # AC = pt - p0 3143 # AC /= np.linalg.norm(AC) 3144 # cosine_angle = np.dot(AB, AC) 3145 # if abs(cosine_angle) < 0.99: 3146 # normal = np.cross(AB, AC) 3147 # return normal / np.linalg.norm(normal) 3148 p0, p1, p2 = pts[0], pts[1], pts[int(len(pts)/2 +0.5)] 3149 AB = p1 - p0 3150 AB /= np.linalg.norm(AB) 3151 AC = p2 - p0 3152 AC /= np.linalg.norm(AC) 3153 normal = np.cross(AB, AC) 3154 return normal / np.linalg.norm(normal) 3155 3156 @property 3157 def center(self) -> np.ndarray: 3158 pts = self.coordinates 3159 return np.mean(pts, axis=0) 3160 3161 def contains(self, points, tol=0) -> np.ndarray: 3162 """ 3163 Check if each of the provided point lies on this plane. 3164 `points` is an array of shape (n, 3). 3165 """ 3166 points = np.array(points, dtype=float) 3167 bounds = self.coordinates 3168 3169 mask = np.isclose(np.dot(points - self.center, self.normal), 0, atol=tol) 3170 3171 for i in [1, 3]: 3172 AB = bounds[i] - bounds[0] 3173 AP = points - bounds[0] 3174 mask_l = np.less_equal(np.dot(AP, AB), np.linalg.norm(AB)) 3175 mask_g = np.greater_equal(np.dot(AP, AB), 0) 3176 mask = np.logical_and(mask, mask_l) 3177 mask = np.logical_and(mask, mask_g) 3178 return mask 3179 3180 3181class Rectangle(Mesh): 3182 """ 3183 Build a rectangle in the xy plane. 3184 """ 3185 3186 def __init__(self, p1=(0, 0), p2=(1, 1), radius=None, res=12, c="gray5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3187 """ 3188 Build a rectangle in the xy plane identified by any two corner points. 3189 3190 Arguments: 3191 p1 : (list) 3192 bottom-left position of the corner 3193 p2 : (list) 3194 top-right position of the corner 3195 radius : (float, list) 3196 smoothing radius of the corner in world units. 3197 A list can be passed with 4 individual values. 3198 """ 3199 if len(p1) == 2: 3200 p1 = np.array([p1[0], p1[1], 0.0]) 3201 else: 3202 p1 = np.array(p1, dtype=float) 3203 if len(p2) == 2: 3204 p2 = np.array([p2[0], p2[1], 0.0]) 3205 else: 3206 p2 = np.array(p2, dtype=float) 3207 3208 self.corner1 = p1 3209 self.corner2 = p2 3210 3211 color = c 3212 smoothr = False 3213 risseq = False 3214 if utils.is_sequence(radius): 3215 risseq = True 3216 smoothr = True 3217 if max(radius) == 0: 3218 smoothr = False 3219 elif radius: 3220 smoothr = True 3221 3222 if not smoothr: 3223 radius = None 3224 self.radius = radius 3225 3226 if smoothr: 3227 r = radius 3228 if not risseq: 3229 r = [r, r, r, r] 3230 rd, ra, rb, rc = r 3231 3232 if p1[0] > p2[0]: # flip p1 - p2 3233 p1, p2 = p2, p1 3234 if p1[1] > p2[1]: # flip p1y - p2y 3235 p1[1], p2[1] = p2[1], p1[1] 3236 3237 px, py, _ = p2 - p1 3238 k = min(px / 2, py / 2) 3239 ra = min(abs(ra), k) 3240 rb = min(abs(rb), k) 3241 rc = min(abs(rc), k) 3242 rd = min(abs(rd), k) 3243 beta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num=res * 4, endpoint=False) 3244 betas = np.split(beta, 4) 3245 rrx = np.cos(betas) 3246 rry = np.sin(betas) 3247 3248 q1 = (rd, 0) 3249 # q2 = (px-ra, 0) 3250 q3 = (px, ra) 3251 # q4 = (px, py-rb) 3252 q5 = (px - rb, py) 3253 # q6 = (rc, py) 3254 q7 = (0, py - rc) 3255 # q8 = (0, rd) 3256 a = np.c_[rrx[3], rry[3]]*ra + [px-ra, ra] if ra else np.array([]) 3257 b = np.c_[rrx[0], rry[0]]*rb + [px-rb, py-rb] if rb else np.array([]) 3258 c = np.c_[rrx[1], rry[1]]*rc + [rc, py-rc] if rc else np.array([]) 3259 d = np.c_[rrx[2], rry[2]]*rd + [rd, rd] if rd else np.array([]) 3260 3261 pts = [q1, *a.tolist(), q3, *b.tolist(), q5, *c.tolist(), q7, *d.tolist()] 3262 faces = [list(range(len(pts)))] 3263 else: 3264 p1r = np.array([p2[0], p1[1], 0.0]) 3265 p2l = np.array([p1[0], p2[1], 0.0]) 3266 pts = ([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], p1r - p1, p2 - p1, p2l - p1) 3267 faces = [(0, 1, 2, 3)] 3268 3269 super().__init__([pts, faces], color, alpha) 3270 self.pos(p1) 3271 self.properties.LightingOff() 3272 self.name = "Rectangle" 3273 3274 3275class Box(Mesh): 3276 """ 3277 Build a box of specified dimensions. 3278 """ 3279 3280 def __init__( 3281 self, 3282 pos=(0, 0, 0), 3283 length=1.0, width=1.0, height=1.0, size=(), c="g4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3284 """ 3285 Build a box of dimensions `x=length, y=width and z=height`. 3286 Alternatively dimensions can be defined by setting `size` keyword with a tuple. 3287 3288 If `pos` is a list of 6 numbers, this will be interpreted as the bounding box: 3289 `[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]` 3290 3291 Note that the shape polygonal data contains duplicated vertices. This is to allow 3292 each face to have its own normal, which is essential for some operations. 3293 Use the `clean()` method to remove duplicate points. 3294 3295 Examples: 3296 - [aspring1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/aspring1.py) 3297 3298 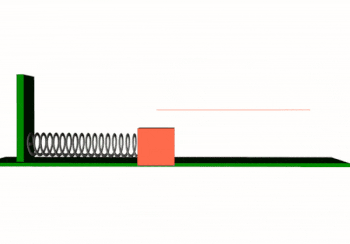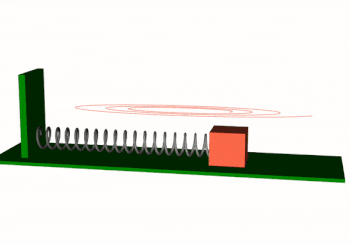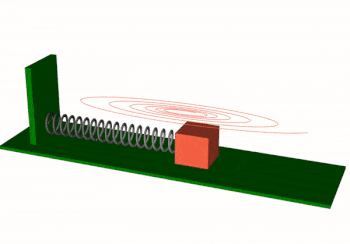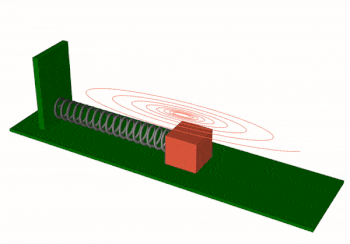 3299 """ 3300 src = vtki.new("CubeSource") 3301 3302 if len(pos) == 2: 3303 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3304 3305 ################# 3306 if len(pos) == 6: 3307 length, width, height = (pos[1] - pos[0]), (pos[3] - pos[2]), (pos[5] - pos[4]) 3308 pos = [(pos[0] + pos[1]) / 2, (pos[2] + pos[3]) / 2, (pos[4] + pos[5]) / 2] 3309 3310 elif len(size) == 3: 3311 length, width, height = size 3312 3313 src.SetXLength(length) 3314 src.SetYLength(width) 3315 src.SetZLength(height) 3316 3317 src.Update() 3318 pd = src.GetOutput() 3319 3320 tc = [ 3321 [0.0, 0.0], 3322 [1.0, 0.0], 3323 [0.0, 1.0], 3324 [1.0, 1.0], 3325 [1.0, 0.0], 3326 [0.0, 0.0], 3327 [1.0, 1.0], 3328 [0.0, 1.0], 3329 [1.0, 1.0], 3330 [1.0, 0.0], 3331 [0.0, 1.0], 3332 [0.0, 0.0], 3333 [0.0, 1.0], 3334 [0.0, 0.0], 3335 [1.0, 1.0], 3336 [1.0, 0.0], 3337 [1.0, 0.0], 3338 [0.0, 0.0], 3339 [1.0, 1.0], 3340 [0.0, 1.0], 3341 [0.0, 0.0], 3342 [1.0, 0.0], 3343 [0.0, 1.0], 3344 [1.0, 1.0], 3345 ] 3346 vtc = utils.numpy2vtk(tc) 3347 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtc) 3348 super().__init__(pd, c, alpha) 3349 self.name = "Box" 3350 self.pos(pos) 3351 3352 3353class Cube(Box): 3354 """ 3355 Build a cube shape. 3356 3357 Note that the shape polygonal data contains duplicated vertices. This is to allow 3358 each face to have its own normal, which is essential for some operations. 3359 Use the `clean()` method to remove duplicate points. 3360 """ 3361 3362 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), side=1.0, c="g4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3363 """Build a cube of size `side`.""" 3364 super().__init__(pos, side, side, side, (), c, alpha) 3365 self.name = "Cube" 3366 3367 3368class TessellatedBox(Mesh): 3369 """ 3370 Build a cubic `Mesh` made of quads. 3371 """ 3372 3373 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), n=10, spacing=(1, 1, 1), bounds=(), c="k5", alpha=0.5) -> None: 3374 """ 3375 Build a cubic `Mesh` made of `n` small quads in the 3 axis directions. 3376 3377 Arguments: 3378 pos : (list) 3379 position of the left bottom corner 3380 n : (int, list) 3381 number of subdivisions along each side 3382 spacing : (float) 3383 size of the side of the single quad in the 3 directions 3384 """ 3385 if utils.is_sequence(n): # slow 3386 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 3387 img.SetDimensions(n[0] + 1, n[1] + 1, n[2] + 1) 3388 img.SetSpacing(spacing) 3389 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 3390 gf.SetInputData(img) 3391 gf.Update() 3392 poly = gf.GetOutput() 3393 else: # fast 3394 n -= 1 3395 tbs = vtki.new("TessellatedBoxSource") 3396 tbs.SetLevel(n) 3397 if len(bounds)>0: 3398 tbs.SetBounds(bounds) 3399 else: 3400 tbs.SetBounds(0, n * spacing[0], 0, n * spacing[1], 0, n * spacing[2]) 3401 tbs.QuadsOn() 3402 #tbs.SetOutputPointsPrecision(vtki.vtkAlgorithm.SINGLE_PRECISION) 3403 tbs.Update() 3404 poly = tbs.GetOutput() 3405 super().__init__(poly, c=c, alpha=alpha) 3406 self.pos(pos) 3407 self.lw(1).lighting("off") 3408 self.name = "TessellatedBox" 3409 3410 3411class Spring(Mesh): 3412 """ 3413 Build a spring model. 3414 """ 3415 3416 def __init__( 3417 self, 3418 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 3419 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 3420 coils=20, 3421 r1=0.1, 3422 r2=None, 3423 thickness=None, 3424 c="gray5", 3425 alpha=1.0, 3426 ) -> None: 3427 """ 3428 Build a spring of specified nr of `coils` between `start_pt` and `end_pt`. 3429 3430 Arguments: 3431 coils : (int) 3432 number of coils 3433 r1 : (float) 3434 radius at start point 3435 r2 : (float) 3436 radius at end point 3437 thickness : (float) 3438 thickness of the coil section 3439 """ 3440 start_pt = utils.make3d(start_pt) 3441 end_pt = utils.make3d(end_pt) 3442 3443 diff = end_pt - start_pt 3444 length = np.linalg.norm(diff) 3445 if not length: 3446 return 3447 if not r1: 3448 r1 = length / 20 3449 trange = np.linspace(0, length, num=50 * coils) 3450 om = 6.283 * (coils - 0.5) / length 3451 if not r2: 3452 r2 = r1 3453 pts = [] 3454 for t in trange: 3455 f = (length - t) / length 3456 rd = r1 * f + r2 * (1 - f) 3457 pts.append([rd * np.cos(om * t), rd * np.sin(om * t), t]) 3458 3459 pts = [[0, 0, 0]] + pts + [[0, 0, length]] 3460 diff = diff / length 3461 theta = np.arccos(diff[2]) 3462 phi = np.arctan2(diff[1], diff[0]) 3463 sp = Line(pts) 3464 3465 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3466 t.Translate(start_pt) 3467 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3468 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3469 3470 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3471 tf.SetInputData(sp.dataset) 3472 tf.SetTransform(t) 3473 tf.Update() 3474 3475 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 3476 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(12) 3477 tuf.CappingOn() 3478 tuf.SetInputData(tf.GetOutput()) 3479 if not thickness: 3480 thickness = r1 / 10 3481 tuf.SetRadius(thickness) 3482 tuf.Update() 3483 3484 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3485 3486 self.phong().lighting("metallic") 3487 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) 3488 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) 3489 self.name = "Spring" 3490 3491 3492class Cylinder(Mesh): 3493 """ 3494 Build a cylinder of specified height and radius. 3495 """ 3496 3497 def __init__( 3498 self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, height=2.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3499 cap=True, res=24, c="teal3", alpha=1.0 3500 ) -> None: 3501 """ 3502 Build a cylinder of specified height and radius `r`, centered at `pos`. 3503 3504 If `pos` is a list of 2 points, e.g. `pos=[v1, v2]`, build a cylinder with base 3505 centered at `v1` and top at `v2`. 3506 3507 Arguments: 3508 cap : (bool) 3509 enable/disable the caps of the cylinder 3510 res : (int) 3511 resolution of the cylinder sides 3512 3513  3514 """ 3515 if utils.is_sequence(pos[0]): # assume user is passing pos=[base, top] 3516 base = np.array(pos[0], dtype=float) 3517 top = np.array(pos[1], dtype=float) 3518 pos = (base + top) / 2 3519 height = np.linalg.norm(top - base) 3520 axis = top - base 3521 axis = utils.versor(axis) 3522 else: 3523 axis = utils.versor(axis) 3524 base = pos - axis * height / 2 3525 top = pos + axis * height / 2 3526 3527 cyl = vtki.new("CylinderSource") 3528 cyl.SetResolution(res) 3529 cyl.SetRadius(r) 3530 cyl.SetHeight(height) 3531 cyl.SetCapping(cap) 3532 cyl.Update() 3533 3534 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 3535 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 3536 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3537 t.PostMultiply() 3538 t.RotateX(90) # put it along Z 3539 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3540 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3541 t.Translate(pos) 3542 3543 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3544 tf.SetInputData(cyl.GetOutput()) 3545 tf.SetTransform(t) 3546 tf.Update() 3547 3548 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3549 3550 self.phong() 3551 self.base = base 3552 self.top = top 3553 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(pos) 3554 self.name = "Cylinder" 3555 3556 3557class Cone(Mesh): 3558 """Build a cone of specified radius and height.""" 3559 3560 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, height=3.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3561 res=48, c="green3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3562 """Build a cone of specified radius `r` and `height`, centered at `pos`.""" 3563 con = vtki.new("ConeSource") 3564 con.SetResolution(res) 3565 con.SetRadius(r) 3566 con.SetHeight(height) 3567 con.SetDirection(axis) 3568 con.Update() 3569 super().__init__(con.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3570 self.phong() 3571 if len(pos) == 2: 3572 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3573 self.pos(pos) 3574 v = utils.versor(axis) * height / 2 3575 self.base = pos - v 3576 self.top = pos + v 3577 self.name = "Cone" 3578 3579 3580class Pyramid(Cone): 3581 """Build a pyramidal shape.""" 3582 3583 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, height=1.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3584 c="green3", alpha=1) -> None: 3585 """Build a pyramid of specified base size `s` and `height`, centered at `pos`.""" 3586 super().__init__(pos, s, height, axis, 4, c, alpha) 3587 self.name = "Pyramid" 3588 3589 3590class Torus(Mesh): 3591 """ 3592 Build a toroidal shape. 3593 """ 3594 3595 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r1=1.0, r2=0.2, res=36, quads=False, c="yellow3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3596 """ 3597 Build a torus of specified outer radius `r1` internal radius `r2`, centered at `pos`. 3598 If `quad=True` a quad-mesh is generated. 3599 """ 3600 if utils.is_sequence(res): 3601 res_u, res_v = res 3602 else: 3603 res_u, res_v = 3 * res, res 3604 3605 if quads: 3606 # https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/issues/710 3607 3608 n = res_v 3609 m = res_u 3610 3611 theta = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, n) 3612 phi = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, m) 3613 theta, phi = np.meshgrid(theta, phi) 3614 t = r1 + r2 * np.cos(theta) 3615 x = t * np.cos(phi) 3616 y = t * np.sin(phi) 3617 z = r2 * np.sin(theta) 3618 pts = np.column_stack((x.ravel(), y.ravel(), z.ravel())) 3619 3620 faces = [] 3621 for j in range(m - 1): 3622 j1n = (j + 1) * n 3623 for i in range(n - 1): 3624 faces.append([i + j * n, i + 1 + j * n, i + 1 + j1n, i + j1n]) 3625 3626 super().__init__([pts, faces], c, alpha) 3627 3628 else: 3629 rs = vtki.new("ParametricTorus") 3630 rs.SetRingRadius(r1) 3631 rs.SetCrossSectionRadius(r2) 3632 pfs = vtki.new("ParametricFunctionSource") 3633 pfs.SetParametricFunction(rs) 3634 pfs.SetUResolution(res_u) 3635 pfs.SetVResolution(res_v) 3636 pfs.Update() 3637 3638 super().__init__(pfs.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3639 3640 self.phong() 3641 if len(pos) == 2: 3642 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3643 self.pos(pos) 3644 self.name = "Torus" 3645 3646 3647class Paraboloid(Mesh): 3648 """ 3649 Build a paraboloid. 3650 """ 3651 3652 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), height=1.0, res=50, c="cyan5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3653 """ 3654 Build a paraboloid of specified height and radius `r`, centered at `pos`. 3655 3656 Full volumetric expression is: 3657 `F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9` 3658 3659  3660 """ 3661 quadric = vtki.new("Quadric") 3662 quadric.SetCoefficients(1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, height / 4, 0) 3663 # F(x,y,z) = a0*x^2 + a1*y^2 + a2*z^2 3664 # + a3*x*y + a4*y*z + a5*x*z 3665 # + a6*x + a7*y + a8*z +a9 3666 sample = vtki.new("SampleFunction") 3667 sample.SetSampleDimensions(res, res, res) 3668 sample.SetImplicitFunction(quadric) 3669 3670 contours = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 3671 contours.SetInputConnection(sample.GetOutputPort()) 3672 contours.GenerateValues(1, 0.01, 0.01) 3673 contours.Update() 3674 3675 super().__init__(contours.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3676 self.compute_normals().phong() 3677 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 3678 self.pos(pos) 3679 self.name = "Paraboloid" 3680 3681 3682class Hyperboloid(Mesh): 3683 """ 3684 Build a hyperboloid. 3685 """ 3686 3687 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), a2=1.0, value=0.5, res=100, c="pink4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3688 """ 3689 Build a hyperboloid of specified aperture `a2` and `height`, centered at `pos`. 3690 3691 Full volumetric expression is: 3692 `F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9` 3693 """ 3694 q = vtki.new("Quadric") 3695 q.SetCoefficients(2, 2, -1 / a2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) 3696 # F(x,y,z) = a0*x^2 + a1*y^2 + a2*z^2 3697 # + a3*x*y + a4*y*z + a5*x*z 3698 # + a6*x + a7*y + a8*z +a9 3699 sample = vtki.new("SampleFunction") 3700 sample.SetSampleDimensions(res, res, res) 3701 sample.SetImplicitFunction(q) 3702 3703 contours = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 3704 contours.SetInputConnection(sample.GetOutputPort()) 3705 contours.GenerateValues(1, value, value) 3706 contours.Update() 3707 3708 super().__init__(contours.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3709 self.compute_normals().phong() 3710 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 3711 self.pos(pos) 3712 self.name = "Hyperboloid" 3713 3714 3715def Marker(symbol, pos=(0, 0, 0), c="k", alpha=1.0, s=0.1, filled=True) -> Any: 3716 """ 3717 Generate a marker shape. Typically used in association with `Glyph`. 3718 """ 3719 if isinstance(symbol, Mesh): 3720 return symbol.c(c).alpha(alpha).lighting("off") 3721 3722 if isinstance(symbol, int): 3723 symbs = [".", "o", "O", "0", "p", "*", "h", "D", "d", "v", "^", ">", "<", "s", "x", "a"] 3724 symbol = symbol % len(symbs) 3725 symbol = symbs[symbol] 3726 3727 if symbol == ".": 3728 mesh = Polygon(nsides=24, r=s * 0.6) 3729 elif symbol == "o": 3730 mesh = Polygon(nsides=24, r=s * 0.75) 3731 elif symbol == "O": 3732 mesh = Disc(r1=s * 0.6, r2=s * 0.75, res=(1, 24)) 3733 elif symbol == "0": 3734 m1 = Disc(r1=s * 0.6, r2=s * 0.75, res=(1, 24)) 3735 m2 = Circle(r=s * 0.36).reverse() 3736 mesh = merge(m1, m2) 3737 elif symbol == "p": 3738 mesh = Polygon(nsides=5, r=s) 3739 elif symbol == "*": 3740 mesh = Star(r1=0.65 * s * 1.1, r2=s * 1.1, line=not filled) 3741 elif symbol == "h": 3742 mesh = Polygon(nsides=6, r=s) 3743 elif symbol == "D": 3744 mesh = Polygon(nsides=4, r=s) 3745 elif symbol == "d": 3746 mesh = Polygon(nsides=4, r=s * 1.1).scale([0.5, 1, 1]) 3747 elif symbol == "v": 3748 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s).rotate_z(180) 3749 elif symbol == "^": 3750 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s) 3751 elif symbol == ">": 3752 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s).rotate_z(-90) 3753 elif symbol == "<": 3754 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s).rotate_z(90) 3755 elif symbol == "s": 3756 mesh = Mesh( 3757 [[[-1, -1, 0], [1, -1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [-1, 1, 0]], [[0, 1, 2, 3]]] 3758 ).scale(s / 1.4) 3759 elif symbol == "x": 3760 mesh = Text3D("+", pos=(0, 0, 0), s=s * 2.6, justify="center", depth=0) 3761 # mesh.rotate_z(45) 3762 elif symbol == "a": 3763 mesh = Text3D("*", pos=(0, 0, 0), s=s * 2.6, justify="center", depth=0) 3764 else: 3765 mesh = Text3D(symbol, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=s * 2, justify="center", depth=0) 3766 mesh.flat().lighting("off").wireframe(not filled).c(c).alpha(alpha) 3767 if len(pos) == 2: 3768 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3769 mesh.pos(pos) 3770 mesh.name = "Marker" 3771 return mesh 3772 3773 3774class Brace(Mesh): 3775 """ 3776 Create a brace (bracket) shape. 3777 """ 3778 3779 def __init__( 3780 self, 3781 q1, 3782 q2, 3783 style="}", 3784 padding1=0.0, 3785 font="Theemim", 3786 comment="", 3787 justify=None, 3788 angle=0.0, 3789 padding2=0.2, 3790 s=1.0, 3791 italic=0, 3792 c="k1", 3793 alpha=1.0, 3794 ) -> None: 3795 """ 3796 Create a brace (bracket) shape which spans from point q1 to point q2. 3797 3798 Arguments: 3799 q1 : (list) 3800 point 1. 3801 q2 : (list) 3802 point 2. 3803 style : (str) 3804 style of the bracket, eg. `{}, [], (), <>`. 3805 padding1 : (float) 3806 padding space in percent form the input points. 3807 font : (str) 3808 font type 3809 comment : (str) 3810 additional text to appear next to the brace symbol. 3811 justify : (str) 3812 specify the anchor point to justify text comment, e.g. "top-left". 3813 italic : float 3814 italicness of the text comment (can be a positive or negative number) 3815 angle : (float) 3816 rotation angle of text. Use `None` to keep it horizontal. 3817 padding2 : (float) 3818 padding space in percent form brace to text comment. 3819 s : (float) 3820 scale factor for the comment 3821 3822 Examples: 3823 - [scatter3.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/scatter3.py) 3824 3825 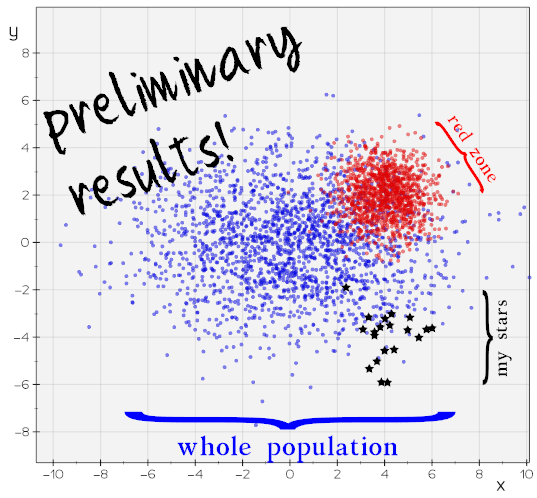 3826 """ 3827 if isinstance(q1, vtki.vtkActor): 3828 q1 = q1.GetPosition() 3829 if isinstance(q2, vtki.vtkActor): 3830 q2 = q2.GetPosition() 3831 if len(q1) == 2: 3832 q1 = [q1[0], q1[1], 0.0] 3833 if len(q2) == 2: 3834 q2 = [q2[0], q2[1], 0.0] 3835 q1 = np.array(q1, dtype=float) 3836 q2 = np.array(q2, dtype=float) 3837 mq = (q1 + q2) / 2 3838 q1 = q1 - mq 3839 q2 = q2 - mq 3840 d = np.linalg.norm(q2 - q1) 3841 q2[2] = q1[2] 3842 3843 if style not in "{}[]()<>|I": 3844 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown style {style}." + "Use {}[]()<>|I") 3845 style = "}" 3846 3847 flip = False 3848 if style in ["{", "[", "(", "<"]: 3849 flip = True 3850 i = ["{", "[", "(", "<"].index(style) 3851 style = ["}", "]", ")", ">"][i] 3852 3853 br = Text3D(style, font="Theemim", justify="center-left") 3854 br.scale([0.4, 1, 1]) 3855 3856 angler = np.arctan2(q2[1], q2[0]) * 180 / np.pi - 90 3857 if flip: 3858 angler += 180 3859 3860 _, x1, y0, y1, _, _ = br.bounds() 3861 if comment: 3862 just = "center-top" 3863 if angle is None: 3864 angle = -angler + 90 3865 if not flip: 3866 angle += 180 3867 3868 if flip: 3869 angle += 180 3870 just = "center-bottom" 3871 if justify is not None: 3872 just = justify 3873 cmt = Text3D(comment, font=font, justify=just, italic=italic) 3874 cx0, cx1 = cmt.xbounds() 3875 cmt.rotate_z(90 + angle) 3876 cmt.scale(1 / (cx1 - cx0) * s * len(comment) / 5) 3877 cmt.shift(x1 * (1 + padding2), 0, 0) 3878 poly = merge(br, cmt).dataset 3879 3880 else: 3881 poly = br.dataset 3882 3883 tr = vtki.vtkTransform() 3884 tr.Translate(mq) 3885 tr.RotateZ(angler) 3886 tr.Translate(padding1 * d, 0, 0) 3887 pscale = 1 3888 tr.Scale(pscale / (y1 - y0) * d, pscale / (y1 - y0) * d, 1) 3889 3890 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3891 tf.SetInputData(poly) 3892 tf.SetTransform(tr) 3893 tf.Update() 3894 poly = tf.GetOutput() 3895 3896 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 3897 3898 self.base = q1 3899 self.top = q2 3900 self.name = "Brace" 3901 3902 3903class Star3D(Mesh): 3904 """ 3905 Build a 3D starred shape. 3906 """ 3907 3908 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, thickness=0.1, c="blue4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3909 """ 3910 Build a 3D star shape of 5 cusps, mainly useful as a 3D marker. 3911 """ 3912 pts = ((1.34, 0., -0.37), (5.75e-3, -0.588, thickness/10), (0.377, 0.,-0.38), 3913 (0.0116, 0., -1.35), (-0.366, 0., -0.384), (-1.33, 0., -0.385), 3914 (-0.600, 0., 0.321), (-0.829, 0., 1.19), (-1.17e-3, 0., 0.761), 3915 (0.824, 0., 1.20), (0.602, 0., 0.328), (6.07e-3, 0.588, thickness/10)) 3916 fcs = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 11,10], [2, 1, 3], [2, 11, 0], [3, 1, 4], [3, 11, 2], 3917 [4, 1, 5], [4, 11, 3], [5, 1, 6], [5, 11, 4], [6, 1, 7], [6, 11, 5], 3918 [7, 1, 8], [7, 11, 6], [8, 1, 9], [8, 11, 7], [9, 1,10], [9, 11, 8], 3919 [10,1, 0],[10,11, 9]] 3920 3921 super().__init__([pts, fcs], c, alpha) 3922 self.rotate_x(90) 3923 self.scale(r).lighting("shiny") 3924 3925 if len(pos) == 2: 3926 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3927 self.pos(pos) 3928 self.name = "Star3D" 3929 3930 3931class Cross3D(Mesh): 3932 """ 3933 Build a 3D cross shape. 3934 """ 3935 3936 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, thickness=0.3, c="b", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3937 """ 3938 Build a 3D cross shape, mainly useful as a 3D marker. 3939 """ 3940 if len(pos) == 2: 3941 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3942 3943 c1 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s) 3944 c2 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s).rotate_x(90) 3945 c3 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s).rotate_y(90) 3946 poly = merge(c1, c2, c3).color(c).alpha(alpha).pos(pos).dataset 3947 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 3948 self.name = "Cross3D" 3949 3950 3951class ParametricShape(Mesh): 3952 """ 3953 A set of built-in shapes mainly for illustration purposes. 3954 """ 3955 3956 def __init__(self, name, res=51, n=25, seed=1): 3957 """ 3958 A set of built-in shapes mainly for illustration purposes. 3959 3960 Name can be an integer or a string in this list: 3961 `['Boy', 'ConicSpiral', 'CrossCap', 'Dini', 'Enneper', 3962 'Figure8Klein', 'Klein', 'Mobius', 'RandomHills', 'Roman', 3963 'SuperEllipsoid', 'BohemianDome', 'Bour', 'CatalanMinimal', 3964 'Henneberg', 'Kuen', 'PluckerConoid', 'Pseudosphere']`. 3965 3966 Example: 3967 ```python 3968 from vedo import * 3969 settings.immediate_rendering = False 3970 plt = Plotter(N=18) 3971 for i in range(18): 3972 ps = ParametricShape(i).color(i) 3973 plt.at(i).show(ps, ps.name) 3974 plt.interactive().close() 3975 ``` 3976 <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/32848391/69181075-bb6aae80-0b0e-11ea-92f7-d0cd3b9087bf.png" width="700"> 3977 """ 3978 3979 shapes = [ 3980 "Boy", 3981 "ConicSpiral", 3982 "CrossCap", 3983 "Enneper", 3984 "Figure8Klein", 3985 "Klein", 3986 "Dini", 3987 "Mobius", 3988 "RandomHills", 3989 "Roman", 3990 "SuperEllipsoid", 3991 "BohemianDome", 3992 "Bour", 3993 "CatalanMinimal", 3994 "Henneberg", 3995 "Kuen", 3996 "PluckerConoid", 3997 "Pseudosphere", 3998 ] 3999 4000 if isinstance(name, int): 4001 name = name % len(shapes) 4002 name = shapes[name] 4003 4004 if name == "Boy": 4005 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBoy") 4006 elif name == "ConicSpiral": 4007 ps = vtki.new("ParametricConicSpiral") 4008 elif name == "CrossCap": 4009 ps = vtki.new("ParametricCrossCap") 4010 elif name == "Dini": 4011 ps = vtki.new("ParametricDini") 4012 elif name == "Enneper": 4013 ps = vtki.new("ParametricEnneper") 4014 elif name == "Figure8Klein": 4015 ps = vtki.new("ParametricFigure8Klein") 4016 elif name == "Klein": 4017 ps = vtki.new("ParametricKlein") 4018 elif name == "Mobius": 4019 ps = vtki.new("ParametricMobius") 4020 ps.SetRadius(2.0) 4021 ps.SetMinimumV(-0.5) 4022 ps.SetMaximumV(0.5) 4023 elif name == "RandomHills": 4024 ps = vtki.new("ParametricRandomHills") 4025 ps.AllowRandomGenerationOn() 4026 ps.SetRandomSeed(seed) 4027 ps.SetNumberOfHills(n) 4028 elif name == "Roman": 4029 ps = vtki.new("ParametricRoman") 4030 elif name == "SuperEllipsoid": 4031 ps = vtki.new("ParametricSuperEllipsoid") 4032 ps.SetN1(0.5) 4033 ps.SetN2(0.4) 4034 elif name == "BohemianDome": 4035 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBohemianDome") 4036 ps.SetA(5.0) 4037 ps.SetB(1.0) 4038 ps.SetC(2.0) 4039 elif name == "Bour": 4040 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBour") 4041 elif name == "CatalanMinimal": 4042 ps = vtki.new("ParametricCatalanMinimal") 4043 elif name == "Henneberg": 4044 ps = vtki.new("ParametricHenneberg") 4045 elif name == "Kuen": 4046 ps = vtki.new("ParametricKuen") 4047 ps.SetDeltaV0(0.001) 4048 elif name == "PluckerConoid": 4049 ps = vtki.new("ParametricPluckerConoid") 4050 elif name == "Pseudosphere": 4051 ps = vtki.new("ParametricPseudosphere") 4052 else: 4053 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown ParametricShape {name}") 4054 return 4055 4056 pfs = vtki.new("ParametricFunctionSource") 4057 pfs.SetParametricFunction(ps) 4058 pfs.SetUResolution(res) 4059 pfs.SetVResolution(res) 4060 pfs.SetWResolution(res) 4061 pfs.SetScalarModeToZ() 4062 pfs.Update() 4063 4064 super().__init__(pfs.GetOutput()) 4065 4066 if name == "RandomHills": self.shift([0,-10,-2.25]) 4067 if name != 'Kuen': self.normalize() 4068 if name == 'Dini': self.scale(0.4) 4069 if name == 'Enneper': self.scale(0.4) 4070 if name == 'ConicSpiral': self.bc('tomato') 4071 self.name = name 4072 4073 4074@lru_cache(None) 4075def _load_font(font) -> np.ndarray: 4076 # print('_load_font()', font) 4077 4078 if utils.is_number(font): 4079 font = list(settings.font_parameters.keys())[int(font)] 4080 4081 if font.endswith(".npz"): # user passed font as a local path 4082 fontfile = font 4083 font = os.path.basename(font).split(".")[0] 4084 4085 elif font.startswith("https"): # user passed URL link, make it a path 4086 try: 4087 fontfile = vedo.file_io.download(font, verbose=False, force=False) 4088 font = os.path.basename(font).split(".")[0] 4089 except: 4090 vedo.logger.warning(f"font {font} not found") 4091 font = settings.default_font 4092 fontfile = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".npz") 4093 4094 else: # user passed font by its standard name 4095 font = font[:1].upper() + font[1:] # capitalize first letter only 4096 fontfile = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".npz") 4097 4098 if font not in settings.font_parameters.keys(): 4099 vedo.logger.warning( 4100 f"Unknown font: {font}\n" 4101 f"Available 3D fonts are: " 4102 f"{list(settings.font_parameters.keys())}\n" 4103 f"Using font Normografo instead." 4104 ) 4105 font = "Normografo" 4106 fontfile = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".npz") 4107 4108 if not settings.font_parameters[font]["islocal"]: 4109 font = "https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/" + font + ".npz" 4110 try: 4111 fontfile = vedo.file_io.download(font, verbose=False, force=False) 4112 font = os.path.basename(font).split(".")[0] 4113 except: 4114 vedo.logger.warning(f"font {font} not found") 4115 font = settings.default_font 4116 fontfile = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".npz") 4117 4118 ##### 4119 try: 4120 font_meshes = np.load(fontfile, allow_pickle=True)["font"][0] 4121 except: 4122 vedo.logger.warning(f"font name {font} not found.") 4123 raise RuntimeError 4124 return font_meshes 4125 4126 4127@lru_cache(None) 4128def _get_font_letter(font, letter): 4129 # print("_get_font_letter", font, letter) 4130 font_meshes = _load_font(font) 4131 try: 4132 pts, faces = font_meshes[letter] 4133 return utils.buildPolyData(pts.astype(float), faces) 4134 except KeyError: 4135 return None 4136 4137 4138class Text3D(Mesh): 4139 """ 4140 Generate a 3D polygonal Mesh to represent a text string. 4141 """ 4142 4143 def __init__( 4144 self, 4145 txt, 4146 pos=(0, 0, 0), 4147 s=1.0, 4148 font="", 4149 hspacing=1.15, 4150 vspacing=2.15, 4151 depth=0.0, 4152 italic=False, 4153 justify="bottom-left", 4154 literal=False, 4155 c=None, 4156 alpha=1.0, 4157 ) -> None: 4158 """ 4159 Generate a 3D polygonal `Mesh` representing a text string. 4160 4161 Can render strings like `3.7 10^9` or `H_2 O` with subscripts and superscripts. 4162 Most Latex symbols are also supported. 4163 4164 Symbols `~ ^ _` are reserved modifiers: 4165 - use ~ to add a short space, 1/4 of the default empty space, 4166 - use ^ and _ to start up/sub scripting, a space terminates their effect. 4167 4168 Monospaced fonts are: `Calco, ComicMono, Glasgo, SmartCouric, VictorMono, Justino`. 4169 4170 More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4171 4172 Arguments: 4173 pos : (list) 4174 position coordinates in 3D space 4175 s : (float) 4176 vertical size of the text (as scaling factor) 4177 depth : (float) 4178 text thickness (along z) 4179 italic : (bool), float 4180 italic font type (can be a signed float too) 4181 justify : (str) 4182 text justification as centering of the bounding box 4183 (bottom-left, bottom-right, top-left, top-right, centered) 4184 font : (str, int) 4185 some of the available 3D-polygonized fonts are: 4186 Bongas, Calco, Comae, ComicMono, Kanopus, Glasgo, Ubuntu, 4187 LogoType, Normografo, Quikhand, SmartCouric, Theemim, VictorMono, VTK, 4188 Capsmall, Cartoons123, Vega, Justino, Spears, Meson. 4189 4190 Check for more at https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4191 4192 Or type in your terminal `vedo --run fonts`. 4193 4194 Default is Normografo, which can be changed using `settings.default_font`. 4195 4196 hspacing : (float) 4197 horizontal spacing of the font 4198 vspacing : (float) 4199 vertical spacing of the font for multiple lines text 4200 literal : (bool) 4201 if set to True will ignore modifiers like _ or ^ 4202 4203 Examples: 4204 - [markpoint.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/markpoint.py) 4205 - [fonts.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/fonts.py) 4206 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 4207 4208 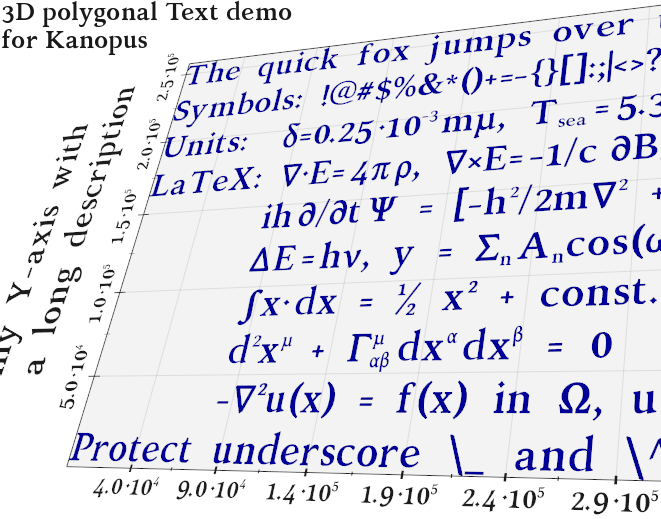 4209 4210 .. note:: Type `vedo -r fonts` for a demo. 4211 """ 4212 if len(pos) == 2: 4213 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 4214 4215 if c is None: # automatic black or white 4216 pli = vedo.plotter_instance 4217 if pli and pli.renderer: 4218 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4219 if pli.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4220 bgcol = pli.renderer.GetBackground2() 4221 else: 4222 bgcol = pli.renderer.GetBackground() 4223 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4224 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4225 else: 4226 c = (0.6, 0.6, 0.6) 4227 4228 tpoly = self._get_text3d_poly( 4229 txt, s, font, hspacing, vspacing, depth, italic, justify, literal 4230 ) 4231 4232 super().__init__(tpoly, c, alpha) 4233 4234 self.pos(pos) 4235 self.lighting("off") 4236 4237 self.actor.PickableOff() 4238 self.actor.DragableOff() 4239 self.init_scale = s 4240 self.name = "Text3D" 4241 self.txt = txt 4242 self.justify = justify 4243 4244 def text( 4245 self, 4246 txt=None, 4247 s=1, 4248 font="", 4249 hspacing=1.15, 4250 vspacing=2.15, 4251 depth=0, 4252 italic=False, 4253 justify="", 4254 literal=False, 4255 ) -> "Text3D": 4256 """ 4257 Update the text and some of its properties. 4258 4259 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 4260 """ 4261 if txt is None: 4262 return self.txt 4263 if not justify: 4264 justify = self.justify 4265 4266 poly = self._get_text3d_poly( 4267 txt, self.init_scale * s, font, hspacing, vspacing, 4268 depth, italic, justify, literal 4269 ) 4270 4271 # apply the current transformation to the new polydata 4272 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 4273 tf.SetInputData(poly) 4274 tf.SetTransform(self.transform.T) 4275 tf.Update() 4276 tpoly = tf.GetOutput() 4277 4278 self._update(tpoly) 4279 self.txt = txt 4280 return self 4281 4282 @staticmethod 4283 def _get_text3d_poly( 4284 txt, 4285 s=1, 4286 font="", 4287 hspacing=1.15, 4288 vspacing=2.15, 4289 depth=0, 4290 italic=False, 4291 justify="bottom-left", 4292 literal=False, 4293 ) -> vtki.vtkPolyData: 4294 if not font: 4295 font = settings.default_font 4296 4297 txt = str(txt) 4298 4299 if font == "VTK": ####################################### 4300 vtt = vtki.new("VectorText") 4301 vtt.SetText(txt) 4302 vtt.Update() 4303 tpoly = vtt.GetOutput() 4304 4305 else: ################################################### 4306 4307 stxt = set(txt) # check here if null or only spaces 4308 if not txt or (len(stxt) == 1 and " " in stxt): 4309 return vtki.vtkPolyData() 4310 4311 if italic is True: 4312 italic = 1 4313 4314 if isinstance(font, int): 4315 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4316 font = font % len(lfonts) 4317 font = lfonts[font] 4318 4319 if font not in settings.font_parameters.keys(): 4320 fpars = settings.font_parameters["Normografo"] 4321 else: 4322 fpars = settings.font_parameters[font] 4323 4324 # ad hoc adjustments 4325 mono = fpars["mono"] 4326 lspacing = fpars["lspacing"] 4327 hspacing *= fpars["hspacing"] 4328 fscale = fpars["fscale"] 4329 dotsep = fpars["dotsep"] 4330 4331 # replacements 4332 if ":" in txt: 4333 for r in _reps: 4334 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4335 4336 if not literal: 4337 reps2 = [ 4338 (r"\_", "┭"), # trick to protect ~ _ and ^ chars 4339 (r"\^", "┮"), # 4340 (r"\~", "┯"), # 4341 ("**", "^"), # order matters 4342 ("e+0", dotsep + "10^"), 4343 ("e-0", dotsep + "10^-"), 4344 ("E+0", dotsep + "10^"), 4345 ("E-0", dotsep + "10^-"), 4346 ("e+", dotsep + "10^"), 4347 ("e-", dotsep + "10^-"), 4348 ("E+", dotsep + "10^"), 4349 ("E-", dotsep + "10^-"), 4350 ] 4351 for r in reps2: 4352 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4353 4354 xmax, ymax, yshift, scale = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 4355 save_xmax = 0.0 4356 4357 notfounds = set() 4358 polyletters = [] 4359 ntxt = len(txt) 4360 for i, t in enumerate(txt): 4361 ########## 4362 if t == "┭": 4363 t = "_" 4364 elif t == "┮": 4365 t = "^" 4366 elif t == "┯": 4367 t = "~" 4368 elif t == "^" and not literal: 4369 if yshift < 0: 4370 xmax = save_xmax 4371 yshift = 0.9 * fscale 4372 scale = 0.5 4373 continue 4374 elif t == "_" and not literal: 4375 if yshift > 0: 4376 xmax = save_xmax 4377 yshift = -0.3 * fscale 4378 scale = 0.5 4379 continue 4380 elif (t in (" ", "\\n")) and yshift: 4381 yshift = 0.0 4382 scale = 1.0 4383 save_xmax = xmax 4384 if t == " ": 4385 continue 4386 elif t == "~": 4387 if i < ntxt - 1 and txt[i + 1] == "_": 4388 continue 4389 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale / 4 4390 continue 4391 4392 ############ 4393 if t == " ": 4394 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale 4395 4396 elif t == "\n": 4397 xmax = 0.0 4398 save_xmax = 0.0 4399 ymax -= vspacing 4400 4401 else: 4402 poly = _get_font_letter(font, t) 4403 if not poly: 4404 notfounds.add(t) 4405 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale 4406 continue 4407 4408 if poly.GetNumberOfPoints() == 0: 4409 continue 4410 4411 tr = vtki.vtkTransform() 4412 tr.Translate(xmax, ymax + yshift, 0) 4413 pscale = scale * fscale / 1000 4414 tr.Scale(pscale, pscale, pscale) 4415 if italic: 4416 tr.Concatenate([1, italic * 0.15, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]) 4417 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 4418 tf.SetInputData(poly) 4419 tf.SetTransform(tr) 4420 tf.Update() 4421 poly = tf.GetOutput() 4422 polyletters.append(poly) 4423 4424 bx = poly.GetBounds() 4425 if mono: 4426 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale 4427 else: 4428 xmax += bx[1] - bx[0] + hspacing * scale * fscale * lspacing 4429 if yshift == 0: 4430 save_xmax = xmax 4431 4432 if len(polyletters) == 1: 4433 tpoly = polyletters[0] 4434 else: 4435 polyapp = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 4436 for polyd in polyletters: 4437 polyapp.AddInputData(polyd) 4438 polyapp.Update() 4439 tpoly = polyapp.GetOutput() 4440 4441 if notfounds: 4442 wmsg = f"unavailable characters in font name '{font}': {notfounds}." 4443 wmsg += '\nType "vedo -r fonts" for a demo.' 4444 vedo.logger.warning(wmsg) 4445 4446 bb = tpoly.GetBounds() 4447 dx, dy = (bb[1] - bb[0]) / 2 * s, (bb[3] - bb[2]) / 2 * s 4448 shift = -np.array([(bb[1] + bb[0]), (bb[3] + bb[2]), (bb[5] + bb[4])]) * s /2 4449 if "bottom" in justify: shift += np.array([ 0, dy, 0.]) 4450 if "top" in justify: shift += np.array([ 0,-dy, 0.]) 4451 if "left" in justify: shift += np.array([ dx, 0, 0.]) 4452 if "right" in justify: shift += np.array([-dx, 0, 0.]) 4453 4454 if tpoly.GetNumberOfPoints(): 4455 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 4456 t.PostMultiply() 4457 t.Scale(s, s, s) 4458 t.Translate(shift) 4459 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 4460 tf.SetInputData(tpoly) 4461 tf.SetTransform(t) 4462 tf.Update() 4463 tpoly = tf.GetOutput() 4464 4465 if depth: 4466 extrude = vtki.new("LinearExtrusionFilter") 4467 extrude.SetInputData(tpoly) 4468 extrude.SetExtrusionTypeToVectorExtrusion() 4469 extrude.SetVector(0, 0, 1) 4470 extrude.SetScaleFactor(depth * dy) 4471 extrude.Update() 4472 tpoly = extrude.GetOutput() 4473 4474 return tpoly 4475 4476 4477class TextBase: 4478 "Base class." 4479 4480 def __init__(self): 4481 "Do not instantiate this base class." 4482 4483 self.rendered_at = set() 4484 # self.properties = None 4485 4486 self.name = "Text" 4487 self.filename = "" 4488 self.time = 0 4489 self.info = {} 4490 4491 if isinstance(settings.default_font, int): 4492 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4493 font = settings.default_font % len(lfonts) 4494 self.fontname = lfonts[font] 4495 else: 4496 self.fontname = settings.default_font 4497 4498 def angle(self, value: float): 4499 """Orientation angle in degrees""" 4500 self.properties.SetOrientation(value) 4501 return self 4502 4503 def line_spacing(self, value: float): 4504 """Set the extra spacing between lines 4505 expressed as a text height multiplicative factor.""" 4506 self.properties.SetLineSpacing(value) 4507 return self 4508 4509 def line_offset(self, value: float): 4510 """Set/Get the vertical offset (measured in pixels).""" 4511 self.properties.SetLineOffset(value) 4512 return self 4513 4514 def bold(self, value=True): 4515 """Set bold face""" 4516 self.properties.SetBold(value) 4517 return self 4518 4519 def italic(self, value=True): 4520 """Set italic face""" 4521 self.properties.SetItalic(value) 4522 return self 4523 4524 def shadow(self, offset=(1, -1)): 4525 """Text shadowing. Set to `None` to disable it.""" 4526 if offset is None: 4527 self.properties.ShadowOff() 4528 else: 4529 self.properties.ShadowOn() 4530 self.properties.SetShadowOffset(offset) 4531 return self 4532 4533 def color(self, c=None): 4534 """Set the text color""" 4535 if c is None: 4536 return get_color(self.properties.GetColor()) 4537 self.properties.SetColor(get_color(c)) 4538 return self 4539 4540 def c(self, color=None): 4541 """Set the text color""" 4542 if color is None: 4543 return get_color(self.properties.GetColor()) 4544 return self.color(color) 4545 4546 def alpha(self, value: float): 4547 """Set the text opacity""" 4548 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(value) 4549 return self 4550 4551 def background(self, color="k9", alpha=1.0): 4552 """Text background. Set to `None` to disable it.""" 4553 bg = get_color(color) 4554 if color is None: 4555 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(0) 4556 else: 4557 self.properties.SetBackgroundColor(bg) 4558 if alpha: 4559 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(alpha) 4560 return self 4561 4562 def frame(self, color="k1", lw=2): 4563 """Border color and width""" 4564 if color is None: 4565 self.properties.FrameOff() 4566 else: 4567 c = get_color(color) 4568 self.properties.FrameOn() 4569 self.properties.SetFrameColor(c) 4570 self.properties.SetFrameWidth(lw) 4571 return self 4572 4573 def font(self, font: str): 4574 """Text font face""" 4575 if isinstance(font, int): 4576 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4577 n = font % len(lfonts) 4578 font = lfonts[n] 4579 self.fontname = font 4580 4581 if not font: # use default font 4582 font = self.fontname 4583 fpath = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".ttf") 4584 elif font.startswith("https"): # user passed URL link, make it a path 4585 fpath = vedo.file_io.download(font, verbose=False, force=False) 4586 elif font.endswith(".ttf"): # user passing a local path to font file 4587 fpath = font 4588 else: # user passing name of preset font 4589 fpath = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".ttf") 4590 4591 if font == "Courier": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToCourier() 4592 elif font == "Times": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToTimes() 4593 elif font == "Arial": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToArial() 4594 else: 4595 fpath = utils.get_font_path(font) 4596 self.properties.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 4597 self.properties.SetFontFile(fpath) 4598 self.fontname = font # io.tonumpy() uses it 4599 4600 return self 4601 4602 def on(self): 4603 """Make text visible""" 4604 self.actor.SetVisibility(True) 4605 return self 4606 4607 def off(self): 4608 """Make text invisible""" 4609 self.actor.SetVisibility(False) 4610 return self 4611 4612class Text2D(TextBase, vedo.visual.Actor2D): 4613 """ 4614 Create a 2D text object. 4615 """ 4616 def __init__( 4617 self, 4618 txt="", 4619 pos="top-left", 4620 s=1.0, 4621 bg=None, 4622 font="", 4623 justify="", 4624 bold=False, 4625 italic=False, 4626 c=None, 4627 alpha=0.5, 4628 ) -> None: 4629 """ 4630 Create a 2D text object. 4631 4632 All properties of the text, and the text itself, can be changed after creation 4633 (which is especially useful in loops). 4634 4635 Arguments: 4636 pos : (str) 4637 text is placed in one of the 8 positions: 4638 - bottom-left 4639 - bottom-right 4640 - top-left 4641 - top-right 4642 - bottom-middle 4643 - middle-right 4644 - middle-left 4645 - top-middle 4646 4647 If a pair (x,y) is passed as input the 2D text is place at that 4648 position in the coordinate system of the 2D screen (with the 4649 origin sitting at the bottom left). 4650 4651 s : (float) 4652 size of text 4653 bg : (color) 4654 background color 4655 alpha : (float) 4656 background opacity 4657 justify : (str) 4658 text justification 4659 4660 font : (str) 4661 built-in available fonts are: 4662 - Antares 4663 - Arial 4664 - Bongas 4665 - Calco 4666 - Comae 4667 - ComicMono 4668 - Courier 4669 - Glasgo 4670 - Kanopus 4671 - LogoType 4672 - Normografo 4673 - Quikhand 4674 - SmartCouric 4675 - Theemim 4676 - Times 4677 - VictorMono 4678 - More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4679 4680 A path to a `.otf` or `.ttf` font-file can also be supplied as input. 4681 4682 Examples: 4683 - [fonts.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/fonts.py) 4684 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 4685 - [colorcubes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/colorcubes.py) 4686 4687  4688 """ 4689 super().__init__() 4690 self.name = "Text2D" 4691 4692 self.mapper = vtki.new("TextMapper") 4693 self.SetMapper(self.mapper) 4694 4695 self.properties = self.mapper.GetTextProperty() 4696 self.actor = self 4697 self.actor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 4698 4699 self.GetPositionCoordinate().SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport() 4700 4701 # automatic black or white 4702 if c is None: 4703 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4704 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 4705 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4706 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground2() 4707 else: 4708 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground() 4709 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4710 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4711 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4712 4713 self.font(font).color(c).background(bg, alpha).bold(bold).italic(italic) 4714 self.pos(pos, justify).size(s).text(txt).line_spacing(1.2).line_offset(5) 4715 self.PickableOff() 4716 4717 def pos(self, pos="top-left", justify=""): 4718 """ 4719 Set position of the text to draw. Keyword `pos` can be a string 4720 or 2D coordinates in the range [0,1], being (0,0) the bottom left corner. 4721 """ 4722 ajustify = "top-left" # autojustify 4723 if isinstance(pos, str): # corners 4724 ajustify = pos 4725 if "top" in pos: 4726 if "left" in pos: 4727 pos = (0.008, 0.994) 4728 elif "right" in pos: 4729 pos = (0.994, 0.994) 4730 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4731 pos = (0.5, 0.994) 4732 elif "bottom" in pos: 4733 if "left" in pos: 4734 pos = (0.008, 0.008) 4735 elif "right" in pos: 4736 pos = (0.994, 0.008) 4737 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4738 pos = (0.5, 0.008) 4739 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4740 if "left" in pos: 4741 pos = (0.008, 0.5) 4742 elif "right" in pos: 4743 pos = (0.994, 0.5) 4744 else: 4745 pos = (0.5, 0.5) 4746 4747 else: 4748 vedo.logger.warning(f"cannot understand text position {pos}") 4749 pos = (0.008, 0.994) 4750 ajustify = "top-left" 4751 4752 elif len(pos) != 2: 4753 vedo.logger.error("pos must be of length 2 or integer value or string") 4754 raise RuntimeError() 4755 4756 if not justify: 4757 justify = ajustify 4758 4759 self.properties.SetJustificationToLeft() 4760 if "top" in justify: 4761 self.properties.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 4762 if "bottom" in justify: 4763 self.properties.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 4764 if "cent" in justify or "mid" in justify: 4765 self.properties.SetJustificationToCentered() 4766 if "left" in justify: 4767 self.properties.SetJustificationToLeft() 4768 if "right" in justify: 4769 self.properties.SetJustificationToRight() 4770 4771 self.SetPosition(pos) 4772 return self 4773 4774 def text(self, txt=None): 4775 """Set/get the input text string.""" 4776 if txt is None: 4777 return self.mapper.GetInput() 4778 4779 if ":" in txt: 4780 for r in _reps: 4781 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4782 else: 4783 txt = str(txt) 4784 4785 self.mapper.SetInput(txt) 4786 return self 4787 4788 def size(self, s): 4789 """Set the font size.""" 4790 self.properties.SetFontSize(int(s * 22.5)) 4791 return self 4792 4793 4794class CornerAnnotation(TextBase, vtki.vtkCornerAnnotation): 4795 # PROBABLY USELESS given that Text2D does pretty much the same ... 4796 """ 4797 Annotate the window corner with 2D text. 4798 4799 See `Text2D` description as the basic functionality is very similar. 4800 4801 The added value of this class is the possibility to manage with one single 4802 object the all corner annotations (instead of creating 4 `Text2D` instances). 4803 4804 Examples: 4805 - [timer_callback2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/timer_callback2.py) 4806 """ 4807 4808 def __init__(self, c=None) -> None: 4809 4810 super().__init__() 4811 4812 self.properties = self.GetTextProperty() 4813 4814 # automatic black or white 4815 if c is None: 4816 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 4817 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4818 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4819 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground2() 4820 else: 4821 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground() 4822 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4823 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4824 else: 4825 c = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) 4826 4827 self.SetNonlinearFontScaleFactor(1 / 2.75) 4828 self.PickableOff() 4829 self.properties.SetColor(get_color(c)) 4830 self.properties.SetBold(False) 4831 self.properties.SetItalic(False) 4832 4833 def size(self, s:float, linear=False) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4834 """ 4835 The font size is calculated as the largest possible value such that the annotations 4836 for the given viewport do not overlap. 4837 4838 This font size can be scaled non-linearly with the viewport size, to maintain an 4839 acceptable readable size at larger viewport sizes, without being too big. 4840 `f' = linearScale * pow(f,nonlinearScale)` 4841 """ 4842 if linear: 4843 self.SetLinearFontScaleFactor(s * 5.5) 4844 else: 4845 self.SetNonlinearFontScaleFactor(s / 2.75) 4846 return self 4847 4848 def text(self, txt: str, pos=2) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4849 """Set text at the assigned position""" 4850 4851 if isinstance(pos, str): # corners 4852 if "top" in pos: 4853 if "left" in pos: pos = 2 4854 elif "right" in pos: pos = 3 4855 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: pos = 7 4856 elif "bottom" in pos: 4857 if "left" in pos: pos = 0 4858 elif "right" in pos: pos = 1 4859 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: pos = 4 4860 else: 4861 if "left" in pos: pos = 6 4862 elif "right" in pos: pos = 5 4863 else: pos = 2 4864 4865 if "\\" in repr(txt): 4866 for r in _reps: 4867 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4868 else: 4869 txt = str(txt) 4870 4871 self.SetText(pos, txt) 4872 return self 4873 4874 def clear(self) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4875 """Remove all text from all corners""" 4876 self.ClearAllTexts() 4877 return self 4878 4879 4880class Latex(Image): 4881 """ 4882 Render Latex text and formulas. 4883 """ 4884 4885 def __init__(self, formula, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, bg=None, res=150, usetex=False, c="k", alpha=1.0) -> None: 4886 """ 4887 Render Latex text and formulas. 4888 4889 Arguments: 4890 formula : (str) 4891 latex text string 4892 pos : (list) 4893 position coordinates in space 4894 bg : (color) 4895 background color box 4896 res : (int) 4897 dpi resolution 4898 usetex : (bool) 4899 use latex compiler of matplotlib if available 4900 4901 You can access the latex formula in `Latex.formula`. 4902 4903 Examples: 4904 - [latex.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/latex.py) 4905 4906 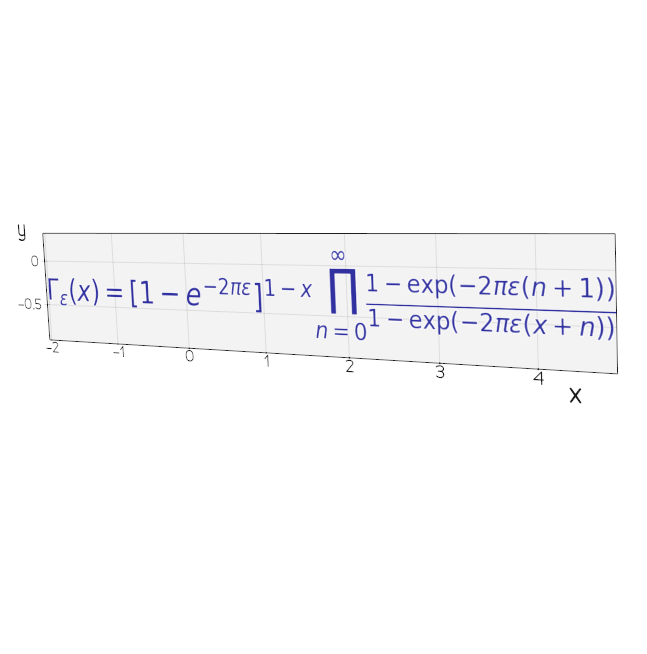 4907 """ 4908 from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile 4909 import matplotlib.pyplot as mpltib 4910 4911 def build_img_plt(formula, tfile): 4912 4913 mpltib.rc("text", usetex=usetex) 4914 4915 formula1 = "$" + formula + "$" 4916 mpltib.axis("off") 4917 col = get_color(c) 4918 if bg: 4919 bx = dict(boxstyle="square", ec=col, fc=get_color(bg)) 4920 else: 4921 bx = None 4922 mpltib.text( 4923 0.5, 4924 0.5, 4925 formula1, 4926 size=res, 4927 color=col, 4928 alpha=alpha, 4929 ha="center", 4930 va="center", 4931 bbox=bx, 4932 ) 4933 mpltib.savefig( 4934 tfile, format="png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight", pad_inches=0 4935 ) 4936 mpltib.close() 4937 4938 if len(pos) == 2: 4939 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 4940 4941 tmp_file = NamedTemporaryFile(delete=True) 4942 tmp_file.name = tmp_file.name + ".png" 4943 4944 build_img_plt(formula, tmp_file.name) 4945 4946 super().__init__(tmp_file.name, channels=4) 4947 self.alpha(alpha) 4948 self.scale([0.25 / res * s, 0.25 / res * s, 0.25 / res * s]) 4949 self.pos(pos) 4950 self.name = "Latex" 4951 self.formula = formula 4952 4953 # except: 4954 # printc("Error in Latex()\n", formula, c="r") 4955 # printc(" latex or dvipng not installed?", c="r") 4956 # printc(" Try: usetex=False", c="r") 4957 # printc(" Try: sudo apt install dvipng", c="r") 4958 4959 4960class ConvexHull(Mesh): 4961 """ 4962 Create the 2D/3D convex hull from a set of points. 4963 """ 4964 4965 def __init__(self, pts) -> None: 4966 """ 4967 Create the 2D/3D convex hull from a set of input points or input Mesh. 4968 4969 Examples: 4970 - [convex_hull.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/convex_hull.py) 4971 4972  4973 """ 4974 if utils.is_sequence(pts): 4975 pts = utils.make3d(pts).astype(float) 4976 mesh = Points(pts) 4977 else: 4978 mesh = pts 4979 apoly = mesh.clean().dataset 4980 4981 # Create the convex hull of the pointcloud 4982 z0, z1 = mesh.zbounds() 4983 d = mesh.diagonal_size() 4984 if (z1 - z0) / d > 0.0001: 4985 delaunay = vtki.new("Delaunay3D") 4986 delaunay.SetInputData(apoly) 4987 delaunay.Update() 4988 surfaceFilter = vtki.new("DataSetSurfaceFilter") 4989 surfaceFilter.SetInputConnection(delaunay.GetOutputPort()) 4990 surfaceFilter.Update() 4991 out = surfaceFilter.GetOutput() 4992 else: 4993 delaunay = vtki.new("Delaunay2D") 4994 delaunay.SetInputData(apoly) 4995 delaunay.Update() 4996 fe = vtki.new("FeatureEdges") 4997 fe.SetInputConnection(delaunay.GetOutputPort()) 4998 fe.BoundaryEdgesOn() 4999 fe.Update() 5000 out = fe.GetOutput() 5001 5002 super().__init__(out, c=mesh.color(), alpha=0.75) 5003 self.flat() 5004 self.name = "ConvexHull" 5005 5006 5007def VedoLogo(distance=0.0, c=None, bc="t", version=False, frame=True) -> "vedo.Assembly": 5008 """ 5009 Create the 3D vedo logo. 5010 5011 Arguments: 5012 distance : (float) 5013 send back logo by this distance from camera 5014 version : (bool) 5015 add version text to the right end of the logo 5016 bc : (color) 5017 text back face color 5018 """ 5019 if c is None: 5020 c = (0, 0, 0) 5021 if vedo.plotter_instance: 5022 if sum(get_color(vedo.plotter_instance.backgrcol)) > 1.5: 5023 c = [0, 0, 0] 5024 else: 5025 c = "linen" 5026 5027 font = "Comae" 5028 vlogo = Text3D("vэdo", font=font, s=1350, depth=0.2, c=c, hspacing=0.8) 5029 vlogo.scale([1, 0.95, 1]).x(-2525).pickable(False).bc(bc) 5030 vlogo.properties.LightingOn() 5031 5032 vr, rul = None, None 5033 if version: 5034 vr = Text3D( 5035 vedo.__version__, font=font, s=165, depth=0.2, c=c, hspacing=1 5036 ).scale([1, 0.7, 1]) 5037 vr.rotate_z(90).pos(2450, 50, 80) 5038 vr.bc(bc).pickable(False) 5039 elif frame: 5040 rul = vedo.RulerAxes( 5041 (-2600, 2110, 0, 1650, 0, 0), 5042 xlabel="European Molecular Biology Laboratory", 5043 ylabel=vedo.__version__, 5044 font=font, 5045 xpadding=0.09, 5046 ypadding=0.04, 5047 ) 5048 fakept = vedo.Point((0, 500, distance * 1725), alpha=0, c=c, r=1).pickable(0) 5049 return vedo.Assembly([vlogo, vr, fakept, rul]).scale(1 / 1725)
3716def Marker(symbol, pos=(0, 0, 0), c="k", alpha=1.0, s=0.1, filled=True) -> Any: 3717 """ 3718 Generate a marker shape. Typically used in association with `Glyph`. 3719 """ 3720 if isinstance(symbol, Mesh): 3721 return symbol.c(c).alpha(alpha).lighting("off") 3722 3723 if isinstance(symbol, int): 3724 symbs = [".", "o", "O", "0", "p", "*", "h", "D", "d", "v", "^", ">", "<", "s", "x", "a"] 3725 symbol = symbol % len(symbs) 3726 symbol = symbs[symbol] 3727 3728 if symbol == ".": 3729 mesh = Polygon(nsides=24, r=s * 0.6) 3730 elif symbol == "o": 3731 mesh = Polygon(nsides=24, r=s * 0.75) 3732 elif symbol == "O": 3733 mesh = Disc(r1=s * 0.6, r2=s * 0.75, res=(1, 24)) 3734 elif symbol == "0": 3735 m1 = Disc(r1=s * 0.6, r2=s * 0.75, res=(1, 24)) 3736 m2 = Circle(r=s * 0.36).reverse() 3737 mesh = merge(m1, m2) 3738 elif symbol == "p": 3739 mesh = Polygon(nsides=5, r=s) 3740 elif symbol == "*": 3741 mesh = Star(r1=0.65 * s * 1.1, r2=s * 1.1, line=not filled) 3742 elif symbol == "h": 3743 mesh = Polygon(nsides=6, r=s) 3744 elif symbol == "D": 3745 mesh = Polygon(nsides=4, r=s) 3746 elif symbol == "d": 3747 mesh = Polygon(nsides=4, r=s * 1.1).scale([0.5, 1, 1]) 3748 elif symbol == "v": 3749 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s).rotate_z(180) 3750 elif symbol == "^": 3751 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s) 3752 elif symbol == ">": 3753 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s).rotate_z(-90) 3754 elif symbol == "<": 3755 mesh = Polygon(nsides=3, r=s).rotate_z(90) 3756 elif symbol == "s": 3757 mesh = Mesh( 3758 [[[-1, -1, 0], [1, -1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [-1, 1, 0]], [[0, 1, 2, 3]]] 3759 ).scale(s / 1.4) 3760 elif symbol == "x": 3761 mesh = Text3D("+", pos=(0, 0, 0), s=s * 2.6, justify="center", depth=0) 3762 # mesh.rotate_z(45) 3763 elif symbol == "a": 3764 mesh = Text3D("*", pos=(0, 0, 0), s=s * 2.6, justify="center", depth=0) 3765 else: 3766 mesh = Text3D(symbol, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=s * 2, justify="center", depth=0) 3767 mesh.flat().lighting("off").wireframe(not filled).c(c).alpha(alpha) 3768 if len(pos) == 2: 3769 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3770 mesh.pos(pos) 3771 mesh.name = "Marker" 3772 return mesh
Generate a marker shape. Typically used in association with Glyph.
395class Line(Mesh): 396 """ 397 Build the line segment between point `p0` and point `p1`. 398 399 If `p0` is already a list of points, return the line connecting them. 400 401 A 2D set of coords can also be passed as `p0=[x..], p1=[y..]`. 402 """ 403 404 def __init__(self, p0, p1=None, closed=False, res=2, lw=1, c="k1", alpha=1.0) -> None: 405 """ 406 Arguments: 407 closed : (bool) 408 join last to first point 409 res : (int) 410 resolution, number of points along the line 411 (only relevant if only 2 points are specified) 412 lw : (int) 413 line width in pixel units 414 """ 415 416 if isinstance(p1, Points): 417 p1 = p1.pos() 418 if isinstance(p0, Points): 419 p0 = p0.pos() 420 try: 421 p0 = p0.dataset 422 except AttributeError: 423 pass 424 425 if isinstance(p0, vtki.vtkPolyData): 426 poly = p0 427 top = np.array([0,0,1]) 428 base = np.array([0,0,0]) 429 430 elif utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): # detect if user is passing a list of points 431 432 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 433 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 434 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(np.asarray(p0), dtype=np.float32)) 435 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 436 npt = len(p0) 437 if closed: 438 lines.InsertNextCell(npt + 1) 439 else: 440 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 441 for i in range(npt): 442 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 443 if closed: 444 lines.InsertCellPoint(0) 445 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 446 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 447 poly.SetLines(lines) 448 top = p0[-1] 449 base = p0[0] 450 if res != 2: 451 printc(f"Warning: calling Line(res={res}), try remove []?", c='y') 452 res = 2 453 454 else: # or just 2 points to link 455 456 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 457 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 458 p1 = utils.make3d(p1) 459 line_source.SetPoint1(p0) 460 line_source.SetPoint2(p1) 461 line_source.SetResolution(res - 1) 462 line_source.Update() 463 poly = line_source.GetOutput() 464 top = np.asarray(p1, dtype=float) 465 base = np.asarray(p0, dtype=float) 466 467 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 468 469 self.slope: List[float] = [] # populated by analysis.fit_line 470 self.center: List[float] = [] 471 self.variances: List[float] = [] 472 473 self.coefficients: List[float] = [] # populated by pyplot.fit() 474 self.covariance_matrix: List[float] = [] 475 self.coefficient_errors: List[float] = [] 476 self.monte_carlo_coefficients: List[float] = [] 477 self.reduced_chi2 = -1 478 self.ndof = 0 479 self.data_sigma = 0 480 self.error_lines: List[Any] = [] 481 self.error_band = None 482 self.res = res 483 self.is_closed = closed 484 485 self.lw(lw) 486 self.properties.LightingOff() 487 self.actor.PickableOff() 488 self.actor.DragableOff() 489 self.base = base 490 self.top = top 491 self.name = "Line" 492 493 def clone(self, deep=True) -> "Line": 494 """ 495 Return a copy of the ``Line`` object. 496 497 Example: 498 ```python 499 from vedo import * 500 ln1 = Line([1,1,1], [2,2,2], lw=3).print() 501 ln2 = ln1.clone().shift(0,0,1).c('red').print() 502 show(ln1, ln2, axes=1, viewup='z').close() 503 ``` 504  505 """ 506 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 507 if deep: 508 poly.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 509 else: 510 poly.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 511 ln = Line(poly) 512 ln.copy_properties_from(self) 513 ln.transform = self.transform.clone() 514 ln.name = self.name 515 ln.base = self.base 516 ln.top = self.top 517 ln.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 518 "clone", parents=[self], shape="diamond", c="#edede9") 519 return ln 520 521 def linecolor(self, lc=None) -> "Line": 522 """Assign a color to the line""" 523 # overrides mesh.linecolor which would have no effect here 524 return self.color(lc) 525 526 def eval(self, x: float) -> np.ndarray: 527 """ 528 Calculate the position of an intermediate point 529 as a fraction of the length of the line, 530 being x=0 the first point and x=1 the last point. 531 This corresponds to an imaginary point that travels along the line 532 at constant speed. 533 534 Can be used in conjunction with `lin_interpolate()` 535 to map any range to the [0,1] range. 536 """ 537 distance1 = 0.0 538 length = self.length() 539 pts = self.coordinates 540 if self.is_closed: 541 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 542 543 for i in range(1, len(pts)): 544 p0 = pts[i - 1] 545 p1 = pts[i] 546 seg = p1 - p0 547 distance0 = distance1 548 distance1 += np.linalg.norm(seg) 549 w1 = distance1 / length 550 if w1 >= x: 551 break 552 w0 = distance0 / length 553 v = p0 + seg * (x - w0) / (w1 - w0) 554 return v 555 556 def eval2d(self, x: float) -> np.ndarray: 557 """ 558 Calculate the position of an intermediate point 559 at the specified value of x in absolute units. 560 Assume the line is in the xy-plane. 561 """ 562 xcoords, ycoords, _ = self.coordinates.T 563 # find the segment where x is located 564 idx = np.where((xcoords[:-1] <= x) & (xcoords[1:] >= x))[0] 565 if len(idx) > 0: 566 i = idx[0] 567 return np.array([x, np.interp(x, xcoords[i:i+2], ycoords[i:i+2])]) 568 return np.array([x, 0.0]) 569 570 def find_index_at_position(self, p) -> float: 571 """ 572 Find the index of the line vertex that is closest to the point `p`. 573 Note that the returned index is fractional as `p` may not be exactly 574 one of the vertices of the line. 575 """ 576 tf = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 577 tf.SetPassLines(True) 578 tf.SetPassVerts(False) 579 tf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 580 tf.Update() 581 polyline = tf.GetOutput() 582 583 if not self.cell_locator: 584 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("StaticCellLocator") 585 self.cell_locator.SetDataSet(polyline) 586 self.cell_locator.BuildLocator() 587 588 q = [0, 0, 0] 589 cid = vtki.mutable(0) 590 dist2 = vtki.mutable(0) 591 subid = vtki.mutable(0) 592 self.cell_locator.FindClosestPoint(p, q, cid, subid, dist2) 593 594 # find the 2 points 595 a = polyline.GetCell(cid).GetPointId(0) 596 b = polyline.GetCell(cid).GetPointId(1) 597 598 pts = self.coordinates 599 if self.is_closed: 600 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 601 d = np.linalg.norm(pts[a] - pts[b]) 602 t = a + np.linalg.norm(pts[a] - q) / d 603 return t 604 605 def pattern(self, stipple, repeats=10) -> "Line": 606 """ 607 Define a stipple pattern for dashing the line. 608 Pass the stipple pattern as a string like `'- - -'`. 609 Repeats controls the number of times the pattern repeats in a single segment. 610 611 Examples are: `'- -', '-- - --'`, etc. 612 613 The resolution of the line (nr of points) can affect how pattern will show up. 614 615 Example: 616 ```python 617 from vedo import Line 618 pts = [[1, 0, 0], [5, 2, 0], [3, 3, 1]] 619 ln = Line(pts, c='r', lw=5).pattern('- -', repeats=10) 620 ln.show(axes=1).close() 621 ``` 622  623 """ 624 stipple = str(stipple) * int(2 * repeats) 625 dimension = len(stipple) 626 627 image = vtki.vtkImageData() 628 image.SetDimensions(dimension, 1, 1) 629 image.AllocateScalars(vtki.VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR, 4) 630 image.SetExtent(0, dimension - 1, 0, 0, 0, 0) 631 i_dim = 0 632 while i_dim < dimension: 633 for i in range(dimension): 634 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 0, 255) 635 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 1, 255) 636 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 2, 255) 637 if stipple[i] == " ": 638 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 3, 0) 639 else: 640 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 3, 255) 641 i_dim += 1 642 643 poly = self.dataset 644 645 # Create texture coordinates 646 tcoords = vtki.vtkDoubleArray() 647 tcoords.SetName("TCoordsStippledLine") 648 tcoords.SetNumberOfComponents(1) 649 tcoords.SetNumberOfTuples(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()) 650 for i in range(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()): 651 tcoords.SetTypedTuple(i, [i / 2]) 652 poly.GetPointData().SetTCoords(tcoords) 653 poly.GetPointData().Modified() 654 texture = vtki.vtkTexture() 655 texture.SetInputData(image) 656 texture.InterpolateOff() 657 texture.RepeatOn() 658 self.actor.SetTexture(texture) 659 return self 660 661 def length(self) -> float: 662 """Calculate length of the line.""" 663 pts = self.coordinates 664 if self.is_closed: 665 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 666 distance = 0.0 667 for i in range(1, len(pts)): 668 distance += np.linalg.norm(pts[i] - pts[i - 1]) 669 return distance 670 671 def tangents(self) -> np.ndarray: 672 """ 673 Compute the tangents of a line in space. 674 675 Example: 676 ```python 677 from vedo import * 678 shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[58] 679 pts = shape.rotate_x(30).coordinates 680 tangents = Line(pts).tangents() 681 arrs = Arrows(pts, pts+tangents, c='blue9') 682 show(shape.c('red5').lw(5), arrs, bg='bb', axes=1).close() 683 ``` 684  685 """ 686 v = np.gradient(self.coordinates)[0] 687 ds_dt = np.linalg.norm(v, axis=1) 688 tangent = np.array([1 / ds_dt] * 3).transpose() * v 689 return tangent 690 691 def curvature(self) -> np.ndarray: 692 """ 693 Compute the signed curvature of a line in space. 694 The signed is computed assuming the line is about coplanar to the xy plane. 695 696 Example: 697 ```python 698 from vedo import * 699 from vedo.pyplot import plot 700 shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[55] 701 curvs = Line(shape.coordinates).curvature() 702 shape.cmap('coolwarm', curvs, vmin=-2,vmax=2).add_scalarbar3d(c='w') 703 shape.render_lines_as_tubes().lw(12) 704 pp = plot(curvs, ac='white', lc='yellow5') 705 show(shape, pp, N=2, bg='bb', sharecam=False).close() 706 ``` 707  708 """ 709 v = np.gradient(self.coordinates)[0] 710 a = np.gradient(v)[0] 711 av = np.cross(a, v) 712 mav = np.linalg.norm(av, axis=1) 713 mv = utils.mag2(v) 714 val = mav * np.sign(av[:, 2]) / np.power(mv, 1.5) 715 val[0] = val[1] 716 val[-1] = val[-2] 717 return val 718 719 def compute_curvature(self, method=0) -> "Line": 720 """ 721 Add a pointdata array named 'Curvatures' which contains 722 the curvature value at each point. 723 724 NB: keyword `method` is overridden in Mesh and has no effect here. 725 """ 726 # overrides mesh.compute_curvature 727 curvs = self.curvature() 728 vmin, vmax = np.min(curvs), np.max(curvs) 729 if vmin < 0 and vmax > 0: 730 v = max(-vmin, vmax) 731 self.cmap("coolwarm", curvs, vmin=-v, vmax=v, name="Curvature") 732 else: 733 self.cmap("coolwarm", curvs, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, name="Curvature") 734 return self 735 736 def plot_scalar( 737 self, 738 radius=0.0, 739 height=1.1, 740 normal=(), 741 camera=None, 742 ) -> "Line": 743 """ 744 Generate a new `Line` which plots the active scalar along the line. 745 746 Arguments: 747 radius : (float) 748 distance radius to the line 749 height: (float) 750 height of the plot 751 normal: (list) 752 normal vector to the plane of the plot 753 camera: (vtkCamera) 754 camera object to use for the plot orientation 755 756 Example: 757 ```python 758 from vedo import * 759 circle = Circle(res=360).rotate_y(20) 760 pts = circle.coordinates 761 bore = Line(pts).lw(5) 762 values = np.arctan2(pts[:,1], pts[:,0]) 763 bore.pointdata["scalars"] = values + np.random.randn(360)/5 764 vap = bore.plot_scalar(radius=0, height=1) 765 show(bore, vap, axes=1, viewup='z').close() 766 ``` 767  768 """ 769 ap = vtki.new("ArcPlotter") 770 ap.SetInputData(self.dataset) 771 ap.SetCamera(camera) 772 ap.SetRadius(radius) 773 ap.SetHeight(height) 774 if len(normal)>0: 775 ap.UseDefaultNormalOn() 776 ap.SetDefaultNormal(normal) 777 ap.Update() 778 vap = Line(ap.GetOutput()) 779 vap.linewidth(3).lighting('off') 780 vap.name = "ArcPlot" 781 return vap 782 783 def sweep(self, direction=(1, 0, 0), res=1) -> "Mesh": 784 """ 785 Sweep the `Line` along the specified vector direction. 786 787 Returns a `Mesh` surface. 788 Line position is updated to allow for additional sweepings. 789 790 Example: 791 ```python 792 from vedo import Line, show 793 aline = Line([(0,0,0),(1,3,0),(2,4,0)]) 794 surf1 = aline.sweep((1,0.2,0), res=3) 795 surf2 = aline.sweep((0.2,0,1)).alpha(0.5) 796 aline.color('r').linewidth(4) 797 show(surf1, surf2, aline, axes=1).close() 798 ``` 799  800 """ 801 line = self.dataset 802 rows = line.GetNumberOfPoints() 803 804 spacing = 1 / res 805 surface = vtki.vtkPolyData() 806 807 res += 1 808 npts = rows * res 809 npolys = (rows - 1) * (res - 1) 810 points = vtki.vtkPoints() 811 points.Allocate(npts) 812 813 cnt = 0 814 x = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0] 815 for row in range(rows): 816 for col in range(res): 817 p = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0] 818 line.GetPoint(row, p) 819 x[0] = p[0] + direction[0] * col * spacing 820 x[1] = p[1] + direction[1] * col * spacing 821 x[2] = p[2] + direction[2] * col * spacing 822 points.InsertPoint(cnt, x) 823 cnt += 1 824 825 # Generate the quads 826 polys = vtki.vtkCellArray() 827 polys.Allocate(npolys * 4) 828 pts = [0, 0, 0, 0] 829 for row in range(rows - 1): 830 for col in range(res - 1): 831 pts[0] = col + row * res 832 pts[1] = pts[0] + 1 833 pts[2] = pts[0] + res + 1 834 pts[3] = pts[0] + res 835 polys.InsertNextCell(4, pts) 836 surface.SetPoints(points) 837 surface.SetPolys(polys) 838 asurface = Mesh(surface) 839 asurface.copy_properties_from(self) 840 asurface.lighting("default") 841 self.coordinates = self.coordinates + direction 842 return asurface 843 844 def reverse(self): 845 """Reverse the points sequence order.""" 846 pts = np.flip(self.coordinates, axis=0) 847 self.coordinates = pts 848 return self
Build the line segment between point p0 and point p1.
If p0 is already a list of points, return the line connecting them.
A 2D set of coords can also be passed as p0=[x..], p1=[y..].
404 def __init__(self, p0, p1=None, closed=False, res=2, lw=1, c="k1", alpha=1.0) -> None: 405 """ 406 Arguments: 407 closed : (bool) 408 join last to first point 409 res : (int) 410 resolution, number of points along the line 411 (only relevant if only 2 points are specified) 412 lw : (int) 413 line width in pixel units 414 """ 415 416 if isinstance(p1, Points): 417 p1 = p1.pos() 418 if isinstance(p0, Points): 419 p0 = p0.pos() 420 try: 421 p0 = p0.dataset 422 except AttributeError: 423 pass 424 425 if isinstance(p0, vtki.vtkPolyData): 426 poly = p0 427 top = np.array([0,0,1]) 428 base = np.array([0,0,0]) 429 430 elif utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): # detect if user is passing a list of points 431 432 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 433 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 434 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(np.asarray(p0), dtype=np.float32)) 435 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 436 npt = len(p0) 437 if closed: 438 lines.InsertNextCell(npt + 1) 439 else: 440 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 441 for i in range(npt): 442 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 443 if closed: 444 lines.InsertCellPoint(0) 445 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 446 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 447 poly.SetLines(lines) 448 top = p0[-1] 449 base = p0[0] 450 if res != 2: 451 printc(f"Warning: calling Line(res={res}), try remove []?", c='y') 452 res = 2 453 454 else: # or just 2 points to link 455 456 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 457 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 458 p1 = utils.make3d(p1) 459 line_source.SetPoint1(p0) 460 line_source.SetPoint2(p1) 461 line_source.SetResolution(res - 1) 462 line_source.Update() 463 poly = line_source.GetOutput() 464 top = np.asarray(p1, dtype=float) 465 base = np.asarray(p0, dtype=float) 466 467 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 468 469 self.slope: List[float] = [] # populated by analysis.fit_line 470 self.center: List[float] = [] 471 self.variances: List[float] = [] 472 473 self.coefficients: List[float] = [] # populated by pyplot.fit() 474 self.covariance_matrix: List[float] = [] 475 self.coefficient_errors: List[float] = [] 476 self.monte_carlo_coefficients: List[float] = [] 477 self.reduced_chi2 = -1 478 self.ndof = 0 479 self.data_sigma = 0 480 self.error_lines: List[Any] = [] 481 self.error_band = None 482 self.res = res 483 self.is_closed = closed 484 485 self.lw(lw) 486 self.properties.LightingOff() 487 self.actor.PickableOff() 488 self.actor.DragableOff() 489 self.base = base 490 self.top = top 491 self.name = "Line"
Arguments:
- closed : (bool) join last to first point
- res : (int) resolution, number of points along the line (only relevant if only 2 points are specified)
- lw : (int) line width in pixel units
400 def is_closed(self) -> bool: 401 """ 402 Return `True` if the mesh is watertight. 403 Note that if the mesh contains coincident points the result may be flase. 404 Use in this case `mesh.clean()` to merge coincident points. 405 """ 406 fe = vtki.new("FeatureEdges") 407 fe.BoundaryEdgesOn() 408 fe.FeatureEdgesOff() 409 fe.NonManifoldEdgesOn() 410 fe.SetInputData(self.dataset) 411 fe.Update() 412 ne = fe.GetOutput().GetNumberOfCells() 413 return not bool(ne)
Return True if the mesh is watertight.
Note that if the mesh contains coincident points the result may be flase.
Use in this case mesh.clean() to merge coincident points.
493 def clone(self, deep=True) -> "Line": 494 """ 495 Return a copy of the ``Line`` object. 496 497 Example: 498 ```python 499 from vedo import * 500 ln1 = Line([1,1,1], [2,2,2], lw=3).print() 501 ln2 = ln1.clone().shift(0,0,1).c('red').print() 502 show(ln1, ln2, axes=1, viewup='z').close() 503 ``` 504  505 """ 506 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 507 if deep: 508 poly.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 509 else: 510 poly.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 511 ln = Line(poly) 512 ln.copy_properties_from(self) 513 ln.transform = self.transform.clone() 514 ln.name = self.name 515 ln.base = self.base 516 ln.top = self.top 517 ln.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 518 "clone", parents=[self], shape="diamond", c="#edede9") 519 return ln
Return a copy of the Line object.
Example:
from vedo import * ln1 = Line([1,1,1], [2,2,2], lw=3).print() ln2 = ln1.clone().shift(0,0,1).c('red').print() show(ln1, ln2, axes=1, viewup='z').close()
521 def linecolor(self, lc=None) -> "Line": 522 """Assign a color to the line""" 523 # overrides mesh.linecolor which would have no effect here 524 return self.color(lc)
Assign a color to the line
526 def eval(self, x: float) -> np.ndarray: 527 """ 528 Calculate the position of an intermediate point 529 as a fraction of the length of the line, 530 being x=0 the first point and x=1 the last point. 531 This corresponds to an imaginary point that travels along the line 532 at constant speed. 533 534 Can be used in conjunction with `lin_interpolate()` 535 to map any range to the [0,1] range. 536 """ 537 distance1 = 0.0 538 length = self.length() 539 pts = self.coordinates 540 if self.is_closed: 541 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 542 543 for i in range(1, len(pts)): 544 p0 = pts[i - 1] 545 p1 = pts[i] 546 seg = p1 - p0 547 distance0 = distance1 548 distance1 += np.linalg.norm(seg) 549 w1 = distance1 / length 550 if w1 >= x: 551 break 552 w0 = distance0 / length 553 v = p0 + seg * (x - w0) / (w1 - w0) 554 return v
Calculate the position of an intermediate point as a fraction of the length of the line, being x=0 the first point and x=1 the last point. This corresponds to an imaginary point that travels along the line at constant speed.
Can be used in conjunction with lin_interpolate()
to map any range to the [0,1] range.
556 def eval2d(self, x: float) -> np.ndarray: 557 """ 558 Calculate the position of an intermediate point 559 at the specified value of x in absolute units. 560 Assume the line is in the xy-plane. 561 """ 562 xcoords, ycoords, _ = self.coordinates.T 563 # find the segment where x is located 564 idx = np.where((xcoords[:-1] <= x) & (xcoords[1:] >= x))[0] 565 if len(idx) > 0: 566 i = idx[0] 567 return np.array([x, np.interp(x, xcoords[i:i+2], ycoords[i:i+2])]) 568 return np.array([x, 0.0])
Calculate the position of an intermediate point at the specified value of x in absolute units. Assume the line is in the xy-plane.
570 def find_index_at_position(self, p) -> float: 571 """ 572 Find the index of the line vertex that is closest to the point `p`. 573 Note that the returned index is fractional as `p` may not be exactly 574 one of the vertices of the line. 575 """ 576 tf = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 577 tf.SetPassLines(True) 578 tf.SetPassVerts(False) 579 tf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 580 tf.Update() 581 polyline = tf.GetOutput() 582 583 if not self.cell_locator: 584 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("StaticCellLocator") 585 self.cell_locator.SetDataSet(polyline) 586 self.cell_locator.BuildLocator() 587 588 q = [0, 0, 0] 589 cid = vtki.mutable(0) 590 dist2 = vtki.mutable(0) 591 subid = vtki.mutable(0) 592 self.cell_locator.FindClosestPoint(p, q, cid, subid, dist2) 593 594 # find the 2 points 595 a = polyline.GetCell(cid).GetPointId(0) 596 b = polyline.GetCell(cid).GetPointId(1) 597 598 pts = self.coordinates 599 if self.is_closed: 600 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 601 d = np.linalg.norm(pts[a] - pts[b]) 602 t = a + np.linalg.norm(pts[a] - q) / d 603 return t
Find the index of the line vertex that is closest to the point p.
Note that the returned index is fractional as p may not be exactly
one of the vertices of the line.
605 def pattern(self, stipple, repeats=10) -> "Line": 606 """ 607 Define a stipple pattern for dashing the line. 608 Pass the stipple pattern as a string like `'- - -'`. 609 Repeats controls the number of times the pattern repeats in a single segment. 610 611 Examples are: `'- -', '-- - --'`, etc. 612 613 The resolution of the line (nr of points) can affect how pattern will show up. 614 615 Example: 616 ```python 617 from vedo import Line 618 pts = [[1, 0, 0], [5, 2, 0], [3, 3, 1]] 619 ln = Line(pts, c='r', lw=5).pattern('- -', repeats=10) 620 ln.show(axes=1).close() 621 ``` 622  623 """ 624 stipple = str(stipple) * int(2 * repeats) 625 dimension = len(stipple) 626 627 image = vtki.vtkImageData() 628 image.SetDimensions(dimension, 1, 1) 629 image.AllocateScalars(vtki.VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR, 4) 630 image.SetExtent(0, dimension - 1, 0, 0, 0, 0) 631 i_dim = 0 632 while i_dim < dimension: 633 for i in range(dimension): 634 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 0, 255) 635 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 1, 255) 636 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 2, 255) 637 if stipple[i] == " ": 638 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 3, 0) 639 else: 640 image.SetScalarComponentFromFloat(i_dim, 0, 0, 3, 255) 641 i_dim += 1 642 643 poly = self.dataset 644 645 # Create texture coordinates 646 tcoords = vtki.vtkDoubleArray() 647 tcoords.SetName("TCoordsStippledLine") 648 tcoords.SetNumberOfComponents(1) 649 tcoords.SetNumberOfTuples(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()) 650 for i in range(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()): 651 tcoords.SetTypedTuple(i, [i / 2]) 652 poly.GetPointData().SetTCoords(tcoords) 653 poly.GetPointData().Modified() 654 texture = vtki.vtkTexture() 655 texture.SetInputData(image) 656 texture.InterpolateOff() 657 texture.RepeatOn() 658 self.actor.SetTexture(texture) 659 return self
Define a stipple pattern for dashing the line.
Pass the stipple pattern as a string like '- - -'.
Repeats controls the number of times the pattern repeats in a single segment.
Examples are: '- -', '-- - --', etc.
The resolution of the line (nr of points) can affect how pattern will show up.
Example:
from vedo import Line pts = [[1, 0, 0], [5, 2, 0], [3, 3, 1]] ln = Line(pts, c='r', lw=5).pattern('- -', repeats=10) ln.show(axes=1).close()
661 def length(self) -> float: 662 """Calculate length of the line.""" 663 pts = self.coordinates 664 if self.is_closed: 665 pts = np.append(pts, [pts[0]], axis=0) 666 distance = 0.0 667 for i in range(1, len(pts)): 668 distance += np.linalg.norm(pts[i] - pts[i - 1]) 669 return distance
Calculate length of the line.
671 def tangents(self) -> np.ndarray: 672 """ 673 Compute the tangents of a line in space. 674 675 Example: 676 ```python 677 from vedo import * 678 shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[58] 679 pts = shape.rotate_x(30).coordinates 680 tangents = Line(pts).tangents() 681 arrs = Arrows(pts, pts+tangents, c='blue9') 682 show(shape.c('red5').lw(5), arrs, bg='bb', axes=1).close() 683 ``` 684  685 """ 686 v = np.gradient(self.coordinates)[0] 687 ds_dt = np.linalg.norm(v, axis=1) 688 tangent = np.array([1 / ds_dt] * 3).transpose() * v 689 return tangent
Compute the tangents of a line in space.
Example:
from vedo import * shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[58] pts = shape.rotate_x(30).coordinates tangents = Line(pts).tangents() arrs = Arrows(pts, pts+tangents, c='blue9') show(shape.c('red5').lw(5), arrs, bg='bb', axes=1).close()
691 def curvature(self) -> np.ndarray: 692 """ 693 Compute the signed curvature of a line in space. 694 The signed is computed assuming the line is about coplanar to the xy plane. 695 696 Example: 697 ```python 698 from vedo import * 699 from vedo.pyplot import plot 700 shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[55] 701 curvs = Line(shape.coordinates).curvature() 702 shape.cmap('coolwarm', curvs, vmin=-2,vmax=2).add_scalarbar3d(c='w') 703 shape.render_lines_as_tubes().lw(12) 704 pp = plot(curvs, ac='white', lc='yellow5') 705 show(shape, pp, N=2, bg='bb', sharecam=False).close() 706 ``` 707  708 """ 709 v = np.gradient(self.coordinates)[0] 710 a = np.gradient(v)[0] 711 av = np.cross(a, v) 712 mav = np.linalg.norm(av, axis=1) 713 mv = utils.mag2(v) 714 val = mav * np.sign(av[:, 2]) / np.power(mv, 1.5) 715 val[0] = val[1] 716 val[-1] = val[-2] 717 return val
Compute the signed curvature of a line in space. The signed is computed assuming the line is about coplanar to the xy plane.
Example:
from vedo import * from vedo.pyplot import plot shape = Assembly(dataurl+"timecourse1d.npy")[55] curvs = Line(shape.coordinates).curvature() shape.cmap('coolwarm', curvs, vmin=-2,vmax=2).add_scalarbar3d(c='w') shape.render_lines_as_tubes().lw(12) pp = plot(curvs, ac='white', lc='yellow5') show(shape, pp, N=2, bg='bb', sharecam=False).close()
719 def compute_curvature(self, method=0) -> "Line": 720 """ 721 Add a pointdata array named 'Curvatures' which contains 722 the curvature value at each point. 723 724 NB: keyword `method` is overridden in Mesh and has no effect here. 725 """ 726 # overrides mesh.compute_curvature 727 curvs = self.curvature() 728 vmin, vmax = np.min(curvs), np.max(curvs) 729 if vmin < 0 and vmax > 0: 730 v = max(-vmin, vmax) 731 self.cmap("coolwarm", curvs, vmin=-v, vmax=v, name="Curvature") 732 else: 733 self.cmap("coolwarm", curvs, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, name="Curvature") 734 return self
Add a pointdata array named 'Curvatures' which contains the curvature value at each point.
NB: keyword method is overridden in Mesh and has no effect here.
736 def plot_scalar( 737 self, 738 radius=0.0, 739 height=1.1, 740 normal=(), 741 camera=None, 742 ) -> "Line": 743 """ 744 Generate a new `Line` which plots the active scalar along the line. 745 746 Arguments: 747 radius : (float) 748 distance radius to the line 749 height: (float) 750 height of the plot 751 normal: (list) 752 normal vector to the plane of the plot 753 camera: (vtkCamera) 754 camera object to use for the plot orientation 755 756 Example: 757 ```python 758 from vedo import * 759 circle = Circle(res=360).rotate_y(20) 760 pts = circle.coordinates 761 bore = Line(pts).lw(5) 762 values = np.arctan2(pts[:,1], pts[:,0]) 763 bore.pointdata["scalars"] = values + np.random.randn(360)/5 764 vap = bore.plot_scalar(radius=0, height=1) 765 show(bore, vap, axes=1, viewup='z').close() 766 ``` 767  768 """ 769 ap = vtki.new("ArcPlotter") 770 ap.SetInputData(self.dataset) 771 ap.SetCamera(camera) 772 ap.SetRadius(radius) 773 ap.SetHeight(height) 774 if len(normal)>0: 775 ap.UseDefaultNormalOn() 776 ap.SetDefaultNormal(normal) 777 ap.Update() 778 vap = Line(ap.GetOutput()) 779 vap.linewidth(3).lighting('off') 780 vap.name = "ArcPlot" 781 return vap
Generate a new Line which plots the active scalar along the line.
Arguments:
- radius : (float) distance radius to the line
- height: (float) height of the plot
- normal: (list) normal vector to the plane of the plot
- camera: (vtkCamera) camera object to use for the plot orientation
Example:
from vedo import * circle = Circle(res=360).rotate_y(20) pts = circle.coordinates bore = Line(pts).lw(5) values = np.arctan2(pts[:,1], pts[:,0]) bore.pointdata["scalars"] = values + np.random.randn(360)/5 vap = bore.plot_scalar(radius=0, height=1) show(bore, vap, axes=1, viewup='z').close()
783 def sweep(self, direction=(1, 0, 0), res=1) -> "Mesh": 784 """ 785 Sweep the `Line` along the specified vector direction. 786 787 Returns a `Mesh` surface. 788 Line position is updated to allow for additional sweepings. 789 790 Example: 791 ```python 792 from vedo import Line, show 793 aline = Line([(0,0,0),(1,3,0),(2,4,0)]) 794 surf1 = aline.sweep((1,0.2,0), res=3) 795 surf2 = aline.sweep((0.2,0,1)).alpha(0.5) 796 aline.color('r').linewidth(4) 797 show(surf1, surf2, aline, axes=1).close() 798 ``` 799  800 """ 801 line = self.dataset 802 rows = line.GetNumberOfPoints() 803 804 spacing = 1 / res 805 surface = vtki.vtkPolyData() 806 807 res += 1 808 npts = rows * res 809 npolys = (rows - 1) * (res - 1) 810 points = vtki.vtkPoints() 811 points.Allocate(npts) 812 813 cnt = 0 814 x = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0] 815 for row in range(rows): 816 for col in range(res): 817 p = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0] 818 line.GetPoint(row, p) 819 x[0] = p[0] + direction[0] * col * spacing 820 x[1] = p[1] + direction[1] * col * spacing 821 x[2] = p[2] + direction[2] * col * spacing 822 points.InsertPoint(cnt, x) 823 cnt += 1 824 825 # Generate the quads 826 polys = vtki.vtkCellArray() 827 polys.Allocate(npolys * 4) 828 pts = [0, 0, 0, 0] 829 for row in range(rows - 1): 830 for col in range(res - 1): 831 pts[0] = col + row * res 832 pts[1] = pts[0] + 1 833 pts[2] = pts[0] + res + 1 834 pts[3] = pts[0] + res 835 polys.InsertNextCell(4, pts) 836 surface.SetPoints(points) 837 surface.SetPolys(polys) 838 asurface = Mesh(surface) 839 asurface.copy_properties_from(self) 840 asurface.lighting("default") 841 self.coordinates = self.coordinates + direction 842 return asurface
Sweep the Line along the specified vector direction.
Returns a Mesh surface.
Line position is updated to allow for additional sweepings.
Example:
from vedo import Line, show aline = Line([(0,0,0),(1,3,0),(2,4,0)]) surf1 = aline.sweep((1,0.2,0), res=3) surf2 = aline.sweep((0.2,0,1)).alpha(0.5) aline.color('r').linewidth(4) show(surf1, surf2, aline, axes=1).close()
851class DashedLine(Mesh): 852 """ 853 Consider using `Line.pattern()` instead. 854 855 Build a dashed line segment between points `p0` and `p1`. 856 If `p0` is a list of points returns the line connecting them. 857 A 2D set of coords can also be passed as `p0=[x..], p1=[y..]`. 858 """ 859 860 def __init__(self, p0, p1=None, spacing=0.1, closed=False, lw=2, c="k5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 861 """ 862 Arguments: 863 closed : (bool) 864 join last to first point 865 spacing : (float) 866 relative size of the dash 867 lw : (int) 868 line width in pixels 869 """ 870 if isinstance(p1, vtki.vtkActor): 871 p1 = p1.GetPosition() 872 if isinstance(p0, vtki.vtkActor): 873 p0 = p0.GetPosition() 874 if isinstance(p0, Points): 875 p0 = p0.coordinates 876 877 # detect if user is passing a 2D list of points as p0=xlist, p1=ylist: 878 if len(p0) > 3: 879 if not utils.is_sequence(p0[0]) and not utils.is_sequence(p1[0]) and len(p0) == len(p1): 880 # assume input is 2D xlist, ylist 881 p0 = np.stack((p0, p1), axis=1) 882 p1 = None 883 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 884 if closed: 885 p0 = np.append(p0, [p0[0]], axis=0) 886 887 if p1 is not None: # assume passing p0=[x,y] 888 if len(p0) == 2 and not utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): 889 p0 = (p0[0], p0[1], 0) 890 if len(p1) == 2 and not utils.is_sequence(p1[0]): 891 p1 = (p1[0], p1[1], 0) 892 893 # detect if user is passing a list of points: 894 if utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): 895 listp = p0 896 else: # or just 2 points to link 897 listp = [p0, p1] 898 899 listp = np.array(listp) 900 if listp.shape[1] == 2: 901 listp = np.c_[listp, np.zeros(listp.shape[0])] 902 903 xmn = np.min(listp, axis=0) 904 xmx = np.max(listp, axis=0) 905 dlen = np.linalg.norm(xmx - xmn) * np.clip(spacing, 0.01, 1.0) / 10 906 if not dlen: 907 super().__init__(vtki.vtkPolyData(), c, alpha) 908 self.name = "DashedLine (void)" 909 return 910 911 qs = [] 912 for ipt in range(len(listp) - 1): 913 p0 = listp[ipt] 914 p1 = listp[ipt + 1] 915 v = p1 - p0 916 vdist = np.linalg.norm(v) 917 n1 = int(vdist / dlen) 918 if not n1: 919 continue 920 921 res = 0.0 922 for i in range(n1 + 2): 923 ist = (i - 0.5) / n1 924 ist = max(ist, 0) 925 qi = p0 + v * (ist - res / vdist) 926 if ist > 1: 927 qi = p1 928 res = np.linalg.norm(qi - p1) 929 qs.append(qi) 930 break 931 qs.append(qi) 932 933 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 934 for i, q1 in enumerate(qs): 935 if not i % 2: 936 continue 937 q0 = qs[i - 1] 938 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 939 line_source.SetPoint1(q0) 940 line_source.SetPoint2(q1) 941 line_source.Update() 942 polylns.AddInputData(line_source.GetOutput()) 943 polylns.Update() 944 945 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 946 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 947 self.base = listp[0] 948 if closed: 949 self.top = listp[-2] 950 else: 951 self.top = listp[-1] 952 self.name = "DashedLine"
Consider using Line.pattern() instead.
Build a dashed line segment between points p0 and p1.
If p0 is a list of points returns the line connecting them.
A 2D set of coords can also be passed as p0=[x..], p1=[y..].
860 def __init__(self, p0, p1=None, spacing=0.1, closed=False, lw=2, c="k5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 861 """ 862 Arguments: 863 closed : (bool) 864 join last to first point 865 spacing : (float) 866 relative size of the dash 867 lw : (int) 868 line width in pixels 869 """ 870 if isinstance(p1, vtki.vtkActor): 871 p1 = p1.GetPosition() 872 if isinstance(p0, vtki.vtkActor): 873 p0 = p0.GetPosition() 874 if isinstance(p0, Points): 875 p0 = p0.coordinates 876 877 # detect if user is passing a 2D list of points as p0=xlist, p1=ylist: 878 if len(p0) > 3: 879 if not utils.is_sequence(p0[0]) and not utils.is_sequence(p1[0]) and len(p0) == len(p1): 880 # assume input is 2D xlist, ylist 881 p0 = np.stack((p0, p1), axis=1) 882 p1 = None 883 p0 = utils.make3d(p0) 884 if closed: 885 p0 = np.append(p0, [p0[0]], axis=0) 886 887 if p1 is not None: # assume passing p0=[x,y] 888 if len(p0) == 2 and not utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): 889 p0 = (p0[0], p0[1], 0) 890 if len(p1) == 2 and not utils.is_sequence(p1[0]): 891 p1 = (p1[0], p1[1], 0) 892 893 # detect if user is passing a list of points: 894 if utils.is_sequence(p0[0]): 895 listp = p0 896 else: # or just 2 points to link 897 listp = [p0, p1] 898 899 listp = np.array(listp) 900 if listp.shape[1] == 2: 901 listp = np.c_[listp, np.zeros(listp.shape[0])] 902 903 xmn = np.min(listp, axis=0) 904 xmx = np.max(listp, axis=0) 905 dlen = np.linalg.norm(xmx - xmn) * np.clip(spacing, 0.01, 1.0) / 10 906 if not dlen: 907 super().__init__(vtki.vtkPolyData(), c, alpha) 908 self.name = "DashedLine (void)" 909 return 910 911 qs = [] 912 for ipt in range(len(listp) - 1): 913 p0 = listp[ipt] 914 p1 = listp[ipt + 1] 915 v = p1 - p0 916 vdist = np.linalg.norm(v) 917 n1 = int(vdist / dlen) 918 if not n1: 919 continue 920 921 res = 0.0 922 for i in range(n1 + 2): 923 ist = (i - 0.5) / n1 924 ist = max(ist, 0) 925 qi = p0 + v * (ist - res / vdist) 926 if ist > 1: 927 qi = p1 928 res = np.linalg.norm(qi - p1) 929 qs.append(qi) 930 break 931 qs.append(qi) 932 933 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 934 for i, q1 in enumerate(qs): 935 if not i % 2: 936 continue 937 q0 = qs[i - 1] 938 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 939 line_source.SetPoint1(q0) 940 line_source.SetPoint2(q1) 941 line_source.Update() 942 polylns.AddInputData(line_source.GetOutput()) 943 polylns.Update() 944 945 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 946 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 947 self.base = listp[0] 948 if closed: 949 self.top = listp[-2] 950 else: 951 self.top = listp[-1] 952 self.name = "DashedLine"
Arguments:
- closed : (bool) join last to first point
- spacing : (float) relative size of the dash
- lw : (int) line width in pixels
955class RoundedLine(Mesh): 956 """ 957 Create a 2D line of specified thickness (in absolute units) passing through 958 a list of input points. Borders of the line are rounded. 959 """ 960 961 def __init__(self, pts, lw, res=10, c="gray4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 962 """ 963 Arguments: 964 pts : (list) 965 a list of points in 2D or 3D (z will be ignored). 966 lw : (float) 967 thickness of the line. 968 res : (int) 969 resolution of the rounded regions 970 971 Example: 972 ```python 973 from vedo import * 974 pts = [(-4,-3),(1,1),(2,4),(4,1),(3,-1),(2,-5),(9,-3)] 975 ln = Line(pts).z(0.01) 976 ln.color("red5").linewidth(2) 977 rl = RoundedLine(pts, 0.6) 978 show(Points(pts), ln, rl, axes=1).close() 979 ``` 980  981 """ 982 pts = utils.make3d(pts) 983 984 def _getpts(pts, revd=False): 985 986 if revd: 987 pts = list(reversed(pts)) 988 989 if len(pts) == 2: 990 p0, p1 = pts 991 v = p1 - p0 992 dv = np.linalg.norm(v) 993 nv = np.cross(v, (0, 0, -1)) 994 nv = nv / np.linalg.norm(nv) * lw 995 return [p0 + nv, p1 + nv] 996 997 ptsnew = [] 998 for k in range(len(pts) - 2): 999 p0 = pts[k] 1000 p1 = pts[k + 1] 1001 p2 = pts[k + 2] 1002 v = p1 - p0 1003 u = p2 - p1 1004 du = np.linalg.norm(u) 1005 dv = np.linalg.norm(v) 1006 nv = np.cross(v, (0, 0, -1)) 1007 nv = nv / np.linalg.norm(nv) * lw 1008 nu = np.cross(u, (0, 0, -1)) 1009 nu = nu / np.linalg.norm(nu) * lw 1010 uv = np.cross(u, v) 1011 if k == 0: 1012 ptsnew.append(p0 + nv) 1013 if uv[2] <= 0: 1014 # the following computation can return a value 1015 # ever so slightly > 1.0 causing arccos to fail. 1016 uv_arg = np.dot(u, v) / du / dv 1017 if uv_arg > 1.0: 1018 # since the argument to arcos is 1, simply 1019 # assign alpha to 0.0 without calculating the 1020 # arccos 1021 alpha = 0.0 1022 else: 1023 alpha = np.arccos(uv_arg) 1024 db = lw * np.tan(alpha / 2) 1025 p1new = p1 + nv - v / dv * db 1026 ptsnew.append(p1new) 1027 else: 1028 p1a = p1 + nv 1029 p1b = p1 + nu 1030 for i in range(0, res + 1): 1031 pab = p1a * (res - i) / res + p1b * i / res 1032 vpab = pab - p1 1033 vpab = vpab / np.linalg.norm(vpab) * lw 1034 ptsnew.append(p1 + vpab) 1035 if k == len(pts) - 3: 1036 ptsnew.append(p2 + nu) 1037 if revd: 1038 ptsnew.append(p2 - nu) 1039 return ptsnew 1040 1041 ptsnew = _getpts(pts) + _getpts(pts, revd=True) 1042 1043 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 1044 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(np.asarray(ptsnew), dtype=np.float32)) 1045 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1046 npt = len(ptsnew) 1047 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 1048 for i in range(npt): 1049 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 1050 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1051 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 1052 poly.SetLines(lines) 1053 vct = vtki.new("ContourTriangulator") 1054 vct.SetInputData(poly) 1055 vct.Update() 1056 1057 super().__init__(vct.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1058 self.flat() 1059 self.properties.LightingOff() 1060 self.name = "RoundedLine" 1061 self.base = ptsnew[0] 1062 self.top = ptsnew[-1]
Create a 2D line of specified thickness (in absolute units) passing through a list of input points. Borders of the line are rounded.
961 def __init__(self, pts, lw, res=10, c="gray4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 962 """ 963 Arguments: 964 pts : (list) 965 a list of points in 2D or 3D (z will be ignored). 966 lw : (float) 967 thickness of the line. 968 res : (int) 969 resolution of the rounded regions 970 971 Example: 972 ```python 973 from vedo import * 974 pts = [(-4,-3),(1,1),(2,4),(4,1),(3,-1),(2,-5),(9,-3)] 975 ln = Line(pts).z(0.01) 976 ln.color("red5").linewidth(2) 977 rl = RoundedLine(pts, 0.6) 978 show(Points(pts), ln, rl, axes=1).close() 979 ``` 980  981 """ 982 pts = utils.make3d(pts) 983 984 def _getpts(pts, revd=False): 985 986 if revd: 987 pts = list(reversed(pts)) 988 989 if len(pts) == 2: 990 p0, p1 = pts 991 v = p1 - p0 992 dv = np.linalg.norm(v) 993 nv = np.cross(v, (0, 0, -1)) 994 nv = nv / np.linalg.norm(nv) * lw 995 return [p0 + nv, p1 + nv] 996 997 ptsnew = [] 998 for k in range(len(pts) - 2): 999 p0 = pts[k] 1000 p1 = pts[k + 1] 1001 p2 = pts[k + 2] 1002 v = p1 - p0 1003 u = p2 - p1 1004 du = np.linalg.norm(u) 1005 dv = np.linalg.norm(v) 1006 nv = np.cross(v, (0, 0, -1)) 1007 nv = nv / np.linalg.norm(nv) * lw 1008 nu = np.cross(u, (0, 0, -1)) 1009 nu = nu / np.linalg.norm(nu) * lw 1010 uv = np.cross(u, v) 1011 if k == 0: 1012 ptsnew.append(p0 + nv) 1013 if uv[2] <= 0: 1014 # the following computation can return a value 1015 # ever so slightly > 1.0 causing arccos to fail. 1016 uv_arg = np.dot(u, v) / du / dv 1017 if uv_arg > 1.0: 1018 # since the argument to arcos is 1, simply 1019 # assign alpha to 0.0 without calculating the 1020 # arccos 1021 alpha = 0.0 1022 else: 1023 alpha = np.arccos(uv_arg) 1024 db = lw * np.tan(alpha / 2) 1025 p1new = p1 + nv - v / dv * db 1026 ptsnew.append(p1new) 1027 else: 1028 p1a = p1 + nv 1029 p1b = p1 + nu 1030 for i in range(0, res + 1): 1031 pab = p1a * (res - i) / res + p1b * i / res 1032 vpab = pab - p1 1033 vpab = vpab / np.linalg.norm(vpab) * lw 1034 ptsnew.append(p1 + vpab) 1035 if k == len(pts) - 3: 1036 ptsnew.append(p2 + nu) 1037 if revd: 1038 ptsnew.append(p2 - nu) 1039 return ptsnew 1040 1041 ptsnew = _getpts(pts) + _getpts(pts, revd=True) 1042 1043 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 1044 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(np.asarray(ptsnew), dtype=np.float32)) 1045 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1046 npt = len(ptsnew) 1047 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 1048 for i in range(npt): 1049 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 1050 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1051 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 1052 poly.SetLines(lines) 1053 vct = vtki.new("ContourTriangulator") 1054 vct.SetInputData(poly) 1055 vct.Update() 1056 1057 super().__init__(vct.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1058 self.flat() 1059 self.properties.LightingOff() 1060 self.name = "RoundedLine" 1061 self.base = ptsnew[0] 1062 self.top = ptsnew[-1]
Arguments:
- pts : (list) a list of points in 2D or 3D (z will be ignored).
- lw : (float) thickness of the line.
- res : (int) resolution of the rounded regions
Example:
from vedo import * pts = [(-4,-3),(1,1),(2,4),(4,1),(3,-1),(2,-5),(9,-3)] ln = Line(pts).z(0.01) ln.color("red5").linewidth(2) rl = RoundedLine(pts, 0.6) show(Points(pts), ln, rl, axes=1).close()
1585class Tube(Mesh): 1586 """ 1587 Build a tube along the line defined by a set of points. 1588 """ 1589 1590 def __init__(self, points, r=1.0, cap=True, res=12, c=None, alpha=1.0) -> None: 1591 """ 1592 Arguments: 1593 r : (float, list) 1594 constant radius or list of radii. 1595 res : (int) 1596 resolution, number of the sides of the tube 1597 c : (color) 1598 constant color or list of colors for each point. 1599 1600 Example: 1601 Create a tube along a line, with data associated to each point: 1602 1603 ```python 1604 from vedo import * 1605 line = Line([(0,0,0), (1,1,1), (2,0,1), (3,1,0)]).lw(5) 1606 scalars = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3]) 1607 line.pointdata["myscalars"] = scalars 1608 tube = Tube(line, r=0.1).lw(1) 1609 tube.cmap('viridis', "myscalars").add_scalarbar3d() 1610 show(line, tube, axes=1).close() 1611 ``` 1612 1613 Examples: 1614 - [ribbon.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/ribbon.py) 1615 - [tube_radii.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/tube_radii.py) 1616 1617  1618 """ 1619 if utils.is_sequence(points): 1620 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 1621 idx = len(points) 1622 for p in points: 1623 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 1624 line = vtki.new("PolyLine") 1625 line.GetPointIds().SetNumberOfIds(idx) 1626 for i in range(idx): 1627 line.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i) 1628 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1629 lines.InsertNextCell(line) 1630 polyln = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1631 polyln.SetPoints(vpoints) 1632 polyln.SetLines(lines) 1633 self.base = np.asarray(points[0], dtype=float) 1634 self.top = np.asarray(points[-1], dtype=float) 1635 1636 elif isinstance(points, Mesh): 1637 polyln = points.dataset 1638 n = polyln.GetNumberOfPoints() 1639 self.base = np.array(polyln.GetPoint(0)) 1640 self.top = np.array(polyln.GetPoint(n - 1)) 1641 1642 # from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersCore import vtkTubeBender 1643 # bender = vtkTubeBender() 1644 # bender.SetInputData(polyln) 1645 # bender.SetRadius(r) 1646 # bender.Update() 1647 # polyln = bender.GetOutput() 1648 1649 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 1650 tuf.SetCapping(cap) 1651 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(res) 1652 tuf.SetInputData(polyln) 1653 if utils.is_sequence(r): 1654 arr = utils.numpy2vtk(r, dtype=float) 1655 arr.SetName("TubeRadius") 1656 polyln.GetPointData().AddArray(arr) 1657 polyln.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("TubeRadius") 1658 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByAbsoluteScalar() 1659 else: 1660 tuf.SetRadius(r) 1661 1662 usingColScals = False 1663 if utils.is_sequence(c): 1664 usingColScals = True 1665 cc = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 1666 cc.SetName("TubeColors") 1667 cc.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 1668 cc.SetNumberOfTuples(len(c)) 1669 for i, ic in enumerate(c): 1670 r, g, b = get_color(ic) 1671 cc.InsertTuple3(i, int(255 * r), int(255 * g), int(255 * b)) 1672 polyln.GetPointData().AddArray(cc) 1673 c = None 1674 tuf.Update() 1675 1676 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1677 self.phong() 1678 if usingColScals: 1679 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointFieldData() 1680 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1681 self.mapper.SelectColorArray("TubeColors") 1682 self.mapper.Modified() 1683 self.name = "Tube"
Build a tube along the line defined by a set of points.
1590 def __init__(self, points, r=1.0, cap=True, res=12, c=None, alpha=1.0) -> None: 1591 """ 1592 Arguments: 1593 r : (float, list) 1594 constant radius or list of radii. 1595 res : (int) 1596 resolution, number of the sides of the tube 1597 c : (color) 1598 constant color or list of colors for each point. 1599 1600 Example: 1601 Create a tube along a line, with data associated to each point: 1602 1603 ```python 1604 from vedo import * 1605 line = Line([(0,0,0), (1,1,1), (2,0,1), (3,1,0)]).lw(5) 1606 scalars = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3]) 1607 line.pointdata["myscalars"] = scalars 1608 tube = Tube(line, r=0.1).lw(1) 1609 tube.cmap('viridis', "myscalars").add_scalarbar3d() 1610 show(line, tube, axes=1).close() 1611 ``` 1612 1613 Examples: 1614 - [ribbon.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/ribbon.py) 1615 - [tube_radii.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/tube_radii.py) 1616 1617  1618 """ 1619 if utils.is_sequence(points): 1620 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 1621 idx = len(points) 1622 for p in points: 1623 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 1624 line = vtki.new("PolyLine") 1625 line.GetPointIds().SetNumberOfIds(idx) 1626 for i in range(idx): 1627 line.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i) 1628 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1629 lines.InsertNextCell(line) 1630 polyln = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1631 polyln.SetPoints(vpoints) 1632 polyln.SetLines(lines) 1633 self.base = np.asarray(points[0], dtype=float) 1634 self.top = np.asarray(points[-1], dtype=float) 1635 1636 elif isinstance(points, Mesh): 1637 polyln = points.dataset 1638 n = polyln.GetNumberOfPoints() 1639 self.base = np.array(polyln.GetPoint(0)) 1640 self.top = np.array(polyln.GetPoint(n - 1)) 1641 1642 # from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersCore import vtkTubeBender 1643 # bender = vtkTubeBender() 1644 # bender.SetInputData(polyln) 1645 # bender.SetRadius(r) 1646 # bender.Update() 1647 # polyln = bender.GetOutput() 1648 1649 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 1650 tuf.SetCapping(cap) 1651 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(res) 1652 tuf.SetInputData(polyln) 1653 if utils.is_sequence(r): 1654 arr = utils.numpy2vtk(r, dtype=float) 1655 arr.SetName("TubeRadius") 1656 polyln.GetPointData().AddArray(arr) 1657 polyln.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("TubeRadius") 1658 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByAbsoluteScalar() 1659 else: 1660 tuf.SetRadius(r) 1661 1662 usingColScals = False 1663 if utils.is_sequence(c): 1664 usingColScals = True 1665 cc = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 1666 cc.SetName("TubeColors") 1667 cc.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 1668 cc.SetNumberOfTuples(len(c)) 1669 for i, ic in enumerate(c): 1670 r, g, b = get_color(ic) 1671 cc.InsertTuple3(i, int(255 * r), int(255 * g), int(255 * b)) 1672 polyln.GetPointData().AddArray(cc) 1673 c = None 1674 tuf.Update() 1675 1676 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1677 self.phong() 1678 if usingColScals: 1679 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointFieldData() 1680 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1681 self.mapper.SelectColorArray("TubeColors") 1682 self.mapper.Modified() 1683 self.name = "Tube"
Arguments:
- r : (float, list) constant radius or list of radii.
- res : (int) resolution, number of the sides of the tube
- c : (color) constant color or list of colors for each point.
Example:
Create a tube along a line, with data associated to each point:
from vedo import * line = Line([(0,0,0), (1,1,1), (2,0,1), (3,1,0)]).lw(5) scalars = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3]) line.pointdata["myscalars"] = scalars tube = Tube(line, r=0.1).lw(1) tube.cmap('viridis', "myscalars").add_scalarbar3d() show(line, tube, axes=1).close()
Examples:
1737class Tubes(Mesh): 1738 """ 1739 Build tubes around a `Lines` object. 1740 """ 1741 def __init__( 1742 self, 1743 lines, 1744 r=1, 1745 vary_radius_by_scalar=False, 1746 vary_radius_by_vector=False, 1747 vary_radius_by_vector_norm=False, 1748 vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar=False, 1749 max_radius_factor=100, 1750 cap=True, 1751 res=12 1752 ) -> None: 1753 """ 1754 Wrap tubes around the input `Lines` object. 1755 1756 Arguments: 1757 lines : (Lines) 1758 input Lines object. 1759 r : (float) 1760 constant radius 1761 vary_radius_by_scalar : (bool) 1762 use scalar array to control radius 1763 vary_radius_by_vector : (bool) 1764 use vector array to control radius 1765 vary_radius_by_vector_norm : (bool) 1766 use vector norm to control radius 1767 vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar : (bool) 1768 use absolute scalar value to control radius 1769 max_radius_factor : (float) 1770 max tube radius as a multiple of the min radius 1771 cap : (bool) 1772 capping of the tube 1773 res : (int) 1774 resolution, number of the sides of the tube 1775 c : (color) 1776 constant color or list of colors for each point. 1777 1778 Examples: 1779 - [streamlines1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/streamlines1.py) 1780 """ 1781 plines = lines.dataset 1782 if plines.GetNumberOfLines() == 0: 1783 vedo.logger.warning("Tubes(): input Lines is empty.") 1784 1785 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 1786 if vary_radius_by_scalar: 1787 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByScalar() 1788 elif vary_radius_by_vector: 1789 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByVector() 1790 elif vary_radius_by_vector_norm: 1791 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByVectorNorm() 1792 elif vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar: 1793 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByAbsoluteScalar() 1794 tuf.SetRadius(r) 1795 tuf.SetCapping(cap) 1796 tuf.SetGenerateTCoords(0) 1797 tuf.SetSidesShareVertices(1) 1798 tuf.SetRadiusFactor(max_radius_factor) 1799 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(res) 1800 tuf.SetInputData(plines) 1801 tuf.Update() 1802 1803 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput()) 1804 self.name = "Tubes"
Build tubes around a Lines object.
1741 def __init__( 1742 self, 1743 lines, 1744 r=1, 1745 vary_radius_by_scalar=False, 1746 vary_radius_by_vector=False, 1747 vary_radius_by_vector_norm=False, 1748 vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar=False, 1749 max_radius_factor=100, 1750 cap=True, 1751 res=12 1752 ) -> None: 1753 """ 1754 Wrap tubes around the input `Lines` object. 1755 1756 Arguments: 1757 lines : (Lines) 1758 input Lines object. 1759 r : (float) 1760 constant radius 1761 vary_radius_by_scalar : (bool) 1762 use scalar array to control radius 1763 vary_radius_by_vector : (bool) 1764 use vector array to control radius 1765 vary_radius_by_vector_norm : (bool) 1766 use vector norm to control radius 1767 vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar : (bool) 1768 use absolute scalar value to control radius 1769 max_radius_factor : (float) 1770 max tube radius as a multiple of the min radius 1771 cap : (bool) 1772 capping of the tube 1773 res : (int) 1774 resolution, number of the sides of the tube 1775 c : (color) 1776 constant color or list of colors for each point. 1777 1778 Examples: 1779 - [streamlines1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/streamlines1.py) 1780 """ 1781 plines = lines.dataset 1782 if plines.GetNumberOfLines() == 0: 1783 vedo.logger.warning("Tubes(): input Lines is empty.") 1784 1785 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 1786 if vary_radius_by_scalar: 1787 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByScalar() 1788 elif vary_radius_by_vector: 1789 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByVector() 1790 elif vary_radius_by_vector_norm: 1791 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByVectorNorm() 1792 elif vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar: 1793 tuf.SetVaryRadiusToVaryRadiusByAbsoluteScalar() 1794 tuf.SetRadius(r) 1795 tuf.SetCapping(cap) 1796 tuf.SetGenerateTCoords(0) 1797 tuf.SetSidesShareVertices(1) 1798 tuf.SetRadiusFactor(max_radius_factor) 1799 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(res) 1800 tuf.SetInputData(plines) 1801 tuf.Update() 1802 1803 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput()) 1804 self.name = "Tubes"
Wrap tubes around the input Lines object.
Arguments:
- lines : (Lines) input Lines object.
- r : (float) constant radius
- vary_radius_by_scalar : (bool) use scalar array to control radius
- vary_radius_by_vector : (bool) use vector array to control radius
- vary_radius_by_vector_norm : (bool) use vector norm to control radius
- vary_radius_by_absolute_scalar : (bool) use absolute scalar value to control radius
- max_radius_factor : (float) max tube radius as a multiple of the min radius
- cap : (bool) capping of the tube
- res : (int) resolution, number of the sides of the tube
- c : (color) constant color or list of colors for each point.
Examples:
1686def ThickTube(pts, r1, r2, res=12, c=None, alpha=1.0) -> Union["Mesh", None]: 1687 """ 1688 Create a tube with a thickness along a line of points. 1689 1690 Example: 1691 ```python 1692 from vedo import * 1693 pts = [[sin(x), cos(x), x/3] for x in np.arange(0.1, 3, 0.3)] 1694 vline = Line(pts, lw=5, c='red5') 1695 thick_tube = ThickTube(vline, r1=0.2, r2=0.3).lw(1) 1696 show(vline, thick_tube, axes=1).close() 1697 ``` 1698  1699 """ 1700 1701 def make_cap(t1, t2): 1702 newpoints = t1.coordinates.tolist() + t2.coordinates.tolist() 1703 newfaces = [] 1704 for i in range(n - 1): 1705 newfaces.append([i, i + 1, i + n]) 1706 newfaces.append([i + n, i + 1, i + n + 1]) 1707 newfaces.append([2 * n - 1, 0, n]) 1708 newfaces.append([2 * n - 1, n - 1, 0]) 1709 capm = utils.buildPolyData(newpoints, newfaces) 1710 return capm 1711 1712 assert r1 < r2 1713 1714 t1 = Tube(pts, r=r1, cap=False, res=res) 1715 t2 = Tube(pts, r=r2, cap=False, res=res) 1716 1717 tc1a, tc1b = t1.boundaries().split() 1718 tc2a, tc2b = t2.boundaries().split() 1719 n = tc1b.npoints 1720 1721 tc1b.join(reset=True).clean() # needed because indices are flipped 1722 tc2b.join(reset=True).clean() 1723 1724 capa = make_cap(tc1a, tc2a) 1725 capb = make_cap(tc1b, tc2b) 1726 1727 thick_tube = merge(t1, t2, capa, capb) 1728 if thick_tube: 1729 thick_tube.c(c).alpha(alpha) 1730 thick_tube.base = t1.base 1731 thick_tube.top = t1.top 1732 thick_tube.name = "ThickTube" 1733 return thick_tube 1734 return None
Create a tube with a thickness along a line of points.
Example:
from vedo import *
pts = [[sin(x), cos(x), x/3] for x in np.arange(0.1, 3, 0.3)]
vline = Line(pts, lw=5, c='red5')
thick_tube = ThickTube(vline, r1=0.2, r2=0.3).lw(1)
show(vline, thick_tube, axes=1).close()

1065class Lines(Mesh): 1066 """ 1067 Build the line segments between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 1068 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 1069 """ 1070 1071 def __init__( 1072 self, start_pts, end_pts=None, dotted=False, res=1, scale=1.0, lw=1, c="k4", alpha=1.0 1073 ) -> None: 1074 """ 1075 Arguments: 1076 scale : (float) 1077 apply a rescaling factor to the lengths. 1078 c : (color, int, str, list) 1079 color name, number, or list of [R,G,B] colors 1080 alpha : (float) 1081 opacity in range [0,1] 1082 lw : (int) 1083 line width in pixel units 1084 dotted : (bool) 1085 draw a dotted line 1086 res : (int) 1087 resolution, number of points along the line 1088 (only relevant if only 2 points are specified) 1089 1090 Examples: 1091 - [fitspheres2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/fitspheres2.py) 1092 1093  1094 """ 1095 1096 if isinstance(start_pts, vtki.vtkPolyData):######## 1097 super().__init__(start_pts, c, alpha) 1098 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1099 self.name = "Lines" 1100 return ######################################## 1101 1102 if utils.is_sequence(start_pts) and len(start_pts)>1 and isinstance(start_pts[0], Line): 1103 # passing a list of Line, see tests/issues/issue_950.py 1104 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1105 for ln in start_pts: 1106 polylns.AddInputData(ln.dataset) 1107 polylns.Update() 1108 1109 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1110 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1111 if dotted: 1112 self.properties.SetLineStipplePattern(0xF0F0) 1113 self.properties.SetLineStippleRepeatFactor(1) 1114 self.name = "Lines" 1115 return ######################################## 1116 1117 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 1118 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 1119 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 1120 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 1121 1122 if end_pts is not None: 1123 start_pts = np.stack((start_pts, end_pts), axis=1) 1124 1125 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1126 1127 if not utils.is_ragged(start_pts): 1128 1129 for twopts in start_pts: 1130 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 1131 line_source.SetResolution(res) 1132 if len(twopts[0]) == 2: 1133 line_source.SetPoint1(twopts[0][0], twopts[0][1], 0.0) 1134 else: 1135 line_source.SetPoint1(twopts[0]) 1136 1137 if scale == 1: 1138 pt2 = twopts[1] 1139 else: 1140 vers = (np.array(twopts[1]) - twopts[0]) * scale 1141 pt2 = np.array(twopts[0]) + vers 1142 1143 if len(pt2) == 2: 1144 line_source.SetPoint2(pt2[0], pt2[1], 0.0) 1145 else: 1146 line_source.SetPoint2(pt2) 1147 polylns.AddInputConnection(line_source.GetOutputPort()) 1148 1149 else: 1150 1151 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1152 for t in start_pts: 1153 t = utils.make3d(t) 1154 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 1155 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(t, dtype=np.float32)) 1156 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1157 npt = len(t) 1158 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 1159 for i in range(npt): 1160 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 1161 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1162 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 1163 poly.SetLines(lines) 1164 polylns.AddInputData(poly) 1165 1166 polylns.Update() 1167 1168 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1169 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1170 if dotted: 1171 self.properties.SetLineStipplePattern(0xF0F0) 1172 self.properties.SetLineStippleRepeatFactor(1) 1173 1174 self.name = "Lines"
Build the line segments between two lists of points start_pts and end_pts.
start_pts can be also passed in the form [[point1, point2], ...].
1071 def __init__( 1072 self, start_pts, end_pts=None, dotted=False, res=1, scale=1.0, lw=1, c="k4", alpha=1.0 1073 ) -> None: 1074 """ 1075 Arguments: 1076 scale : (float) 1077 apply a rescaling factor to the lengths. 1078 c : (color, int, str, list) 1079 color name, number, or list of [R,G,B] colors 1080 alpha : (float) 1081 opacity in range [0,1] 1082 lw : (int) 1083 line width in pixel units 1084 dotted : (bool) 1085 draw a dotted line 1086 res : (int) 1087 resolution, number of points along the line 1088 (only relevant if only 2 points are specified) 1089 1090 Examples: 1091 - [fitspheres2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/fitspheres2.py) 1092 1093  1094 """ 1095 1096 if isinstance(start_pts, vtki.vtkPolyData):######## 1097 super().__init__(start_pts, c, alpha) 1098 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1099 self.name = "Lines" 1100 return ######################################## 1101 1102 if utils.is_sequence(start_pts) and len(start_pts)>1 and isinstance(start_pts[0], Line): 1103 # passing a list of Line, see tests/issues/issue_950.py 1104 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1105 for ln in start_pts: 1106 polylns.AddInputData(ln.dataset) 1107 polylns.Update() 1108 1109 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1110 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1111 if dotted: 1112 self.properties.SetLineStipplePattern(0xF0F0) 1113 self.properties.SetLineStippleRepeatFactor(1) 1114 self.name = "Lines" 1115 return ######################################## 1116 1117 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 1118 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 1119 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 1120 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 1121 1122 if end_pts is not None: 1123 start_pts = np.stack((start_pts, end_pts), axis=1) 1124 1125 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1126 1127 if not utils.is_ragged(start_pts): 1128 1129 for twopts in start_pts: 1130 line_source = vtki.new("LineSource") 1131 line_source.SetResolution(res) 1132 if len(twopts[0]) == 2: 1133 line_source.SetPoint1(twopts[0][0], twopts[0][1], 0.0) 1134 else: 1135 line_source.SetPoint1(twopts[0]) 1136 1137 if scale == 1: 1138 pt2 = twopts[1] 1139 else: 1140 vers = (np.array(twopts[1]) - twopts[0]) * scale 1141 pt2 = np.array(twopts[0]) + vers 1142 1143 if len(pt2) == 2: 1144 line_source.SetPoint2(pt2[0], pt2[1], 0.0) 1145 else: 1146 line_source.SetPoint2(pt2) 1147 polylns.AddInputConnection(line_source.GetOutputPort()) 1148 1149 else: 1150 1151 polylns = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1152 for t in start_pts: 1153 t = utils.make3d(t) 1154 ppoints = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline 1155 ppoints.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(t, dtype=np.float32)) 1156 lines = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1157 npt = len(t) 1158 lines.InsertNextCell(npt) 1159 for i in range(npt): 1160 lines.InsertCellPoint(i) 1161 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1162 poly.SetPoints(ppoints) 1163 poly.SetLines(lines) 1164 polylns.AddInputData(poly) 1165 1166 polylns.Update() 1167 1168 super().__init__(polylns.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1169 self.lw(lw).lighting("off") 1170 if dotted: 1171 self.properties.SetLineStipplePattern(0xF0F0) 1172 self.properties.SetLineStippleRepeatFactor(1) 1173 1174 self.name = "Lines"
Arguments:
- scale : (float) apply a rescaling factor to the lengths.
- c : (color, int, str, list) color name, number, or list of [R,G,B] colors
- alpha : (float) opacity in range [0,1]
- lw : (int) line width in pixel units
- dotted : (bool) draw a dotted line
- res : (int) resolution, number of points along the line (only relevant if only 2 points are specified)
Examples:
1257class Spline(Line): 1258 """ 1259 Find the B-Spline curve through a set of points. This curve does not necessarily 1260 pass exactly through all the input points. Needs to import `scipy`. 1261 """ 1262 1263 def __init__(self, points, smooth=0.0, degree=2, closed=False, res=None, easing="") -> None: 1264 """ 1265 Arguments: 1266 smooth : (float) 1267 smoothing factor. 1268 - 0 = interpolate points exactly [default]. 1269 - 1 = average point positions. 1270 degree : (int) 1271 degree of the spline (between 1 and 5). 1272 easing : (str) 1273 control sensity of points along the spline. 1274 Available options are 1275 `[InSine, OutSine, Sine, InQuad, OutQuad, InCubic, OutCubic, InQuart, OutQuart, InCirc, OutCirc].` 1276 Can be used to create animations (move objects at varying speed). 1277 See e.g.: https://easings.net 1278 res : (int) 1279 number of points on the spline 1280 1281 See also: `CSpline` and `KSpline`. 1282 1283 Examples: 1284 - [spline_ease.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/spline_ease.py) 1285 1286  1287 """ 1288 from scipy.interpolate import splprep, splev 1289 1290 if isinstance(points, Points): 1291 points = points.coordinates 1292 1293 points = utils.make3d(points) 1294 1295 per = 0 1296 if closed: 1297 points = np.append(points, [points[0]], axis=0) 1298 per = 1 1299 1300 if res is None: 1301 res = len(points) * 10 1302 1303 points = np.array(points, dtype=float) 1304 1305 minx, miny, minz = np.min(points, axis=0) 1306 maxx, maxy, maxz = np.max(points, axis=0) 1307 maxb = max(maxx - minx, maxy - miny, maxz - minz) 1308 smooth *= maxb / 2 # must be in absolute units 1309 1310 x = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, res) 1311 if easing: 1312 if easing == "InSine": 1313 x = 1.0 - np.cos((x * np.pi) / 2) 1314 elif easing == "OutSine": 1315 x = np.sin((x * np.pi) / 2) 1316 elif easing == "Sine": 1317 x = -(np.cos(np.pi * x) - 1) / 2 1318 elif easing == "InQuad": 1319 x = x * x 1320 elif easing == "OutQuad": 1321 x = 1.0 - (1 - x) * (1 - x) 1322 elif easing == "InCubic": 1323 x = x * x 1324 elif easing == "OutCubic": 1325 x = 1.0 - np.power(1 - x, 3) 1326 elif easing == "InQuart": 1327 x = x * x * x * x 1328 elif easing == "OutQuart": 1329 x = 1.0 - np.power(1 - x, 4) 1330 elif easing == "InCirc": 1331 x = 1.0 - np.sqrt(1 - np.power(x, 2)) 1332 elif easing == "OutCirc": 1333 x = np.sqrt(1.0 - np.power(x - 1, 2)) 1334 else: 1335 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown ease mode {easing}") 1336 1337 # find the knots 1338 tckp, _ = splprep(points.T, task=0, s=smooth, k=degree, per=per) 1339 # evaluate spLine, including interpolated points: 1340 xnew, ynew, znew = splev(x, tckp) 1341 1342 super().__init__(np.c_[xnew, ynew, znew], lw=2) 1343 self.name = "Spline"
Find the B-Spline curve through a set of points. This curve does not necessarily
pass exactly through all the input points. Needs to import scipy.
1263 def __init__(self, points, smooth=0.0, degree=2, closed=False, res=None, easing="") -> None: 1264 """ 1265 Arguments: 1266 smooth : (float) 1267 smoothing factor. 1268 - 0 = interpolate points exactly [default]. 1269 - 1 = average point positions. 1270 degree : (int) 1271 degree of the spline (between 1 and 5). 1272 easing : (str) 1273 control sensity of points along the spline. 1274 Available options are 1275 `[InSine, OutSine, Sine, InQuad, OutQuad, InCubic, OutCubic, InQuart, OutQuart, InCirc, OutCirc].` 1276 Can be used to create animations (move objects at varying speed). 1277 See e.g.: https://easings.net 1278 res : (int) 1279 number of points on the spline 1280 1281 See also: `CSpline` and `KSpline`. 1282 1283 Examples: 1284 - [spline_ease.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/spline_ease.py) 1285 1286  1287 """ 1288 from scipy.interpolate import splprep, splev 1289 1290 if isinstance(points, Points): 1291 points = points.coordinates 1292 1293 points = utils.make3d(points) 1294 1295 per = 0 1296 if closed: 1297 points = np.append(points, [points[0]], axis=0) 1298 per = 1 1299 1300 if res is None: 1301 res = len(points) * 10 1302 1303 points = np.array(points, dtype=float) 1304 1305 minx, miny, minz = np.min(points, axis=0) 1306 maxx, maxy, maxz = np.max(points, axis=0) 1307 maxb = max(maxx - minx, maxy - miny, maxz - minz) 1308 smooth *= maxb / 2 # must be in absolute units 1309 1310 x = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, res) 1311 if easing: 1312 if easing == "InSine": 1313 x = 1.0 - np.cos((x * np.pi) / 2) 1314 elif easing == "OutSine": 1315 x = np.sin((x * np.pi) / 2) 1316 elif easing == "Sine": 1317 x = -(np.cos(np.pi * x) - 1) / 2 1318 elif easing == "InQuad": 1319 x = x * x 1320 elif easing == "OutQuad": 1321 x = 1.0 - (1 - x) * (1 - x) 1322 elif easing == "InCubic": 1323 x = x * x 1324 elif easing == "OutCubic": 1325 x = 1.0 - np.power(1 - x, 3) 1326 elif easing == "InQuart": 1327 x = x * x * x * x 1328 elif easing == "OutQuart": 1329 x = 1.0 - np.power(1 - x, 4) 1330 elif easing == "InCirc": 1331 x = 1.0 - np.sqrt(1 - np.power(x, 2)) 1332 elif easing == "OutCirc": 1333 x = np.sqrt(1.0 - np.power(x - 1, 2)) 1334 else: 1335 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown ease mode {easing}") 1336 1337 # find the knots 1338 tckp, _ = splprep(points.T, task=0, s=smooth, k=degree, per=per) 1339 # evaluate spLine, including interpolated points: 1340 xnew, ynew, znew = splev(x, tckp) 1341 1342 super().__init__(np.c_[xnew, ynew, znew], lw=2) 1343 self.name = "Spline"
Arguments:
- smooth : (float)
smoothing factor.
- 0 = interpolate points exactly [default].
- 1 = average point positions.
- degree : (int) degree of the spline (between 1 and 5).
- easing : (str)
control sensity of points along the spline.
Available options are
[InSine, OutSine, Sine, InQuad, OutQuad, InCubic, OutCubic, InQuart, OutQuart, InCirc, OutCirc].Can be used to create animations (move objects at varying speed). See e.g.: https://easings.net - res : (int) number of points on the spline
See also: CSpline and KSpline.
Examples:
1346class KSpline(Line): 1347 """ 1348 Return a [Kochanek spline](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kochanek%E2%80%93Bartels_spline) 1349 which runs exactly through all the input points. 1350 """ 1351 1352 def __init__(self, points, 1353 continuity=0.0, tension=0.0, bias=0.0, closed=False, res=None) -> None: 1354 """ 1355 Arguments: 1356 continuity : (float) 1357 changes the sharpness in change between tangents 1358 tension : (float) 1359 changes the length of the tangent vector 1360 bias : (float) 1361 changes the direction of the tangent vector 1362 closed : (bool) 1363 join last to first point to produce a closed curve 1364 res : (int) 1365 approximate resolution of the output line. 1366 Default is 20 times the number of input points. 1367 1368  1369 1370 Warning: 1371 This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points 1372 as requested by `res`. Some points may be concident and removed. 1373 1374 See also: `Spline` and `CSpline`. 1375 """ 1376 if isinstance(points, Points): 1377 points = points.coordinates 1378 1379 if not res: 1380 res = len(points) * 20 1381 1382 points = utils.make3d(points).astype(float) 1383 1384 vtkKochanekSpline = vtki.get_class("KochanekSpline") 1385 xspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1386 yspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1387 zspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1388 for s in [xspline, yspline, zspline]: 1389 if bias: 1390 s.SetDefaultBias(bias) 1391 if tension: 1392 s.SetDefaultTension(tension) 1393 if continuity: 1394 s.SetDefaultContinuity(continuity) 1395 s.SetClosed(closed) 1396 1397 lenp = len(points[0]) > 2 1398 1399 for i, p in enumerate(points): 1400 xspline.AddPoint(i, p[0]) 1401 yspline.AddPoint(i, p[1]) 1402 if lenp: 1403 zspline.AddPoint(i, p[2]) 1404 1405 ln = [] 1406 for pos in np.linspace(0, len(points), res): 1407 x = xspline.Evaluate(pos) 1408 y = yspline.Evaluate(pos) 1409 z = 0 1410 if lenp: 1411 z = zspline.Evaluate(pos) 1412 ln.append((x, y, z)) 1413 1414 super().__init__(ln, lw=2) 1415 self.clean() 1416 self.lighting("off") 1417 self.name = "KSpline" 1418 self.base = np.array(points[0], dtype=float) 1419 self.top = np.array(points[-1], dtype=float)
Return a Kochanek spline which runs exactly through all the input points.
1352 def __init__(self, points, 1353 continuity=0.0, tension=0.0, bias=0.0, closed=False, res=None) -> None: 1354 """ 1355 Arguments: 1356 continuity : (float) 1357 changes the sharpness in change between tangents 1358 tension : (float) 1359 changes the length of the tangent vector 1360 bias : (float) 1361 changes the direction of the tangent vector 1362 closed : (bool) 1363 join last to first point to produce a closed curve 1364 res : (int) 1365 approximate resolution of the output line. 1366 Default is 20 times the number of input points. 1367 1368  1369 1370 Warning: 1371 This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points 1372 as requested by `res`. Some points may be concident and removed. 1373 1374 See also: `Spline` and `CSpline`. 1375 """ 1376 if isinstance(points, Points): 1377 points = points.coordinates 1378 1379 if not res: 1380 res = len(points) * 20 1381 1382 points = utils.make3d(points).astype(float) 1383 1384 vtkKochanekSpline = vtki.get_class("KochanekSpline") 1385 xspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1386 yspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1387 zspline = vtkKochanekSpline() 1388 for s in [xspline, yspline, zspline]: 1389 if bias: 1390 s.SetDefaultBias(bias) 1391 if tension: 1392 s.SetDefaultTension(tension) 1393 if continuity: 1394 s.SetDefaultContinuity(continuity) 1395 s.SetClosed(closed) 1396 1397 lenp = len(points[0]) > 2 1398 1399 for i, p in enumerate(points): 1400 xspline.AddPoint(i, p[0]) 1401 yspline.AddPoint(i, p[1]) 1402 if lenp: 1403 zspline.AddPoint(i, p[2]) 1404 1405 ln = [] 1406 for pos in np.linspace(0, len(points), res): 1407 x = xspline.Evaluate(pos) 1408 y = yspline.Evaluate(pos) 1409 z = 0 1410 if lenp: 1411 z = zspline.Evaluate(pos) 1412 ln.append((x, y, z)) 1413 1414 super().__init__(ln, lw=2) 1415 self.clean() 1416 self.lighting("off") 1417 self.name = "KSpline" 1418 self.base = np.array(points[0], dtype=float) 1419 self.top = np.array(points[-1], dtype=float)
Arguments:
- continuity : (float) changes the sharpness in change between tangents
- tension : (float) changes the length of the tangent vector
- bias : (float) changes the direction of the tangent vector
- closed : (bool) join last to first point to produce a closed curve
- res : (int) approximate resolution of the output line. Default is 20 times the number of input points.

Warning:
This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points as requested by
res. Some points may be concident and removed.
1422class CSpline(Line): 1423 """ 1424 Return a Cardinal spline which runs exactly through all the input points. 1425 """ 1426 1427 def __init__(self, points, closed=False, res=None) -> None: 1428 """ 1429 Arguments: 1430 closed : (bool) 1431 join last to first point to produce a closed curve 1432 res : (int) 1433 approximate resolution of the output line. 1434 Default is 20 times the number of input points. 1435 1436 Warning: 1437 This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points 1438 as requested by `res`. Some points may be concident and removed. 1439 1440 See also: `Spline` and `KSpline`. 1441 """ 1442 1443 if isinstance(points, Points): 1444 points = points.coordinates 1445 1446 if not res: 1447 res = len(points) * 20 1448 1449 points = utils.make3d(points).astype(float) 1450 1451 vtkCardinalSpline = vtki.get_class("CardinalSpline") 1452 xspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1453 yspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1454 zspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1455 for s in [xspline, yspline, zspline]: 1456 s.SetClosed(closed) 1457 1458 lenp = len(points[0]) > 2 1459 1460 for i, p in enumerate(points): 1461 xspline.AddPoint(i, p[0]) 1462 yspline.AddPoint(i, p[1]) 1463 if lenp: 1464 zspline.AddPoint(i, p[2]) 1465 1466 ln = [] 1467 for pos in np.linspace(0, len(points), res): 1468 x = xspline.Evaluate(pos) 1469 y = yspline.Evaluate(pos) 1470 z = 0 1471 if lenp: 1472 z = zspline.Evaluate(pos) 1473 ln.append((x, y, z)) 1474 1475 super().__init__(ln, lw=2) 1476 self.clean() 1477 self.lighting("off") 1478 self.name = "CSpline" 1479 self.base = points[0] 1480 self.top = points[-1]
Return a Cardinal spline which runs exactly through all the input points.
1427 def __init__(self, points, closed=False, res=None) -> None: 1428 """ 1429 Arguments: 1430 closed : (bool) 1431 join last to first point to produce a closed curve 1432 res : (int) 1433 approximate resolution of the output line. 1434 Default is 20 times the number of input points. 1435 1436 Warning: 1437 This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points 1438 as requested by `res`. Some points may be concident and removed. 1439 1440 See also: `Spline` and `KSpline`. 1441 """ 1442 1443 if isinstance(points, Points): 1444 points = points.coordinates 1445 1446 if not res: 1447 res = len(points) * 20 1448 1449 points = utils.make3d(points).astype(float) 1450 1451 vtkCardinalSpline = vtki.get_class("CardinalSpline") 1452 xspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1453 yspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1454 zspline = vtkCardinalSpline() 1455 for s in [xspline, yspline, zspline]: 1456 s.SetClosed(closed) 1457 1458 lenp = len(points[0]) > 2 1459 1460 for i, p in enumerate(points): 1461 xspline.AddPoint(i, p[0]) 1462 yspline.AddPoint(i, p[1]) 1463 if lenp: 1464 zspline.AddPoint(i, p[2]) 1465 1466 ln = [] 1467 for pos in np.linspace(0, len(points), res): 1468 x = xspline.Evaluate(pos) 1469 y = yspline.Evaluate(pos) 1470 z = 0 1471 if lenp: 1472 z = zspline.Evaluate(pos) 1473 ln.append((x, y, z)) 1474 1475 super().__init__(ln, lw=2) 1476 self.clean() 1477 self.lighting("off") 1478 self.name = "CSpline" 1479 self.base = points[0] 1480 self.top = points[-1]
Arguments:
- closed : (bool) join last to first point to produce a closed curve
- res : (int) approximate resolution of the output line. Default is 20 times the number of input points.
Warning:
This class is not necessarily generating the exact number of points as requested by
res. Some points may be concident and removed.
1483class Bezier(Line): 1484 """ 1485 Generate the Bezier line that links the first to the last point. 1486 """ 1487 1488 def __init__(self, points, res=None) -> None: 1489 """ 1490 Example: 1491 ```python 1492 from vedo import * 1493 import numpy as np 1494 pts = np.random.randn(25,3) 1495 for i,p in enumerate(pts): 1496 p += [5*i, 15*sin(i/2), i*i*i/200] 1497 show(Points(pts), Bezier(pts), axes=1).close() 1498 ``` 1499  1500 """ 1501 N = len(points) 1502 if res is None: 1503 res = 10 * N 1504 t = np.linspace(0, 1, num=res) 1505 bcurve = np.zeros((res, len(points[0]))) 1506 1507 def binom(n, k): 1508 b = 1 1509 for t in range(1, min(k, n - k) + 1): 1510 b *= n / t 1511 n -= 1 1512 return b 1513 1514 def bernstein(n, k): 1515 coeff = binom(n, k) 1516 1517 def _bpoly(x): 1518 return coeff * x ** k * (1 - x) ** (n - k) 1519 1520 return _bpoly 1521 1522 for ii in range(N): 1523 b = bernstein(N - 1, ii)(t) 1524 bcurve += np.outer(b, points[ii]) 1525 super().__init__(bcurve, lw=2) 1526 self.name = "BezierLine"
Generate the Bezier line that links the first to the last point.
1488 def __init__(self, points, res=None) -> None: 1489 """ 1490 Example: 1491 ```python 1492 from vedo import * 1493 import numpy as np 1494 pts = np.random.randn(25,3) 1495 for i,p in enumerate(pts): 1496 p += [5*i, 15*sin(i/2), i*i*i/200] 1497 show(Points(pts), Bezier(pts), axes=1).close() 1498 ``` 1499  1500 """ 1501 N = len(points) 1502 if res is None: 1503 res = 10 * N 1504 t = np.linspace(0, 1, num=res) 1505 bcurve = np.zeros((res, len(points[0]))) 1506 1507 def binom(n, k): 1508 b = 1 1509 for t in range(1, min(k, n - k) + 1): 1510 b *= n / t 1511 n -= 1 1512 return b 1513 1514 def bernstein(n, k): 1515 coeff = binom(n, k) 1516 1517 def _bpoly(x): 1518 return coeff * x ** k * (1 - x) ** (n - k) 1519 1520 return _bpoly 1521 1522 for ii in range(N): 1523 b = bernstein(N - 1, ii)(t) 1524 bcurve += np.outer(b, points[ii]) 1525 super().__init__(bcurve, lw=2) 1526 self.name = "BezierLine"
Example:
from vedo import * import numpy as np pts = np.random.randn(25,3) for i,p in enumerate(pts): p += [5*i, 15*sin(i/2), i*i*i/200] show(Points(pts), Bezier(pts), axes=1).close()
3775class Brace(Mesh): 3776 """ 3777 Create a brace (bracket) shape. 3778 """ 3779 3780 def __init__( 3781 self, 3782 q1, 3783 q2, 3784 style="}", 3785 padding1=0.0, 3786 font="Theemim", 3787 comment="", 3788 justify=None, 3789 angle=0.0, 3790 padding2=0.2, 3791 s=1.0, 3792 italic=0, 3793 c="k1", 3794 alpha=1.0, 3795 ) -> None: 3796 """ 3797 Create a brace (bracket) shape which spans from point q1 to point q2. 3798 3799 Arguments: 3800 q1 : (list) 3801 point 1. 3802 q2 : (list) 3803 point 2. 3804 style : (str) 3805 style of the bracket, eg. `{}, [], (), <>`. 3806 padding1 : (float) 3807 padding space in percent form the input points. 3808 font : (str) 3809 font type 3810 comment : (str) 3811 additional text to appear next to the brace symbol. 3812 justify : (str) 3813 specify the anchor point to justify text comment, e.g. "top-left". 3814 italic : float 3815 italicness of the text comment (can be a positive or negative number) 3816 angle : (float) 3817 rotation angle of text. Use `None` to keep it horizontal. 3818 padding2 : (float) 3819 padding space in percent form brace to text comment. 3820 s : (float) 3821 scale factor for the comment 3822 3823 Examples: 3824 - [scatter3.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/scatter3.py) 3825 3826  3827 """ 3828 if isinstance(q1, vtki.vtkActor): 3829 q1 = q1.GetPosition() 3830 if isinstance(q2, vtki.vtkActor): 3831 q2 = q2.GetPosition() 3832 if len(q1) == 2: 3833 q1 = [q1[0], q1[1], 0.0] 3834 if len(q2) == 2: 3835 q2 = [q2[0], q2[1], 0.0] 3836 q1 = np.array(q1, dtype=float) 3837 q2 = np.array(q2, dtype=float) 3838 mq = (q1 + q2) / 2 3839 q1 = q1 - mq 3840 q2 = q2 - mq 3841 d = np.linalg.norm(q2 - q1) 3842 q2[2] = q1[2] 3843 3844 if style not in "{}[]()<>|I": 3845 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown style {style}." + "Use {}[]()<>|I") 3846 style = "}" 3847 3848 flip = False 3849 if style in ["{", "[", "(", "<"]: 3850 flip = True 3851 i = ["{", "[", "(", "<"].index(style) 3852 style = ["}", "]", ")", ">"][i] 3853 3854 br = Text3D(style, font="Theemim", justify="center-left") 3855 br.scale([0.4, 1, 1]) 3856 3857 angler = np.arctan2(q2[1], q2[0]) * 180 / np.pi - 90 3858 if flip: 3859 angler += 180 3860 3861 _, x1, y0, y1, _, _ = br.bounds() 3862 if comment: 3863 just = "center-top" 3864 if angle is None: 3865 angle = -angler + 90 3866 if not flip: 3867 angle += 180 3868 3869 if flip: 3870 angle += 180 3871 just = "center-bottom" 3872 if justify is not None: 3873 just = justify 3874 cmt = Text3D(comment, font=font, justify=just, italic=italic) 3875 cx0, cx1 = cmt.xbounds() 3876 cmt.rotate_z(90 + angle) 3877 cmt.scale(1 / (cx1 - cx0) * s * len(comment) / 5) 3878 cmt.shift(x1 * (1 + padding2), 0, 0) 3879 poly = merge(br, cmt).dataset 3880 3881 else: 3882 poly = br.dataset 3883 3884 tr = vtki.vtkTransform() 3885 tr.Translate(mq) 3886 tr.RotateZ(angler) 3887 tr.Translate(padding1 * d, 0, 0) 3888 pscale = 1 3889 tr.Scale(pscale / (y1 - y0) * d, pscale / (y1 - y0) * d, 1) 3890 3891 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3892 tf.SetInputData(poly) 3893 tf.SetTransform(tr) 3894 tf.Update() 3895 poly = tf.GetOutput() 3896 3897 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 3898 3899 self.base = q1 3900 self.top = q2 3901 self.name = "Brace"
Create a brace (bracket) shape.
3780 def __init__( 3781 self, 3782 q1, 3783 q2, 3784 style="}", 3785 padding1=0.0, 3786 font="Theemim", 3787 comment="", 3788 justify=None, 3789 angle=0.0, 3790 padding2=0.2, 3791 s=1.0, 3792 italic=0, 3793 c="k1", 3794 alpha=1.0, 3795 ) -> None: 3796 """ 3797 Create a brace (bracket) shape which spans from point q1 to point q2. 3798 3799 Arguments: 3800 q1 : (list) 3801 point 1. 3802 q2 : (list) 3803 point 2. 3804 style : (str) 3805 style of the bracket, eg. `{}, [], (), <>`. 3806 padding1 : (float) 3807 padding space in percent form the input points. 3808 font : (str) 3809 font type 3810 comment : (str) 3811 additional text to appear next to the brace symbol. 3812 justify : (str) 3813 specify the anchor point to justify text comment, e.g. "top-left". 3814 italic : float 3815 italicness of the text comment (can be a positive or negative number) 3816 angle : (float) 3817 rotation angle of text. Use `None` to keep it horizontal. 3818 padding2 : (float) 3819 padding space in percent form brace to text comment. 3820 s : (float) 3821 scale factor for the comment 3822 3823 Examples: 3824 - [scatter3.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/scatter3.py) 3825 3826  3827 """ 3828 if isinstance(q1, vtki.vtkActor): 3829 q1 = q1.GetPosition() 3830 if isinstance(q2, vtki.vtkActor): 3831 q2 = q2.GetPosition() 3832 if len(q1) == 2: 3833 q1 = [q1[0], q1[1], 0.0] 3834 if len(q2) == 2: 3835 q2 = [q2[0], q2[1], 0.0] 3836 q1 = np.array(q1, dtype=float) 3837 q2 = np.array(q2, dtype=float) 3838 mq = (q1 + q2) / 2 3839 q1 = q1 - mq 3840 q2 = q2 - mq 3841 d = np.linalg.norm(q2 - q1) 3842 q2[2] = q1[2] 3843 3844 if style not in "{}[]()<>|I": 3845 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown style {style}." + "Use {}[]()<>|I") 3846 style = "}" 3847 3848 flip = False 3849 if style in ["{", "[", "(", "<"]: 3850 flip = True 3851 i = ["{", "[", "(", "<"].index(style) 3852 style = ["}", "]", ")", ">"][i] 3853 3854 br = Text3D(style, font="Theemim", justify="center-left") 3855 br.scale([0.4, 1, 1]) 3856 3857 angler = np.arctan2(q2[1], q2[0]) * 180 / np.pi - 90 3858 if flip: 3859 angler += 180 3860 3861 _, x1, y0, y1, _, _ = br.bounds() 3862 if comment: 3863 just = "center-top" 3864 if angle is None: 3865 angle = -angler + 90 3866 if not flip: 3867 angle += 180 3868 3869 if flip: 3870 angle += 180 3871 just = "center-bottom" 3872 if justify is not None: 3873 just = justify 3874 cmt = Text3D(comment, font=font, justify=just, italic=italic) 3875 cx0, cx1 = cmt.xbounds() 3876 cmt.rotate_z(90 + angle) 3877 cmt.scale(1 / (cx1 - cx0) * s * len(comment) / 5) 3878 cmt.shift(x1 * (1 + padding2), 0, 0) 3879 poly = merge(br, cmt).dataset 3880 3881 else: 3882 poly = br.dataset 3883 3884 tr = vtki.vtkTransform() 3885 tr.Translate(mq) 3886 tr.RotateZ(angler) 3887 tr.Translate(padding1 * d, 0, 0) 3888 pscale = 1 3889 tr.Scale(pscale / (y1 - y0) * d, pscale / (y1 - y0) * d, 1) 3890 3891 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3892 tf.SetInputData(poly) 3893 tf.SetTransform(tr) 3894 tf.Update() 3895 poly = tf.GetOutput() 3896 3897 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 3898 3899 self.base = q1 3900 self.top = q2 3901 self.name = "Brace"
Create a brace (bracket) shape which spans from point q1 to point q2.
Arguments:
- q1 : (list) point 1.
- q2 : (list) point 2.
- style : (str)
style of the bracket, eg.
{}, [], (), <>. - padding1 : (float) padding space in percent form the input points.
- font : (str) font type
- comment : (str) additional text to appear next to the brace symbol.
- justify : (str) specify the anchor point to justify text comment, e.g. "top-left".
- italic : float italicness of the text comment (can be a positive or negative number)
- angle : (float)
rotation angle of text. Use
Noneto keep it horizontal. - padding2 : (float) padding space in percent form brace to text comment.
- s : (float) scale factor for the comment
Examples:
1529class NormalLines(Mesh): 1530 """ 1531 Build an `Glyph` to show the normals at cell centers or at mesh vertices. 1532 1533 Arguments: 1534 ratio : (int) 1535 show 1 normal every `ratio` cells. 1536 on : (str) 1537 either "cells" or "points". 1538 scale : (float) 1539 scale factor to control size. 1540 """ 1541 1542 def __init__(self, msh, ratio=1, on="cells", scale=1.0) -> None: 1543 1544 poly = msh.clone().dataset 1545 1546 if "cell" in on: 1547 centers = vtki.new("CellCenters") 1548 centers.SetInputData(poly) 1549 centers.Update() 1550 poly = centers.GetOutput() 1551 1552 mask_pts = vtki.new("MaskPoints") 1553 mask_pts.SetInputData(poly) 1554 mask_pts.SetOnRatio(ratio) 1555 mask_pts.RandomModeOff() 1556 mask_pts.Update() 1557 1558 ln = vtki.new("LineSource") 1559 ln.SetPoint1(0, 0, 0) 1560 ln.SetPoint2(1, 0, 0) 1561 ln.Update() 1562 glyph = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 1563 glyph.SetSourceData(ln.GetOutput()) 1564 glyph.SetInputData(mask_pts.GetOutput()) 1565 glyph.SetVectorModeToUseNormal() 1566 1567 b = poly.GetBounds() 1568 f = max([b[1] - b[0], b[3] - b[2], b[5] - b[4]]) / 50 * scale 1569 glyph.SetScaleFactor(f) 1570 glyph.OrientOn() 1571 glyph.Update() 1572 1573 super().__init__(glyph.GetOutput()) 1574 1575 self.actor.PickableOff() 1576 prop = vtki.vtkProperty() 1577 prop.DeepCopy(msh.properties) 1578 self.actor.SetProperty(prop) 1579 self.properties = prop 1580 self.properties.LightingOff() 1581 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 1582 self.name = "NormalLines"
Build an Glyph to show the normals at cell centers or at mesh vertices.
Arguments:
- ratio : (int)
show 1 normal every
ratiocells. - on : (str) either "cells" or "points".
- scale : (float) scale factor to control size.
1542 def __init__(self, msh, ratio=1, on="cells", scale=1.0) -> None: 1543 1544 poly = msh.clone().dataset 1545 1546 if "cell" in on: 1547 centers = vtki.new("CellCenters") 1548 centers.SetInputData(poly) 1549 centers.Update() 1550 poly = centers.GetOutput() 1551 1552 mask_pts = vtki.new("MaskPoints") 1553 mask_pts.SetInputData(poly) 1554 mask_pts.SetOnRatio(ratio) 1555 mask_pts.RandomModeOff() 1556 mask_pts.Update() 1557 1558 ln = vtki.new("LineSource") 1559 ln.SetPoint1(0, 0, 0) 1560 ln.SetPoint2(1, 0, 0) 1561 ln.Update() 1562 glyph = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 1563 glyph.SetSourceData(ln.GetOutput()) 1564 glyph.SetInputData(mask_pts.GetOutput()) 1565 glyph.SetVectorModeToUseNormal() 1566 1567 b = poly.GetBounds() 1568 f = max([b[1] - b[0], b[3] - b[2], b[5] - b[4]]) / 50 * scale 1569 glyph.SetScaleFactor(f) 1570 glyph.OrientOn() 1571 glyph.Update() 1572 1573 super().__init__(glyph.GetOutput()) 1574 1575 self.actor.PickableOff() 1576 prop = vtki.vtkProperty() 1577 prop.DeepCopy(msh.properties) 1578 self.actor.SetProperty(prop) 1579 self.properties = prop 1580 self.properties.LightingOff() 1581 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 1582 self.name = "NormalLines"
Initialize a Mesh object.
Arguments:
- inputobj : (str, vtkPolyData, vtkActor, vedo.Mesh)
If inputobj is
Nonean empty mesh is created. If inputobj is astrthen it is interpreted as the name of a file to load as mesh. If inputobj is anvtkPolyDataorvtkActororvedo.Meshthen a shallow copy of it is created. If inputobj is avedo.Meshthen a shallow copy of it is created.
Examples:
- buildmesh.py (and many others!)
1807class Ribbon(Mesh): 1808 """ 1809 Connect two lines to generate the surface inbetween. 1810 Set the mode by which to create the ruled surface. 1811 1812 It also works with a single line in input. In this case the ribbon 1813 is formed by following the local plane of the line in space. 1814 """ 1815 1816 def __init__( 1817 self, 1818 line1, 1819 line2=None, 1820 mode=0, 1821 closed=False, 1822 width=None, 1823 res=(200, 5), 1824 c="indigo3", 1825 alpha=1.0, 1826 ) -> None: 1827 """ 1828 Arguments: 1829 mode : (int) 1830 If mode=0, resample evenly the input lines (based on length) 1831 and generates triangle strips. 1832 1833 If mode=1, use the existing points and walks around the 1834 polyline using existing points. 1835 1836 closed : (bool) 1837 if True, join the last point with the first to form a closed surface 1838 1839 res : (list) 1840 ribbon resolutions along the line and perpendicularly to it. 1841 1842 Examples: 1843 - [ribbon.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/ribbon.py) 1844 1845  1846 """ 1847 1848 if isinstance(line1, Points): 1849 line1 = line1.coordinates 1850 1851 if isinstance(line2, Points): 1852 line2 = line2.coordinates 1853 1854 elif line2 is None: 1855 ############################################# 1856 ribbon_filter = vtki.new("RibbonFilter") 1857 aline = Line(line1) 1858 ribbon_filter.SetInputData(aline.dataset) 1859 if width is None: 1860 width = aline.diagonal_size() / 20.0 1861 ribbon_filter.SetWidth(width) 1862 ribbon_filter.Update() 1863 # convert triangle strips to polygons 1864 tris = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 1865 tris.SetInputData(ribbon_filter.GetOutput()) 1866 tris.Update() 1867 1868 super().__init__(tris.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1869 self.name = "Ribbon" 1870 ############################################## 1871 return ###################################### 1872 ############################################## 1873 1874 line1 = np.asarray(line1) 1875 line2 = np.asarray(line2) 1876 1877 if closed: 1878 line1 = line1.tolist() 1879 line1 += [line1[0]] 1880 line2 = line2.tolist() 1881 line2 += [line2[0]] 1882 line1 = np.array(line1) 1883 line2 = np.array(line2) 1884 1885 if len(line1[0]) == 2: 1886 line1 = np.c_[line1, np.zeros(len(line1))] 1887 if len(line2[0]) == 2: 1888 line2 = np.c_[line2, np.zeros(len(line2))] 1889 1890 ppoints1 = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline1 1891 ppoints1.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(line1, dtype=np.float32)) 1892 lines1 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1893 lines1.InsertNextCell(len(line1)) 1894 for i in range(len(line1)): 1895 lines1.InsertCellPoint(i) 1896 poly1 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1897 poly1.SetPoints(ppoints1) 1898 poly1.SetLines(lines1) 1899 1900 ppoints2 = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline2 1901 ppoints2.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(line2, dtype=np.float32)) 1902 lines2 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1903 lines2.InsertNextCell(len(line2)) 1904 for i in range(len(line2)): 1905 lines2.InsertCellPoint(i) 1906 poly2 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1907 poly2.SetPoints(ppoints2) 1908 poly2.SetLines(lines2) 1909 1910 # build the lines 1911 lines1 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1912 lines1.InsertNextCell(poly1.GetNumberOfPoints()) 1913 for i in range(poly1.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1914 lines1.InsertCellPoint(i) 1915 1916 polygon1 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1917 polygon1.SetPoints(ppoints1) 1918 polygon1.SetLines(lines1) 1919 1920 lines2 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1921 lines2.InsertNextCell(poly2.GetNumberOfPoints()) 1922 for i in range(poly2.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1923 lines2.InsertCellPoint(i) 1924 1925 polygon2 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1926 polygon2.SetPoints(ppoints2) 1927 polygon2.SetLines(lines2) 1928 1929 merged_pd = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1930 merged_pd.AddInputData(polygon1) 1931 merged_pd.AddInputData(polygon2) 1932 merged_pd.Update() 1933 1934 rsf = vtki.new("RuledSurfaceFilter") 1935 rsf.CloseSurfaceOff() 1936 rsf.SetRuledMode(mode) 1937 rsf.SetResolution(res[0], res[1]) 1938 rsf.SetInputData(merged_pd.GetOutput()) 1939 rsf.Update() 1940 # convert triangle strips to polygons 1941 tris = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 1942 tris.SetInputData(rsf.GetOutput()) 1943 tris.Update() 1944 out = tris.GetOutput() 1945 1946 super().__init__(out, c, alpha) 1947 1948 self.name = "Ribbon"
Connect two lines to generate the surface inbetween. Set the mode by which to create the ruled surface.
It also works with a single line in input. In this case the ribbon is formed by following the local plane of the line in space.
1816 def __init__( 1817 self, 1818 line1, 1819 line2=None, 1820 mode=0, 1821 closed=False, 1822 width=None, 1823 res=(200, 5), 1824 c="indigo3", 1825 alpha=1.0, 1826 ) -> None: 1827 """ 1828 Arguments: 1829 mode : (int) 1830 If mode=0, resample evenly the input lines (based on length) 1831 and generates triangle strips. 1832 1833 If mode=1, use the existing points and walks around the 1834 polyline using existing points. 1835 1836 closed : (bool) 1837 if True, join the last point with the first to form a closed surface 1838 1839 res : (list) 1840 ribbon resolutions along the line and perpendicularly to it. 1841 1842 Examples: 1843 - [ribbon.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/ribbon.py) 1844 1845  1846 """ 1847 1848 if isinstance(line1, Points): 1849 line1 = line1.coordinates 1850 1851 if isinstance(line2, Points): 1852 line2 = line2.coordinates 1853 1854 elif line2 is None: 1855 ############################################# 1856 ribbon_filter = vtki.new("RibbonFilter") 1857 aline = Line(line1) 1858 ribbon_filter.SetInputData(aline.dataset) 1859 if width is None: 1860 width = aline.diagonal_size() / 20.0 1861 ribbon_filter.SetWidth(width) 1862 ribbon_filter.Update() 1863 # convert triangle strips to polygons 1864 tris = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 1865 tris.SetInputData(ribbon_filter.GetOutput()) 1866 tris.Update() 1867 1868 super().__init__(tris.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1869 self.name = "Ribbon" 1870 ############################################## 1871 return ###################################### 1872 ############################################## 1873 1874 line1 = np.asarray(line1) 1875 line2 = np.asarray(line2) 1876 1877 if closed: 1878 line1 = line1.tolist() 1879 line1 += [line1[0]] 1880 line2 = line2.tolist() 1881 line2 += [line2[0]] 1882 line1 = np.array(line1) 1883 line2 = np.array(line2) 1884 1885 if len(line1[0]) == 2: 1886 line1 = np.c_[line1, np.zeros(len(line1))] 1887 if len(line2[0]) == 2: 1888 line2 = np.c_[line2, np.zeros(len(line2))] 1889 1890 ppoints1 = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline1 1891 ppoints1.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(line1, dtype=np.float32)) 1892 lines1 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1893 lines1.InsertNextCell(len(line1)) 1894 for i in range(len(line1)): 1895 lines1.InsertCellPoint(i) 1896 poly1 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1897 poly1.SetPoints(ppoints1) 1898 poly1.SetLines(lines1) 1899 1900 ppoints2 = vtki.vtkPoints() # Generate the polyline2 1901 ppoints2.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(line2, dtype=np.float32)) 1902 lines2 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1903 lines2.InsertNextCell(len(line2)) 1904 for i in range(len(line2)): 1905 lines2.InsertCellPoint(i) 1906 poly2 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1907 poly2.SetPoints(ppoints2) 1908 poly2.SetLines(lines2) 1909 1910 # build the lines 1911 lines1 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1912 lines1.InsertNextCell(poly1.GetNumberOfPoints()) 1913 for i in range(poly1.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1914 lines1.InsertCellPoint(i) 1915 1916 polygon1 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1917 polygon1.SetPoints(ppoints1) 1918 polygon1.SetLines(lines1) 1919 1920 lines2 = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1921 lines2.InsertNextCell(poly2.GetNumberOfPoints()) 1922 for i in range(poly2.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1923 lines2.InsertCellPoint(i) 1924 1925 polygon2 = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1926 polygon2.SetPoints(ppoints2) 1927 polygon2.SetLines(lines2) 1928 1929 merged_pd = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1930 merged_pd.AddInputData(polygon1) 1931 merged_pd.AddInputData(polygon2) 1932 merged_pd.Update() 1933 1934 rsf = vtki.new("RuledSurfaceFilter") 1935 rsf.CloseSurfaceOff() 1936 rsf.SetRuledMode(mode) 1937 rsf.SetResolution(res[0], res[1]) 1938 rsf.SetInputData(merged_pd.GetOutput()) 1939 rsf.Update() 1940 # convert triangle strips to polygons 1941 tris = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 1942 tris.SetInputData(rsf.GetOutput()) 1943 tris.Update() 1944 out = tris.GetOutput() 1945 1946 super().__init__(out, c, alpha) 1947 1948 self.name = "Ribbon"
Arguments:
mode : (int) If mode=0, resample evenly the input lines (based on length) and generates triangle strips.
If mode=1, use the existing points and walks around the polyline using existing points.
- closed : (bool) if True, join the last point with the first to form a closed surface
- res : (list) ribbon resolutions along the line and perpendicularly to it.
Examples:
1951class Arrow(Mesh): 1952 """ 1953 Build a 3D arrow from `start_pt` to `end_pt` of section size `s`, 1954 expressed as the fraction of the window size. 1955 """ 1956 1957 def __init__( 1958 self, 1959 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 1960 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 1961 s=None, 1962 shaft_radius=None, 1963 head_radius=None, 1964 head_length=None, 1965 res=12, 1966 c="r4", 1967 alpha=1.0, 1968 ) -> None: 1969 """ 1970 If `c` is a `float` less than 1, the arrow is rendered as a in a color scale 1971 from white to red. 1972 1973 .. note:: If `s=None` the arrow is scaled proportionally to its length 1974 1975  1976 """ 1977 # in case user is passing meshs 1978 if isinstance(start_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 1979 start_pt = start_pt.GetPosition() 1980 if isinstance(end_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 1981 end_pt = end_pt.GetPosition() 1982 1983 axis = np.asarray(end_pt) - np.asarray(start_pt) 1984 length = float(np.linalg.norm(axis)) 1985 if length: 1986 axis = axis / length 1987 if len(axis) < 3: # its 2d 1988 theta = np.pi / 2 1989 start_pt = [start_pt[0], start_pt[1], 0.0] 1990 end_pt = [end_pt[0], end_pt[1], 0.0] 1991 else: 1992 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 1993 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 1994 self.source = vtki.new("ArrowSource") 1995 self.source.SetShaftResolution(res) 1996 self.source.SetTipResolution(res) 1997 1998 if s: 1999 sz = 0.02 2000 self.source.SetTipRadius(sz) 2001 self.source.SetShaftRadius(sz / 1.75) 2002 self.source.SetTipLength(sz * 15) 2003 2004 if head_length: 2005 self.source.SetTipLength(head_length) 2006 if head_radius: 2007 self.source.SetTipRadius(head_radius) 2008 if shaft_radius: 2009 self.source.SetShaftRadius(shaft_radius) 2010 2011 self.source.Update() 2012 2013 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 2014 t.Translate(start_pt) 2015 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 2016 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 2017 t.RotateY(-90) # put it along Z 2018 if s: 2019 sz = 800 * s 2020 t.Scale(length, sz, sz) 2021 else: 2022 t.Scale(length, length, length) 2023 2024 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 2025 tf.SetInputData(self.source.GetOutput()) 2026 tf.SetTransform(t) 2027 tf.Update() 2028 2029 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2030 2031 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(start_pt) 2032 2033 self.phong().lighting("plastic") 2034 self.actor.PickableOff() 2035 self.actor.DragableOff() 2036 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2037 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2038 self.top_index = self.source.GetTipResolution() * 4 2039 self.fill = True # used by pyplot.__iadd__() 2040 self.s = s if s is not None else 1 # used by pyplot.__iadd__() 2041 self.name = "Arrow" 2042 2043 def top_point(self): 2044 """Return the current coordinates of the tip of the Arrow.""" 2045 return self.transform.transform_point(self.top) 2046 2047 def base_point(self): 2048 """Return the current coordinates of the base of the Arrow.""" 2049 return self.transform.transform_point(self.base)
Build a 3D arrow from start_pt to end_pt of section size s,
expressed as the fraction of the window size.
1957 def __init__( 1958 self, 1959 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 1960 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 1961 s=None, 1962 shaft_radius=None, 1963 head_radius=None, 1964 head_length=None, 1965 res=12, 1966 c="r4", 1967 alpha=1.0, 1968 ) -> None: 1969 """ 1970 If `c` is a `float` less than 1, the arrow is rendered as a in a color scale 1971 from white to red. 1972 1973 .. note:: If `s=None` the arrow is scaled proportionally to its length 1974 1975  1976 """ 1977 # in case user is passing meshs 1978 if isinstance(start_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 1979 start_pt = start_pt.GetPosition() 1980 if isinstance(end_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 1981 end_pt = end_pt.GetPosition() 1982 1983 axis = np.asarray(end_pt) - np.asarray(start_pt) 1984 length = float(np.linalg.norm(axis)) 1985 if length: 1986 axis = axis / length 1987 if len(axis) < 3: # its 2d 1988 theta = np.pi / 2 1989 start_pt = [start_pt[0], start_pt[1], 0.0] 1990 end_pt = [end_pt[0], end_pt[1], 0.0] 1991 else: 1992 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 1993 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 1994 self.source = vtki.new("ArrowSource") 1995 self.source.SetShaftResolution(res) 1996 self.source.SetTipResolution(res) 1997 1998 if s: 1999 sz = 0.02 2000 self.source.SetTipRadius(sz) 2001 self.source.SetShaftRadius(sz / 1.75) 2002 self.source.SetTipLength(sz * 15) 2003 2004 if head_length: 2005 self.source.SetTipLength(head_length) 2006 if head_radius: 2007 self.source.SetTipRadius(head_radius) 2008 if shaft_radius: 2009 self.source.SetShaftRadius(shaft_radius) 2010 2011 self.source.Update() 2012 2013 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 2014 t.Translate(start_pt) 2015 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 2016 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 2017 t.RotateY(-90) # put it along Z 2018 if s: 2019 sz = 800 * s 2020 t.Scale(length, sz, sz) 2021 else: 2022 t.Scale(length, length, length) 2023 2024 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 2025 tf.SetInputData(self.source.GetOutput()) 2026 tf.SetTransform(t) 2027 tf.Update() 2028 2029 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2030 2031 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(start_pt) 2032 2033 self.phong().lighting("plastic") 2034 self.actor.PickableOff() 2035 self.actor.DragableOff() 2036 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2037 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2038 self.top_index = self.source.GetTipResolution() * 4 2039 self.fill = True # used by pyplot.__iadd__() 2040 self.s = s if s is not None else 1 # used by pyplot.__iadd__() 2041 self.name = "Arrow"
If c is a float less than 1, the arrow is rendered as a in a color scale
from white to red.
If s=None the arrow is scaled proportionally to its length

2051class Arrows(Glyph): 2052 """ 2053 Build arrows between two lists of points. 2054 """ 2055 2056 def __init__( 2057 self, 2058 start_pts, 2059 end_pts=None, 2060 s=None, 2061 shaft_radius=None, 2062 head_radius=None, 2063 head_length=None, 2064 thickness=1.0, 2065 res=6, 2066 c='k3', 2067 alpha=1.0, 2068 ) -> None: 2069 """ 2070 Build arrows between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 2071 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 2072 2073 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows. 2074 2075 Arguments: 2076 s : (float) 2077 fix aspect-ratio of the arrow and scale its cross section 2078 c : (color) 2079 color or color map name 2080 alpha : (float) 2081 set object opacity 2082 res : (int) 2083 set arrow resolution 2084 2085 Examples: 2086 - [glyphs2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs2.py) 2087 2088  2089 """ 2090 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 2091 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 2092 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 2093 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 2094 2095 start_pts = np.asarray(start_pts) 2096 if end_pts is None: 2097 strt = start_pts[:, 0] 2098 end_pts = start_pts[:, 1] 2099 start_pts = strt 2100 else: 2101 end_pts = np.asarray(end_pts) 2102 2103 start_pts = utils.make3d(start_pts) 2104 end_pts = utils.make3d(end_pts) 2105 2106 arr = vtki.new("ArrowSource") 2107 arr.SetShaftResolution(res) 2108 arr.SetTipResolution(res) 2109 2110 if s: 2111 sz = 0.02 * s 2112 arr.SetTipRadius(sz * 2) 2113 arr.SetShaftRadius(sz * thickness) 2114 arr.SetTipLength(sz * 10) 2115 2116 if head_radius: 2117 arr.SetTipRadius(head_radius) 2118 if shaft_radius: 2119 arr.SetShaftRadius(shaft_radius) 2120 if head_length: 2121 arr.SetTipLength(head_length) 2122 2123 arr.Update() 2124 out = arr.GetOutput() 2125 2126 orients = end_pts - start_pts 2127 2128 color_by_vector_size = utils.is_sequence(c) or c in cmaps_names 2129 2130 super().__init__( 2131 start_pts, 2132 out, 2133 orientation_array=orients, 2134 scale_by_vector_size=True, 2135 color_by_vector_size=color_by_vector_size, 2136 c=c, 2137 alpha=alpha, 2138 ) 2139 self.lighting("off") 2140 if color_by_vector_size: 2141 vals = np.linalg.norm(orients, axis=1) 2142 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(vals.min(), vals.max()) 2143 else: 2144 self.c(c) 2145 self.name = "Arrows"
Build arrows between two lists of points.
2056 def __init__( 2057 self, 2058 start_pts, 2059 end_pts=None, 2060 s=None, 2061 shaft_radius=None, 2062 head_radius=None, 2063 head_length=None, 2064 thickness=1.0, 2065 res=6, 2066 c='k3', 2067 alpha=1.0, 2068 ) -> None: 2069 """ 2070 Build arrows between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 2071 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 2072 2073 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows. 2074 2075 Arguments: 2076 s : (float) 2077 fix aspect-ratio of the arrow and scale its cross section 2078 c : (color) 2079 color or color map name 2080 alpha : (float) 2081 set object opacity 2082 res : (int) 2083 set arrow resolution 2084 2085 Examples: 2086 - [glyphs2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs2.py) 2087 2088  2089 """ 2090 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 2091 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 2092 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 2093 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 2094 2095 start_pts = np.asarray(start_pts) 2096 if end_pts is None: 2097 strt = start_pts[:, 0] 2098 end_pts = start_pts[:, 1] 2099 start_pts = strt 2100 else: 2101 end_pts = np.asarray(end_pts) 2102 2103 start_pts = utils.make3d(start_pts) 2104 end_pts = utils.make3d(end_pts) 2105 2106 arr = vtki.new("ArrowSource") 2107 arr.SetShaftResolution(res) 2108 arr.SetTipResolution(res) 2109 2110 if s: 2111 sz = 0.02 * s 2112 arr.SetTipRadius(sz * 2) 2113 arr.SetShaftRadius(sz * thickness) 2114 arr.SetTipLength(sz * 10) 2115 2116 if head_radius: 2117 arr.SetTipRadius(head_radius) 2118 if shaft_radius: 2119 arr.SetShaftRadius(shaft_radius) 2120 if head_length: 2121 arr.SetTipLength(head_length) 2122 2123 arr.Update() 2124 out = arr.GetOutput() 2125 2126 orients = end_pts - start_pts 2127 2128 color_by_vector_size = utils.is_sequence(c) or c in cmaps_names 2129 2130 super().__init__( 2131 start_pts, 2132 out, 2133 orientation_array=orients, 2134 scale_by_vector_size=True, 2135 color_by_vector_size=color_by_vector_size, 2136 c=c, 2137 alpha=alpha, 2138 ) 2139 self.lighting("off") 2140 if color_by_vector_size: 2141 vals = np.linalg.norm(orients, axis=1) 2142 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(vals.min(), vals.max()) 2143 else: 2144 self.c(c) 2145 self.name = "Arrows"
Build arrows between two lists of points start_pts and end_pts.
start_pts can be also passed in the form [[point1, point2], ...].
Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows.
Arguments:
- s : (float) fix aspect-ratio of the arrow and scale its cross section
- c : (color) color or color map name
- alpha : (float) set object opacity
- res : (int) set arrow resolution
Examples:
2148class Arrow2D(Mesh): 2149 """ 2150 Build a 2D arrow. 2151 """ 2152 2153 def __init__( 2154 self, 2155 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 2156 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 2157 s=1, 2158 rotation=0.0, 2159 shaft_length=0.85, 2160 shaft_width=0.055, 2161 head_length=0.175, 2162 head_width=0.175, 2163 fill=True, 2164 c="red4", 2165 alpha=1.0, 2166 ) -> None: 2167 """ 2168 Build a 2D arrow from `start_pt` to `end_pt`. 2169 2170 Arguments: 2171 s : (float) 2172 a global multiplicative convenience factor controlling the arrow size 2173 shaft_length : (float) 2174 fractional shaft length 2175 shaft_width : (float) 2176 fractional shaft width 2177 head_length : (float) 2178 fractional head length 2179 head_width : (float) 2180 fractional head width 2181 fill : (bool) 2182 if False only generate the outline 2183 """ 2184 self.fill = fill ## needed by pyplot.__iadd() 2185 self.s = s ## needed by pyplot.__iadd() 2186 2187 if s != 1: 2188 shaft_width *= s 2189 head_width *= np.sqrt(s) 2190 2191 # in case user is passing meshs 2192 if isinstance(start_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 2193 start_pt = start_pt.GetPosition() 2194 if isinstance(end_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 2195 end_pt = end_pt.GetPosition() 2196 if len(start_pt) == 2: 2197 start_pt = [start_pt[0], start_pt[1], 0] 2198 if len(end_pt) == 2: 2199 end_pt = [end_pt[0], end_pt[1], 0] 2200 2201 headBase = 1 - head_length 2202 head_width = max(head_width, shaft_width) 2203 if head_length is None or headBase > shaft_length: 2204 headBase = shaft_length 2205 2206 verts = [] 2207 verts.append([0, -shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2208 verts.append([shaft_length, -shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2209 verts.append([headBase, -head_width / 2, 0]) 2210 verts.append([1, 0, 0]) 2211 verts.append([headBase, head_width / 2, 0]) 2212 verts.append([shaft_length, shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2213 verts.append([0, shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2214 if fill: 2215 faces = ((0, 1, 3, 5, 6), (5, 3, 4), (1, 2, 3)) 2216 poly = utils.buildPolyData(verts, faces) 2217 else: 2218 lines = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0) 2219 poly = utils.buildPolyData(verts, [], lines=lines) 2220 2221 axis = np.array(end_pt) - np.array(start_pt) 2222 length = float(np.linalg.norm(axis)) 2223 if length: 2224 axis = axis / length 2225 theta = 0 2226 if len(axis) > 2: 2227 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 2228 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 2229 2230 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 2231 t.Translate(start_pt) 2232 if phi: 2233 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 2234 if theta: 2235 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 2236 t.RotateY(-90) # put it along Z 2237 if rotation: 2238 t.RotateX(rotation) 2239 t.Scale(length, length, length) 2240 2241 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 2242 tf.SetInputData(poly) 2243 tf.SetTransform(t) 2244 tf.Update() 2245 2246 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2247 2248 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(start_pt) 2249 2250 self.lighting("off") 2251 self.actor.DragableOff() 2252 self.actor.PickableOff() 2253 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2254 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2255 self.name = "Arrow2D"
Build a 2D arrow.
2153 def __init__( 2154 self, 2155 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 2156 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 2157 s=1, 2158 rotation=0.0, 2159 shaft_length=0.85, 2160 shaft_width=0.055, 2161 head_length=0.175, 2162 head_width=0.175, 2163 fill=True, 2164 c="red4", 2165 alpha=1.0, 2166 ) -> None: 2167 """ 2168 Build a 2D arrow from `start_pt` to `end_pt`. 2169 2170 Arguments: 2171 s : (float) 2172 a global multiplicative convenience factor controlling the arrow size 2173 shaft_length : (float) 2174 fractional shaft length 2175 shaft_width : (float) 2176 fractional shaft width 2177 head_length : (float) 2178 fractional head length 2179 head_width : (float) 2180 fractional head width 2181 fill : (bool) 2182 if False only generate the outline 2183 """ 2184 self.fill = fill ## needed by pyplot.__iadd() 2185 self.s = s ## needed by pyplot.__iadd() 2186 2187 if s != 1: 2188 shaft_width *= s 2189 head_width *= np.sqrt(s) 2190 2191 # in case user is passing meshs 2192 if isinstance(start_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 2193 start_pt = start_pt.GetPosition() 2194 if isinstance(end_pt, vtki.vtkActor): 2195 end_pt = end_pt.GetPosition() 2196 if len(start_pt) == 2: 2197 start_pt = [start_pt[0], start_pt[1], 0] 2198 if len(end_pt) == 2: 2199 end_pt = [end_pt[0], end_pt[1], 0] 2200 2201 headBase = 1 - head_length 2202 head_width = max(head_width, shaft_width) 2203 if head_length is None or headBase > shaft_length: 2204 headBase = shaft_length 2205 2206 verts = [] 2207 verts.append([0, -shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2208 verts.append([shaft_length, -shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2209 verts.append([headBase, -head_width / 2, 0]) 2210 verts.append([1, 0, 0]) 2211 verts.append([headBase, head_width / 2, 0]) 2212 verts.append([shaft_length, shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2213 verts.append([0, shaft_width / 2, 0]) 2214 if fill: 2215 faces = ((0, 1, 3, 5, 6), (5, 3, 4), (1, 2, 3)) 2216 poly = utils.buildPolyData(verts, faces) 2217 else: 2218 lines = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0) 2219 poly = utils.buildPolyData(verts, [], lines=lines) 2220 2221 axis = np.array(end_pt) - np.array(start_pt) 2222 length = float(np.linalg.norm(axis)) 2223 if length: 2224 axis = axis / length 2225 theta = 0 2226 if len(axis) > 2: 2227 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 2228 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 2229 2230 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 2231 t.Translate(start_pt) 2232 if phi: 2233 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 2234 if theta: 2235 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 2236 t.RotateY(-90) # put it along Z 2237 if rotation: 2238 t.RotateX(rotation) 2239 t.Scale(length, length, length) 2240 2241 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 2242 tf.SetInputData(poly) 2243 tf.SetTransform(t) 2244 tf.Update() 2245 2246 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2247 2248 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(start_pt) 2249 2250 self.lighting("off") 2251 self.actor.DragableOff() 2252 self.actor.PickableOff() 2253 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2254 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) # used by pyplot 2255 self.name = "Arrow2D"
Build a 2D arrow from start_pt to end_pt.
Arguments:
- s : (float) a global multiplicative convenience factor controlling the arrow size
- shaft_length : (float) fractional shaft length
- shaft_width : (float) fractional shaft width
- head_length : (float) fractional head length
- head_width : (float) fractional head width
- fill : (bool) if False only generate the outline
2258class Arrows2D(Glyph): 2259 """ 2260 Build 2D arrows between two lists of points. 2261 """ 2262 2263 def __init__( 2264 self, 2265 start_pts, 2266 end_pts=None, 2267 s=1.0, 2268 rotation=0.0, 2269 shaft_length=0.8, 2270 shaft_width=0.05, 2271 head_length=0.225, 2272 head_width=0.175, 2273 fill=True, 2274 c=None, 2275 alpha=1.0, 2276 ) -> None: 2277 """ 2278 Build 2D arrows between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 2279 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 2280 2281 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows. 2282 2283 Arguments: 2284 shaft_length : (float) 2285 fractional shaft length 2286 shaft_width : (float) 2287 fractional shaft width 2288 head_length : (float) 2289 fractional head length 2290 head_width : (float) 2291 fractional head width 2292 fill : (bool) 2293 if False only generate the outline 2294 """ 2295 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 2296 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 2297 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 2298 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 2299 2300 start_pts = np.asarray(start_pts, dtype=float) 2301 if end_pts is None: 2302 strt = start_pts[:, 0] 2303 end_pts = start_pts[:, 1] 2304 start_pts = strt 2305 else: 2306 end_pts = np.asarray(end_pts, dtype=float) 2307 2308 if head_length is None: 2309 head_length = 1 - shaft_length 2310 2311 arr = Arrow2D( 2312 (0, 0, 0), 2313 (1, 0, 0), 2314 s=s, 2315 rotation=rotation, 2316 shaft_length=shaft_length, 2317 shaft_width=shaft_width, 2318 head_length=head_length, 2319 head_width=head_width, 2320 fill=fill, 2321 ) 2322 2323 orients = end_pts - start_pts 2324 orients = utils.make3d(orients) 2325 2326 pts = Points(start_pts) 2327 super().__init__( 2328 pts, 2329 arr, 2330 orientation_array=orients, 2331 scale_by_vector_size=True, 2332 c=c, 2333 alpha=alpha, 2334 ) 2335 self.flat().lighting("off").pickable(False) 2336 if c is not None: 2337 self.color(c) 2338 self.name = "Arrows2D"
Build 2D arrows between two lists of points.
2263 def __init__( 2264 self, 2265 start_pts, 2266 end_pts=None, 2267 s=1.0, 2268 rotation=0.0, 2269 shaft_length=0.8, 2270 shaft_width=0.05, 2271 head_length=0.225, 2272 head_width=0.175, 2273 fill=True, 2274 c=None, 2275 alpha=1.0, 2276 ) -> None: 2277 """ 2278 Build 2D arrows between two lists of points `start_pts` and `end_pts`. 2279 `start_pts` can be also passed in the form `[[point1, point2], ...]`. 2280 2281 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows. 2282 2283 Arguments: 2284 shaft_length : (float) 2285 fractional shaft length 2286 shaft_width : (float) 2287 fractional shaft width 2288 head_length : (float) 2289 fractional head length 2290 head_width : (float) 2291 fractional head width 2292 fill : (bool) 2293 if False only generate the outline 2294 """ 2295 if isinstance(start_pts, Points): 2296 start_pts = start_pts.coordinates 2297 if isinstance(end_pts, Points): 2298 end_pts = end_pts.coordinates 2299 2300 start_pts = np.asarray(start_pts, dtype=float) 2301 if end_pts is None: 2302 strt = start_pts[:, 0] 2303 end_pts = start_pts[:, 1] 2304 start_pts = strt 2305 else: 2306 end_pts = np.asarray(end_pts, dtype=float) 2307 2308 if head_length is None: 2309 head_length = 1 - shaft_length 2310 2311 arr = Arrow2D( 2312 (0, 0, 0), 2313 (1, 0, 0), 2314 s=s, 2315 rotation=rotation, 2316 shaft_length=shaft_length, 2317 shaft_width=shaft_width, 2318 head_length=head_length, 2319 head_width=head_width, 2320 fill=fill, 2321 ) 2322 2323 orients = end_pts - start_pts 2324 orients = utils.make3d(orients) 2325 2326 pts = Points(start_pts) 2327 super().__init__( 2328 pts, 2329 arr, 2330 orientation_array=orients, 2331 scale_by_vector_size=True, 2332 c=c, 2333 alpha=alpha, 2334 ) 2335 self.flat().lighting("off").pickable(False) 2336 if c is not None: 2337 self.color(c) 2338 self.name = "Arrows2D"
Build 2D arrows between two lists of points start_pts and end_pts.
start_pts can be also passed in the form [[point1, point2], ...].
Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the arrows.
Arguments:
- shaft_length : (float) fractional shaft length
- shaft_width : (float) fractional shaft width
- head_length : (float) fractional head length
- head_width : (float) fractional head width
- fill : (bool) if False only generate the outline
2341class FlatArrow(Ribbon): 2342 """ 2343 Build a 2D arrow in 3D space by joining two close lines. 2344 """ 2345 2346 def __init__(self, line1, line2, tip_size=1.0, tip_width=1.0) -> None: 2347 """ 2348 Build a 2D arrow in 3D space by joining two close lines. 2349 2350 Examples: 2351 - [flatarrow.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/flatarrow.py) 2352 2353  2354 """ 2355 if isinstance(line1, Points): 2356 line1 = line1.coordinates 2357 if isinstance(line2, Points): 2358 line2 = line2.coordinates 2359 2360 sm1, sm2 = np.array(line1[-1], dtype=float), np.array(line2[-1], dtype=float) 2361 2362 v = (sm1 - sm2) / 3 * tip_width 2363 p1 = sm1 + v 2364 p2 = sm2 - v 2365 pm1 = (sm1 + sm2) / 2 2366 pm2 = (np.array(line1[-2]) + np.array(line2[-2])) / 2 2367 pm12 = pm1 - pm2 2368 tip = pm12 / np.linalg.norm(pm12) * np.linalg.norm(v) * 3 * tip_size / tip_width + pm1 2369 2370 line1.append(p1) 2371 line1.append(tip) 2372 line2.append(p2) 2373 line2.append(tip) 2374 resm = max(100, len(line1)) 2375 2376 super().__init__(line1, line2, res=(resm, 1)) 2377 self.phong().lighting("off") 2378 self.actor.PickableOff() 2379 self.actor.DragableOff() 2380 self.name = "FlatArrow"
Build a 2D arrow in 3D space by joining two close lines.
2346 def __init__(self, line1, line2, tip_size=1.0, tip_width=1.0) -> None: 2347 """ 2348 Build a 2D arrow in 3D space by joining two close lines. 2349 2350 Examples: 2351 - [flatarrow.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/flatarrow.py) 2352 2353  2354 """ 2355 if isinstance(line1, Points): 2356 line1 = line1.coordinates 2357 if isinstance(line2, Points): 2358 line2 = line2.coordinates 2359 2360 sm1, sm2 = np.array(line1[-1], dtype=float), np.array(line2[-1], dtype=float) 2361 2362 v = (sm1 - sm2) / 3 * tip_width 2363 p1 = sm1 + v 2364 p2 = sm2 - v 2365 pm1 = (sm1 + sm2) / 2 2366 pm2 = (np.array(line1[-2]) + np.array(line2[-2])) / 2 2367 pm12 = pm1 - pm2 2368 tip = pm12 / np.linalg.norm(pm12) * np.linalg.norm(v) * 3 * tip_size / tip_width + pm1 2369 2370 line1.append(p1) 2371 line1.append(tip) 2372 line2.append(p2) 2373 line2.append(tip) 2374 resm = max(100, len(line1)) 2375 2376 super().__init__(line1, line2, res=(resm, 1)) 2377 self.phong().lighting("off") 2378 self.actor.PickableOff() 2379 self.actor.DragableOff() 2380 self.name = "FlatArrow"
2393class Polygon(Mesh): 2394 """ 2395 Build a polygon in the `xy` plane. 2396 """ 2397 2398 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), nsides=6, r=1.0, c="coral", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2399 """ 2400 Build a polygon in the `xy` plane of `nsides` of radius `r`. 2401 2402  2403 """ 2404 t = np.linspace(np.pi / 2, 5 / 2 * np.pi, num=nsides, endpoint=False) 2405 pts = pol2cart(np.ones_like(t) * r, t).T 2406 faces = [list(range(nsides))] 2407 # do not use: vtkRegularPolygonSource 2408 super().__init__([pts, faces], c, alpha) 2409 if len(pos) == 2: 2410 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 2411 self.pos(pos) 2412 self.properties.LightingOff() 2413 self.name = "Polygon " + str(nsides)
Build a polygon in the xy plane.
2398 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), nsides=6, r=1.0, c="coral", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2399 """ 2400 Build a polygon in the `xy` plane of `nsides` of radius `r`. 2401 2402  2403 """ 2404 t = np.linspace(np.pi / 2, 5 / 2 * np.pi, num=nsides, endpoint=False) 2405 pts = pol2cart(np.ones_like(t) * r, t).T 2406 faces = [list(range(nsides))] 2407 # do not use: vtkRegularPolygonSource 2408 super().__init__([pts, faces], c, alpha) 2409 if len(pos) == 2: 2410 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 2411 self.pos(pos) 2412 self.properties.LightingOff() 2413 self.name = "Polygon " + str(nsides)
Build a polygon in the xy plane of nsides of radius r.

2383class Triangle(Mesh): 2384 """Create a triangle from 3 points in space.""" 2385 2386 def __init__(self, p1, p2, p3, c="green7", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2387 """Create a triangle from 3 points in space.""" 2388 super().__init__([[p1, p2, p3], [[0, 1, 2]]], c, alpha) 2389 self.properties.LightingOff() 2390 self.name = "Triangle"
Create a triangle from 3 points in space.
2386 def __init__(self, p1, p2, p3, c="green7", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2387 """Create a triangle from 3 points in space.""" 2388 super().__init__([[p1, p2, p3], [[0, 1, 2]]], c, alpha) 2389 self.properties.LightingOff() 2390 self.name = "Triangle"
Create a triangle from 3 points in space.
3182class Rectangle(Mesh): 3183 """ 3184 Build a rectangle in the xy plane. 3185 """ 3186 3187 def __init__(self, p1=(0, 0), p2=(1, 1), radius=None, res=12, c="gray5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3188 """ 3189 Build a rectangle in the xy plane identified by any two corner points. 3190 3191 Arguments: 3192 p1 : (list) 3193 bottom-left position of the corner 3194 p2 : (list) 3195 top-right position of the corner 3196 radius : (float, list) 3197 smoothing radius of the corner in world units. 3198 A list can be passed with 4 individual values. 3199 """ 3200 if len(p1) == 2: 3201 p1 = np.array([p1[0], p1[1], 0.0]) 3202 else: 3203 p1 = np.array(p1, dtype=float) 3204 if len(p2) == 2: 3205 p2 = np.array([p2[0], p2[1], 0.0]) 3206 else: 3207 p2 = np.array(p2, dtype=float) 3208 3209 self.corner1 = p1 3210 self.corner2 = p2 3211 3212 color = c 3213 smoothr = False 3214 risseq = False 3215 if utils.is_sequence(radius): 3216 risseq = True 3217 smoothr = True 3218 if max(radius) == 0: 3219 smoothr = False 3220 elif radius: 3221 smoothr = True 3222 3223 if not smoothr: 3224 radius = None 3225 self.radius = radius 3226 3227 if smoothr: 3228 r = radius 3229 if not risseq: 3230 r = [r, r, r, r] 3231 rd, ra, rb, rc = r 3232 3233 if p1[0] > p2[0]: # flip p1 - p2 3234 p1, p2 = p2, p1 3235 if p1[1] > p2[1]: # flip p1y - p2y 3236 p1[1], p2[1] = p2[1], p1[1] 3237 3238 px, py, _ = p2 - p1 3239 k = min(px / 2, py / 2) 3240 ra = min(abs(ra), k) 3241 rb = min(abs(rb), k) 3242 rc = min(abs(rc), k) 3243 rd = min(abs(rd), k) 3244 beta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num=res * 4, endpoint=False) 3245 betas = np.split(beta, 4) 3246 rrx = np.cos(betas) 3247 rry = np.sin(betas) 3248 3249 q1 = (rd, 0) 3250 # q2 = (px-ra, 0) 3251 q3 = (px, ra) 3252 # q4 = (px, py-rb) 3253 q5 = (px - rb, py) 3254 # q6 = (rc, py) 3255 q7 = (0, py - rc) 3256 # q8 = (0, rd) 3257 a = np.c_[rrx[3], rry[3]]*ra + [px-ra, ra] if ra else np.array([]) 3258 b = np.c_[rrx[0], rry[0]]*rb + [px-rb, py-rb] if rb else np.array([]) 3259 c = np.c_[rrx[1], rry[1]]*rc + [rc, py-rc] if rc else np.array([]) 3260 d = np.c_[rrx[2], rry[2]]*rd + [rd, rd] if rd else np.array([]) 3261 3262 pts = [q1, *a.tolist(), q3, *b.tolist(), q5, *c.tolist(), q7, *d.tolist()] 3263 faces = [list(range(len(pts)))] 3264 else: 3265 p1r = np.array([p2[0], p1[1], 0.0]) 3266 p2l = np.array([p1[0], p2[1], 0.0]) 3267 pts = ([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], p1r - p1, p2 - p1, p2l - p1) 3268 faces = [(0, 1, 2, 3)] 3269 3270 super().__init__([pts, faces], color, alpha) 3271 self.pos(p1) 3272 self.properties.LightingOff() 3273 self.name = "Rectangle"
Build a rectangle in the xy plane.
3187 def __init__(self, p1=(0, 0), p2=(1, 1), radius=None, res=12, c="gray5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3188 """ 3189 Build a rectangle in the xy plane identified by any two corner points. 3190 3191 Arguments: 3192 p1 : (list) 3193 bottom-left position of the corner 3194 p2 : (list) 3195 top-right position of the corner 3196 radius : (float, list) 3197 smoothing radius of the corner in world units. 3198 A list can be passed with 4 individual values. 3199 """ 3200 if len(p1) == 2: 3201 p1 = np.array([p1[0], p1[1], 0.0]) 3202 else: 3203 p1 = np.array(p1, dtype=float) 3204 if len(p2) == 2: 3205 p2 = np.array([p2[0], p2[1], 0.0]) 3206 else: 3207 p2 = np.array(p2, dtype=float) 3208 3209 self.corner1 = p1 3210 self.corner2 = p2 3211 3212 color = c 3213 smoothr = False 3214 risseq = False 3215 if utils.is_sequence(radius): 3216 risseq = True 3217 smoothr = True 3218 if max(radius) == 0: 3219 smoothr = False 3220 elif radius: 3221 smoothr = True 3222 3223 if not smoothr: 3224 radius = None 3225 self.radius = radius 3226 3227 if smoothr: 3228 r = radius 3229 if not risseq: 3230 r = [r, r, r, r] 3231 rd, ra, rb, rc = r 3232 3233 if p1[0] > p2[0]: # flip p1 - p2 3234 p1, p2 = p2, p1 3235 if p1[1] > p2[1]: # flip p1y - p2y 3236 p1[1], p2[1] = p2[1], p1[1] 3237 3238 px, py, _ = p2 - p1 3239 k = min(px / 2, py / 2) 3240 ra = min(abs(ra), k) 3241 rb = min(abs(rb), k) 3242 rc = min(abs(rc), k) 3243 rd = min(abs(rd), k) 3244 beta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num=res * 4, endpoint=False) 3245 betas = np.split(beta, 4) 3246 rrx = np.cos(betas) 3247 rry = np.sin(betas) 3248 3249 q1 = (rd, 0) 3250 # q2 = (px-ra, 0) 3251 q3 = (px, ra) 3252 # q4 = (px, py-rb) 3253 q5 = (px - rb, py) 3254 # q6 = (rc, py) 3255 q7 = (0, py - rc) 3256 # q8 = (0, rd) 3257 a = np.c_[rrx[3], rry[3]]*ra + [px-ra, ra] if ra else np.array([]) 3258 b = np.c_[rrx[0], rry[0]]*rb + [px-rb, py-rb] if rb else np.array([]) 3259 c = np.c_[rrx[1], rry[1]]*rc + [rc, py-rc] if rc else np.array([]) 3260 d = np.c_[rrx[2], rry[2]]*rd + [rd, rd] if rd else np.array([]) 3261 3262 pts = [q1, *a.tolist(), q3, *b.tolist(), q5, *c.tolist(), q7, *d.tolist()] 3263 faces = [list(range(len(pts)))] 3264 else: 3265 p1r = np.array([p2[0], p1[1], 0.0]) 3266 p2l = np.array([p1[0], p2[1], 0.0]) 3267 pts = ([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], p1r - p1, p2 - p1, p2l - p1) 3268 faces = [(0, 1, 2, 3)] 3269 3270 super().__init__([pts, faces], color, alpha) 3271 self.pos(p1) 3272 self.properties.LightingOff() 3273 self.name = "Rectangle"
Build a rectangle in the xy plane identified by any two corner points.
Arguments:
- p1 : (list) bottom-left position of the corner
- p2 : (list) top-right position of the corner
- radius : (float, list) smoothing radius of the corner in world units. A list can be passed with 4 individual values.
2524class Disc(Mesh): 2525 """ 2526 Build a 2D disc. 2527 """ 2528 2529 def __init__( 2530 self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r1=0.5, r2=1.0, res=(1, 120), angle_range=(), c="gray4", alpha=1.0 2531 ) -> None: 2532 """ 2533 Build a 2D disc of inner radius `r1` and outer radius `r2`. 2534 2535 Set `res` as the resolution in R and Phi (can be a list). 2536 2537 Use `angle_range` to create a disc sector between the 2 specified angles. 2538 2539  2540 """ 2541 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2542 res_r, res_phi = res 2543 else: 2544 res_r, res_phi = res, 12 * res 2545 2546 if len(angle_range) == 0: 2547 ps = vtki.new("DiskSource") 2548 else: 2549 ps = vtki.new("SectorSource") 2550 ps.SetStartAngle(angle_range[0]) 2551 ps.SetEndAngle(angle_range[1]) 2552 2553 ps.SetInnerRadius(r1) 2554 ps.SetOuterRadius(r2) 2555 ps.SetRadialResolution(res_r) 2556 ps.SetCircumferentialResolution(res_phi) 2557 ps.Update() 2558 super().__init__(ps.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2559 self.flat() 2560 self.pos(utils.make3d(pos)) 2561 self.name = "Disc"
Build a 2D disc.
2529 def __init__( 2530 self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r1=0.5, r2=1.0, res=(1, 120), angle_range=(), c="gray4", alpha=1.0 2531 ) -> None: 2532 """ 2533 Build a 2D disc of inner radius `r1` and outer radius `r2`. 2534 2535 Set `res` as the resolution in R and Phi (can be a list). 2536 2537 Use `angle_range` to create a disc sector between the 2 specified angles. 2538 2539  2540 """ 2541 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2542 res_r, res_phi = res 2543 else: 2544 res_r, res_phi = res, 12 * res 2545 2546 if len(angle_range) == 0: 2547 ps = vtki.new("DiskSource") 2548 else: 2549 ps = vtki.new("SectorSource") 2550 ps.SetStartAngle(angle_range[0]) 2551 ps.SetEndAngle(angle_range[1]) 2552 2553 ps.SetInnerRadius(r1) 2554 ps.SetOuterRadius(r2) 2555 ps.SetRadialResolution(res_r) 2556 ps.SetCircumferentialResolution(res_phi) 2557 ps.Update() 2558 super().__init__(ps.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2559 self.flat() 2560 self.pos(utils.make3d(pos)) 2561 self.name = "Disc"
Build a 2D disc of inner radius r1 and outer radius r2.
Set res as the resolution in R and Phi (can be a list).
Use angle_range to create a disc sector between the 2 specified angles.

2416class Circle(Polygon): 2417 """ 2418 Build a Circle of radius `r`. 2419 """ 2420 2421 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, res=120, c="gray5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2422 """ 2423 Build a Circle of radius `r`. 2424 """ 2425 super().__init__(pos, nsides=res, r=r) 2426 2427 self.nr_of_points = 0 2428 self.va = 0 2429 self.vb = 0 2430 self.axis1: List[float] = [] 2431 self.axis2: List[float] = [] 2432 self.center: List[float] = [] # filled by pointcloud.pca_ellipse() 2433 self.pvalue = 0.0 # filled by pointcloud.pca_ellipse() 2434 self.alpha(alpha).c(c) 2435 self.name = "Circle" 2436 2437 def acircularity(self) -> float: 2438 """ 2439 Return a measure of how different an ellipse is from a circle. 2440 Values close to zero correspond to a circular object. 2441 """ 2442 a, b = self.va, self.vb 2443 value = 0.0 2444 if a+b: 2445 value = ((a-b)/(a+b))**2 2446 return value
Build a Circle of radius r.
2421 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, res=120, c="gray5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2422 """ 2423 Build a Circle of radius `r`. 2424 """ 2425 super().__init__(pos, nsides=res, r=r) 2426 2427 self.nr_of_points = 0 2428 self.va = 0 2429 self.vb = 0 2430 self.axis1: List[float] = [] 2431 self.axis2: List[float] = [] 2432 self.center: List[float] = [] # filled by pointcloud.pca_ellipse() 2433 self.pvalue = 0.0 # filled by pointcloud.pca_ellipse() 2434 self.alpha(alpha).c(c) 2435 self.name = "Circle"
Build a Circle of radius r.
2437 def acircularity(self) -> float: 2438 """ 2439 Return a measure of how different an ellipse is from a circle. 2440 Values close to zero correspond to a circular object. 2441 """ 2442 a, b = self.va, self.vb 2443 value = 0.0 2444 if a+b: 2445 value = ((a-b)/(a+b))**2 2446 return value
Return a measure of how different an ellipse is from a circle. Values close to zero correspond to a circular object.
2448class GeoCircle(Polygon): 2449 """ 2450 Build a Circle of radius `r`. 2451 """ 2452 2453 def __init__(self, lat, lon, r=1.0, res=60, c="red4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2454 """ 2455 Build a Circle of radius `r` as projected on a geographic map. 2456 Circles near the poles will look very squashed. 2457 2458 See example: 2459 ```bash 2460 vedo -r earthquake 2461 ``` 2462 """ 2463 coords = [] 2464 sinr, cosr = np.sin(r), np.cos(r) 2465 sinlat, coslat = np.sin(lat), np.cos(lat) 2466 for phi in np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num=res, endpoint=False): 2467 clat = np.arcsin(sinlat * cosr + coslat * sinr * np.cos(phi)) 2468 clng = lon + np.arctan2(np.sin(phi) * sinr * coslat, cosr - sinlat * np.sin(clat)) 2469 coords.append([clng / np.pi + 1, clat * 2 / np.pi + 1, 0]) 2470 2471 super().__init__(nsides=res, c=c, alpha=alpha) 2472 self.coordinates = coords # warp polygon points to match geo projection 2473 self.name = "Circle"
Build a Circle of radius r.
2453 def __init__(self, lat, lon, r=1.0, res=60, c="red4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2454 """ 2455 Build a Circle of radius `r` as projected on a geographic map. 2456 Circles near the poles will look very squashed. 2457 2458 See example: 2459 ```bash 2460 vedo -r earthquake 2461 ``` 2462 """ 2463 coords = [] 2464 sinr, cosr = np.sin(r), np.cos(r) 2465 sinlat, coslat = np.sin(lat), np.cos(lat) 2466 for phi in np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num=res, endpoint=False): 2467 clat = np.arcsin(sinlat * cosr + coslat * sinr * np.cos(phi)) 2468 clng = lon + np.arctan2(np.sin(phi) * sinr * coslat, cosr - sinlat * np.sin(clat)) 2469 coords.append([clng / np.pi + 1, clat * 2 / np.pi + 1, 0]) 2470 2471 super().__init__(nsides=res, c=c, alpha=alpha) 2472 self.coordinates = coords # warp polygon points to match geo projection 2473 self.name = "Circle"
Build a Circle of radius r as projected on a geographic map.
Circles near the poles will look very squashed.
See example:
vedo -r earthquake
1177class Arc(Line): 1178 """ 1179 Build a 2D circular arc between 2 points. 1180 """ 1181 1182 def __init__( 1183 self, 1184 center=None, 1185 point1=None, 1186 point2=None, 1187 normal=None, 1188 angle=None, 1189 invert=False, 1190 res=60, 1191 c="k3", 1192 alpha=1.0, 1193 ) -> None: 1194 """ 1195 Build a 2D circular arc between 2 points. 1196 Two modes are available: 1197 1. [center, point1, point2] are specified 1198 1199 2. [point1, normal, angle] are specified. 1200 1201 In the first case it creates an arc defined by two endpoints and a center. 1202 In the second the arc spans the shortest angular sector defined by 1203 a starting point, a normal and a spanning angle. 1204 if `invert=True`, then the opposite happens. 1205 1206 Example 1: 1207 ```python 1208 from vedo import * 1209 center = [0,1,0] 1210 p1 = [1,2,0.4] 1211 p2 = [0.5,3,-1] 1212 arc = Arc(center, p1, p2).lw(5).c("purple5") 1213 line2 = Line(center, p2) 1214 pts = Points([center, p1,p2], r=9, c='r') 1215 show(pts, line2, arc, f"length={arc.length()}", axes=1).close() 1216 ``` 1217 1218 Example 2: 1219 ```python 1220 from vedo import * 1221 arc = Arc(point1=[0,1,0], normal=[0,0,1], angle=270) 1222 arc.lw(5).c("purple5") 1223 origin = Point([0,0,0], r=9, c='r') 1224 show(origin, arc, arc.labels2d(), axes=1).close() 1225 ``` 1226 """ 1227 ar = vtki.new("ArcSource") 1228 if point2 is not None: 1229 center = utils.make3d(center) 1230 point1 = utils.make3d(point1) 1231 point2 = utils.make3d(point2) 1232 ar.UseNormalAndAngleOff() 1233 ar.SetPoint1(point1-center) 1234 ar.SetPoint2(point2-center) 1235 elif normal is not None and angle and point1 is not None: 1236 normal = utils.make3d(normal) 1237 point1 = utils.make3d(point1) 1238 ar.UseNormalAndAngleOn() 1239 ar.SetAngle(angle) 1240 ar.SetPolarVector(point1) 1241 ar.SetNormal(normal) 1242 self.top = normal 1243 else: 1244 vedo.logger.error("in Arc(), incorrect input combination.") 1245 raise TypeError 1246 ar.SetNegative(invert) 1247 ar.SetResolution(res) 1248 ar.Update() 1249 1250 super().__init__(ar.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1251 self.lw(2).lighting("off") 1252 if point2 is not None: # nb: not center 1253 self.pos(center) 1254 self.name = "Arc"
Build a 2D circular arc between 2 points.
1182 def __init__( 1183 self, 1184 center=None, 1185 point1=None, 1186 point2=None, 1187 normal=None, 1188 angle=None, 1189 invert=False, 1190 res=60, 1191 c="k3", 1192 alpha=1.0, 1193 ) -> None: 1194 """ 1195 Build a 2D circular arc between 2 points. 1196 Two modes are available: 1197 1. [center, point1, point2] are specified 1198 1199 2. [point1, normal, angle] are specified. 1200 1201 In the first case it creates an arc defined by two endpoints and a center. 1202 In the second the arc spans the shortest angular sector defined by 1203 a starting point, a normal and a spanning angle. 1204 if `invert=True`, then the opposite happens. 1205 1206 Example 1: 1207 ```python 1208 from vedo import * 1209 center = [0,1,0] 1210 p1 = [1,2,0.4] 1211 p2 = [0.5,3,-1] 1212 arc = Arc(center, p1, p2).lw(5).c("purple5") 1213 line2 = Line(center, p2) 1214 pts = Points([center, p1,p2], r=9, c='r') 1215 show(pts, line2, arc, f"length={arc.length()}", axes=1).close() 1216 ``` 1217 1218 Example 2: 1219 ```python 1220 from vedo import * 1221 arc = Arc(point1=[0,1,0], normal=[0,0,1], angle=270) 1222 arc.lw(5).c("purple5") 1223 origin = Point([0,0,0], r=9, c='r') 1224 show(origin, arc, arc.labels2d(), axes=1).close() 1225 ``` 1226 """ 1227 ar = vtki.new("ArcSource") 1228 if point2 is not None: 1229 center = utils.make3d(center) 1230 point1 = utils.make3d(point1) 1231 point2 = utils.make3d(point2) 1232 ar.UseNormalAndAngleOff() 1233 ar.SetPoint1(point1-center) 1234 ar.SetPoint2(point2-center) 1235 elif normal is not None and angle and point1 is not None: 1236 normal = utils.make3d(normal) 1237 point1 = utils.make3d(point1) 1238 ar.UseNormalAndAngleOn() 1239 ar.SetAngle(angle) 1240 ar.SetPolarVector(point1) 1241 ar.SetNormal(normal) 1242 self.top = normal 1243 else: 1244 vedo.logger.error("in Arc(), incorrect input combination.") 1245 raise TypeError 1246 ar.SetNegative(invert) 1247 ar.SetResolution(res) 1248 ar.Update() 1249 1250 super().__init__(ar.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 1251 self.lw(2).lighting("off") 1252 if point2 is not None: # nb: not center 1253 self.pos(center) 1254 self.name = "Arc"
Build a 2D circular arc between 2 points.
Two modes are available:
[center, point1, point2] are specified
[point1, normal, angle] are specified.
In the first case it creates an arc defined by two endpoints and a center.
In the second the arc spans the shortest angular sector defined by
a starting point, a normal and a spanning angle.
if invert=True, then the opposite happens.
Example 1:
from vedo import *
center = [0,1,0]
p1 = [1,2,0.4]
p2 = [0.5,3,-1]
arc = Arc(center, p1, p2).lw(5).c("purple5")
line2 = Line(center, p2)
pts = Points([center, p1,p2], r=9, c='r')
show(pts, line2, arc, f"length={arc.length()}", axes=1).close()
Example 2:
from vedo import *
arc = Arc(point1=[0,1,0], normal=[0,0,1], angle=270)
arc.lw(5).c("purple5")
origin = Point([0,0,0], r=9, c='r')
show(origin, arc, arc.labels2d(), axes=1).close()
2476class Star(Mesh): 2477 """ 2478 Build a 2D star shape. 2479 """ 2480 2481 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), n=5, r1=0.7, r2=1.0, line=False, c="blue6", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2482 """ 2483 Build a 2D star shape of `n` cusps of inner radius `r1` and outer radius `r2`. 2484 2485 If line is True then only build the outer line (no internal surface meshing). 2486 2487 Example: 2488 - [extrude.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/extrude.py) 2489 2490  2491 """ 2492 t = np.linspace(np.pi / 2, 5 / 2 * np.pi, num=n, endpoint=False) 2493 x, y = pol2cart(np.ones_like(t) * r2, t) 2494 pts = np.c_[x, y, np.zeros_like(x)] 2495 2496 apts = [] 2497 for i, p in enumerate(pts): 2498 apts.append(p) 2499 if i + 1 < n: 2500 apts.append((p + pts[i + 1]) / 2 * r1 / r2) 2501 apts.append((pts[-1] + pts[0]) / 2 * r1 / r2) 2502 2503 if line: 2504 apts.append(pts[0]) 2505 poly = utils.buildPolyData(apts, lines=list(range(len(apts)))) 2506 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 2507 self.lw(2) 2508 else: 2509 apts.append((0, 0, 0)) 2510 cells = [] 2511 for i in range(2 * n - 1): 2512 cell = [2 * n, i, i + 1] 2513 cells.append(cell) 2514 cells.append([2 * n, i + 1, 0]) 2515 super().__init__([apts, cells], c, alpha) 2516 2517 if len(pos) == 2: 2518 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 2519 2520 self.properties.LightingOff() 2521 self.name = "Star"
Build a 2D star shape.
2481 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), n=5, r1=0.7, r2=1.0, line=False, c="blue6", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2482 """ 2483 Build a 2D star shape of `n` cusps of inner radius `r1` and outer radius `r2`. 2484 2485 If line is True then only build the outer line (no internal surface meshing). 2486 2487 Example: 2488 - [extrude.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/extrude.py) 2489 2490  2491 """ 2492 t = np.linspace(np.pi / 2, 5 / 2 * np.pi, num=n, endpoint=False) 2493 x, y = pol2cart(np.ones_like(t) * r2, t) 2494 pts = np.c_[x, y, np.zeros_like(x)] 2495 2496 apts = [] 2497 for i, p in enumerate(pts): 2498 apts.append(p) 2499 if i + 1 < n: 2500 apts.append((p + pts[i + 1]) / 2 * r1 / r2) 2501 apts.append((pts[-1] + pts[0]) / 2 * r1 / r2) 2502 2503 if line: 2504 apts.append(pts[0]) 2505 poly = utils.buildPolyData(apts, lines=list(range(len(apts)))) 2506 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 2507 self.lw(2) 2508 else: 2509 apts.append((0, 0, 0)) 2510 cells = [] 2511 for i in range(2 * n - 1): 2512 cell = [2 * n, i, i + 1] 2513 cells.append(cell) 2514 cells.append([2 * n, i + 1, 0]) 2515 super().__init__([apts, cells], c, alpha) 2516 2517 if len(pos) == 2: 2518 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 2519 2520 self.properties.LightingOff() 2521 self.name = "Star"
Build a 2D star shape of n cusps of inner radius r1 and outer radius r2.
If line is True then only build the outer line (no internal surface meshing).
Example:
3904class Star3D(Mesh): 3905 """ 3906 Build a 3D starred shape. 3907 """ 3908 3909 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, thickness=0.1, c="blue4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3910 """ 3911 Build a 3D star shape of 5 cusps, mainly useful as a 3D marker. 3912 """ 3913 pts = ((1.34, 0., -0.37), (5.75e-3, -0.588, thickness/10), (0.377, 0.,-0.38), 3914 (0.0116, 0., -1.35), (-0.366, 0., -0.384), (-1.33, 0., -0.385), 3915 (-0.600, 0., 0.321), (-0.829, 0., 1.19), (-1.17e-3, 0., 0.761), 3916 (0.824, 0., 1.20), (0.602, 0., 0.328), (6.07e-3, 0.588, thickness/10)) 3917 fcs = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 11,10], [2, 1, 3], [2, 11, 0], [3, 1, 4], [3, 11, 2], 3918 [4, 1, 5], [4, 11, 3], [5, 1, 6], [5, 11, 4], [6, 1, 7], [6, 11, 5], 3919 [7, 1, 8], [7, 11, 6], [8, 1, 9], [8, 11, 7], [9, 1,10], [9, 11, 8], 3920 [10,1, 0],[10,11, 9]] 3921 3922 super().__init__([pts, fcs], c, alpha) 3923 self.rotate_x(90) 3924 self.scale(r).lighting("shiny") 3925 3926 if len(pos) == 2: 3927 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3928 self.pos(pos) 3929 self.name = "Star3D"
Build a 3D starred shape.
3909 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, thickness=0.1, c="blue4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3910 """ 3911 Build a 3D star shape of 5 cusps, mainly useful as a 3D marker. 3912 """ 3913 pts = ((1.34, 0., -0.37), (5.75e-3, -0.588, thickness/10), (0.377, 0.,-0.38), 3914 (0.0116, 0., -1.35), (-0.366, 0., -0.384), (-1.33, 0., -0.385), 3915 (-0.600, 0., 0.321), (-0.829, 0., 1.19), (-1.17e-3, 0., 0.761), 3916 (0.824, 0., 1.20), (0.602, 0., 0.328), (6.07e-3, 0.588, thickness/10)) 3917 fcs = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 11,10], [2, 1, 3], [2, 11, 0], [3, 1, 4], [3, 11, 2], 3918 [4, 1, 5], [4, 11, 3], [5, 1, 6], [5, 11, 4], [6, 1, 7], [6, 11, 5], 3919 [7, 1, 8], [7, 11, 6], [8, 1, 9], [8, 11, 7], [9, 1,10], [9, 11, 8], 3920 [10,1, 0],[10,11, 9]] 3921 3922 super().__init__([pts, fcs], c, alpha) 3923 self.rotate_x(90) 3924 self.scale(r).lighting("shiny") 3925 3926 if len(pos) == 2: 3927 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3928 self.pos(pos) 3929 self.name = "Star3D"
Build a 3D star shape of 5 cusps, mainly useful as a 3D marker.
3932class Cross3D(Mesh): 3933 """ 3934 Build a 3D cross shape. 3935 """ 3936 3937 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, thickness=0.3, c="b", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3938 """ 3939 Build a 3D cross shape, mainly useful as a 3D marker. 3940 """ 3941 if len(pos) == 2: 3942 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3943 3944 c1 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s) 3945 c2 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s).rotate_x(90) 3946 c3 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s).rotate_y(90) 3947 poly = merge(c1, c2, c3).color(c).alpha(alpha).pos(pos).dataset 3948 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 3949 self.name = "Cross3D"
Build a 3D cross shape.
3937 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, thickness=0.3, c="b", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3938 """ 3939 Build a 3D cross shape, mainly useful as a 3D marker. 3940 """ 3941 if len(pos) == 2: 3942 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3943 3944 c1 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s) 3945 c2 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s).rotate_x(90) 3946 c3 = Cylinder(r=thickness * s, height=2 * s).rotate_y(90) 3947 poly = merge(c1, c2, c3).color(c).alpha(alpha).pos(pos).dataset 3948 super().__init__(poly, c, alpha) 3949 self.name = "Cross3D"
Build a 3D cross shape, mainly useful as a 3D marker.
2563class IcoSphere(Mesh): 2564 """ 2565 Create a sphere made of a uniform triangle mesh. 2566 """ 2567 2568 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, subdivisions=4, c="r5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2569 """ 2570 Create a sphere made of a uniform triangle mesh 2571 (from recursive subdivision of an icosahedron). 2572 2573 Example: 2574 ```python 2575 from vedo import * 2576 icos = IcoSphere(subdivisions=3) 2577 icos.compute_quality().cmap('coolwarm') 2578 icos.show(axes=1).close() 2579 ``` 2580  2581 """ 2582 subdivisions = int(min(subdivisions, 9)) # to avoid disasters 2583 2584 t = (1.0 + np.sqrt(5.0)) / 2.0 2585 points = np.array( 2586 [ 2587 [-1, t, 0], 2588 [1, t, 0], 2589 [-1, -t, 0], 2590 [1, -t, 0], 2591 [0, -1, t], 2592 [0, 1, t], 2593 [0, -1, -t], 2594 [0, 1, -t], 2595 [t, 0, -1], 2596 [t, 0, 1], 2597 [-t, 0, -1], 2598 [-t, 0, 1], 2599 ] 2600 ) 2601 faces = [ 2602 [0, 11, 5], 2603 [0, 5, 1], 2604 [0, 1, 7], 2605 [0, 7, 10], 2606 [0, 10, 11], 2607 [1, 5, 9], 2608 [5, 11, 4], 2609 [11, 10, 2], 2610 [10, 7, 6], 2611 [7, 1, 8], 2612 [3, 9, 4], 2613 [3, 4, 2], 2614 [3, 2, 6], 2615 [3, 6, 8], 2616 [3, 8, 9], 2617 [4, 9, 5], 2618 [2, 4, 11], 2619 [6, 2, 10], 2620 [8, 6, 7], 2621 [9, 8, 1], 2622 ] 2623 super().__init__([points * r, faces], c=c, alpha=alpha) 2624 2625 for _ in range(subdivisions): 2626 self.subdivide(method=1) 2627 pts = utils.versor(self.coordinates) * r 2628 self.coordinates = pts 2629 2630 self.pos(pos) 2631 self.name = "IcoSphere"
Create a sphere made of a uniform triangle mesh.
2568 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, subdivisions=4, c="r5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2569 """ 2570 Create a sphere made of a uniform triangle mesh 2571 (from recursive subdivision of an icosahedron). 2572 2573 Example: 2574 ```python 2575 from vedo import * 2576 icos = IcoSphere(subdivisions=3) 2577 icos.compute_quality().cmap('coolwarm') 2578 icos.show(axes=1).close() 2579 ``` 2580  2581 """ 2582 subdivisions = int(min(subdivisions, 9)) # to avoid disasters 2583 2584 t = (1.0 + np.sqrt(5.0)) / 2.0 2585 points = np.array( 2586 [ 2587 [-1, t, 0], 2588 [1, t, 0], 2589 [-1, -t, 0], 2590 [1, -t, 0], 2591 [0, -1, t], 2592 [0, 1, t], 2593 [0, -1, -t], 2594 [0, 1, -t], 2595 [t, 0, -1], 2596 [t, 0, 1], 2597 [-t, 0, -1], 2598 [-t, 0, 1], 2599 ] 2600 ) 2601 faces = [ 2602 [0, 11, 5], 2603 [0, 5, 1], 2604 [0, 1, 7], 2605 [0, 7, 10], 2606 [0, 10, 11], 2607 [1, 5, 9], 2608 [5, 11, 4], 2609 [11, 10, 2], 2610 [10, 7, 6], 2611 [7, 1, 8], 2612 [3, 9, 4], 2613 [3, 4, 2], 2614 [3, 2, 6], 2615 [3, 6, 8], 2616 [3, 8, 9], 2617 [4, 9, 5], 2618 [2, 4, 11], 2619 [6, 2, 10], 2620 [8, 6, 7], 2621 [9, 8, 1], 2622 ] 2623 super().__init__([points * r, faces], c=c, alpha=alpha) 2624 2625 for _ in range(subdivisions): 2626 self.subdivide(method=1) 2627 pts = utils.versor(self.coordinates) * r 2628 self.coordinates = pts 2629 2630 self.pos(pos) 2631 self.name = "IcoSphere"
Create a sphere made of a uniform triangle mesh (from recursive subdivision of an icosahedron).
Example:
from vedo import *
icos = IcoSphere(subdivisions=3)
icos.compute_quality().cmap('coolwarm')
icos.show(axes=1).close()

2634class Sphere(Mesh): 2635 """ 2636 Build a sphere. 2637 """ 2638 2639 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, res=24, quads=False, c="r5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2640 """ 2641 Build a sphere at position `pos` of radius `r`. 2642 2643 Arguments: 2644 r : (float) 2645 sphere radius 2646 res : (int, list) 2647 resolution in phi, resolution in theta is by default `2*res` 2648 quads : (bool) 2649 sphere mesh will be made of quads instead of triangles 2650 2651 [](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/32848391/72433092-f0a31e00-3798-11ea-85f7-b2f5fcc31568.png) 2652 """ 2653 if len(pos) == 2: 2654 pos = np.asarray([pos[0], pos[1], 0]) 2655 2656 self.radius = r # used by fitSphere 2657 self.center = pos 2658 self.residue = 0 2659 2660 if quads: 2661 res = max(res, 4) 2662 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 2663 img.SetDimensions(res - 1, res - 1, res - 1) 2664 rs = 1.0 / (res - 2) 2665 img.SetSpacing(rs, rs, rs) 2666 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 2667 gf.SetInputData(img) 2668 gf.Update() 2669 super().__init__(gf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2670 self.lw(0.1) 2671 2672 cgpts = self.coordinates - (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) 2673 2674 x, y, z = cgpts.T 2675 x = x * (1 + x * x) / 2 2676 y = y * (1 + y * y) / 2 2677 z = z * (1 + z * z) / 2 2678 _, theta, phi = cart2spher(x, y, z) 2679 2680 pts = spher2cart(np.ones_like(phi) * r, theta, phi).T 2681 self.coordinates = pts 2682 2683 else: 2684 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2685 res_t, res_phi = res 2686 else: 2687 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2688 2689 ss = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2690 ss.SetRadius(r) 2691 ss.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2692 ss.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2693 ss.Update() 2694 2695 super().__init__(ss.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2696 2697 self.phong() 2698 self.pos(pos) 2699 self.name = "Sphere"
Build a sphere.
2639 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, res=24, quads=False, c="r5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2640 """ 2641 Build a sphere at position `pos` of radius `r`. 2642 2643 Arguments: 2644 r : (float) 2645 sphere radius 2646 res : (int, list) 2647 resolution in phi, resolution in theta is by default `2*res` 2648 quads : (bool) 2649 sphere mesh will be made of quads instead of triangles 2650 2651 [](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/32848391/72433092-f0a31e00-3798-11ea-85f7-b2f5fcc31568.png) 2652 """ 2653 if len(pos) == 2: 2654 pos = np.asarray([pos[0], pos[1], 0]) 2655 2656 self.radius = r # used by fitSphere 2657 self.center = pos 2658 self.residue = 0 2659 2660 if quads: 2661 res = max(res, 4) 2662 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 2663 img.SetDimensions(res - 1, res - 1, res - 1) 2664 rs = 1.0 / (res - 2) 2665 img.SetSpacing(rs, rs, rs) 2666 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 2667 gf.SetInputData(img) 2668 gf.Update() 2669 super().__init__(gf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2670 self.lw(0.1) 2671 2672 cgpts = self.coordinates - (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) 2673 2674 x, y, z = cgpts.T 2675 x = x * (1 + x * x) / 2 2676 y = y * (1 + y * y) / 2 2677 z = z * (1 + z * z) / 2 2678 _, theta, phi = cart2spher(x, y, z) 2679 2680 pts = spher2cart(np.ones_like(phi) * r, theta, phi).T 2681 self.coordinates = pts 2682 2683 else: 2684 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2685 res_t, res_phi = res 2686 else: 2687 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2688 2689 ss = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2690 ss.SetRadius(r) 2691 ss.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2692 ss.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2693 ss.Update() 2694 2695 super().__init__(ss.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2696 2697 self.phong() 2698 self.pos(pos) 2699 self.name = "Sphere"
Build a sphere at position pos of radius r.
Arguments:
- r : (float) sphere radius
- res : (int, list)
resolution in phi, resolution in theta is by default
2*res - quads : (bool) sphere mesh will be made of quads instead of triangles
2702class Spheres(Mesh): 2703 """ 2704 Build a large set of spheres. 2705 """ 2706 2707 def __init__(self, centers, r=1.0, res=8, c="red5", alpha=1) -> None: 2708 """ 2709 Build a (possibly large) set of spheres at `centers` of radius `r`. 2710 2711 Either `c` or `r` can be a list of RGB colors or radii. 2712 2713 Examples: 2714 - [manyspheres.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/manyspheres.py) 2715 2716  2717 """ 2718 2719 if isinstance(centers, Points): 2720 centers = centers.coordinates 2721 centers = np.asarray(centers, dtype=float) 2722 base = centers[0] 2723 2724 cisseq = False 2725 if utils.is_sequence(c): 2726 cisseq = True 2727 2728 if cisseq: 2729 if len(centers) != len(c): 2730 vedo.logger.error(f"mismatch #centers {len(centers)} != {len(c)} #colors") 2731 raise RuntimeError() 2732 2733 risseq = False 2734 if utils.is_sequence(r): 2735 risseq = True 2736 2737 if risseq: 2738 if len(centers) != len(r): 2739 vedo.logger.error(f"mismatch #centers {len(centers)} != {len(r)} #radii") 2740 raise RuntimeError() 2741 if cisseq and risseq: 2742 vedo.logger.error("Limitation: c and r cannot be both sequences.") 2743 raise RuntimeError() 2744 2745 src = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2746 if not risseq: 2747 src.SetRadius(r) 2748 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2749 res_t, res_phi = res 2750 else: 2751 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2752 2753 src.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2754 src.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2755 src.Update() 2756 2757 psrc = vtki.new("PointSource") 2758 psrc.SetNumberOfPoints(len(centers)) 2759 psrc.Update() 2760 pd = psrc.GetOutput() 2761 vpts = pd.GetPoints() 2762 2763 glyph = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 2764 glyph.SetSourceConnection(src.GetOutputPort()) 2765 2766 if cisseq: 2767 glyph.SetColorModeToColorByScalar() 2768 ucols = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 2769 ucols.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 2770 ucols.SetName("Colors") 2771 for acol in c: 2772 cx, cy, cz = get_color(acol) 2773 ucols.InsertNextTuple3(cx * 255, cy * 255, cz * 255) 2774 pd.GetPointData().AddArray(ucols) 2775 pd.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("Colors") 2776 glyph.ScalingOff() 2777 elif risseq: 2778 glyph.SetScaleModeToScaleByScalar() 2779 urads = utils.numpy2vtk(2 * np.ascontiguousarray(r), dtype=np.float32) 2780 urads.SetName("Radii") 2781 pd.GetPointData().AddArray(urads) 2782 pd.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("Radii") 2783 2784 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(centers - base, dtype=np.float32)) 2785 2786 glyph.SetInputData(pd) 2787 glyph.Update() 2788 2789 super().__init__(glyph.GetOutput(), alpha=alpha) 2790 self.pos(base) 2791 self.phong() 2792 if cisseq: 2793 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 2794 else: 2795 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2796 self.c(c) 2797 self.name = "Spheres"
Build a large set of spheres.
2707 def __init__(self, centers, r=1.0, res=8, c="red5", alpha=1) -> None: 2708 """ 2709 Build a (possibly large) set of spheres at `centers` of radius `r`. 2710 2711 Either `c` or `r` can be a list of RGB colors or radii. 2712 2713 Examples: 2714 - [manyspheres.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/manyspheres.py) 2715 2716  2717 """ 2718 2719 if isinstance(centers, Points): 2720 centers = centers.coordinates 2721 centers = np.asarray(centers, dtype=float) 2722 base = centers[0] 2723 2724 cisseq = False 2725 if utils.is_sequence(c): 2726 cisseq = True 2727 2728 if cisseq: 2729 if len(centers) != len(c): 2730 vedo.logger.error(f"mismatch #centers {len(centers)} != {len(c)} #colors") 2731 raise RuntimeError() 2732 2733 risseq = False 2734 if utils.is_sequence(r): 2735 risseq = True 2736 2737 if risseq: 2738 if len(centers) != len(r): 2739 vedo.logger.error(f"mismatch #centers {len(centers)} != {len(r)} #radii") 2740 raise RuntimeError() 2741 if cisseq and risseq: 2742 vedo.logger.error("Limitation: c and r cannot be both sequences.") 2743 raise RuntimeError() 2744 2745 src = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2746 if not risseq: 2747 src.SetRadius(r) 2748 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2749 res_t, res_phi = res 2750 else: 2751 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2752 2753 src.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2754 src.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2755 src.Update() 2756 2757 psrc = vtki.new("PointSource") 2758 psrc.SetNumberOfPoints(len(centers)) 2759 psrc.Update() 2760 pd = psrc.GetOutput() 2761 vpts = pd.GetPoints() 2762 2763 glyph = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 2764 glyph.SetSourceConnection(src.GetOutputPort()) 2765 2766 if cisseq: 2767 glyph.SetColorModeToColorByScalar() 2768 ucols = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 2769 ucols.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 2770 ucols.SetName("Colors") 2771 for acol in c: 2772 cx, cy, cz = get_color(acol) 2773 ucols.InsertNextTuple3(cx * 255, cy * 255, cz * 255) 2774 pd.GetPointData().AddArray(ucols) 2775 pd.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("Colors") 2776 glyph.ScalingOff() 2777 elif risseq: 2778 glyph.SetScaleModeToScaleByScalar() 2779 urads = utils.numpy2vtk(2 * np.ascontiguousarray(r), dtype=np.float32) 2780 urads.SetName("Radii") 2781 pd.GetPointData().AddArray(urads) 2782 pd.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("Radii") 2783 2784 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(centers - base, dtype=np.float32)) 2785 2786 glyph.SetInputData(pd) 2787 glyph.Update() 2788 2789 super().__init__(glyph.GetOutput(), alpha=alpha) 2790 self.pos(base) 2791 self.phong() 2792 if cisseq: 2793 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 2794 else: 2795 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2796 self.c(c) 2797 self.name = "Spheres"
Build a (possibly large) set of spheres at centers of radius r.
Either c or r can be a list of RGB colors or radii.
Examples:
2800class Earth(Mesh): 2801 """ 2802 Build a textured mesh representing the Earth. 2803 """ 2804 2805 def __init__(self, style=1, r=1.0) -> None: 2806 """ 2807 Build a textured mesh representing the Earth. 2808 2809 Example: 2810 - [geodesic_curve.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/geodesic_curve.py) 2811 2812  2813 """ 2814 tss = vtki.new("TexturedSphereSource") 2815 tss.SetRadius(r) 2816 tss.SetThetaResolution(72) 2817 tss.SetPhiResolution(36) 2818 tss.Update() 2819 super().__init__(tss.GetOutput(), c="w") 2820 atext = vtki.vtkTexture() 2821 pnm_reader = vtki.new("JPEGReader") 2822 fn = vedo.file_io.download(vedo.dataurl + f"textures/earth{style}.jpg", verbose=False) 2823 pnm_reader.SetFileName(fn) 2824 atext.SetInputConnection(pnm_reader.GetOutputPort()) 2825 atext.InterpolateOn() 2826 self.texture(atext) 2827 self.name = "Earth"
Build a textured mesh representing the Earth.
2805 def __init__(self, style=1, r=1.0) -> None: 2806 """ 2807 Build a textured mesh representing the Earth. 2808 2809 Example: 2810 - [geodesic_curve.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/geodesic_curve.py) 2811 2812  2813 """ 2814 tss = vtki.new("TexturedSphereSource") 2815 tss.SetRadius(r) 2816 tss.SetThetaResolution(72) 2817 tss.SetPhiResolution(36) 2818 tss.Update() 2819 super().__init__(tss.GetOutput(), c="w") 2820 atext = vtki.vtkTexture() 2821 pnm_reader = vtki.new("JPEGReader") 2822 fn = vedo.file_io.download(vedo.dataurl + f"textures/earth{style}.jpg", verbose=False) 2823 pnm_reader.SetFileName(fn) 2824 atext.SetInputConnection(pnm_reader.GetOutputPort()) 2825 atext.InterpolateOn() 2826 self.texture(atext) 2827 self.name = "Earth"
2830class Ellipsoid(Mesh): 2831 """Build a 3D ellipsoid.""" 2832 def __init__( 2833 self, 2834 pos=(0, 0, 0), 2835 axis1=(0.5, 0, 0), 2836 axis2=(0, 1, 0), 2837 axis3=(0, 0, 1.5), 2838 res=24, 2839 c="cyan4", 2840 alpha=1.0, 2841 ) -> None: 2842 """ 2843 Build a 3D ellipsoid centered at position `pos`. 2844 2845 Arguments: 2846 axis1 : (list) 2847 First axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2848 axis2 : (list) 2849 Second axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2850 axis3 : (list) 2851 Third axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2852 """ 2853 self.center = utils.make3d(pos) 2854 2855 self.axis1 = utils.make3d(axis1) 2856 self.axis2 = utils.make3d(axis2) 2857 self.axis3 = utils.make3d(axis3) 2858 2859 self.va = np.linalg.norm(self.axis1) 2860 self.vb = np.linalg.norm(self.axis2) 2861 self.vc = np.linalg.norm(self.axis3) 2862 2863 self.va_error = 0 2864 self.vb_error = 0 2865 self.vc_error = 0 2866 2867 self.nr_of_points = 1 # used by pointcloud.pca_ellipsoid() 2868 self.pvalue = 0 # used by pointcloud.pca_ellipsoid() 2869 2870 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2871 res_t, res_phi = res 2872 else: 2873 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2874 2875 elli_source = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2876 elli_source.SetRadius(1) 2877 elli_source.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2878 elli_source.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2879 elli_source.Update() 2880 2881 super().__init__(elli_source.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2882 2883 matrix = np.c_[self.axis1, self.axis2, self.axis3] 2884 lt = LinearTransform(matrix).translate(pos) 2885 self.apply_transform(lt) 2886 self.name = "Ellipsoid" 2887 2888 def asphericity(self) -> float: 2889 """ 2890 Return a measure of how different an ellipsoid is from a sphere. 2891 Values close to zero correspond to a spheric object. 2892 """ 2893 a, b, c = self.va, self.vb, self.vc 2894 asp = ( ((a-b)/(a+b))**2 2895 + ((a-c)/(a+c))**2 2896 + ((b-c)/(b+c))**2 ) / 3. * 4. 2897 return float(asp) 2898 2899 def asphericity_error(self) -> float: 2900 """ 2901 Calculate statistical error on the asphericity value. 2902 2903 Errors on the main axes are stored in 2904 `Ellipsoid.va_error`, Ellipsoid.vb_error` and `Ellipsoid.vc_error`. 2905 """ 2906 a, b, c = self.va, self.vb, self.vc 2907 sqrtn = np.sqrt(self.nr_of_points) 2908 ea, eb, ec = a / 2 / sqrtn, b / 2 / sqrtn, b / 2 / sqrtn 2909 2910 # from sympy import * 2911 # init_printing(use_unicode=True) 2912 # a, b, c, ea, eb, ec = symbols("a b c, ea, eb,ec") 2913 # L = ( 2914 # (((a - b) / (a + b)) ** 2 + ((c - b) / (c + b)) ** 2 + ((a - c) / (a + c)) ** 2) 2915 # / 3 * 4) 2916 # dl2 = (diff(L, a) * ea) ** 2 + (diff(L, b) * eb) ** 2 + (diff(L, c) * ec) ** 2 2917 # print(dl2) 2918 # exit() 2919 2920 dL2 = ( 2921 ea ** 2 2922 * ( 2923 -8 * (a - b) ** 2 / (3 * (a + b) ** 3) 2924 - 8 * (a - c) ** 2 / (3 * (a + c) ** 3) 2925 + 4 * (2 * a - 2 * c) / (3 * (a + c) ** 2) 2926 + 4 * (2 * a - 2 * b) / (3 * (a + b) ** 2) 2927 ) ** 2 2928 + eb ** 2 2929 * ( 2930 4 * (-2 * a + 2 * b) / (3 * (a + b) ** 2) 2931 - 8 * (a - b) ** 2 / (3 * (a + b) ** 3) 2932 - 8 * (-b + c) ** 2 / (3 * (b + c) ** 3) 2933 + 4 * (2 * b - 2 * c) / (3 * (b + c) ** 2) 2934 ) ** 2 2935 + ec ** 2 2936 * ( 2937 4 * (-2 * a + 2 * c) / (3 * (a + c) ** 2) 2938 - 8 * (a - c) ** 2 / (3 * (a + c) ** 3) 2939 + 4 * (-2 * b + 2 * c) / (3 * (b + c) ** 2) 2940 - 8 * (-b + c) ** 2 / (3 * (b + c) ** 3) 2941 ) ** 2 2942 ) 2943 err = np.sqrt(dL2) 2944 self.va_error = ea 2945 self.vb_error = eb 2946 self.vc_error = ec 2947 return err
Build a 3D ellipsoid.
2832 def __init__( 2833 self, 2834 pos=(0, 0, 0), 2835 axis1=(0.5, 0, 0), 2836 axis2=(0, 1, 0), 2837 axis3=(0, 0, 1.5), 2838 res=24, 2839 c="cyan4", 2840 alpha=1.0, 2841 ) -> None: 2842 """ 2843 Build a 3D ellipsoid centered at position `pos`. 2844 2845 Arguments: 2846 axis1 : (list) 2847 First axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2848 axis2 : (list) 2849 Second axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2850 axis3 : (list) 2851 Third axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis. 2852 """ 2853 self.center = utils.make3d(pos) 2854 2855 self.axis1 = utils.make3d(axis1) 2856 self.axis2 = utils.make3d(axis2) 2857 self.axis3 = utils.make3d(axis3) 2858 2859 self.va = np.linalg.norm(self.axis1) 2860 self.vb = np.linalg.norm(self.axis2) 2861 self.vc = np.linalg.norm(self.axis3) 2862 2863 self.va_error = 0 2864 self.vb_error = 0 2865 self.vc_error = 0 2866 2867 self.nr_of_points = 1 # used by pointcloud.pca_ellipsoid() 2868 self.pvalue = 0 # used by pointcloud.pca_ellipsoid() 2869 2870 if utils.is_sequence(res): 2871 res_t, res_phi = res 2872 else: 2873 res_t, res_phi = 2 * res, res 2874 2875 elli_source = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2876 elli_source.SetRadius(1) 2877 elli_source.SetThetaResolution(res_t) 2878 elli_source.SetPhiResolution(res_phi) 2879 elli_source.Update() 2880 2881 super().__init__(elli_source.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 2882 2883 matrix = np.c_[self.axis1, self.axis2, self.axis3] 2884 lt = LinearTransform(matrix).translate(pos) 2885 self.apply_transform(lt) 2886 self.name = "Ellipsoid"
Build a 3D ellipsoid centered at position pos.
Arguments:
- axis1 : (list) First axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis.
- axis2 : (list) Second axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis.
- axis3 : (list) Third axis. Length corresponds to semi-axis.
2888 def asphericity(self) -> float: 2889 """ 2890 Return a measure of how different an ellipsoid is from a sphere. 2891 Values close to zero correspond to a spheric object. 2892 """ 2893 a, b, c = self.va, self.vb, self.vc 2894 asp = ( ((a-b)/(a+b))**2 2895 + ((a-c)/(a+c))**2 2896 + ((b-c)/(b+c))**2 ) / 3. * 4. 2897 return float(asp)
Return a measure of how different an ellipsoid is from a sphere. Values close to zero correspond to a spheric object.
2899 def asphericity_error(self) -> float: 2900 """ 2901 Calculate statistical error on the asphericity value. 2902 2903 Errors on the main axes are stored in 2904 `Ellipsoid.va_error`, Ellipsoid.vb_error` and `Ellipsoid.vc_error`. 2905 """ 2906 a, b, c = self.va, self.vb, self.vc 2907 sqrtn = np.sqrt(self.nr_of_points) 2908 ea, eb, ec = a / 2 / sqrtn, b / 2 / sqrtn, b / 2 / sqrtn 2909 2910 # from sympy import * 2911 # init_printing(use_unicode=True) 2912 # a, b, c, ea, eb, ec = symbols("a b c, ea, eb,ec") 2913 # L = ( 2914 # (((a - b) / (a + b)) ** 2 + ((c - b) / (c + b)) ** 2 + ((a - c) / (a + c)) ** 2) 2915 # / 3 * 4) 2916 # dl2 = (diff(L, a) * ea) ** 2 + (diff(L, b) * eb) ** 2 + (diff(L, c) * ec) ** 2 2917 # print(dl2) 2918 # exit() 2919 2920 dL2 = ( 2921 ea ** 2 2922 * ( 2923 -8 * (a - b) ** 2 / (3 * (a + b) ** 3) 2924 - 8 * (a - c) ** 2 / (3 * (a + c) ** 3) 2925 + 4 * (2 * a - 2 * c) / (3 * (a + c) ** 2) 2926 + 4 * (2 * a - 2 * b) / (3 * (a + b) ** 2) 2927 ) ** 2 2928 + eb ** 2 2929 * ( 2930 4 * (-2 * a + 2 * b) / (3 * (a + b) ** 2) 2931 - 8 * (a - b) ** 2 / (3 * (a + b) ** 3) 2932 - 8 * (-b + c) ** 2 / (3 * (b + c) ** 3) 2933 + 4 * (2 * b - 2 * c) / (3 * (b + c) ** 2) 2934 ) ** 2 2935 + ec ** 2 2936 * ( 2937 4 * (-2 * a + 2 * c) / (3 * (a + c) ** 2) 2938 - 8 * (a - c) ** 2 / (3 * (a + c) ** 3) 2939 + 4 * (-2 * b + 2 * c) / (3 * (b + c) ** 2) 2940 - 8 * (-b + c) ** 2 / (3 * (b + c) ** 3) 2941 ) ** 2 2942 ) 2943 err = np.sqrt(dL2) 2944 self.va_error = ea 2945 self.vb_error = eb 2946 self.vc_error = ec 2947 return err
Calculate statistical error on the asphericity value.
Errors on the main axes are stored in
Ellipsoid.va_error, Ellipsoid.vb_errorandEllipsoid.vc_error`.
2950class Grid(Mesh): 2951 """ 2952 An even or uneven 2D grid. 2953 """ 2954 2955 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=(1, 1), res=(10, 10), lw=1, c="k3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2956 """ 2957 Create an even or uneven 2D grid. 2958 Can also be created from a `np.mgrid` object (see example). 2959 2960 Arguments: 2961 pos : (list, Points, Mesh) 2962 position in space, can also be passed as a bounding box [xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax]. 2963 s : (float, list) 2964 if a float is provided it is interpreted as the total size along x and y, 2965 if a list of coords is provided they are interpreted as the vertices of the grid along x and y. 2966 In this case keyword `res` is ignored (see example below). 2967 res : (list) 2968 resolutions along x and y, e.i. the number of subdivisions 2969 lw : (int) 2970 line width 2971 2972 Example: 2973 ```python 2974 from vedo import * 2975 xcoords = np.arange(0, 2, 0.2) 2976 ycoords = np.arange(0, 1, 0.2) 2977 sqrtx = sqrt(xcoords) 2978 grid = Grid(s=(sqrtx, ycoords)).lw(2) 2979 grid.show(axes=8).close() 2980 2981 # Can also create a grid from a np.mgrid: 2982 X, Y = np.mgrid[-12:12:10*1j, 200:215:10*1j] 2983 vgrid = Grid(s=(X[:,0], Y[0])) 2984 vgrid.show(axes=8).close() 2985 ``` 2986  2987 """ 2988 resx, resy = res 2989 sx, sy = s 2990 2991 try: 2992 bb = pos.bounds() 2993 pos = [(bb[0] + bb[1])/2, (bb[2] + bb[3])/2, (bb[4] + bb[5])/2] 2994 sx = bb[1] - bb[0] 2995 sy = bb[3] - bb[2] 2996 except AttributeError: 2997 pass 2998 2999 if len(pos) == 2: 3000 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3001 elif len(pos) in [4,6]: # passing a bounding box 3002 bb = pos 3003 pos = [(bb[0] + bb[1])/2, (bb[2] + bb[3])/2, 0] 3004 sx = bb[1] - bb[0] 3005 sy = bb[3] - bb[2] 3006 if len(pos)==6: 3007 pos[2] = bb[4] - bb[5] 3008 3009 if utils.is_sequence(sx) and utils.is_sequence(sy): 3010 verts = [] 3011 for y in sy: 3012 for x in sx: 3013 verts.append([x, y, 0]) 3014 faces = [] 3015 n = len(sx) 3016 m = len(sy) 3017 for j in range(m - 1): 3018 j1n = (j + 1) * n 3019 for i in range(n - 1): 3020 faces.append([i + j * n, i + 1 + j * n, i + 1 + j1n, i + j1n]) 3021 3022 super().__init__([verts, faces], c, alpha) 3023 3024 else: 3025 ps = vtki.new("PlaneSource") 3026 ps.SetResolution(resx, resy) 3027 ps.Update() 3028 3029 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3030 t.Translate(pos) 3031 t.Scale(sx, sy, 1) 3032 3033 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3034 tf.SetInputData(ps.GetOutput()) 3035 tf.SetTransform(t) 3036 tf.Update() 3037 3038 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3039 3040 self.wireframe().lw(lw) 3041 self.properties.LightingOff() 3042 self.name = "Grid"
An even or uneven 2D grid.
2955 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=(1, 1), res=(10, 10), lw=1, c="k3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 2956 """ 2957 Create an even or uneven 2D grid. 2958 Can also be created from a `np.mgrid` object (see example). 2959 2960 Arguments: 2961 pos : (list, Points, Mesh) 2962 position in space, can also be passed as a bounding box [xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax]. 2963 s : (float, list) 2964 if a float is provided it is interpreted as the total size along x and y, 2965 if a list of coords is provided they are interpreted as the vertices of the grid along x and y. 2966 In this case keyword `res` is ignored (see example below). 2967 res : (list) 2968 resolutions along x and y, e.i. the number of subdivisions 2969 lw : (int) 2970 line width 2971 2972 Example: 2973 ```python 2974 from vedo import * 2975 xcoords = np.arange(0, 2, 0.2) 2976 ycoords = np.arange(0, 1, 0.2) 2977 sqrtx = sqrt(xcoords) 2978 grid = Grid(s=(sqrtx, ycoords)).lw(2) 2979 grid.show(axes=8).close() 2980 2981 # Can also create a grid from a np.mgrid: 2982 X, Y = np.mgrid[-12:12:10*1j, 200:215:10*1j] 2983 vgrid = Grid(s=(X[:,0], Y[0])) 2984 vgrid.show(axes=8).close() 2985 ``` 2986  2987 """ 2988 resx, resy = res 2989 sx, sy = s 2990 2991 try: 2992 bb = pos.bounds() 2993 pos = [(bb[0] + bb[1])/2, (bb[2] + bb[3])/2, (bb[4] + bb[5])/2] 2994 sx = bb[1] - bb[0] 2995 sy = bb[3] - bb[2] 2996 except AttributeError: 2997 pass 2998 2999 if len(pos) == 2: 3000 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3001 elif len(pos) in [4,6]: # passing a bounding box 3002 bb = pos 3003 pos = [(bb[0] + bb[1])/2, (bb[2] + bb[3])/2, 0] 3004 sx = bb[1] - bb[0] 3005 sy = bb[3] - bb[2] 3006 if len(pos)==6: 3007 pos[2] = bb[4] - bb[5] 3008 3009 if utils.is_sequence(sx) and utils.is_sequence(sy): 3010 verts = [] 3011 for y in sy: 3012 for x in sx: 3013 verts.append([x, y, 0]) 3014 faces = [] 3015 n = len(sx) 3016 m = len(sy) 3017 for j in range(m - 1): 3018 j1n = (j + 1) * n 3019 for i in range(n - 1): 3020 faces.append([i + j * n, i + 1 + j * n, i + 1 + j1n, i + j1n]) 3021 3022 super().__init__([verts, faces], c, alpha) 3023 3024 else: 3025 ps = vtki.new("PlaneSource") 3026 ps.SetResolution(resx, resy) 3027 ps.Update() 3028 3029 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3030 t.Translate(pos) 3031 t.Scale(sx, sy, 1) 3032 3033 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3034 tf.SetInputData(ps.GetOutput()) 3035 tf.SetTransform(t) 3036 tf.Update() 3037 3038 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3039 3040 self.wireframe().lw(lw) 3041 self.properties.LightingOff() 3042 self.name = "Grid"
Create an even or uneven 2D grid.
Can also be created from a np.mgrid object (see example).
Arguments:
- pos : (list, Points, Mesh) position in space, can also be passed as a bounding box [xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax].
- s : (float, list)
if a float is provided it is interpreted as the total size along x and y,
if a list of coords is provided they are interpreted as the vertices of the grid along x and y.
In this case keyword
resis ignored (see example below). - res : (list) resolutions along x and y, e.i. the number of subdivisions
- lw : (int) line width
Example:
from vedo import * xcoords = np.arange(0, 2, 0.2) ycoords = np.arange(0, 1, 0.2) sqrtx = sqrt(xcoords) grid = Grid(s=(sqrtx, ycoords)).lw(2) grid.show(axes=8).close() # Can also create a grid from a np.mgrid: X, Y = np.mgrid[-12:12:10*1j, 200:215:10*1j] vgrid = Grid(s=(X[:,0], Y[0])) vgrid.show(axes=8).close()
3369class TessellatedBox(Mesh): 3370 """ 3371 Build a cubic `Mesh` made of quads. 3372 """ 3373 3374 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), n=10, spacing=(1, 1, 1), bounds=(), c="k5", alpha=0.5) -> None: 3375 """ 3376 Build a cubic `Mesh` made of `n` small quads in the 3 axis directions. 3377 3378 Arguments: 3379 pos : (list) 3380 position of the left bottom corner 3381 n : (int, list) 3382 number of subdivisions along each side 3383 spacing : (float) 3384 size of the side of the single quad in the 3 directions 3385 """ 3386 if utils.is_sequence(n): # slow 3387 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 3388 img.SetDimensions(n[0] + 1, n[1] + 1, n[2] + 1) 3389 img.SetSpacing(spacing) 3390 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 3391 gf.SetInputData(img) 3392 gf.Update() 3393 poly = gf.GetOutput() 3394 else: # fast 3395 n -= 1 3396 tbs = vtki.new("TessellatedBoxSource") 3397 tbs.SetLevel(n) 3398 if len(bounds)>0: 3399 tbs.SetBounds(bounds) 3400 else: 3401 tbs.SetBounds(0, n * spacing[0], 0, n * spacing[1], 0, n * spacing[2]) 3402 tbs.QuadsOn() 3403 #tbs.SetOutputPointsPrecision(vtki.vtkAlgorithm.SINGLE_PRECISION) 3404 tbs.Update() 3405 poly = tbs.GetOutput() 3406 super().__init__(poly, c=c, alpha=alpha) 3407 self.pos(pos) 3408 self.lw(1).lighting("off") 3409 self.name = "TessellatedBox"
Build a cubic Mesh made of quads.
3374 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), n=10, spacing=(1, 1, 1), bounds=(), c="k5", alpha=0.5) -> None: 3375 """ 3376 Build a cubic `Mesh` made of `n` small quads in the 3 axis directions. 3377 3378 Arguments: 3379 pos : (list) 3380 position of the left bottom corner 3381 n : (int, list) 3382 number of subdivisions along each side 3383 spacing : (float) 3384 size of the side of the single quad in the 3 directions 3385 """ 3386 if utils.is_sequence(n): # slow 3387 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 3388 img.SetDimensions(n[0] + 1, n[1] + 1, n[2] + 1) 3389 img.SetSpacing(spacing) 3390 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 3391 gf.SetInputData(img) 3392 gf.Update() 3393 poly = gf.GetOutput() 3394 else: # fast 3395 n -= 1 3396 tbs = vtki.new("TessellatedBoxSource") 3397 tbs.SetLevel(n) 3398 if len(bounds)>0: 3399 tbs.SetBounds(bounds) 3400 else: 3401 tbs.SetBounds(0, n * spacing[0], 0, n * spacing[1], 0, n * spacing[2]) 3402 tbs.QuadsOn() 3403 #tbs.SetOutputPointsPrecision(vtki.vtkAlgorithm.SINGLE_PRECISION) 3404 tbs.Update() 3405 poly = tbs.GetOutput() 3406 super().__init__(poly, c=c, alpha=alpha) 3407 self.pos(pos) 3408 self.lw(1).lighting("off") 3409 self.name = "TessellatedBox"
Build a cubic Mesh made of n small quads in the 3 axis directions.
Arguments:
- pos : (list) position of the left bottom corner
- n : (int, list) number of subdivisions along each side
- spacing : (float) size of the side of the single quad in the 3 directions
3045class Plane(Mesh): 3046 """Create a plane in space.""" 3047 def __init__( 3048 self, 3049 pos=(0, 0, 0), 3050 normal=(0, 0, 1), 3051 s=(1, 1), 3052 res=(1, 1), 3053 edge_direction=(), 3054 c="gray5", 3055 alpha=1.0, 3056 ) -> None: 3057 """ 3058 Create a plane of size `s=(xsize, ysize)` oriented perpendicular 3059 to vector `normal` so that it passes through point `pos`, optionally 3060 aligning an edge with `direction`. 3061 3062 Arguments: 3063 pos : (list) 3064 position of the plane center 3065 normal : (list) 3066 normal vector to the plane 3067 s : (list) 3068 size of the plane along x and y 3069 res : (list) 3070 resolution of the plane along x and y 3071 edge_direction : (list) 3072 direction vector to align one edge of the plane 3073 """ 3074 if isinstance(pos, vtki.vtkPolyData): 3075 super().__init__(pos, c, alpha) 3076 3077 else: 3078 ps = vtki.new("PlaneSource") 3079 ps.SetResolution(res[0], res[1]) 3080 tri = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 3081 tri.SetInputConnection(ps.GetOutputPort()) 3082 tri.Update() 3083 super().__init__(tri.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3084 3085 pos = utils.make3d(pos) 3086 normal = np.asarray(normal, dtype=float) 3087 axis = normal / np.linalg.norm(normal) 3088 3089 # Calculate orientation using normal 3090 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 3091 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 3092 3093 t = LinearTransform() 3094 t.scale([s[0], s[1], 1]) 3095 3096 # Rotate to align normal 3097 t.rotate_y(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3098 t.rotate_z(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3099 3100 # Additional direction alignment 3101 if len(edge_direction) >= 2: 3102 direction = utils.make3d(edge_direction).astype(float) 3103 direction /= np.linalg.norm(direction) 3104 3105 if s[0] <= s[1]: 3106 current_direction = np.asarray([0,1,0]) 3107 else: 3108 current_direction = np.asarray([1,0,0]) 3109 3110 transformed_current_direction = t.transform_point(current_direction) 3111 n = transformed_current_direction / np.linalg.norm(transformed_current_direction) 3112 3113 if np.linalg.norm(transformed_current_direction) >= 1e-6: 3114 angle = np.arccos(np.dot(n, direction)) 3115 t.rotate(axis=axis, angle=np.rad2deg(angle)) 3116 3117 t.translate(pos) 3118 self.apply_transform(t) 3119 3120 self.lighting("off") 3121 self.name = "Plane" 3122 self.variance = 0 # used by pointcloud.fit_plane() 3123 3124 def clone(self, deep=True) -> "Plane": 3125 newplane = Plane() 3126 if deep: 3127 newplane.dataset.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 3128 else: 3129 newplane.dataset.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 3130 newplane.copy_properties_from(self) 3131 newplane.transform = self.transform.clone() 3132 newplane.variance = 0 3133 return newplane 3134 3135 @property 3136 def normal(self) -> np.ndarray: 3137 pts = self.coordinates 3138 # this is necessary because plane can have high resolution 3139 # p0, p1 = pts[0], pts[1] 3140 # AB = p1 - p0 3141 # AB /= np.linalg.norm(AB) 3142 # for pt in pts[2:]: 3143 # AC = pt - p0 3144 # AC /= np.linalg.norm(AC) 3145 # cosine_angle = np.dot(AB, AC) 3146 # if abs(cosine_angle) < 0.99: 3147 # normal = np.cross(AB, AC) 3148 # return normal / np.linalg.norm(normal) 3149 p0, p1, p2 = pts[0], pts[1], pts[int(len(pts)/2 +0.5)] 3150 AB = p1 - p0 3151 AB /= np.linalg.norm(AB) 3152 AC = p2 - p0 3153 AC /= np.linalg.norm(AC) 3154 normal = np.cross(AB, AC) 3155 return normal / np.linalg.norm(normal) 3156 3157 @property 3158 def center(self) -> np.ndarray: 3159 pts = self.coordinates 3160 return np.mean(pts, axis=0) 3161 3162 def contains(self, points, tol=0) -> np.ndarray: 3163 """ 3164 Check if each of the provided point lies on this plane. 3165 `points` is an array of shape (n, 3). 3166 """ 3167 points = np.array(points, dtype=float) 3168 bounds = self.coordinates 3169 3170 mask = np.isclose(np.dot(points - self.center, self.normal), 0, atol=tol) 3171 3172 for i in [1, 3]: 3173 AB = bounds[i] - bounds[0] 3174 AP = points - bounds[0] 3175 mask_l = np.less_equal(np.dot(AP, AB), np.linalg.norm(AB)) 3176 mask_g = np.greater_equal(np.dot(AP, AB), 0) 3177 mask = np.logical_and(mask, mask_l) 3178 mask = np.logical_and(mask, mask_g) 3179 return mask
Create a plane in space.
3047 def __init__( 3048 self, 3049 pos=(0, 0, 0), 3050 normal=(0, 0, 1), 3051 s=(1, 1), 3052 res=(1, 1), 3053 edge_direction=(), 3054 c="gray5", 3055 alpha=1.0, 3056 ) -> None: 3057 """ 3058 Create a plane of size `s=(xsize, ysize)` oriented perpendicular 3059 to vector `normal` so that it passes through point `pos`, optionally 3060 aligning an edge with `direction`. 3061 3062 Arguments: 3063 pos : (list) 3064 position of the plane center 3065 normal : (list) 3066 normal vector to the plane 3067 s : (list) 3068 size of the plane along x and y 3069 res : (list) 3070 resolution of the plane along x and y 3071 edge_direction : (list) 3072 direction vector to align one edge of the plane 3073 """ 3074 if isinstance(pos, vtki.vtkPolyData): 3075 super().__init__(pos, c, alpha) 3076 3077 else: 3078 ps = vtki.new("PlaneSource") 3079 ps.SetResolution(res[0], res[1]) 3080 tri = vtki.new("TriangleFilter") 3081 tri.SetInputConnection(ps.GetOutputPort()) 3082 tri.Update() 3083 super().__init__(tri.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3084 3085 pos = utils.make3d(pos) 3086 normal = np.asarray(normal, dtype=float) 3087 axis = normal / np.linalg.norm(normal) 3088 3089 # Calculate orientation using normal 3090 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 3091 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 3092 3093 t = LinearTransform() 3094 t.scale([s[0], s[1], 1]) 3095 3096 # Rotate to align normal 3097 t.rotate_y(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3098 t.rotate_z(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3099 3100 # Additional direction alignment 3101 if len(edge_direction) >= 2: 3102 direction = utils.make3d(edge_direction).astype(float) 3103 direction /= np.linalg.norm(direction) 3104 3105 if s[0] <= s[1]: 3106 current_direction = np.asarray([0,1,0]) 3107 else: 3108 current_direction = np.asarray([1,0,0]) 3109 3110 transformed_current_direction = t.transform_point(current_direction) 3111 n = transformed_current_direction / np.linalg.norm(transformed_current_direction) 3112 3113 if np.linalg.norm(transformed_current_direction) >= 1e-6: 3114 angle = np.arccos(np.dot(n, direction)) 3115 t.rotate(axis=axis, angle=np.rad2deg(angle)) 3116 3117 t.translate(pos) 3118 self.apply_transform(t) 3119 3120 self.lighting("off") 3121 self.name = "Plane" 3122 self.variance = 0 # used by pointcloud.fit_plane()
Create a plane of size s=(xsize, ysize) oriented perpendicular
to vector normal so that it passes through point pos, optionally
aligning an edge with direction.
Arguments:
- pos : (list) position of the plane center
- normal : (list) normal vector to the plane
- s : (list) size of the plane along x and y
- res : (list) resolution of the plane along x and y
- edge_direction : (list) direction vector to align one edge of the plane
3124 def clone(self, deep=True) -> "Plane": 3125 newplane = Plane() 3126 if deep: 3127 newplane.dataset.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 3128 else: 3129 newplane.dataset.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 3130 newplane.copy_properties_from(self) 3131 newplane.transform = self.transform.clone() 3132 newplane.variance = 0 3133 return newplane
3162 def contains(self, points, tol=0) -> np.ndarray: 3163 """ 3164 Check if each of the provided point lies on this plane. 3165 `points` is an array of shape (n, 3). 3166 """ 3167 points = np.array(points, dtype=float) 3168 bounds = self.coordinates 3169 3170 mask = np.isclose(np.dot(points - self.center, self.normal), 0, atol=tol) 3171 3172 for i in [1, 3]: 3173 AB = bounds[i] - bounds[0] 3174 AP = points - bounds[0] 3175 mask_l = np.less_equal(np.dot(AP, AB), np.linalg.norm(AB)) 3176 mask_g = np.greater_equal(np.dot(AP, AB), 0) 3177 mask = np.logical_and(mask, mask_l) 3178 mask = np.logical_and(mask, mask_g) 3179 return mask
Check if each of the provided point lies on this plane.
points is an array of shape (n, 3).
3276class Box(Mesh): 3277 """ 3278 Build a box of specified dimensions. 3279 """ 3280 3281 def __init__( 3282 self, 3283 pos=(0, 0, 0), 3284 length=1.0, width=1.0, height=1.0, size=(), c="g4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3285 """ 3286 Build a box of dimensions `x=length, y=width and z=height`. 3287 Alternatively dimensions can be defined by setting `size` keyword with a tuple. 3288 3289 If `pos` is a list of 6 numbers, this will be interpreted as the bounding box: 3290 `[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]` 3291 3292 Note that the shape polygonal data contains duplicated vertices. This is to allow 3293 each face to have its own normal, which is essential for some operations. 3294 Use the `clean()` method to remove duplicate points. 3295 3296 Examples: 3297 - [aspring1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/aspring1.py) 3298 3299  3300 """ 3301 src = vtki.new("CubeSource") 3302 3303 if len(pos) == 2: 3304 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3305 3306 ################# 3307 if len(pos) == 6: 3308 length, width, height = (pos[1] - pos[0]), (pos[3] - pos[2]), (pos[5] - pos[4]) 3309 pos = [(pos[0] + pos[1]) / 2, (pos[2] + pos[3]) / 2, (pos[4] + pos[5]) / 2] 3310 3311 elif len(size) == 3: 3312 length, width, height = size 3313 3314 src.SetXLength(length) 3315 src.SetYLength(width) 3316 src.SetZLength(height) 3317 3318 src.Update() 3319 pd = src.GetOutput() 3320 3321 tc = [ 3322 [0.0, 0.0], 3323 [1.0, 0.0], 3324 [0.0, 1.0], 3325 [1.0, 1.0], 3326 [1.0, 0.0], 3327 [0.0, 0.0], 3328 [1.0, 1.0], 3329 [0.0, 1.0], 3330 [1.0, 1.0], 3331 [1.0, 0.0], 3332 [0.0, 1.0], 3333 [0.0, 0.0], 3334 [0.0, 1.0], 3335 [0.0, 0.0], 3336 [1.0, 1.0], 3337 [1.0, 0.0], 3338 [1.0, 0.0], 3339 [0.0, 0.0], 3340 [1.0, 1.0], 3341 [0.0, 1.0], 3342 [0.0, 0.0], 3343 [1.0, 0.0], 3344 [0.0, 1.0], 3345 [1.0, 1.0], 3346 ] 3347 vtc = utils.numpy2vtk(tc) 3348 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtc) 3349 super().__init__(pd, c, alpha) 3350 self.name = "Box" 3351 self.pos(pos)
Build a box of specified dimensions.
3281 def __init__( 3282 self, 3283 pos=(0, 0, 0), 3284 length=1.0, width=1.0, height=1.0, size=(), c="g4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3285 """ 3286 Build a box of dimensions `x=length, y=width and z=height`. 3287 Alternatively dimensions can be defined by setting `size` keyword with a tuple. 3288 3289 If `pos` is a list of 6 numbers, this will be interpreted as the bounding box: 3290 `[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]` 3291 3292 Note that the shape polygonal data contains duplicated vertices. This is to allow 3293 each face to have its own normal, which is essential for some operations. 3294 Use the `clean()` method to remove duplicate points. 3295 3296 Examples: 3297 - [aspring1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/aspring1.py) 3298 3299  3300 """ 3301 src = vtki.new("CubeSource") 3302 3303 if len(pos) == 2: 3304 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3305 3306 ################# 3307 if len(pos) == 6: 3308 length, width, height = (pos[1] - pos[0]), (pos[3] - pos[2]), (pos[5] - pos[4]) 3309 pos = [(pos[0] + pos[1]) / 2, (pos[2] + pos[3]) / 2, (pos[4] + pos[5]) / 2] 3310 3311 elif len(size) == 3: 3312 length, width, height = size 3313 3314 src.SetXLength(length) 3315 src.SetYLength(width) 3316 src.SetZLength(height) 3317 3318 src.Update() 3319 pd = src.GetOutput() 3320 3321 tc = [ 3322 [0.0, 0.0], 3323 [1.0, 0.0], 3324 [0.0, 1.0], 3325 [1.0, 1.0], 3326 [1.0, 0.0], 3327 [0.0, 0.0], 3328 [1.0, 1.0], 3329 [0.0, 1.0], 3330 [1.0, 1.0], 3331 [1.0, 0.0], 3332 [0.0, 1.0], 3333 [0.0, 0.0], 3334 [0.0, 1.0], 3335 [0.0, 0.0], 3336 [1.0, 1.0], 3337 [1.0, 0.0], 3338 [1.0, 0.0], 3339 [0.0, 0.0], 3340 [1.0, 1.0], 3341 [0.0, 1.0], 3342 [0.0, 0.0], 3343 [1.0, 0.0], 3344 [0.0, 1.0], 3345 [1.0, 1.0], 3346 ] 3347 vtc = utils.numpy2vtk(tc) 3348 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtc) 3349 super().__init__(pd, c, alpha) 3350 self.name = "Box" 3351 self.pos(pos)
Build a box of dimensions x=length, y=width and z=height.
Alternatively dimensions can be defined by setting size keyword with a tuple.
If pos is a list of 6 numbers, this will be interpreted as the bounding box:
[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]
Note that the shape polygonal data contains duplicated vertices. This is to allow
each face to have its own normal, which is essential for some operations.
Use the clean() method to remove duplicate points.
Examples:
3354class Cube(Box): 3355 """ 3356 Build a cube shape. 3357 3358 Note that the shape polygonal data contains duplicated vertices. This is to allow 3359 each face to have its own normal, which is essential for some operations. 3360 Use the `clean()` method to remove duplicate points. 3361 """ 3362 3363 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), side=1.0, c="g4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3364 """Build a cube of size `side`.""" 3365 super().__init__(pos, side, side, side, (), c, alpha) 3366 self.name = "Cube"
Build a cube shape.
Note that the shape polygonal data contains duplicated vertices. This is to allow
each face to have its own normal, which is essential for some operations.
Use the clean() method to remove duplicate points.
3412class Spring(Mesh): 3413 """ 3414 Build a spring model. 3415 """ 3416 3417 def __init__( 3418 self, 3419 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 3420 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 3421 coils=20, 3422 r1=0.1, 3423 r2=None, 3424 thickness=None, 3425 c="gray5", 3426 alpha=1.0, 3427 ) -> None: 3428 """ 3429 Build a spring of specified nr of `coils` between `start_pt` and `end_pt`. 3430 3431 Arguments: 3432 coils : (int) 3433 number of coils 3434 r1 : (float) 3435 radius at start point 3436 r2 : (float) 3437 radius at end point 3438 thickness : (float) 3439 thickness of the coil section 3440 """ 3441 start_pt = utils.make3d(start_pt) 3442 end_pt = utils.make3d(end_pt) 3443 3444 diff = end_pt - start_pt 3445 length = np.linalg.norm(diff) 3446 if not length: 3447 return 3448 if not r1: 3449 r1 = length / 20 3450 trange = np.linspace(0, length, num=50 * coils) 3451 om = 6.283 * (coils - 0.5) / length 3452 if not r2: 3453 r2 = r1 3454 pts = [] 3455 for t in trange: 3456 f = (length - t) / length 3457 rd = r1 * f + r2 * (1 - f) 3458 pts.append([rd * np.cos(om * t), rd * np.sin(om * t), t]) 3459 3460 pts = [[0, 0, 0]] + pts + [[0, 0, length]] 3461 diff = diff / length 3462 theta = np.arccos(diff[2]) 3463 phi = np.arctan2(diff[1], diff[0]) 3464 sp = Line(pts) 3465 3466 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3467 t.Translate(start_pt) 3468 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3469 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3470 3471 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3472 tf.SetInputData(sp.dataset) 3473 tf.SetTransform(t) 3474 tf.Update() 3475 3476 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 3477 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(12) 3478 tuf.CappingOn() 3479 tuf.SetInputData(tf.GetOutput()) 3480 if not thickness: 3481 thickness = r1 / 10 3482 tuf.SetRadius(thickness) 3483 tuf.Update() 3484 3485 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3486 3487 self.phong().lighting("metallic") 3488 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) 3489 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) 3490 self.name = "Spring"
Build a spring model.
3417 def __init__( 3418 self, 3419 start_pt=(0, 0, 0), 3420 end_pt=(1, 0, 0), 3421 coils=20, 3422 r1=0.1, 3423 r2=None, 3424 thickness=None, 3425 c="gray5", 3426 alpha=1.0, 3427 ) -> None: 3428 """ 3429 Build a spring of specified nr of `coils` between `start_pt` and `end_pt`. 3430 3431 Arguments: 3432 coils : (int) 3433 number of coils 3434 r1 : (float) 3435 radius at start point 3436 r2 : (float) 3437 radius at end point 3438 thickness : (float) 3439 thickness of the coil section 3440 """ 3441 start_pt = utils.make3d(start_pt) 3442 end_pt = utils.make3d(end_pt) 3443 3444 diff = end_pt - start_pt 3445 length = np.linalg.norm(diff) 3446 if not length: 3447 return 3448 if not r1: 3449 r1 = length / 20 3450 trange = np.linspace(0, length, num=50 * coils) 3451 om = 6.283 * (coils - 0.5) / length 3452 if not r2: 3453 r2 = r1 3454 pts = [] 3455 for t in trange: 3456 f = (length - t) / length 3457 rd = r1 * f + r2 * (1 - f) 3458 pts.append([rd * np.cos(om * t), rd * np.sin(om * t), t]) 3459 3460 pts = [[0, 0, 0]] + pts + [[0, 0, length]] 3461 diff = diff / length 3462 theta = np.arccos(diff[2]) 3463 phi = np.arctan2(diff[1], diff[0]) 3464 sp = Line(pts) 3465 3466 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3467 t.Translate(start_pt) 3468 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3469 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3470 3471 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3472 tf.SetInputData(sp.dataset) 3473 tf.SetTransform(t) 3474 tf.Update() 3475 3476 tuf = vtki.new("TubeFilter") 3477 tuf.SetNumberOfSides(12) 3478 tuf.CappingOn() 3479 tuf.SetInputData(tf.GetOutput()) 3480 if not thickness: 3481 thickness = r1 / 10 3482 tuf.SetRadius(thickness) 3483 tuf.Update() 3484 3485 super().__init__(tuf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3486 3487 self.phong().lighting("metallic") 3488 self.base = np.array(start_pt, dtype=float) 3489 self.top = np.array(end_pt, dtype=float) 3490 self.name = "Spring"
Build a spring of specified nr of coils between start_pt and end_pt.
Arguments:
- coils : (int) number of coils
- r1 : (float) radius at start point
- r2 : (float) radius at end point
- thickness : (float) thickness of the coil section
3493class Cylinder(Mesh): 3494 """ 3495 Build a cylinder of specified height and radius. 3496 """ 3497 3498 def __init__( 3499 self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, height=2.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3500 cap=True, res=24, c="teal3", alpha=1.0 3501 ) -> None: 3502 """ 3503 Build a cylinder of specified height and radius `r`, centered at `pos`. 3504 3505 If `pos` is a list of 2 points, e.g. `pos=[v1, v2]`, build a cylinder with base 3506 centered at `v1` and top at `v2`. 3507 3508 Arguments: 3509 cap : (bool) 3510 enable/disable the caps of the cylinder 3511 res : (int) 3512 resolution of the cylinder sides 3513 3514  3515 """ 3516 if utils.is_sequence(pos[0]): # assume user is passing pos=[base, top] 3517 base = np.array(pos[0], dtype=float) 3518 top = np.array(pos[1], dtype=float) 3519 pos = (base + top) / 2 3520 height = np.linalg.norm(top - base) 3521 axis = top - base 3522 axis = utils.versor(axis) 3523 else: 3524 axis = utils.versor(axis) 3525 base = pos - axis * height / 2 3526 top = pos + axis * height / 2 3527 3528 cyl = vtki.new("CylinderSource") 3529 cyl.SetResolution(res) 3530 cyl.SetRadius(r) 3531 cyl.SetHeight(height) 3532 cyl.SetCapping(cap) 3533 cyl.Update() 3534 3535 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 3536 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 3537 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3538 t.PostMultiply() 3539 t.RotateX(90) # put it along Z 3540 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3541 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3542 t.Translate(pos) 3543 3544 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3545 tf.SetInputData(cyl.GetOutput()) 3546 tf.SetTransform(t) 3547 tf.Update() 3548 3549 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3550 3551 self.phong() 3552 self.base = base 3553 self.top = top 3554 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(pos) 3555 self.name = "Cylinder"
Build a cylinder of specified height and radius.
3498 def __init__( 3499 self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, height=2.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3500 cap=True, res=24, c="teal3", alpha=1.0 3501 ) -> None: 3502 """ 3503 Build a cylinder of specified height and radius `r`, centered at `pos`. 3504 3505 If `pos` is a list of 2 points, e.g. `pos=[v1, v2]`, build a cylinder with base 3506 centered at `v1` and top at `v2`. 3507 3508 Arguments: 3509 cap : (bool) 3510 enable/disable the caps of the cylinder 3511 res : (int) 3512 resolution of the cylinder sides 3513 3514  3515 """ 3516 if utils.is_sequence(pos[0]): # assume user is passing pos=[base, top] 3517 base = np.array(pos[0], dtype=float) 3518 top = np.array(pos[1], dtype=float) 3519 pos = (base + top) / 2 3520 height = np.linalg.norm(top - base) 3521 axis = top - base 3522 axis = utils.versor(axis) 3523 else: 3524 axis = utils.versor(axis) 3525 base = pos - axis * height / 2 3526 top = pos + axis * height / 2 3527 3528 cyl = vtki.new("CylinderSource") 3529 cyl.SetResolution(res) 3530 cyl.SetRadius(r) 3531 cyl.SetHeight(height) 3532 cyl.SetCapping(cap) 3533 cyl.Update() 3534 3535 theta = np.arccos(axis[2]) 3536 phi = np.arctan2(axis[1], axis[0]) 3537 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 3538 t.PostMultiply() 3539 t.RotateX(90) # put it along Z 3540 t.RotateY(np.rad2deg(theta)) 3541 t.RotateZ(np.rad2deg(phi)) 3542 t.Translate(pos) 3543 3544 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 3545 tf.SetInputData(cyl.GetOutput()) 3546 tf.SetTransform(t) 3547 tf.Update() 3548 3549 super().__init__(tf.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3550 3551 self.phong() 3552 self.base = base 3553 self.top = top 3554 self.transform = LinearTransform().translate(pos) 3555 self.name = "Cylinder"
3558class Cone(Mesh): 3559 """Build a cone of specified radius and height.""" 3560 3561 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, height=3.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3562 res=48, c="green3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3563 """Build a cone of specified radius `r` and `height`, centered at `pos`.""" 3564 con = vtki.new("ConeSource") 3565 con.SetResolution(res) 3566 con.SetRadius(r) 3567 con.SetHeight(height) 3568 con.SetDirection(axis) 3569 con.Update() 3570 super().__init__(con.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3571 self.phong() 3572 if len(pos) == 2: 3573 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3574 self.pos(pos) 3575 v = utils.versor(axis) * height / 2 3576 self.base = pos - v 3577 self.top = pos + v 3578 self.name = "Cone"
Build a cone of specified radius and height.
3561 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, height=3.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3562 res=48, c="green3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3563 """Build a cone of specified radius `r` and `height`, centered at `pos`.""" 3564 con = vtki.new("ConeSource") 3565 con.SetResolution(res) 3566 con.SetRadius(r) 3567 con.SetHeight(height) 3568 con.SetDirection(axis) 3569 con.Update() 3570 super().__init__(con.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3571 self.phong() 3572 if len(pos) == 2: 3573 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3574 self.pos(pos) 3575 v = utils.versor(axis) * height / 2 3576 self.base = pos - v 3577 self.top = pos + v 3578 self.name = "Cone"
Build a cone of specified radius r and height, centered at pos.
3581class Pyramid(Cone): 3582 """Build a pyramidal shape.""" 3583 3584 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, height=1.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3585 c="green3", alpha=1) -> None: 3586 """Build a pyramid of specified base size `s` and `height`, centered at `pos`.""" 3587 super().__init__(pos, s, height, axis, 4, c, alpha) 3588 self.name = "Pyramid"
Build a pyramidal shape.
3584 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, height=1.0, axis=(0, 0, 1), 3585 c="green3", alpha=1) -> None: 3586 """Build a pyramid of specified base size `s` and `height`, centered at `pos`.""" 3587 super().__init__(pos, s, height, axis, 4, c, alpha) 3588 self.name = "Pyramid"
Build a pyramid of specified base size s and height, centered at pos.
3591class Torus(Mesh): 3592 """ 3593 Build a toroidal shape. 3594 """ 3595 3596 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r1=1.0, r2=0.2, res=36, quads=False, c="yellow3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3597 """ 3598 Build a torus of specified outer radius `r1` internal radius `r2`, centered at `pos`. 3599 If `quad=True` a quad-mesh is generated. 3600 """ 3601 if utils.is_sequence(res): 3602 res_u, res_v = res 3603 else: 3604 res_u, res_v = 3 * res, res 3605 3606 if quads: 3607 # https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/issues/710 3608 3609 n = res_v 3610 m = res_u 3611 3612 theta = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, n) 3613 phi = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, m) 3614 theta, phi = np.meshgrid(theta, phi) 3615 t = r1 + r2 * np.cos(theta) 3616 x = t * np.cos(phi) 3617 y = t * np.sin(phi) 3618 z = r2 * np.sin(theta) 3619 pts = np.column_stack((x.ravel(), y.ravel(), z.ravel())) 3620 3621 faces = [] 3622 for j in range(m - 1): 3623 j1n = (j + 1) * n 3624 for i in range(n - 1): 3625 faces.append([i + j * n, i + 1 + j * n, i + 1 + j1n, i + j1n]) 3626 3627 super().__init__([pts, faces], c, alpha) 3628 3629 else: 3630 rs = vtki.new("ParametricTorus") 3631 rs.SetRingRadius(r1) 3632 rs.SetCrossSectionRadius(r2) 3633 pfs = vtki.new("ParametricFunctionSource") 3634 pfs.SetParametricFunction(rs) 3635 pfs.SetUResolution(res_u) 3636 pfs.SetVResolution(res_v) 3637 pfs.Update() 3638 3639 super().__init__(pfs.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3640 3641 self.phong() 3642 if len(pos) == 2: 3643 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3644 self.pos(pos) 3645 self.name = "Torus"
Build a toroidal shape.
3596 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), r1=1.0, r2=0.2, res=36, quads=False, c="yellow3", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3597 """ 3598 Build a torus of specified outer radius `r1` internal radius `r2`, centered at `pos`. 3599 If `quad=True` a quad-mesh is generated. 3600 """ 3601 if utils.is_sequence(res): 3602 res_u, res_v = res 3603 else: 3604 res_u, res_v = 3 * res, res 3605 3606 if quads: 3607 # https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/issues/710 3608 3609 n = res_v 3610 m = res_u 3611 3612 theta = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, n) 3613 phi = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, m) 3614 theta, phi = np.meshgrid(theta, phi) 3615 t = r1 + r2 * np.cos(theta) 3616 x = t * np.cos(phi) 3617 y = t * np.sin(phi) 3618 z = r2 * np.sin(theta) 3619 pts = np.column_stack((x.ravel(), y.ravel(), z.ravel())) 3620 3621 faces = [] 3622 for j in range(m - 1): 3623 j1n = (j + 1) * n 3624 for i in range(n - 1): 3625 faces.append([i + j * n, i + 1 + j * n, i + 1 + j1n, i + j1n]) 3626 3627 super().__init__([pts, faces], c, alpha) 3628 3629 else: 3630 rs = vtki.new("ParametricTorus") 3631 rs.SetRingRadius(r1) 3632 rs.SetCrossSectionRadius(r2) 3633 pfs = vtki.new("ParametricFunctionSource") 3634 pfs.SetParametricFunction(rs) 3635 pfs.SetUResolution(res_u) 3636 pfs.SetVResolution(res_v) 3637 pfs.Update() 3638 3639 super().__init__(pfs.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3640 3641 self.phong() 3642 if len(pos) == 2: 3643 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 3644 self.pos(pos) 3645 self.name = "Torus"
Build a torus of specified outer radius r1 internal radius r2, centered at pos.
If quad=True a quad-mesh is generated.
3648class Paraboloid(Mesh): 3649 """ 3650 Build a paraboloid. 3651 """ 3652 3653 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), height=1.0, res=50, c="cyan5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3654 """ 3655 Build a paraboloid of specified height and radius `r`, centered at `pos`. 3656 3657 Full volumetric expression is: 3658 `F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9` 3659 3660  3661 """ 3662 quadric = vtki.new("Quadric") 3663 quadric.SetCoefficients(1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, height / 4, 0) 3664 # F(x,y,z) = a0*x^2 + a1*y^2 + a2*z^2 3665 # + a3*x*y + a4*y*z + a5*x*z 3666 # + a6*x + a7*y + a8*z +a9 3667 sample = vtki.new("SampleFunction") 3668 sample.SetSampleDimensions(res, res, res) 3669 sample.SetImplicitFunction(quadric) 3670 3671 contours = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 3672 contours.SetInputConnection(sample.GetOutputPort()) 3673 contours.GenerateValues(1, 0.01, 0.01) 3674 contours.Update() 3675 3676 super().__init__(contours.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3677 self.compute_normals().phong() 3678 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 3679 self.pos(pos) 3680 self.name = "Paraboloid"
Build a paraboloid.
3653 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), height=1.0, res=50, c="cyan5", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3654 """ 3655 Build a paraboloid of specified height and radius `r`, centered at `pos`. 3656 3657 Full volumetric expression is: 3658 `F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9` 3659 3660  3661 """ 3662 quadric = vtki.new("Quadric") 3663 quadric.SetCoefficients(1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, height / 4, 0) 3664 # F(x,y,z) = a0*x^2 + a1*y^2 + a2*z^2 3665 # + a3*x*y + a4*y*z + a5*x*z 3666 # + a6*x + a7*y + a8*z +a9 3667 sample = vtki.new("SampleFunction") 3668 sample.SetSampleDimensions(res, res, res) 3669 sample.SetImplicitFunction(quadric) 3670 3671 contours = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 3672 contours.SetInputConnection(sample.GetOutputPort()) 3673 contours.GenerateValues(1, 0.01, 0.01) 3674 contours.Update() 3675 3676 super().__init__(contours.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3677 self.compute_normals().phong() 3678 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 3679 self.pos(pos) 3680 self.name = "Paraboloid"
Build a paraboloid of specified height and radius r, centered at pos.
Full volumetric expression is:
F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9

3683class Hyperboloid(Mesh): 3684 """ 3685 Build a hyperboloid. 3686 """ 3687 3688 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), a2=1.0, value=0.5, res=100, c="pink4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3689 """ 3690 Build a hyperboloid of specified aperture `a2` and `height`, centered at `pos`. 3691 3692 Full volumetric expression is: 3693 `F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9` 3694 """ 3695 q = vtki.new("Quadric") 3696 q.SetCoefficients(2, 2, -1 / a2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) 3697 # F(x,y,z) = a0*x^2 + a1*y^2 + a2*z^2 3698 # + a3*x*y + a4*y*z + a5*x*z 3699 # + a6*x + a7*y + a8*z +a9 3700 sample = vtki.new("SampleFunction") 3701 sample.SetSampleDimensions(res, res, res) 3702 sample.SetImplicitFunction(q) 3703 3704 contours = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 3705 contours.SetInputConnection(sample.GetOutputPort()) 3706 contours.GenerateValues(1, value, value) 3707 contours.Update() 3708 3709 super().__init__(contours.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3710 self.compute_normals().phong() 3711 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 3712 self.pos(pos) 3713 self.name = "Hyperboloid"
Build a hyperboloid.
3688 def __init__(self, pos=(0, 0, 0), a2=1.0, value=0.5, res=100, c="pink4", alpha=1.0) -> None: 3689 """ 3690 Build a hyperboloid of specified aperture `a2` and `height`, centered at `pos`. 3691 3692 Full volumetric expression is: 3693 `F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9` 3694 """ 3695 q = vtki.new("Quadric") 3696 q.SetCoefficients(2, 2, -1 / a2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) 3697 # F(x,y,z) = a0*x^2 + a1*y^2 + a2*z^2 3698 # + a3*x*y + a4*y*z + a5*x*z 3699 # + a6*x + a7*y + a8*z +a9 3700 sample = vtki.new("SampleFunction") 3701 sample.SetSampleDimensions(res, res, res) 3702 sample.SetImplicitFunction(q) 3703 3704 contours = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 3705 contours.SetInputConnection(sample.GetOutputPort()) 3706 contours.GenerateValues(1, value, value) 3707 contours.Update() 3708 3709 super().__init__(contours.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 3710 self.compute_normals().phong() 3711 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 3712 self.pos(pos) 3713 self.name = "Hyperboloid"
Build a hyperboloid of specified aperture a2 and height, centered at pos.
Full volumetric expression is:
F(x,y,z)=a_0x^2+a_1y^2+a_2z^2+a_3xy+a_4yz+a_5xz+ a_6x+a_7y+a_8z+a_9
4478class TextBase: 4479 "Base class." 4480 4481 def __init__(self): 4482 "Do not instantiate this base class." 4483 4484 self.rendered_at = set() 4485 # self.properties = None 4486 4487 self.name = "Text" 4488 self.filename = "" 4489 self.time = 0 4490 self.info = {} 4491 4492 if isinstance(settings.default_font, int): 4493 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4494 font = settings.default_font % len(lfonts) 4495 self.fontname = lfonts[font] 4496 else: 4497 self.fontname = settings.default_font 4498 4499 def angle(self, value: float): 4500 """Orientation angle in degrees""" 4501 self.properties.SetOrientation(value) 4502 return self 4503 4504 def line_spacing(self, value: float): 4505 """Set the extra spacing between lines 4506 expressed as a text height multiplicative factor.""" 4507 self.properties.SetLineSpacing(value) 4508 return self 4509 4510 def line_offset(self, value: float): 4511 """Set/Get the vertical offset (measured in pixels).""" 4512 self.properties.SetLineOffset(value) 4513 return self 4514 4515 def bold(self, value=True): 4516 """Set bold face""" 4517 self.properties.SetBold(value) 4518 return self 4519 4520 def italic(self, value=True): 4521 """Set italic face""" 4522 self.properties.SetItalic(value) 4523 return self 4524 4525 def shadow(self, offset=(1, -1)): 4526 """Text shadowing. Set to `None` to disable it.""" 4527 if offset is None: 4528 self.properties.ShadowOff() 4529 else: 4530 self.properties.ShadowOn() 4531 self.properties.SetShadowOffset(offset) 4532 return self 4533 4534 def color(self, c=None): 4535 """Set the text color""" 4536 if c is None: 4537 return get_color(self.properties.GetColor()) 4538 self.properties.SetColor(get_color(c)) 4539 return self 4540 4541 def c(self, color=None): 4542 """Set the text color""" 4543 if color is None: 4544 return get_color(self.properties.GetColor()) 4545 return self.color(color) 4546 4547 def alpha(self, value: float): 4548 """Set the text opacity""" 4549 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(value) 4550 return self 4551 4552 def background(self, color="k9", alpha=1.0): 4553 """Text background. Set to `None` to disable it.""" 4554 bg = get_color(color) 4555 if color is None: 4556 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(0) 4557 else: 4558 self.properties.SetBackgroundColor(bg) 4559 if alpha: 4560 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(alpha) 4561 return self 4562 4563 def frame(self, color="k1", lw=2): 4564 """Border color and width""" 4565 if color is None: 4566 self.properties.FrameOff() 4567 else: 4568 c = get_color(color) 4569 self.properties.FrameOn() 4570 self.properties.SetFrameColor(c) 4571 self.properties.SetFrameWidth(lw) 4572 return self 4573 4574 def font(self, font: str): 4575 """Text font face""" 4576 if isinstance(font, int): 4577 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4578 n = font % len(lfonts) 4579 font = lfonts[n] 4580 self.fontname = font 4581 4582 if not font: # use default font 4583 font = self.fontname 4584 fpath = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".ttf") 4585 elif font.startswith("https"): # user passed URL link, make it a path 4586 fpath = vedo.file_io.download(font, verbose=False, force=False) 4587 elif font.endswith(".ttf"): # user passing a local path to font file 4588 fpath = font 4589 else: # user passing name of preset font 4590 fpath = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".ttf") 4591 4592 if font == "Courier": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToCourier() 4593 elif font == "Times": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToTimes() 4594 elif font == "Arial": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToArial() 4595 else: 4596 fpath = utils.get_font_path(font) 4597 self.properties.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 4598 self.properties.SetFontFile(fpath) 4599 self.fontname = font # io.tonumpy() uses it 4600 4601 return self 4602 4603 def on(self): 4604 """Make text visible""" 4605 self.actor.SetVisibility(True) 4606 return self 4607 4608 def off(self): 4609 """Make text invisible""" 4610 self.actor.SetVisibility(False) 4611 return self
Base class.
4481 def __init__(self): 4482 "Do not instantiate this base class." 4483 4484 self.rendered_at = set() 4485 # self.properties = None 4486 4487 self.name = "Text" 4488 self.filename = "" 4489 self.time = 0 4490 self.info = {} 4491 4492 if isinstance(settings.default_font, int): 4493 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4494 font = settings.default_font % len(lfonts) 4495 self.fontname = lfonts[font] 4496 else: 4497 self.fontname = settings.default_font
Do not instantiate this base class.
4499 def angle(self, value: float): 4500 """Orientation angle in degrees""" 4501 self.properties.SetOrientation(value) 4502 return self
Orientation angle in degrees
4504 def line_spacing(self, value: float): 4505 """Set the extra spacing between lines 4506 expressed as a text height multiplicative factor.""" 4507 self.properties.SetLineSpacing(value) 4508 return self
Set the extra spacing between lines expressed as a text height multiplicative factor.
4510 def line_offset(self, value: float): 4511 """Set/Get the vertical offset (measured in pixels).""" 4512 self.properties.SetLineOffset(value) 4513 return self
Set/Get the vertical offset (measured in pixels).
4515 def bold(self, value=True): 4516 """Set bold face""" 4517 self.properties.SetBold(value) 4518 return self
Set bold face
4520 def italic(self, value=True): 4521 """Set italic face""" 4522 self.properties.SetItalic(value) 4523 return self
Set italic face
4525 def shadow(self, offset=(1, -1)): 4526 """Text shadowing. Set to `None` to disable it.""" 4527 if offset is None: 4528 self.properties.ShadowOff() 4529 else: 4530 self.properties.ShadowOn() 4531 self.properties.SetShadowOffset(offset) 4532 return self
Text shadowing. Set to None to disable it.
4534 def color(self, c=None): 4535 """Set the text color""" 4536 if c is None: 4537 return get_color(self.properties.GetColor()) 4538 self.properties.SetColor(get_color(c)) 4539 return self
Set the text color
4541 def c(self, color=None): 4542 """Set the text color""" 4543 if color is None: 4544 return get_color(self.properties.GetColor()) 4545 return self.color(color)
Set the text color
4547 def alpha(self, value: float): 4548 """Set the text opacity""" 4549 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(value) 4550 return self
Set the text opacity
4552 def background(self, color="k9", alpha=1.0): 4553 """Text background. Set to `None` to disable it.""" 4554 bg = get_color(color) 4555 if color is None: 4556 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(0) 4557 else: 4558 self.properties.SetBackgroundColor(bg) 4559 if alpha: 4560 self.properties.SetBackgroundOpacity(alpha) 4561 return self
Text background. Set to None to disable it.
4563 def frame(self, color="k1", lw=2): 4564 """Border color and width""" 4565 if color is None: 4566 self.properties.FrameOff() 4567 else: 4568 c = get_color(color) 4569 self.properties.FrameOn() 4570 self.properties.SetFrameColor(c) 4571 self.properties.SetFrameWidth(lw) 4572 return self
Border color and width
4574 def font(self, font: str): 4575 """Text font face""" 4576 if isinstance(font, int): 4577 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4578 n = font % len(lfonts) 4579 font = lfonts[n] 4580 self.fontname = font 4581 4582 if not font: # use default font 4583 font = self.fontname 4584 fpath = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".ttf") 4585 elif font.startswith("https"): # user passed URL link, make it a path 4586 fpath = vedo.file_io.download(font, verbose=False, force=False) 4587 elif font.endswith(".ttf"): # user passing a local path to font file 4588 fpath = font 4589 else: # user passing name of preset font 4590 fpath = os.path.join(vedo.fonts_path, font + ".ttf") 4591 4592 if font == "Courier": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToCourier() 4593 elif font == "Times": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToTimes() 4594 elif font == "Arial": self.properties.SetFontFamilyToArial() 4595 else: 4596 fpath = utils.get_font_path(font) 4597 self.properties.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 4598 self.properties.SetFontFile(fpath) 4599 self.fontname = font # io.tonumpy() uses it 4600 4601 return self
Text font face
4139class Text3D(Mesh): 4140 """ 4141 Generate a 3D polygonal Mesh to represent a text string. 4142 """ 4143 4144 def __init__( 4145 self, 4146 txt, 4147 pos=(0, 0, 0), 4148 s=1.0, 4149 font="", 4150 hspacing=1.15, 4151 vspacing=2.15, 4152 depth=0.0, 4153 italic=False, 4154 justify="bottom-left", 4155 literal=False, 4156 c=None, 4157 alpha=1.0, 4158 ) -> None: 4159 """ 4160 Generate a 3D polygonal `Mesh` representing a text string. 4161 4162 Can render strings like `3.7 10^9` or `H_2 O` with subscripts and superscripts. 4163 Most Latex symbols are also supported. 4164 4165 Symbols `~ ^ _` are reserved modifiers: 4166 - use ~ to add a short space, 1/4 of the default empty space, 4167 - use ^ and _ to start up/sub scripting, a space terminates their effect. 4168 4169 Monospaced fonts are: `Calco, ComicMono, Glasgo, SmartCouric, VictorMono, Justino`. 4170 4171 More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4172 4173 Arguments: 4174 pos : (list) 4175 position coordinates in 3D space 4176 s : (float) 4177 vertical size of the text (as scaling factor) 4178 depth : (float) 4179 text thickness (along z) 4180 italic : (bool), float 4181 italic font type (can be a signed float too) 4182 justify : (str) 4183 text justification as centering of the bounding box 4184 (bottom-left, bottom-right, top-left, top-right, centered) 4185 font : (str, int) 4186 some of the available 3D-polygonized fonts are: 4187 Bongas, Calco, Comae, ComicMono, Kanopus, Glasgo, Ubuntu, 4188 LogoType, Normografo, Quikhand, SmartCouric, Theemim, VictorMono, VTK, 4189 Capsmall, Cartoons123, Vega, Justino, Spears, Meson. 4190 4191 Check for more at https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4192 4193 Or type in your terminal `vedo --run fonts`. 4194 4195 Default is Normografo, which can be changed using `settings.default_font`. 4196 4197 hspacing : (float) 4198 horizontal spacing of the font 4199 vspacing : (float) 4200 vertical spacing of the font for multiple lines text 4201 literal : (bool) 4202 if set to True will ignore modifiers like _ or ^ 4203 4204 Examples: 4205 - [markpoint.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/markpoint.py) 4206 - [fonts.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/fonts.py) 4207 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 4208 4209  4210 4211 .. note:: Type `vedo -r fonts` for a demo. 4212 """ 4213 if len(pos) == 2: 4214 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 4215 4216 if c is None: # automatic black or white 4217 pli = vedo.plotter_instance 4218 if pli and pli.renderer: 4219 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4220 if pli.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4221 bgcol = pli.renderer.GetBackground2() 4222 else: 4223 bgcol = pli.renderer.GetBackground() 4224 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4225 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4226 else: 4227 c = (0.6, 0.6, 0.6) 4228 4229 tpoly = self._get_text3d_poly( 4230 txt, s, font, hspacing, vspacing, depth, italic, justify, literal 4231 ) 4232 4233 super().__init__(tpoly, c, alpha) 4234 4235 self.pos(pos) 4236 self.lighting("off") 4237 4238 self.actor.PickableOff() 4239 self.actor.DragableOff() 4240 self.init_scale = s 4241 self.name = "Text3D" 4242 self.txt = txt 4243 self.justify = justify 4244 4245 def text( 4246 self, 4247 txt=None, 4248 s=1, 4249 font="", 4250 hspacing=1.15, 4251 vspacing=2.15, 4252 depth=0, 4253 italic=False, 4254 justify="", 4255 literal=False, 4256 ) -> "Text3D": 4257 """ 4258 Update the text and some of its properties. 4259 4260 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 4261 """ 4262 if txt is None: 4263 return self.txt 4264 if not justify: 4265 justify = self.justify 4266 4267 poly = self._get_text3d_poly( 4268 txt, self.init_scale * s, font, hspacing, vspacing, 4269 depth, italic, justify, literal 4270 ) 4271 4272 # apply the current transformation to the new polydata 4273 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 4274 tf.SetInputData(poly) 4275 tf.SetTransform(self.transform.T) 4276 tf.Update() 4277 tpoly = tf.GetOutput() 4278 4279 self._update(tpoly) 4280 self.txt = txt 4281 return self 4282 4283 @staticmethod 4284 def _get_text3d_poly( 4285 txt, 4286 s=1, 4287 font="", 4288 hspacing=1.15, 4289 vspacing=2.15, 4290 depth=0, 4291 italic=False, 4292 justify="bottom-left", 4293 literal=False, 4294 ) -> vtki.vtkPolyData: 4295 if not font: 4296 font = settings.default_font 4297 4298 txt = str(txt) 4299 4300 if font == "VTK": ####################################### 4301 vtt = vtki.new("VectorText") 4302 vtt.SetText(txt) 4303 vtt.Update() 4304 tpoly = vtt.GetOutput() 4305 4306 else: ################################################### 4307 4308 stxt = set(txt) # check here if null or only spaces 4309 if not txt or (len(stxt) == 1 and " " in stxt): 4310 return vtki.vtkPolyData() 4311 4312 if italic is True: 4313 italic = 1 4314 4315 if isinstance(font, int): 4316 lfonts = list(settings.font_parameters.keys()) 4317 font = font % len(lfonts) 4318 font = lfonts[font] 4319 4320 if font not in settings.font_parameters.keys(): 4321 fpars = settings.font_parameters["Normografo"] 4322 else: 4323 fpars = settings.font_parameters[font] 4324 4325 # ad hoc adjustments 4326 mono = fpars["mono"] 4327 lspacing = fpars["lspacing"] 4328 hspacing *= fpars["hspacing"] 4329 fscale = fpars["fscale"] 4330 dotsep = fpars["dotsep"] 4331 4332 # replacements 4333 if ":" in txt: 4334 for r in _reps: 4335 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4336 4337 if not literal: 4338 reps2 = [ 4339 (r"\_", "┭"), # trick to protect ~ _ and ^ chars 4340 (r"\^", "┮"), # 4341 (r"\~", "┯"), # 4342 ("**", "^"), # order matters 4343 ("e+0", dotsep + "10^"), 4344 ("e-0", dotsep + "10^-"), 4345 ("E+0", dotsep + "10^"), 4346 ("E-0", dotsep + "10^-"), 4347 ("e+", dotsep + "10^"), 4348 ("e-", dotsep + "10^-"), 4349 ("E+", dotsep + "10^"), 4350 ("E-", dotsep + "10^-"), 4351 ] 4352 for r in reps2: 4353 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4354 4355 xmax, ymax, yshift, scale = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 4356 save_xmax = 0.0 4357 4358 notfounds = set() 4359 polyletters = [] 4360 ntxt = len(txt) 4361 for i, t in enumerate(txt): 4362 ########## 4363 if t == "┭": 4364 t = "_" 4365 elif t == "┮": 4366 t = "^" 4367 elif t == "┯": 4368 t = "~" 4369 elif t == "^" and not literal: 4370 if yshift < 0: 4371 xmax = save_xmax 4372 yshift = 0.9 * fscale 4373 scale = 0.5 4374 continue 4375 elif t == "_" and not literal: 4376 if yshift > 0: 4377 xmax = save_xmax 4378 yshift = -0.3 * fscale 4379 scale = 0.5 4380 continue 4381 elif (t in (" ", "\\n")) and yshift: 4382 yshift = 0.0 4383 scale = 1.0 4384 save_xmax = xmax 4385 if t == " ": 4386 continue 4387 elif t == "~": 4388 if i < ntxt - 1 and txt[i + 1] == "_": 4389 continue 4390 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale / 4 4391 continue 4392 4393 ############ 4394 if t == " ": 4395 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale 4396 4397 elif t == "\n": 4398 xmax = 0.0 4399 save_xmax = 0.0 4400 ymax -= vspacing 4401 4402 else: 4403 poly = _get_font_letter(font, t) 4404 if not poly: 4405 notfounds.add(t) 4406 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale 4407 continue 4408 4409 if poly.GetNumberOfPoints() == 0: 4410 continue 4411 4412 tr = vtki.vtkTransform() 4413 tr.Translate(xmax, ymax + yshift, 0) 4414 pscale = scale * fscale / 1000 4415 tr.Scale(pscale, pscale, pscale) 4416 if italic: 4417 tr.Concatenate([1, italic * 0.15, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]) 4418 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 4419 tf.SetInputData(poly) 4420 tf.SetTransform(tr) 4421 tf.Update() 4422 poly = tf.GetOutput() 4423 polyletters.append(poly) 4424 4425 bx = poly.GetBounds() 4426 if mono: 4427 xmax += hspacing * scale * fscale 4428 else: 4429 xmax += bx[1] - bx[0] + hspacing * scale * fscale * lspacing 4430 if yshift == 0: 4431 save_xmax = xmax 4432 4433 if len(polyletters) == 1: 4434 tpoly = polyletters[0] 4435 else: 4436 polyapp = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 4437 for polyd in polyletters: 4438 polyapp.AddInputData(polyd) 4439 polyapp.Update() 4440 tpoly = polyapp.GetOutput() 4441 4442 if notfounds: 4443 wmsg = f"unavailable characters in font name '{font}': {notfounds}." 4444 wmsg += '\nType "vedo -r fonts" for a demo.' 4445 vedo.logger.warning(wmsg) 4446 4447 bb = tpoly.GetBounds() 4448 dx, dy = (bb[1] - bb[0]) / 2 * s, (bb[3] - bb[2]) / 2 * s 4449 shift = -np.array([(bb[1] + bb[0]), (bb[3] + bb[2]), (bb[5] + bb[4])]) * s /2 4450 if "bottom" in justify: shift += np.array([ 0, dy, 0.]) 4451 if "top" in justify: shift += np.array([ 0,-dy, 0.]) 4452 if "left" in justify: shift += np.array([ dx, 0, 0.]) 4453 if "right" in justify: shift += np.array([-dx, 0, 0.]) 4454 4455 if tpoly.GetNumberOfPoints(): 4456 t = vtki.vtkTransform() 4457 t.PostMultiply() 4458 t.Scale(s, s, s) 4459 t.Translate(shift) 4460 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 4461 tf.SetInputData(tpoly) 4462 tf.SetTransform(t) 4463 tf.Update() 4464 tpoly = tf.GetOutput() 4465 4466 if depth: 4467 extrude = vtki.new("LinearExtrusionFilter") 4468 extrude.SetInputData(tpoly) 4469 extrude.SetExtrusionTypeToVectorExtrusion() 4470 extrude.SetVector(0, 0, 1) 4471 extrude.SetScaleFactor(depth * dy) 4472 extrude.Update() 4473 tpoly = extrude.GetOutput() 4474 4475 return tpoly
Generate a 3D polygonal Mesh to represent a text string.
4144 def __init__( 4145 self, 4146 txt, 4147 pos=(0, 0, 0), 4148 s=1.0, 4149 font="", 4150 hspacing=1.15, 4151 vspacing=2.15, 4152 depth=0.0, 4153 italic=False, 4154 justify="bottom-left", 4155 literal=False, 4156 c=None, 4157 alpha=1.0, 4158 ) -> None: 4159 """ 4160 Generate a 3D polygonal `Mesh` representing a text string. 4161 4162 Can render strings like `3.7 10^9` or `H_2 O` with subscripts and superscripts. 4163 Most Latex symbols are also supported. 4164 4165 Symbols `~ ^ _` are reserved modifiers: 4166 - use ~ to add a short space, 1/4 of the default empty space, 4167 - use ^ and _ to start up/sub scripting, a space terminates their effect. 4168 4169 Monospaced fonts are: `Calco, ComicMono, Glasgo, SmartCouric, VictorMono, Justino`. 4170 4171 More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4172 4173 Arguments: 4174 pos : (list) 4175 position coordinates in 3D space 4176 s : (float) 4177 vertical size of the text (as scaling factor) 4178 depth : (float) 4179 text thickness (along z) 4180 italic : (bool), float 4181 italic font type (can be a signed float too) 4182 justify : (str) 4183 text justification as centering of the bounding box 4184 (bottom-left, bottom-right, top-left, top-right, centered) 4185 font : (str, int) 4186 some of the available 3D-polygonized fonts are: 4187 Bongas, Calco, Comae, ComicMono, Kanopus, Glasgo, Ubuntu, 4188 LogoType, Normografo, Quikhand, SmartCouric, Theemim, VictorMono, VTK, 4189 Capsmall, Cartoons123, Vega, Justino, Spears, Meson. 4190 4191 Check for more at https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4192 4193 Or type in your terminal `vedo --run fonts`. 4194 4195 Default is Normografo, which can be changed using `settings.default_font`. 4196 4197 hspacing : (float) 4198 horizontal spacing of the font 4199 vspacing : (float) 4200 vertical spacing of the font for multiple lines text 4201 literal : (bool) 4202 if set to True will ignore modifiers like _ or ^ 4203 4204 Examples: 4205 - [markpoint.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/markpoint.py) 4206 - [fonts.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/fonts.py) 4207 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 4208 4209  4210 4211 .. note:: Type `vedo -r fonts` for a demo. 4212 """ 4213 if len(pos) == 2: 4214 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 4215 4216 if c is None: # automatic black or white 4217 pli = vedo.plotter_instance 4218 if pli and pli.renderer: 4219 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4220 if pli.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4221 bgcol = pli.renderer.GetBackground2() 4222 else: 4223 bgcol = pli.renderer.GetBackground() 4224 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4225 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4226 else: 4227 c = (0.6, 0.6, 0.6) 4228 4229 tpoly = self._get_text3d_poly( 4230 txt, s, font, hspacing, vspacing, depth, italic, justify, literal 4231 ) 4232 4233 super().__init__(tpoly, c, alpha) 4234 4235 self.pos(pos) 4236 self.lighting("off") 4237 4238 self.actor.PickableOff() 4239 self.actor.DragableOff() 4240 self.init_scale = s 4241 self.name = "Text3D" 4242 self.txt = txt 4243 self.justify = justify
Generate a 3D polygonal Mesh representing a text string.
Can render strings like 3.7 10^9 or H_2 O with subscripts and superscripts.
Most Latex symbols are also supported.
Symbols ~ ^ _ are reserved modifiers:
- use ~ to add a short space, 1/4 of the default empty space,
- use ^ and _ to start up/sub scripting, a space terminates their effect.
Monospaced fonts are: Calco, ComicMono, Glasgo, SmartCouric, VictorMono, Justino.
More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/
Arguments:
- pos : (list) position coordinates in 3D space
- s : (float) vertical size of the text (as scaling factor)
- depth : (float) text thickness (along z)
- italic : (bool), float italic font type (can be a signed float too)
- justify : (str) text justification as centering of the bounding box (bottom-left, bottom-right, top-left, top-right, centered)
font : (str, int) some of the available 3D-polygonized fonts are: Bongas, Calco, Comae, ComicMono, Kanopus, Glasgo, Ubuntu, LogoType, Normografo, Quikhand, SmartCouric, Theemim, VictorMono, VTK, Capsmall, Cartoons123, Vega, Justino, Spears, Meson.
Check for more at https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/
Or type in your terminal
vedo --run fonts.Default is Normografo, which can be changed using
settings.default_font.- hspacing : (float) horizontal spacing of the font
- vspacing : (float) vertical spacing of the font for multiple lines text
- literal : (bool) if set to True will ignore modifiers like _ or ^
Examples:
Type vedo -r fonts for a demo.
4245 def text( 4246 self, 4247 txt=None, 4248 s=1, 4249 font="", 4250 hspacing=1.15, 4251 vspacing=2.15, 4252 depth=0, 4253 italic=False, 4254 justify="", 4255 literal=False, 4256 ) -> "Text3D": 4257 """ 4258 Update the text and some of its properties. 4259 4260 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 4261 """ 4262 if txt is None: 4263 return self.txt 4264 if not justify: 4265 justify = self.justify 4266 4267 poly = self._get_text3d_poly( 4268 txt, self.init_scale * s, font, hspacing, vspacing, 4269 depth, italic, justify, literal 4270 ) 4271 4272 # apply the current transformation to the new polydata 4273 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 4274 tf.SetInputData(poly) 4275 tf.SetTransform(self.transform.T) 4276 tf.Update() 4277 tpoly = tf.GetOutput() 4278 4279 self._update(tpoly) 4280 self.txt = txt 4281 return self
Update the text and some of its properties.
Check available fonts here.
4613class Text2D(TextBase, vedo.visual.Actor2D): 4614 """ 4615 Create a 2D text object. 4616 """ 4617 def __init__( 4618 self, 4619 txt="", 4620 pos="top-left", 4621 s=1.0, 4622 bg=None, 4623 font="", 4624 justify="", 4625 bold=False, 4626 italic=False, 4627 c=None, 4628 alpha=0.5, 4629 ) -> None: 4630 """ 4631 Create a 2D text object. 4632 4633 All properties of the text, and the text itself, can be changed after creation 4634 (which is especially useful in loops). 4635 4636 Arguments: 4637 pos : (str) 4638 text is placed in one of the 8 positions: 4639 - bottom-left 4640 - bottom-right 4641 - top-left 4642 - top-right 4643 - bottom-middle 4644 - middle-right 4645 - middle-left 4646 - top-middle 4647 4648 If a pair (x,y) is passed as input the 2D text is place at that 4649 position in the coordinate system of the 2D screen (with the 4650 origin sitting at the bottom left). 4651 4652 s : (float) 4653 size of text 4654 bg : (color) 4655 background color 4656 alpha : (float) 4657 background opacity 4658 justify : (str) 4659 text justification 4660 4661 font : (str) 4662 built-in available fonts are: 4663 - Antares 4664 - Arial 4665 - Bongas 4666 - Calco 4667 - Comae 4668 - ComicMono 4669 - Courier 4670 - Glasgo 4671 - Kanopus 4672 - LogoType 4673 - Normografo 4674 - Quikhand 4675 - SmartCouric 4676 - Theemim 4677 - Times 4678 - VictorMono 4679 - More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4680 4681 A path to a `.otf` or `.ttf` font-file can also be supplied as input. 4682 4683 Examples: 4684 - [fonts.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/fonts.py) 4685 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 4686 - [colorcubes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/colorcubes.py) 4687 4688  4689 """ 4690 super().__init__() 4691 self.name = "Text2D" 4692 4693 self.mapper = vtki.new("TextMapper") 4694 self.SetMapper(self.mapper) 4695 4696 self.properties = self.mapper.GetTextProperty() 4697 self.actor = self 4698 self.actor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 4699 4700 self.GetPositionCoordinate().SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport() 4701 4702 # automatic black or white 4703 if c is None: 4704 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4705 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 4706 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4707 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground2() 4708 else: 4709 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground() 4710 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4711 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4712 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4713 4714 self.font(font).color(c).background(bg, alpha).bold(bold).italic(italic) 4715 self.pos(pos, justify).size(s).text(txt).line_spacing(1.2).line_offset(5) 4716 self.PickableOff() 4717 4718 def pos(self, pos="top-left", justify=""): 4719 """ 4720 Set position of the text to draw. Keyword `pos` can be a string 4721 or 2D coordinates in the range [0,1], being (0,0) the bottom left corner. 4722 """ 4723 ajustify = "top-left" # autojustify 4724 if isinstance(pos, str): # corners 4725 ajustify = pos 4726 if "top" in pos: 4727 if "left" in pos: 4728 pos = (0.008, 0.994) 4729 elif "right" in pos: 4730 pos = (0.994, 0.994) 4731 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4732 pos = (0.5, 0.994) 4733 elif "bottom" in pos: 4734 if "left" in pos: 4735 pos = (0.008, 0.008) 4736 elif "right" in pos: 4737 pos = (0.994, 0.008) 4738 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4739 pos = (0.5, 0.008) 4740 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4741 if "left" in pos: 4742 pos = (0.008, 0.5) 4743 elif "right" in pos: 4744 pos = (0.994, 0.5) 4745 else: 4746 pos = (0.5, 0.5) 4747 4748 else: 4749 vedo.logger.warning(f"cannot understand text position {pos}") 4750 pos = (0.008, 0.994) 4751 ajustify = "top-left" 4752 4753 elif len(pos) != 2: 4754 vedo.logger.error("pos must be of length 2 or integer value or string") 4755 raise RuntimeError() 4756 4757 if not justify: 4758 justify = ajustify 4759 4760 self.properties.SetJustificationToLeft() 4761 if "top" in justify: 4762 self.properties.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 4763 if "bottom" in justify: 4764 self.properties.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 4765 if "cent" in justify or "mid" in justify: 4766 self.properties.SetJustificationToCentered() 4767 if "left" in justify: 4768 self.properties.SetJustificationToLeft() 4769 if "right" in justify: 4770 self.properties.SetJustificationToRight() 4771 4772 self.SetPosition(pos) 4773 return self 4774 4775 def text(self, txt=None): 4776 """Set/get the input text string.""" 4777 if txt is None: 4778 return self.mapper.GetInput() 4779 4780 if ":" in txt: 4781 for r in _reps: 4782 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4783 else: 4784 txt = str(txt) 4785 4786 self.mapper.SetInput(txt) 4787 return self 4788 4789 def size(self, s): 4790 """Set the font size.""" 4791 self.properties.SetFontSize(int(s * 22.5)) 4792 return self
Create a 2D text object.
4617 def __init__( 4618 self, 4619 txt="", 4620 pos="top-left", 4621 s=1.0, 4622 bg=None, 4623 font="", 4624 justify="", 4625 bold=False, 4626 italic=False, 4627 c=None, 4628 alpha=0.5, 4629 ) -> None: 4630 """ 4631 Create a 2D text object. 4632 4633 All properties of the text, and the text itself, can be changed after creation 4634 (which is especially useful in loops). 4635 4636 Arguments: 4637 pos : (str) 4638 text is placed in one of the 8 positions: 4639 - bottom-left 4640 - bottom-right 4641 - top-left 4642 - top-right 4643 - bottom-middle 4644 - middle-right 4645 - middle-left 4646 - top-middle 4647 4648 If a pair (x,y) is passed as input the 2D text is place at that 4649 position in the coordinate system of the 2D screen (with the 4650 origin sitting at the bottom left). 4651 4652 s : (float) 4653 size of text 4654 bg : (color) 4655 background color 4656 alpha : (float) 4657 background opacity 4658 justify : (str) 4659 text justification 4660 4661 font : (str) 4662 built-in available fonts are: 4663 - Antares 4664 - Arial 4665 - Bongas 4666 - Calco 4667 - Comae 4668 - ComicMono 4669 - Courier 4670 - Glasgo 4671 - Kanopus 4672 - LogoType 4673 - Normografo 4674 - Quikhand 4675 - SmartCouric 4676 - Theemim 4677 - Times 4678 - VictorMono 4679 - More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/ 4680 4681 A path to a `.otf` or `.ttf` font-file can also be supplied as input. 4682 4683 Examples: 4684 - [fonts.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/fonts.py) 4685 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 4686 - [colorcubes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/colorcubes.py) 4687 4688  4689 """ 4690 super().__init__() 4691 self.name = "Text2D" 4692 4693 self.mapper = vtki.new("TextMapper") 4694 self.SetMapper(self.mapper) 4695 4696 self.properties = self.mapper.GetTextProperty() 4697 self.actor = self 4698 self.actor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 4699 4700 self.GetPositionCoordinate().SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport() 4701 4702 # automatic black or white 4703 if c is None: 4704 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4705 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 4706 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4707 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground2() 4708 else: 4709 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground() 4710 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4711 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4712 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4713 4714 self.font(font).color(c).background(bg, alpha).bold(bold).italic(italic) 4715 self.pos(pos, justify).size(s).text(txt).line_spacing(1.2).line_offset(5) 4716 self.PickableOff()
Create a 2D text object.
All properties of the text, and the text itself, can be changed after creation (which is especially useful in loops).
Arguments:
pos : (str) text is placed in one of the 8 positions:
- bottom-left
- bottom-right
- top-left
- top-right
- bottom-middle
- middle-right
- middle-left
- top-middle
If a pair (x,y) is passed as input the 2D text is place at that position in the coordinate system of the 2D screen (with the origin sitting at the bottom left).
- s : (float) size of text
- bg : (color) background color
- alpha : (float) background opacity
- justify : (str) text justification
font : (str) built-in available fonts are:
- Antares
- Arial
- Bongas
- Calco
- Comae
- ComicMono
- Courier
- Glasgo
- Kanopus
- LogoType
- Normografo
- Quikhand
- SmartCouric
- Theemim
- Times
- VictorMono
- More fonts at: https://vedo.embl.es/fonts/
A path to a
.otfor.ttffont-file can also be supplied as input.
Examples:
591 @property 592 def mapper(self): 593 """Get the internal vtkMapper.""" 594 return self.GetMapper()
Get the internal vtkMapper.
4718 def pos(self, pos="top-left", justify=""): 4719 """ 4720 Set position of the text to draw. Keyword `pos` can be a string 4721 or 2D coordinates in the range [0,1], being (0,0) the bottom left corner. 4722 """ 4723 ajustify = "top-left" # autojustify 4724 if isinstance(pos, str): # corners 4725 ajustify = pos 4726 if "top" in pos: 4727 if "left" in pos: 4728 pos = (0.008, 0.994) 4729 elif "right" in pos: 4730 pos = (0.994, 0.994) 4731 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4732 pos = (0.5, 0.994) 4733 elif "bottom" in pos: 4734 if "left" in pos: 4735 pos = (0.008, 0.008) 4736 elif "right" in pos: 4737 pos = (0.994, 0.008) 4738 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4739 pos = (0.5, 0.008) 4740 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: 4741 if "left" in pos: 4742 pos = (0.008, 0.5) 4743 elif "right" in pos: 4744 pos = (0.994, 0.5) 4745 else: 4746 pos = (0.5, 0.5) 4747 4748 else: 4749 vedo.logger.warning(f"cannot understand text position {pos}") 4750 pos = (0.008, 0.994) 4751 ajustify = "top-left" 4752 4753 elif len(pos) != 2: 4754 vedo.logger.error("pos must be of length 2 or integer value or string") 4755 raise RuntimeError() 4756 4757 if not justify: 4758 justify = ajustify 4759 4760 self.properties.SetJustificationToLeft() 4761 if "top" in justify: 4762 self.properties.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 4763 if "bottom" in justify: 4764 self.properties.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 4765 if "cent" in justify or "mid" in justify: 4766 self.properties.SetJustificationToCentered() 4767 if "left" in justify: 4768 self.properties.SetJustificationToLeft() 4769 if "right" in justify: 4770 self.properties.SetJustificationToRight() 4771 4772 self.SetPosition(pos) 4773 return self
Set position of the text to draw. Keyword pos can be a string
or 2D coordinates in the range [0,1], being (0,0) the bottom left corner.
4775 def text(self, txt=None): 4776 """Set/get the input text string.""" 4777 if txt is None: 4778 return self.mapper.GetInput() 4779 4780 if ":" in txt: 4781 for r in _reps: 4782 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4783 else: 4784 txt = str(txt) 4785 4786 self.mapper.SetInput(txt) 4787 return self
Set/get the input text string.
4795class CornerAnnotation(TextBase, vtki.vtkCornerAnnotation): 4796 # PROBABLY USELESS given that Text2D does pretty much the same ... 4797 """ 4798 Annotate the window corner with 2D text. 4799 4800 See `Text2D` description as the basic functionality is very similar. 4801 4802 The added value of this class is the possibility to manage with one single 4803 object the all corner annotations (instead of creating 4 `Text2D` instances). 4804 4805 Examples: 4806 - [timer_callback2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/timer_callback2.py) 4807 """ 4808 4809 def __init__(self, c=None) -> None: 4810 4811 super().__init__() 4812 4813 self.properties = self.GetTextProperty() 4814 4815 # automatic black or white 4816 if c is None: 4817 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 4818 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4819 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4820 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground2() 4821 else: 4822 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground() 4823 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4824 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4825 else: 4826 c = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) 4827 4828 self.SetNonlinearFontScaleFactor(1 / 2.75) 4829 self.PickableOff() 4830 self.properties.SetColor(get_color(c)) 4831 self.properties.SetBold(False) 4832 self.properties.SetItalic(False) 4833 4834 def size(self, s:float, linear=False) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4835 """ 4836 The font size is calculated as the largest possible value such that the annotations 4837 for the given viewport do not overlap. 4838 4839 This font size can be scaled non-linearly with the viewport size, to maintain an 4840 acceptable readable size at larger viewport sizes, without being too big. 4841 `f' = linearScale * pow(f,nonlinearScale)` 4842 """ 4843 if linear: 4844 self.SetLinearFontScaleFactor(s * 5.5) 4845 else: 4846 self.SetNonlinearFontScaleFactor(s / 2.75) 4847 return self 4848 4849 def text(self, txt: str, pos=2) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4850 """Set text at the assigned position""" 4851 4852 if isinstance(pos, str): # corners 4853 if "top" in pos: 4854 if "left" in pos: pos = 2 4855 elif "right" in pos: pos = 3 4856 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: pos = 7 4857 elif "bottom" in pos: 4858 if "left" in pos: pos = 0 4859 elif "right" in pos: pos = 1 4860 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: pos = 4 4861 else: 4862 if "left" in pos: pos = 6 4863 elif "right" in pos: pos = 5 4864 else: pos = 2 4865 4866 if "\\" in repr(txt): 4867 for r in _reps: 4868 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4869 else: 4870 txt = str(txt) 4871 4872 self.SetText(pos, txt) 4873 return self 4874 4875 def clear(self) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4876 """Remove all text from all corners""" 4877 self.ClearAllTexts() 4878 return self
Annotate the window corner with 2D text.
See Text2D description as the basic functionality is very similar.
The added value of this class is the possibility to manage with one single
object the all corner annotations (instead of creating 4 Text2D instances).
Examples:
4809 def __init__(self, c=None) -> None: 4810 4811 super().__init__() 4812 4813 self.properties = self.GetTextProperty() 4814 4815 # automatic black or white 4816 if c is None: 4817 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 4818 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 4819 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetGradientBackground(): 4820 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground2() 4821 else: 4822 bgcol = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer.GetBackground() 4823 if np.sum(bgcol) > 1.5: 4824 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 4825 else: 4826 c = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) 4827 4828 self.SetNonlinearFontScaleFactor(1 / 2.75) 4829 self.PickableOff() 4830 self.properties.SetColor(get_color(c)) 4831 self.properties.SetBold(False) 4832 self.properties.SetItalic(False)
Do not instantiate this base class.
4834 def size(self, s:float, linear=False) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4835 """ 4836 The font size is calculated as the largest possible value such that the annotations 4837 for the given viewport do not overlap. 4838 4839 This font size can be scaled non-linearly with the viewport size, to maintain an 4840 acceptable readable size at larger viewport sizes, without being too big. 4841 `f' = linearScale * pow(f,nonlinearScale)` 4842 """ 4843 if linear: 4844 self.SetLinearFontScaleFactor(s * 5.5) 4845 else: 4846 self.SetNonlinearFontScaleFactor(s / 2.75) 4847 return self
The font size is calculated as the largest possible value such that the annotations for the given viewport do not overlap.
This font size can be scaled non-linearly with the viewport size, to maintain an
acceptable readable size at larger viewport sizes, without being too big.
f' = linearScale * pow(f,nonlinearScale)
4849 def text(self, txt: str, pos=2) -> "CornerAnnotation": 4850 """Set text at the assigned position""" 4851 4852 if isinstance(pos, str): # corners 4853 if "top" in pos: 4854 if "left" in pos: pos = 2 4855 elif "right" in pos: pos = 3 4856 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: pos = 7 4857 elif "bottom" in pos: 4858 if "left" in pos: pos = 0 4859 elif "right" in pos: pos = 1 4860 elif "mid" in pos or "cent" in pos: pos = 4 4861 else: 4862 if "left" in pos: pos = 6 4863 elif "right" in pos: pos = 5 4864 else: pos = 2 4865 4866 if "\\" in repr(txt): 4867 for r in _reps: 4868 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 4869 else: 4870 txt = str(txt) 4871 4872 self.SetText(pos, txt) 4873 return self
Set text at the assigned position
4881class Latex(Image): 4882 """ 4883 Render Latex text and formulas. 4884 """ 4885 4886 def __init__(self, formula, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, bg=None, res=150, usetex=False, c="k", alpha=1.0) -> None: 4887 """ 4888 Render Latex text and formulas. 4889 4890 Arguments: 4891 formula : (str) 4892 latex text string 4893 pos : (list) 4894 position coordinates in space 4895 bg : (color) 4896 background color box 4897 res : (int) 4898 dpi resolution 4899 usetex : (bool) 4900 use latex compiler of matplotlib if available 4901 4902 You can access the latex formula in `Latex.formula`. 4903 4904 Examples: 4905 - [latex.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/latex.py) 4906 4907  4908 """ 4909 from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile 4910 import matplotlib.pyplot as mpltib 4911 4912 def build_img_plt(formula, tfile): 4913 4914 mpltib.rc("text", usetex=usetex) 4915 4916 formula1 = "$" + formula + "$" 4917 mpltib.axis("off") 4918 col = get_color(c) 4919 if bg: 4920 bx = dict(boxstyle="square", ec=col, fc=get_color(bg)) 4921 else: 4922 bx = None 4923 mpltib.text( 4924 0.5, 4925 0.5, 4926 formula1, 4927 size=res, 4928 color=col, 4929 alpha=alpha, 4930 ha="center", 4931 va="center", 4932 bbox=bx, 4933 ) 4934 mpltib.savefig( 4935 tfile, format="png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight", pad_inches=0 4936 ) 4937 mpltib.close() 4938 4939 if len(pos) == 2: 4940 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 4941 4942 tmp_file = NamedTemporaryFile(delete=True) 4943 tmp_file.name = tmp_file.name + ".png" 4944 4945 build_img_plt(formula, tmp_file.name) 4946 4947 super().__init__(tmp_file.name, channels=4) 4948 self.alpha(alpha) 4949 self.scale([0.25 / res * s, 0.25 / res * s, 0.25 / res * s]) 4950 self.pos(pos) 4951 self.name = "Latex" 4952 self.formula = formula 4953 4954 # except: 4955 # printc("Error in Latex()\n", formula, c="r") 4956 # printc(" latex or dvipng not installed?", c="r") 4957 # printc(" Try: usetex=False", c="r") 4958 # printc(" Try: sudo apt install dvipng", c="r")
Render Latex text and formulas.
4886 def __init__(self, formula, pos=(0, 0, 0), s=1.0, bg=None, res=150, usetex=False, c="k", alpha=1.0) -> None: 4887 """ 4888 Render Latex text and formulas. 4889 4890 Arguments: 4891 formula : (str) 4892 latex text string 4893 pos : (list) 4894 position coordinates in space 4895 bg : (color) 4896 background color box 4897 res : (int) 4898 dpi resolution 4899 usetex : (bool) 4900 use latex compiler of matplotlib if available 4901 4902 You can access the latex formula in `Latex.formula`. 4903 4904 Examples: 4905 - [latex.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/latex.py) 4906 4907  4908 """ 4909 from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile 4910 import matplotlib.pyplot as mpltib 4911 4912 def build_img_plt(formula, tfile): 4913 4914 mpltib.rc("text", usetex=usetex) 4915 4916 formula1 = "$" + formula + "$" 4917 mpltib.axis("off") 4918 col = get_color(c) 4919 if bg: 4920 bx = dict(boxstyle="square", ec=col, fc=get_color(bg)) 4921 else: 4922 bx = None 4923 mpltib.text( 4924 0.5, 4925 0.5, 4926 formula1, 4927 size=res, 4928 color=col, 4929 alpha=alpha, 4930 ha="center", 4931 va="center", 4932 bbox=bx, 4933 ) 4934 mpltib.savefig( 4935 tfile, format="png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight", pad_inches=0 4936 ) 4937 mpltib.close() 4938 4939 if len(pos) == 2: 4940 pos = (pos[0], pos[1], 0) 4941 4942 tmp_file = NamedTemporaryFile(delete=True) 4943 tmp_file.name = tmp_file.name + ".png" 4944 4945 build_img_plt(formula, tmp_file.name) 4946 4947 super().__init__(tmp_file.name, channels=4) 4948 self.alpha(alpha) 4949 self.scale([0.25 / res * s, 0.25 / res * s, 0.25 / res * s]) 4950 self.pos(pos) 4951 self.name = "Latex" 4952 self.formula = formula 4953 4954 # except: 4955 # printc("Error in Latex()\n", formula, c="r") 4956 # printc(" latex or dvipng not installed?", c="r") 4957 # printc(" Try: usetex=False", c="r") 4958 # printc(" Try: sudo apt install dvipng", c="r")
Render Latex text and formulas.
Arguments:
- formula : (str) latex text string
- pos : (list) position coordinates in space
- bg : (color) background color box
- res : (int) dpi resolution
- usetex : (bool) use latex compiler of matplotlib if available
You can access the latex formula in Latex.formula.
Examples:
153class Glyph(Mesh): 154 """ 155 At each vertex of a mesh, another mesh, i.e. a "glyph", is shown with 156 various orientation options and coloring. 157 158 The input can also be a simple list of 2D or 3D coordinates. 159 Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the orientation 160 vectors in `orientation_array`. 161 """ 162 163 def __init__( 164 self, 165 mesh, 166 glyph, 167 orientation_array=None, 168 scale_by_scalar=False, 169 scale_by_vector_size=False, 170 scale_by_vector_components=False, 171 color_by_scalar=False, 172 color_by_vector_size=False, 173 c="k8", 174 alpha=1.0, 175 ) -> None: 176 """ 177 Arguments: 178 orientation_array: (list, str, vtkArray) 179 list of vectors, `vtkArray` or name of an already existing pointdata array 180 scale_by_scalar : (bool) 181 glyph mesh is scaled by the active scalars 182 scale_by_vector_size : (bool) 183 glyph mesh is scaled by the size of the vectors 184 scale_by_vector_components : (bool) 185 glyph mesh is scaled by the 3 vectors components 186 color_by_scalar : (bool) 187 glyph mesh is colored based on the scalar value 188 color_by_vector_size : (bool) 189 glyph mesh is colored based on the vector size 190 191 Examples: 192 - [glyphs1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs1.py) 193 - [glyphs2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs2.py) 194 195  196 """ 197 if utils.is_sequence(mesh): 198 # create a cloud of points 199 poly = utils.buildPolyData(mesh) 200 else: 201 poly = mesh.dataset 202 203 cmap = "" 204 if isinstance(c, str) and c in cmaps_names: 205 cmap = c 206 c = None 207 elif utils.is_sequence(c): # user passing an array of point colors 208 ucols = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 209 ucols.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 210 ucols.SetName("GlyphRGB") 211 for col in c: 212 cl = get_color(col) 213 ucols.InsertNextTuple3(cl[0] * 255, cl[1] * 255, cl[2] * 255) 214 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(ucols) 215 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("GlyphRGB") 216 c = None 217 218 gly = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 219 gly.GeneratePointIdsOn() 220 gly.SetInputData(poly) 221 try: 222 gly.SetSourceData(glyph) 223 except TypeError: 224 gly.SetSourceData(glyph.dataset) 225 226 if scale_by_scalar: 227 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByScalar() 228 elif scale_by_vector_size: 229 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByVector() 230 elif scale_by_vector_components: 231 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByVectorComponents() 232 else: 233 gly.SetScaleModeToDataScalingOff() 234 235 if color_by_vector_size: 236 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 237 gly.SetColorModeToColorByVector() 238 elif color_by_scalar: 239 gly.SetColorModeToColorByScalar() 240 else: 241 gly.SetColorModeToColorByScale() 242 243 if orientation_array is not None: 244 gly.OrientOn() 245 if isinstance(orientation_array, str): 246 if orientation_array.lower() == "normals": 247 gly.SetVectorModeToUseNormal() 248 else: # passing a name 249 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveVectors(orientation_array) 250 gly.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, 0, orientation_array) 251 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 252 elif utils.is_sequence(orientation_array): # passing a list 253 varr = vtki.vtkFloatArray() 254 varr.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 255 varr.SetName("glyph_vectors") 256 for v in orientation_array: 257 varr.InsertNextTuple(v) 258 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 259 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveVectors("glyph_vectors") 260 gly.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, 0, "glyph_vectors") 261 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 262 263 gly.Update() 264 265 super().__init__(gly.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 266 self.flat() 267 268 if cmap: 269 self.cmap(cmap, "VectorMagnitude") 270 elif c is None: 271 self.pointdata.select("GlyphRGB") 272 273 self.name = "Glyph"
At each vertex of a mesh, another mesh, i.e. a "glyph", is shown with various orientation options and coloring.
The input can also be a simple list of 2D or 3D coordinates.
Color can be specified as a colormap which maps the size of the orientation
vectors in orientation_array.
163 def __init__( 164 self, 165 mesh, 166 glyph, 167 orientation_array=None, 168 scale_by_scalar=False, 169 scale_by_vector_size=False, 170 scale_by_vector_components=False, 171 color_by_scalar=False, 172 color_by_vector_size=False, 173 c="k8", 174 alpha=1.0, 175 ) -> None: 176 """ 177 Arguments: 178 orientation_array: (list, str, vtkArray) 179 list of vectors, `vtkArray` or name of an already existing pointdata array 180 scale_by_scalar : (bool) 181 glyph mesh is scaled by the active scalars 182 scale_by_vector_size : (bool) 183 glyph mesh is scaled by the size of the vectors 184 scale_by_vector_components : (bool) 185 glyph mesh is scaled by the 3 vectors components 186 color_by_scalar : (bool) 187 glyph mesh is colored based on the scalar value 188 color_by_vector_size : (bool) 189 glyph mesh is colored based on the vector size 190 191 Examples: 192 - [glyphs1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs1.py) 193 - [glyphs2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/glyphs2.py) 194 195  196 """ 197 if utils.is_sequence(mesh): 198 # create a cloud of points 199 poly = utils.buildPolyData(mesh) 200 else: 201 poly = mesh.dataset 202 203 cmap = "" 204 if isinstance(c, str) and c in cmaps_names: 205 cmap = c 206 c = None 207 elif utils.is_sequence(c): # user passing an array of point colors 208 ucols = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 209 ucols.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 210 ucols.SetName("GlyphRGB") 211 for col in c: 212 cl = get_color(col) 213 ucols.InsertNextTuple3(cl[0] * 255, cl[1] * 255, cl[2] * 255) 214 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(ucols) 215 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("GlyphRGB") 216 c = None 217 218 gly = vtki.vtkGlyph3D() 219 gly.GeneratePointIdsOn() 220 gly.SetInputData(poly) 221 try: 222 gly.SetSourceData(glyph) 223 except TypeError: 224 gly.SetSourceData(glyph.dataset) 225 226 if scale_by_scalar: 227 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByScalar() 228 elif scale_by_vector_size: 229 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByVector() 230 elif scale_by_vector_components: 231 gly.SetScaleModeToScaleByVectorComponents() 232 else: 233 gly.SetScaleModeToDataScalingOff() 234 235 if color_by_vector_size: 236 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 237 gly.SetColorModeToColorByVector() 238 elif color_by_scalar: 239 gly.SetColorModeToColorByScalar() 240 else: 241 gly.SetColorModeToColorByScale() 242 243 if orientation_array is not None: 244 gly.OrientOn() 245 if isinstance(orientation_array, str): 246 if orientation_array.lower() == "normals": 247 gly.SetVectorModeToUseNormal() 248 else: # passing a name 249 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveVectors(orientation_array) 250 gly.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, 0, orientation_array) 251 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 252 elif utils.is_sequence(orientation_array): # passing a list 253 varr = vtki.vtkFloatArray() 254 varr.SetNumberOfComponents(3) 255 varr.SetName("glyph_vectors") 256 for v in orientation_array: 257 varr.InsertNextTuple(v) 258 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 259 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveVectors("glyph_vectors") 260 gly.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, 0, "glyph_vectors") 261 gly.SetVectorModeToUseVector() 262 263 gly.Update() 264 265 super().__init__(gly.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 266 self.flat() 267 268 if cmap: 269 self.cmap(cmap, "VectorMagnitude") 270 elif c is None: 271 self.pointdata.select("GlyphRGB") 272 273 self.name = "Glyph"
Arguments:
- orientation_array: (list, str, vtkArray)
list of vectors,
vtkArrayor name of an already existing pointdata array - scale_by_scalar : (bool) glyph mesh is scaled by the active scalars
- scale_by_vector_size : (bool) glyph mesh is scaled by the size of the vectors
- scale_by_vector_components : (bool) glyph mesh is scaled by the 3 vectors components
- color_by_scalar : (bool) glyph mesh is colored based on the scalar value
- color_by_vector_size : (bool) glyph mesh is colored based on the vector size
Examples:
276class Tensors(Mesh): 277 """ 278 Geometric representation of tensors defined on a domain or set of points. 279 Tensors can be scaled and/or rotated according to the source at each input point. 280 Scaling and rotation is controlled by the eigenvalues/eigenvectors of the 281 symmetrical part of the tensor as follows: 282 283 For each tensor, the eigenvalues (and associated eigenvectors) are sorted 284 to determine the major, medium, and minor eigenvalues/eigenvectors. 285 The eigenvalue decomposition only makes sense for symmetric tensors, 286 hence the need to only consider the symmetric part of the tensor, 287 which is `1/2*(T+T.transposed())`. 288 """ 289 290 def __init__( 291 self, 292 domain, 293 source="ellipsoid", 294 use_eigenvalues=True, 295 is_symmetric=True, 296 three_axes=False, 297 scale=1.0, 298 max_scale=None, 299 length=None, 300 res=24, 301 c=None, 302 alpha=1.0, 303 ) -> None: 304 """ 305 Arguments: 306 source : (str, Mesh) 307 preset types of source shapes is "ellipsoid", "cylinder", "cube" or a `Mesh` object. 308 use_eigenvalues : (bool) 309 color source glyph using the eigenvalues or by scalars 310 three_axes : (bool) 311 if `False` scale the source in the x-direction, 312 the medium in the y-direction, and the minor in the z-direction. 313 Then, the source is rotated so that the glyph's local x-axis lies 314 along the major eigenvector, y-axis along the medium eigenvector, 315 and z-axis along the minor. 316 317 If `True` three sources are produced, each of them oriented along an eigenvector 318 and scaled according to the corresponding eigenvector. 319 is_symmetric : (bool) 320 If `True` each source glyph is mirrored (2 or 6 glyphs will be produced). 321 The x-axis of the source glyph will correspond to the eigenvector on output. 322 length : (float) 323 distance from the origin to the tip of the source glyph along the x-axis 324 scale : (float) 325 scaling factor of the source glyph. 326 max_scale : (float) 327 clamp scaling at this factor. 328 329 Examples: 330 - [tensors.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/volumetric/tensors.py) 331 - [tensor_grid1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/tensor_grid1.py) 332 - [tensor_grid2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/tensor_grid2.py) 333 334  335 """ 336 if isinstance(source, Points): 337 src = source.dataset 338 else: # is string 339 if "ellip" in source: 340 src = vtki.new("SphereSource") 341 src.SetPhiResolution(res) 342 src.SetThetaResolution(res*2) 343 elif "cyl" in source: 344 src = vtki.new("CylinderSource") 345 src.SetResolution(res) 346 src.CappingOn() 347 elif source == "cube": 348 src = vtki.new("CubeSource") 349 else: 350 vedo.logger.error(f"Unknown source type {source}") 351 raise ValueError() 352 src.Update() 353 src = src.GetOutput() 354 355 tg = vtki.new("TensorGlyph") 356 if isinstance(domain, vtki.vtkPolyData): 357 tg.SetInputData(domain) 358 else: 359 tg.SetInputData(domain.dataset) 360 tg.SetSourceData(src) 361 362 if c is None: 363 tg.ColorGlyphsOn() 364 else: 365 tg.ColorGlyphsOff() 366 367 tg.SetSymmetric(int(is_symmetric)) 368 369 if length is not None: 370 tg.SetLength(length) 371 if use_eigenvalues: 372 tg.ExtractEigenvaluesOn() 373 tg.SetColorModeToEigenvalues() 374 else: 375 tg.SetColorModeToScalars() 376 377 tg.SetThreeGlyphs(three_axes) 378 tg.ScalingOn() 379 tg.SetScaleFactor(scale) 380 if max_scale is None: 381 tg.ClampScalingOn() 382 max_scale = scale * 10 383 tg.SetMaxScaleFactor(max_scale) 384 385 tg.Update() 386 tgn = vtki.new("PolyDataNormals") 387 tgn.ComputeCellNormalsOff() 388 tgn.SetInputData(tg.GetOutput()) 389 tgn.Update() 390 391 super().__init__(tgn.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 392 self.name = "Tensors"
Geometric representation of tensors defined on a domain or set of points. Tensors can be scaled and/or rotated according to the source at each input point. Scaling and rotation is controlled by the eigenvalues/eigenvectors of the symmetrical part of the tensor as follows:
For each tensor, the eigenvalues (and associated eigenvectors) are sorted
to determine the major, medium, and minor eigenvalues/eigenvectors.
The eigenvalue decomposition only makes sense for symmetric tensors,
hence the need to only consider the symmetric part of the tensor,
which is 1/2*(T+T.transposed()).
290 def __init__( 291 self, 292 domain, 293 source="ellipsoid", 294 use_eigenvalues=True, 295 is_symmetric=True, 296 three_axes=False, 297 scale=1.0, 298 max_scale=None, 299 length=None, 300 res=24, 301 c=None, 302 alpha=1.0, 303 ) -> None: 304 """ 305 Arguments: 306 source : (str, Mesh) 307 preset types of source shapes is "ellipsoid", "cylinder", "cube" or a `Mesh` object. 308 use_eigenvalues : (bool) 309 color source glyph using the eigenvalues or by scalars 310 three_axes : (bool) 311 if `False` scale the source in the x-direction, 312 the medium in the y-direction, and the minor in the z-direction. 313 Then, the source is rotated so that the glyph's local x-axis lies 314 along the major eigenvector, y-axis along the medium eigenvector, 315 and z-axis along the minor. 316 317 If `True` three sources are produced, each of them oriented along an eigenvector 318 and scaled according to the corresponding eigenvector. 319 is_symmetric : (bool) 320 If `True` each source glyph is mirrored (2 or 6 glyphs will be produced). 321 The x-axis of the source glyph will correspond to the eigenvector on output. 322 length : (float) 323 distance from the origin to the tip of the source glyph along the x-axis 324 scale : (float) 325 scaling factor of the source glyph. 326 max_scale : (float) 327 clamp scaling at this factor. 328 329 Examples: 330 - [tensors.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/volumetric/tensors.py) 331 - [tensor_grid1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/tensor_grid1.py) 332 - [tensor_grid2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/tensor_grid2.py) 333 334  335 """ 336 if isinstance(source, Points): 337 src = source.dataset 338 else: # is string 339 if "ellip" in source: 340 src = vtki.new("SphereSource") 341 src.SetPhiResolution(res) 342 src.SetThetaResolution(res*2) 343 elif "cyl" in source: 344 src = vtki.new("CylinderSource") 345 src.SetResolution(res) 346 src.CappingOn() 347 elif source == "cube": 348 src = vtki.new("CubeSource") 349 else: 350 vedo.logger.error(f"Unknown source type {source}") 351 raise ValueError() 352 src.Update() 353 src = src.GetOutput() 354 355 tg = vtki.new("TensorGlyph") 356 if isinstance(domain, vtki.vtkPolyData): 357 tg.SetInputData(domain) 358 else: 359 tg.SetInputData(domain.dataset) 360 tg.SetSourceData(src) 361 362 if c is None: 363 tg.ColorGlyphsOn() 364 else: 365 tg.ColorGlyphsOff() 366 367 tg.SetSymmetric(int(is_symmetric)) 368 369 if length is not None: 370 tg.SetLength(length) 371 if use_eigenvalues: 372 tg.ExtractEigenvaluesOn() 373 tg.SetColorModeToEigenvalues() 374 else: 375 tg.SetColorModeToScalars() 376 377 tg.SetThreeGlyphs(three_axes) 378 tg.ScalingOn() 379 tg.SetScaleFactor(scale) 380 if max_scale is None: 381 tg.ClampScalingOn() 382 max_scale = scale * 10 383 tg.SetMaxScaleFactor(max_scale) 384 385 tg.Update() 386 tgn = vtki.new("PolyDataNormals") 387 tgn.ComputeCellNormalsOff() 388 tgn.SetInputData(tg.GetOutput()) 389 tgn.Update() 390 391 super().__init__(tgn.GetOutput(), c, alpha) 392 self.name = "Tensors"
Arguments:
- source : (str, Mesh)
preset types of source shapes is "ellipsoid", "cylinder", "cube" or a
Meshobject. - use_eigenvalues : (bool) color source glyph using the eigenvalues or by scalars
three_axes : (bool) if
Falsescale the source in the x-direction, the medium in the y-direction, and the minor in the z-direction. Then, the source is rotated so that the glyph's local x-axis lies along the major eigenvector, y-axis along the medium eigenvector, and z-axis along the minor.If
Truethree sources are produced, each of them oriented along an eigenvector and scaled according to the corresponding eigenvector.- is_symmetric : (bool)
If
Trueeach source glyph is mirrored (2 or 6 glyphs will be produced). The x-axis of the source glyph will correspond to the eigenvector on output. - length : (float) distance from the origin to the tip of the source glyph along the x-axis
- scale : (float) scaling factor of the source glyph.
- max_scale : (float) clamp scaling at this factor.
Examples:
3952class ParametricShape(Mesh): 3953 """ 3954 A set of built-in shapes mainly for illustration purposes. 3955 """ 3956 3957 def __init__(self, name, res=51, n=25, seed=1): 3958 """ 3959 A set of built-in shapes mainly for illustration purposes. 3960 3961 Name can be an integer or a string in this list: 3962 `['Boy', 'ConicSpiral', 'CrossCap', 'Dini', 'Enneper', 3963 'Figure8Klein', 'Klein', 'Mobius', 'RandomHills', 'Roman', 3964 'SuperEllipsoid', 'BohemianDome', 'Bour', 'CatalanMinimal', 3965 'Henneberg', 'Kuen', 'PluckerConoid', 'Pseudosphere']`. 3966 3967 Example: 3968 ```python 3969 from vedo import * 3970 settings.immediate_rendering = False 3971 plt = Plotter(N=18) 3972 for i in range(18): 3973 ps = ParametricShape(i).color(i) 3974 plt.at(i).show(ps, ps.name) 3975 plt.interactive().close() 3976 ``` 3977 <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/32848391/69181075-bb6aae80-0b0e-11ea-92f7-d0cd3b9087bf.png" width="700"> 3978 """ 3979 3980 shapes = [ 3981 "Boy", 3982 "ConicSpiral", 3983 "CrossCap", 3984 "Enneper", 3985 "Figure8Klein", 3986 "Klein", 3987 "Dini", 3988 "Mobius", 3989 "RandomHills", 3990 "Roman", 3991 "SuperEllipsoid", 3992 "BohemianDome", 3993 "Bour", 3994 "CatalanMinimal", 3995 "Henneberg", 3996 "Kuen", 3997 "PluckerConoid", 3998 "Pseudosphere", 3999 ] 4000 4001 if isinstance(name, int): 4002 name = name % len(shapes) 4003 name = shapes[name] 4004 4005 if name == "Boy": 4006 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBoy") 4007 elif name == "ConicSpiral": 4008 ps = vtki.new("ParametricConicSpiral") 4009 elif name == "CrossCap": 4010 ps = vtki.new("ParametricCrossCap") 4011 elif name == "Dini": 4012 ps = vtki.new("ParametricDini") 4013 elif name == "Enneper": 4014 ps = vtki.new("ParametricEnneper") 4015 elif name == "Figure8Klein": 4016 ps = vtki.new("ParametricFigure8Klein") 4017 elif name == "Klein": 4018 ps = vtki.new("ParametricKlein") 4019 elif name == "Mobius": 4020 ps = vtki.new("ParametricMobius") 4021 ps.SetRadius(2.0) 4022 ps.SetMinimumV(-0.5) 4023 ps.SetMaximumV(0.5) 4024 elif name == "RandomHills": 4025 ps = vtki.new("ParametricRandomHills") 4026 ps.AllowRandomGenerationOn() 4027 ps.SetRandomSeed(seed) 4028 ps.SetNumberOfHills(n) 4029 elif name == "Roman": 4030 ps = vtki.new("ParametricRoman") 4031 elif name == "SuperEllipsoid": 4032 ps = vtki.new("ParametricSuperEllipsoid") 4033 ps.SetN1(0.5) 4034 ps.SetN2(0.4) 4035 elif name == "BohemianDome": 4036 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBohemianDome") 4037 ps.SetA(5.0) 4038 ps.SetB(1.0) 4039 ps.SetC(2.0) 4040 elif name == "Bour": 4041 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBour") 4042 elif name == "CatalanMinimal": 4043 ps = vtki.new("ParametricCatalanMinimal") 4044 elif name == "Henneberg": 4045 ps = vtki.new("ParametricHenneberg") 4046 elif name == "Kuen": 4047 ps = vtki.new("ParametricKuen") 4048 ps.SetDeltaV0(0.001) 4049 elif name == "PluckerConoid": 4050 ps = vtki.new("ParametricPluckerConoid") 4051 elif name == "Pseudosphere": 4052 ps = vtki.new("ParametricPseudosphere") 4053 else: 4054 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown ParametricShape {name}") 4055 return 4056 4057 pfs = vtki.new("ParametricFunctionSource") 4058 pfs.SetParametricFunction(ps) 4059 pfs.SetUResolution(res) 4060 pfs.SetVResolution(res) 4061 pfs.SetWResolution(res) 4062 pfs.SetScalarModeToZ() 4063 pfs.Update() 4064 4065 super().__init__(pfs.GetOutput()) 4066 4067 if name == "RandomHills": self.shift([0,-10,-2.25]) 4068 if name != 'Kuen': self.normalize() 4069 if name == 'Dini': self.scale(0.4) 4070 if name == 'Enneper': self.scale(0.4) 4071 if name == 'ConicSpiral': self.bc('tomato') 4072 self.name = name
A set of built-in shapes mainly for illustration purposes.
3957 def __init__(self, name, res=51, n=25, seed=1): 3958 """ 3959 A set of built-in shapes mainly for illustration purposes. 3960 3961 Name can be an integer or a string in this list: 3962 `['Boy', 'ConicSpiral', 'CrossCap', 'Dini', 'Enneper', 3963 'Figure8Klein', 'Klein', 'Mobius', 'RandomHills', 'Roman', 3964 'SuperEllipsoid', 'BohemianDome', 'Bour', 'CatalanMinimal', 3965 'Henneberg', 'Kuen', 'PluckerConoid', 'Pseudosphere']`. 3966 3967 Example: 3968 ```python 3969 from vedo import * 3970 settings.immediate_rendering = False 3971 plt = Plotter(N=18) 3972 for i in range(18): 3973 ps = ParametricShape(i).color(i) 3974 plt.at(i).show(ps, ps.name) 3975 plt.interactive().close() 3976 ``` 3977 <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/32848391/69181075-bb6aae80-0b0e-11ea-92f7-d0cd3b9087bf.png" width="700"> 3978 """ 3979 3980 shapes = [ 3981 "Boy", 3982 "ConicSpiral", 3983 "CrossCap", 3984 "Enneper", 3985 "Figure8Klein", 3986 "Klein", 3987 "Dini", 3988 "Mobius", 3989 "RandomHills", 3990 "Roman", 3991 "SuperEllipsoid", 3992 "BohemianDome", 3993 "Bour", 3994 "CatalanMinimal", 3995 "Henneberg", 3996 "Kuen", 3997 "PluckerConoid", 3998 "Pseudosphere", 3999 ] 4000 4001 if isinstance(name, int): 4002 name = name % len(shapes) 4003 name = shapes[name] 4004 4005 if name == "Boy": 4006 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBoy") 4007 elif name == "ConicSpiral": 4008 ps = vtki.new("ParametricConicSpiral") 4009 elif name == "CrossCap": 4010 ps = vtki.new("ParametricCrossCap") 4011 elif name == "Dini": 4012 ps = vtki.new("ParametricDini") 4013 elif name == "Enneper": 4014 ps = vtki.new("ParametricEnneper") 4015 elif name == "Figure8Klein": 4016 ps = vtki.new("ParametricFigure8Klein") 4017 elif name == "Klein": 4018 ps = vtki.new("ParametricKlein") 4019 elif name == "Mobius": 4020 ps = vtki.new("ParametricMobius") 4021 ps.SetRadius(2.0) 4022 ps.SetMinimumV(-0.5) 4023 ps.SetMaximumV(0.5) 4024 elif name == "RandomHills": 4025 ps = vtki.new("ParametricRandomHills") 4026 ps.AllowRandomGenerationOn() 4027 ps.SetRandomSeed(seed) 4028 ps.SetNumberOfHills(n) 4029 elif name == "Roman": 4030 ps = vtki.new("ParametricRoman") 4031 elif name == "SuperEllipsoid": 4032 ps = vtki.new("ParametricSuperEllipsoid") 4033 ps.SetN1(0.5) 4034 ps.SetN2(0.4) 4035 elif name == "BohemianDome": 4036 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBohemianDome") 4037 ps.SetA(5.0) 4038 ps.SetB(1.0) 4039 ps.SetC(2.0) 4040 elif name == "Bour": 4041 ps = vtki.new("ParametricBour") 4042 elif name == "CatalanMinimal": 4043 ps = vtki.new("ParametricCatalanMinimal") 4044 elif name == "Henneberg": 4045 ps = vtki.new("ParametricHenneberg") 4046 elif name == "Kuen": 4047 ps = vtki.new("ParametricKuen") 4048 ps.SetDeltaV0(0.001) 4049 elif name == "PluckerConoid": 4050 ps = vtki.new("ParametricPluckerConoid") 4051 elif name == "Pseudosphere": 4052 ps = vtki.new("ParametricPseudosphere") 4053 else: 4054 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown ParametricShape {name}") 4055 return 4056 4057 pfs = vtki.new("ParametricFunctionSource") 4058 pfs.SetParametricFunction(ps) 4059 pfs.SetUResolution(res) 4060 pfs.SetVResolution(res) 4061 pfs.SetWResolution(res) 4062 pfs.SetScalarModeToZ() 4063 pfs.Update() 4064 4065 super().__init__(pfs.GetOutput()) 4066 4067 if name == "RandomHills": self.shift([0,-10,-2.25]) 4068 if name != 'Kuen': self.normalize() 4069 if name == 'Dini': self.scale(0.4) 4070 if name == 'Enneper': self.scale(0.4) 4071 if name == 'ConicSpiral': self.bc('tomato') 4072 self.name = name
A set of built-in shapes mainly for illustration purposes.
Name can be an integer or a string in this list:
['Boy', 'ConicSpiral', 'CrossCap', 'Dini', 'Enneper', 'Figure8Klein', 'Klein', 'Mobius', 'RandomHills', 'Roman', 'SuperEllipsoid', 'BohemianDome', 'Bour', 'CatalanMinimal', 'Henneberg', 'Kuen', 'PluckerConoid', 'Pseudosphere'].
Example:
from vedo import * settings.immediate_rendering = False plt = Plotter(N=18) for i in range(18): ps = ParametricShape(i).color(i) plt.at(i).show(ps, ps.name) plt.interactive().close()
4961class ConvexHull(Mesh): 4962 """ 4963 Create the 2D/3D convex hull from a set of points. 4964 """ 4965 4966 def __init__(self, pts) -> None: 4967 """ 4968 Create the 2D/3D convex hull from a set of input points or input Mesh. 4969 4970 Examples: 4971 - [convex_hull.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/convex_hull.py) 4972 4973  4974 """ 4975 if utils.is_sequence(pts): 4976 pts = utils.make3d(pts).astype(float) 4977 mesh = Points(pts) 4978 else: 4979 mesh = pts 4980 apoly = mesh.clean().dataset 4981 4982 # Create the convex hull of the pointcloud 4983 z0, z1 = mesh.zbounds() 4984 d = mesh.diagonal_size() 4985 if (z1 - z0) / d > 0.0001: 4986 delaunay = vtki.new("Delaunay3D") 4987 delaunay.SetInputData(apoly) 4988 delaunay.Update() 4989 surfaceFilter = vtki.new("DataSetSurfaceFilter") 4990 surfaceFilter.SetInputConnection(delaunay.GetOutputPort()) 4991 surfaceFilter.Update() 4992 out = surfaceFilter.GetOutput() 4993 else: 4994 delaunay = vtki.new("Delaunay2D") 4995 delaunay.SetInputData(apoly) 4996 delaunay.Update() 4997 fe = vtki.new("FeatureEdges") 4998 fe.SetInputConnection(delaunay.GetOutputPort()) 4999 fe.BoundaryEdgesOn() 5000 fe.Update() 5001 out = fe.GetOutput() 5002 5003 super().__init__(out, c=mesh.color(), alpha=0.75) 5004 self.flat() 5005 self.name = "ConvexHull"
Create the 2D/3D convex hull from a set of points.
4966 def __init__(self, pts) -> None: 4967 """ 4968 Create the 2D/3D convex hull from a set of input points or input Mesh. 4969 4970 Examples: 4971 - [convex_hull.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/convex_hull.py) 4972 4973  4974 """ 4975 if utils.is_sequence(pts): 4976 pts = utils.make3d(pts).astype(float) 4977 mesh = Points(pts) 4978 else: 4979 mesh = pts 4980 apoly = mesh.clean().dataset 4981 4982 # Create the convex hull of the pointcloud 4983 z0, z1 = mesh.zbounds() 4984 d = mesh.diagonal_size() 4985 if (z1 - z0) / d > 0.0001: 4986 delaunay = vtki.new("Delaunay3D") 4987 delaunay.SetInputData(apoly) 4988 delaunay.Update() 4989 surfaceFilter = vtki.new("DataSetSurfaceFilter") 4990 surfaceFilter.SetInputConnection(delaunay.GetOutputPort()) 4991 surfaceFilter.Update() 4992 out = surfaceFilter.GetOutput() 4993 else: 4994 delaunay = vtki.new("Delaunay2D") 4995 delaunay.SetInputData(apoly) 4996 delaunay.Update() 4997 fe = vtki.new("FeatureEdges") 4998 fe.SetInputConnection(delaunay.GetOutputPort()) 4999 fe.BoundaryEdgesOn() 5000 fe.Update() 5001 out = fe.GetOutput() 5002 5003 super().__init__(out, c=mesh.color(), alpha=0.75) 5004 self.flat() 5005 self.name = "ConvexHull"
5008def VedoLogo(distance=0.0, c=None, bc="t", version=False, frame=True) -> "vedo.Assembly": 5009 """ 5010 Create the 3D vedo logo. 5011 5012 Arguments: 5013 distance : (float) 5014 send back logo by this distance from camera 5015 version : (bool) 5016 add version text to the right end of the logo 5017 bc : (color) 5018 text back face color 5019 """ 5020 if c is None: 5021 c = (0, 0, 0) 5022 if vedo.plotter_instance: 5023 if sum(get_color(vedo.plotter_instance.backgrcol)) > 1.5: 5024 c = [0, 0, 0] 5025 else: 5026 c = "linen" 5027 5028 font = "Comae" 5029 vlogo = Text3D("vэdo", font=font, s=1350, depth=0.2, c=c, hspacing=0.8) 5030 vlogo.scale([1, 0.95, 1]).x(-2525).pickable(False).bc(bc) 5031 vlogo.properties.LightingOn() 5032 5033 vr, rul = None, None 5034 if version: 5035 vr = Text3D( 5036 vedo.__version__, font=font, s=165, depth=0.2, c=c, hspacing=1 5037 ).scale([1, 0.7, 1]) 5038 vr.rotate_z(90).pos(2450, 50, 80) 5039 vr.bc(bc).pickable(False) 5040 elif frame: 5041 rul = vedo.RulerAxes( 5042 (-2600, 2110, 0, 1650, 0, 0), 5043 xlabel="European Molecular Biology Laboratory", 5044 ylabel=vedo.__version__, 5045 font=font, 5046 xpadding=0.09, 5047 ypadding=0.04, 5048 ) 5049 fakept = vedo.Point((0, 500, distance * 1725), alpha=0, c=c, r=1).pickable(0) 5050 return vedo.Assembly([vlogo, vr, fakept, rul]).scale(1 / 1725)
Create the 3D vedo logo.
Arguments:
- distance : (float) send back logo by this distance from camera
- version : (bool) add version text to the right end of the logo
- bc : (color) text back face color