vedo.visual
Base classes to manage visualization and apperance of objects and their properties.
1#!/usr/bin/env python3 2# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3import os 4from weakref import ref as weak_ref_to 5 6from typing import Union 7from typing_extensions import Self 8import numpy as np 9 10import vedo.vtkclasses as vtki 11 12import vedo 13from vedo import colors 14from vedo import utils 15 16 17__docformat__ = "google" 18 19__doc__ = """ 20Base classes to manage visualization and apperance of objects and their properties. 21""" 22 23__all__ = [ 24 "CommonVisual", 25 "PointsVisual", 26 "VolumeVisual", 27 "MeshVisual", 28 "ImageVisual", 29 "Actor2D", 30 "LightKit", 31] 32 33 34################################################### 35class CommonVisual: 36 """Class to manage the visual aspects common to all objects.""" 37 38 def __init__(self): 39 # print("init CommonVisual", type(self)) 40 41 self.properties = None 42 43 self.scalarbar = None 44 self.pipeline = None 45 46 self.trail = None 47 self.trail_points = [] 48 self.trail_segment_size = 0 49 self.trail_offset = None 50 51 self.shadows = [] 52 53 self.axes = None 54 self.picked3d = None 55 56 self.rendered_at = set() 57 58 self._ligthingnr = 0 # index of the lighting mode changed from CLI 59 self._cmap_name = "" # remember the cmap name for self._keypress 60 self._caption = None 61 62 self.actor = None 63 64 65 def print(self): 66 """Print object info.""" 67 print(self.__str__()) 68 return self 69 70 @property 71 def LUT(self) -> np.ndarray: 72 """Return the lookup table of the object as a numpy object.""" 73 try: 74 _lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 75 values = [] 76 for i in range(_lut.GetTable().GetNumberOfTuples()): 77 # print("LUT i =", i, "value =", _lut.GetTableValue(i)) 78 values.append(_lut.GetTableValue(i)) 79 return np.array(values) 80 except AttributeError: 81 return np.array([], dtype=float) 82 83 @LUT.setter 84 def LUT(self, arr): 85 """ 86 Set the lookup table of the object from a numpy or `vtkLookupTable` object. 87 Consider using `cmap()` or `build_lut()` instead as it allows 88 to set the range of the LUT and to use a string name for the color map. 89 """ 90 if isinstance(arr, vtki.vtkLookupTable): 91 newlut = arr 92 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(newlut.GetRange()) 93 else: 94 newlut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 95 newlut.SetNumberOfTableValues(len(arr)) 96 if len(arr[0]) == 3: 97 arr = np.insert(arr, 3, 1, axis=1) 98 for i, v in enumerate(arr): 99 newlut.SetTableValue(i, v) 100 newlut.SetRange(self.mapper.GetScalarRange()) 101 # print("newlut.GetRange() =", newlut.GetRange()) 102 # print("self.mapper.GetScalarRange() =", self.mapper.GetScalarRange()) 103 newlut.Build() 104 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(newlut) 105 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 106 107 def scalar_range(self, vmin=None, vmax=None): 108 """Set the range of the scalar value for visualization.""" 109 if vmin is None and vmax is None: 110 return np.array(self.mapper.GetScalarRange()) 111 if vmax is None: 112 vmin, vmax = vmin # assume it is a list 113 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(float(vmin), float(vmax)) 114 return self 115 116 def add_observer(self, event_name, func, priority=0) -> int: 117 """Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.""" 118 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 119 idd = self.actor.AddObserver(event_name, func, priority) 120 return idd 121 122 def invoke_event(self, event_name) -> Self: 123 """Invoke an event.""" 124 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 125 self.actor.InvokeEvent(event_name) 126 return self 127 128 # def abort_event(self, obs_id): 129 # """Abort an event.""" 130 # cmd = self.actor.GetCommand(obs_id) # vtkCommand 131 # if cmd: 132 # cmd.AbortFlagOn() 133 # return self 134 135 def show(self, **options) -> Union["vedo.Plotter", None]: 136 """ 137 Create on the fly an instance of class `Plotter` or use the last existing one to 138 show one single object. 139 140 This method is meant as a shortcut. If more than one object needs to be visualised 141 please use the syntax `show(mesh1, mesh2, volume, ..., options)`. 142 143 Returns the `Plotter` class instance. 144 """ 145 return vedo.plotter.show(self, **options) 146 147 def thumbnail(self, zoom=1.25, size=(200, 200), bg="white", azimuth=0, elevation=0, axes=False) -> np.ndarray: 148 """Build a thumbnail of the object and return it as an array.""" 149 # speed is about 20Hz for size=[200,200] 150 ren = vtki.vtkRenderer() 151 152 actor = self.actor 153 if isinstance(self, vedo.UnstructuredGrid): 154 geo = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 155 geo.SetInputData(self.dataset) 156 geo.Update() 157 actor = vedo.Mesh(geo.GetOutput()).cmap("rainbow").actor 158 159 ren.AddActor(actor) 160 if axes: 161 axes = vedo.addons.Axes(self) 162 ren.AddActor(axes.actor) 163 ren.ResetCamera() 164 cam = ren.GetActiveCamera() 165 cam.Zoom(zoom) 166 cam.Elevation(elevation) 167 cam.Azimuth(azimuth) 168 169 ren_win = vtki.vtkRenderWindow() 170 ren_win.SetOffScreenRendering(True) 171 ren_win.SetSize(size) 172 ren.SetBackground(colors.get_color(bg)) 173 ren_win.AddRenderer(ren) 174 ren.ResetCameraClippingRange() 175 ren_win.Render() 176 177 nx, ny = ren_win.GetSize() 178 arr = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 179 ren_win.GetRGBACharPixelData(0, 0, nx - 1, ny - 1, 0, arr) 180 narr = utils.vtk2numpy(arr).T[:3].T.reshape([ny, nx, 3]) 181 narr = np.ascontiguousarray(np.flip(narr, axis=0)) 182 183 ren.RemoveActor(actor) 184 if axes: 185 ren.RemoveActor(axes.actor) 186 ren_win.Finalize() 187 del ren_win 188 return narr 189 190 def pickable(self, value=None) -> Self: 191 """Set/get the pickability property of an object.""" 192 if value is None: 193 return self.actor.GetPickable() 194 self.actor.SetPickable(value) 195 return self 196 197 def use_bounds(self, value=True) -> Self: 198 """ 199 Instruct the current camera to either take into account or ignore 200 the object bounds when resetting. 201 """ 202 self.actor.SetUseBounds(value) 203 return self 204 205 def draggable(self, value=None) -> Self: # NOT FUNCTIONAL? 206 """Set/get the draggability property of an object.""" 207 if value is None: 208 return self.actor.GetDragable() 209 self.actor.SetDragable(value) 210 return self 211 212 def on(self) -> Self: 213 """Switch on object visibility. Object is not removed.""" 214 self.actor.VisibilityOn() 215 try: 216 self.scalarbar.actor.VisibilityOn() 217 except AttributeError: 218 pass 219 try: 220 self.trail.actor.VisibilityOn() 221 except AttributeError: 222 pass 223 try: 224 for sh in self.shadows: 225 sh.actor.VisibilityOn() 226 except AttributeError: 227 pass 228 return self 229 230 def off(self) -> Self: 231 """Switch off object visibility. Object is not removed.""" 232 self.actor.VisibilityOff() 233 try: 234 self.scalarbar.actor.VisibilityOff() 235 except AttributeError: 236 pass 237 try: 238 self.trail.actor.VisibilityOff() 239 except AttributeError: 240 pass 241 try: 242 for sh in self.shadows: 243 sh.actor.VisibilityOff() 244 except AttributeError: 245 pass 246 return self 247 248 def toggle(self) -> Self: 249 """Toggle object visibility on/off.""" 250 v = self.actor.GetVisibility() 251 if v: 252 self.off() 253 else: 254 self.on() 255 return self 256 257 def add_scalarbar( 258 self, 259 title="", 260 pos=(), 261 size=(80, 400), 262 font_size=14, 263 title_yoffset=15, 264 nlabels=None, 265 c=None, 266 horizontal=False, 267 use_alpha=True, 268 label_format=":6.3g", 269 ) -> Self: 270 """ 271 Add a 2D scalar bar for the specified object. 272 273 Arguments: 274 title : (str) 275 scalar bar title 276 pos : (list) 277 position coordinates of the bottom left corner. 278 Can also be a pair of (x,y) values in the range [0,1] 279 to indicate the position of the bottom left and top right corners. 280 size : (float,float) 281 size of the scalarbar in number of pixels (width, height) 282 font_size : (float) 283 size of font for title and numeric labels 284 title_yoffset : (float) 285 vertical space offset between title and color scalarbar 286 nlabels : (int) 287 number of numeric labels 288 c : (list) 289 color of the scalar bar text 290 horizontal : (bool) 291 lay the scalarbar horizontally 292 use_alpha : (bool) 293 render transparency in the color bar itself 294 label_format : (str) 295 c-style format string for numeric labels 296 297 Examples: 298 - [mesh_coloring.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_coloring.py) 299 - [scalarbars.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/scalarbars.py) 300 """ 301 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 302 303 if plt and plt.renderer: 304 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 305 if np.sum(plt.renderer.GetBackground()) > 1.5: 306 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 307 if isinstance(self.scalarbar, vtki.vtkActor): 308 plt.renderer.RemoveActor(self.scalarbar) 309 elif isinstance(self.scalarbar, vedo.Assembly): 310 for a in self.scalarbar.unpack(): 311 plt.renderer.RemoveActor(a) 312 if c is None: 313 c = "gray" 314 315 sb = vedo.addons.ScalarBar( 316 self, 317 title, 318 pos, 319 size, 320 font_size, 321 title_yoffset, 322 nlabels, 323 c, 324 horizontal, 325 use_alpha, 326 label_format, 327 ) 328 self.scalarbar = sb 329 return self 330 331 def add_scalarbar3d( 332 self, 333 title="", 334 pos=None, 335 size=(0, 0), 336 title_font="", 337 title_xoffset=-1.2, 338 title_yoffset=0.0, 339 title_size=1.5, 340 title_rotation=0.0, 341 nlabels=9, 342 label_font="", 343 label_size=1, 344 label_offset=0.375, 345 label_rotation=0, 346 label_format="", 347 italic=0, 348 c=None, 349 draw_box=True, 350 above_text=None, 351 below_text=None, 352 nan_text="NaN", 353 categories=None, 354 ) -> Self: 355 """ 356 Associate a 3D scalar bar to the object and add it to the scene. 357 The new scalarbar object (Assembly) will be accessible as obj.scalarbar 358 359 Arguments: 360 size : (list) 361 (thickness, length) of scalarbar 362 title : (str) 363 scalar bar title 364 title_xoffset : (float) 365 horizontal space btw title and color scalarbar 366 title_yoffset : (float) 367 vertical space offset 368 title_size : (float) 369 size of title wrt numeric labels 370 title_rotation : (float) 371 title rotation in degrees 372 nlabels : (int) 373 number of numeric labels 374 label_font : (str) 375 font type for labels 376 label_size : (float) 377 label scale factor 378 label_offset : (float) 379 space btw numeric labels and scale 380 label_rotation : (float) 381 label rotation in degrees 382 label_format : (str) 383 label format for floats and integers (e.g. `':.2f'`) 384 draw_box : (bool) 385 draw a box around the colorbar 386 categories : (list) 387 make a categorical scalarbar, 388 the input list will have the format `[value, color, alpha, textlabel]` 389 390 Examples: 391 - [scalarbars.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/scalarbars.py) 392 """ 393 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 394 if plt and c is None: # automatic black or white 395 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 396 if np.sum(vedo.get_color(plt.backgrcol)) > 1.5: 397 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 398 if c is None: 399 c = (0, 0, 0) 400 c = vedo.get_color(c) 401 402 self.scalarbar = vedo.addons.ScalarBar3D( 403 self, 404 title, 405 pos, 406 size, 407 title_font, 408 title_xoffset, 409 title_yoffset, 410 title_size, 411 title_rotation, 412 nlabels, 413 label_font, 414 label_size, 415 label_offset, 416 label_rotation, 417 label_format, 418 italic, 419 c, 420 draw_box, 421 above_text, 422 below_text, 423 nan_text, 424 categories, 425 ) 426 return self 427 428 def color(self, col, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None): 429 """ 430 Assign a color or a set of colors along the range of the scalar value. 431 A single constant color can also be assigned. 432 Any matplotlib color map name is also accepted, e.g. `volume.color('jet')`. 433 434 E.g.: say that your cells scalar runs from -3 to 6, 435 and you want -3 to show red and 1.5 violet and 6 green, then just set: 436 437 `volume.color(['red', 'violet', 'green'])` 438 439 You can also assign a specific color to a aspecific value with eg.: 440 441 `volume.color([(0,'red'), (0.5,'violet'), (1,'green')])` 442 443 Arguments: 444 alpha : (list) 445 use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range 446 vmin : (float) 447 force the min of the scalar range to be this value 448 vmax : (float) 449 force the max of the scalar range to be this value 450 """ 451 # supersedes method in Points, Mesh 452 453 if col is None: 454 return self 455 456 if vmin is None: 457 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 458 if vmax is None: 459 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 460 ctf = self.properties.GetRGBTransferFunction() 461 ctf.RemoveAllPoints() 462 463 if utils.is_sequence(col): 464 if utils.is_sequence(col[0]) and len(col[0]) == 2: 465 # user passing [(value1, color1), ...] 466 for x, ci in col: 467 r, g, b = colors.get_color(ci) 468 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 469 # colors.printc('color at', round(x, 1), 470 # 'set to', colors.get_color_name((r, g, b)), bold=0) 471 else: 472 # user passing [color1, color2, ..] 473 for i, ci in enumerate(col): 474 r, g, b = colors.get_color(ci) 475 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(col) - 1) 476 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 477 elif isinstance(col, str): 478 if col in colors.colors.keys() or col in colors.color_nicks.keys(): 479 r, g, b = colors.get_color(col) 480 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmin, r, g, b) # constant color 481 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmax, r, g, b) 482 else: # assume it's a colormap 483 for x in np.linspace(vmin, vmax, num=64, endpoint=True): 484 r, g, b = colors.color_map(x, name=col, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax) 485 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 486 elif isinstance(col, int): 487 r, g, b = colors.get_color(col) 488 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmin, r, g, b) # constant color 489 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmax, r, g, b) 490 elif isinstance(col, vtki.vtkLookupTable): 491 alpha=[] 492 nt = col.GetNumberOfTableValues() 493 for i in range(nt): 494 r, g, b, a = col.GetTableValue(i) 495 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (nt - 1) 496 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 497 alpha.append(a) 498 elif hasattr(col, "resampled"): # cover the case of LinearSegmentedColormap 499 N = col.N 500 cs = np.array([col(i/N) for i in range(N)]) 501 alpha = cs[:,3].copy() 502 for i, v in enumerate(cs): 503 r, g, b, _ = v 504 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (N - 1) 505 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 506 elif hasattr(col, "to_rgba"): # col is a matplotlib colormap 507 for i in range(256): 508 r, g, b, a = col(i / 255) 509 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / 255 510 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 511 alpha.append(a) 512 else: 513 vedo.logger.warning(f"in color() unknown input type {type(col)}") 514 515 if alpha is not None: 516 self.alpha(alpha, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax) 517 return self 518 519 def alpha(self, alpha, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 520 """ 521 Assign a set of tranparencies along the range of the scalar value. 522 A single constant value can also be assigned. 523 524 E.g.: say `alpha=(0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1)` and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150. 525 Then all cells with a value close to -10 will be completely transparent, cells at 1/4 526 of the range will get an alpha equal to 0.3 and voxels with value close to 150 527 will be completely opaque. 528 529 As a second option one can set explicit (x, alpha_x) pairs to define the transfer function. 530 531 E.g.: say `alpha=[(-5, 0), (35, 0.4) (123,0.9)]` and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150. 532 Then all cells below -5 will be completely transparent, cells with a scalar value of 35 533 will get an opacity of 40% and above 123 alpha is set to 90%. 534 """ 535 if vmin is None: 536 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 537 if vmax is None: 538 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 539 otf = self.properties.GetScalarOpacity() 540 otf.RemoveAllPoints() 541 542 if utils.is_sequence(alpha): 543 alpha = np.array(alpha) 544 if len(alpha.shape) == 1: # user passing a flat list e.g. (0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1) 545 for i, al in enumerate(alpha): 546 xalpha = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(alpha) - 1) 547 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 548 otf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 549 # print("alpha at", round(xalpha, 1), "\tset to", al) 550 elif len(alpha.shape) == 2: # user passing [(x0,alpha0), ...] 551 otf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha[0][1]) 552 for xalpha, al in alpha: 553 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 554 otf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 555 otf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha[-1][1]) 556 557 else: 558 559 otf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha) # constant alpha 560 otf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha) 561 562 return self 563 564 565######################################################################################## 566class Actor2D(vtki.vtkActor2D): 567 """Wrapping of `vtkActor2D` class.""" 568 569 def __init__(self, dataset=None): 570 """Manage 2D objects.""" 571 super().__init__() 572 573 self.dataset = None 574 self.name = "Actor2D" 575 self.filename = "" 576 self.file_size = 0 577 self.pipeline = None 578 self.shape = [] # for images 579 self.coordinate = None 580 581 if dataset is not None: 582 mapper = vtki.new("PolyDataMapper2D") 583 mapper.SetInputData(dataset) 584 self.SetMapper(mapper) 585 586 self.dataset = dataset 587 self.properties = self.GetProperty() 588 589 590 @property 591 def mapper(self): 592 """Get the internal vtkMapper.""" 593 return self.GetMapper() 594 595 # not usable 596 # @property 597 # def properties(self): 598 # """Get the internal vtkProperty.""" 599 # return self.GetProperty() 600 601 # @properties.setter 602 # def properties(self, prop): 603 # """Set the internal vtkProperty.""" 604 # self.SetProperty(prop) 605 606 @mapper.setter 607 def mapper(self, amapper): 608 """Set the internal vtkMapper.""" 609 self.SetMapper(amapper) 610 611 def layer(self, value=None): 612 """Set/Get the layer number in the overlay planes into which to render.""" 613 if value is None: 614 return self.GetLayerNumber() 615 self.SetLayerNumber(value) 616 return self 617 618 def pos(self, px=None, py=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 619 """Set/Get the screen-coordinate position.""" 620 if isinstance(px, str): 621 vedo.logger.error("Use string descriptors only inside the constructor") 622 return self 623 if px is None: 624 return np.array(self.GetPosition(), dtype=int) 625 if py is not None: 626 p = [px, py] 627 else: 628 p = px 629 assert len(p) == 2, "Error: len(pos) must be 2 for Actor2D" 630 self.SetPosition(p) 631 return self 632 633 def coordinate_system(self, value=None) -> Self: 634 """ 635 Set/get the coordinate system which this coordinate is defined in. 636 637 The options are: 638 0. Display 639 1. Normalized Display 640 2. Viewport 641 3. Normalized Viewport 642 4. View 643 5. Pose 644 6. World 645 """ 646 coor = self.GetPositionCoordinate() 647 if value is None: 648 return coor.GetCoordinateSystem() 649 coor.SetCoordinateSystem(value) 650 return self 651 652 def set_position_coordinates(self, p1, p2): 653 """Set the position coordinates.""" 654 self.GetPositionCoordinate().SetValue(*p1) 655 self.GetPosition2Coordinate().SetValue(*p2) 656 return self 657 658 def on(self) -> Self: 659 """Set object visibility.""" 660 self.VisibilityOn() 661 return self 662 663 def off(self) -> Self: 664 """Set object visibility.""" 665 self.VisibilityOn() 666 return self 667 668 def toggle(self) -> Self: 669 """Toggle object visibility.""" 670 self.SetVisibility(not self.GetVisibility()) 671 return self 672 673 def visibility(self, value=None) -> bool: 674 """Get/Set object visibility.""" 675 if value is not None: 676 self.SetVisibility(value) 677 return self.GetVisibility() 678 679 def pickable(self, value=True) -> Self: 680 """Set object pickability.""" 681 self.SetPickable(value) 682 return self 683 684 def color(self, value=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 685 """Set/Get the object color.""" 686 if value is None: 687 return self.properties.GetColor() 688 self.properties.SetColor(colors.get_color(value)) 689 return self 690 691 def c(self, value=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 692 """Set/Get the object color.""" 693 return self.color(value) 694 695 def alpha(self, value=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 696 """Set/Get the object opacity.""" 697 if value is None: 698 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 699 self.properties.SetOpacity(value) 700 return self 701 702 def ps(self, point_size=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 703 """Set/Get the point size of the object. Same as `point_size()`.""" 704 if point_size is None: 705 return self.properties.GetPointSize() 706 self.properties.SetPointSize(point_size) 707 return self 708 709 def lw(self, line_width=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 710 """Set/Get the line width of the object. Same as `line_width()`.""" 711 if line_width is None: 712 return self.properties.GetLineWidth() 713 self.properties.SetLineWidth(line_width) 714 return self 715 716 def ontop(self, value=True) -> Self: 717 """Keep the object always on top of everything else.""" 718 if value: 719 self.properties.SetDisplayLocationToForeground() 720 else: 721 self.properties.SetDisplayLocationToBackground() 722 return self 723 724 def add_observer(self, event_name, func, priority=0) -> int: 725 """Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.""" 726 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 727 idd = self.AddObserver(event_name, func, priority) 728 return idd 729 730######################################################################################## 731class Actor3DHelper: 732 """Helper class for 3D actors.""" 733 734 def apply_transform(self, LT) -> Self: 735 """Apply a linear transformation to the actor.""" 736 self.transform.concatenate(LT) 737 self.actor.SetPosition(self.transform.T.GetPosition()) 738 self.actor.SetOrientation(self.transform.T.GetOrientation()) 739 self.actor.SetScale(self.transform.T.GetScale()) 740 return self 741 742 def pos(self, x=None, y=None, z=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 743 """Set/Get object position.""" 744 if x is None: # get functionality 745 return self.transform.position 746 747 if z is None and y is None: # assume x is of the form (x,y,z) 748 if len(x) == 3: 749 x, y, z = x 750 else: 751 x, y = x 752 z = 0 753 elif z is None: # assume x,y is of the form x, y 754 z = 0 755 756 q = self.transform.position 757 LT = vedo.LinearTransform().translate([x,y,z]-q) 758 return self.apply_transform(LT) 759 760 def shift(self, dx, dy=0, dz=0) -> Self: 761 """Add a vector to the current object position.""" 762 if vedo.utils.is_sequence(dx): 763 vedo.utils.make3d(dx) 764 dx, dy, dz = dx 765 LT = vedo.LinearTransform().translate([dx, dy, dz]) 766 return self.apply_transform(LT) 767 768 def origin(self, point=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 769 """ 770 Set/get origin of object. 771 Useful for defining pivoting point when rotating and/or scaling. 772 """ 773 if point is None: 774 return np.array(self.actor.GetOrigin()) 775 self.actor.SetOrigin(point) 776 return self 777 778 def scale(self, s, origin=True) -> Self: 779 """Multiply object size by `s` factor.""" 780 LT = vedo.LinearTransform().scale(s, origin=origin) 781 return self.apply_transform(LT) 782 783 def x(self, val=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 784 """Set/Get object position along x axis.""" 785 p = self.transform.position 786 if val is None: 787 return p[0] 788 self.pos(val, p[1], p[2]) 789 return self 790 791 def y(self, val=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 792 """Set/Get object position along y axis.""" 793 p = self.transform.position 794 if val is None: 795 return p[1] 796 self.pos(p[0], val, p[2]) 797 return self 798 799 def z(self, val=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 800 """Set/Get object position along z axis.""" 801 p = self.transform.position 802 if val is None: 803 return p[2] 804 self.pos(p[0], p[1], val) 805 return self 806 807 def rotate_x(self, angle) -> Self: 808 """Rotate object around x axis.""" 809 LT = vedo.LinearTransform().rotate_x(angle) 810 return self.apply_transform(LT) 811 812 def rotate_y(self, angle) -> Self: 813 """Rotate object around y axis.""" 814 LT = vedo.LinearTransform().rotate_y(angle) 815 return self.apply_transform(LT) 816 817 def rotate_z(self, angle) -> Self: 818 """Rotate object around z axis.""" 819 LT = vedo.LinearTransform().rotate_z(angle) 820 return self.apply_transform(LT) 821 822 def reorient(self, old_axis, new_axis, rotation=0, rad=False) -> Self: 823 """Rotate object to a new orientation.""" 824 if rad: 825 rotation *= 180 / np.pi 826 axis = old_axis / np.linalg.norm(old_axis) 827 direction = new_axis / np.linalg.norm(new_axis) 828 angle = np.arccos(np.dot(axis, direction)) * 180 / np.pi 829 self.actor.RotateZ(rotation) 830 a,b,c = np.cross(axis, direction) 831 self.actor.RotateWXYZ(angle, c,b,a) 832 return self 833 834 def bounds(self) -> np.ndarray: 835 """ 836 Get the object bounds. 837 Returns a list in format `[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]`. 838 """ 839 return np.array(self.actor.GetBounds()) 840 841 def xbounds(self, i=None) -> Union[float, tuple]: 842 """Get the bounds `[xmin,xmax]`. Can specify upper or lower with i (0,1).""" 843 b = self.bounds() 844 if i is not None: 845 return b[i] 846 return (b[0], b[1]) 847 848 def ybounds(self, i=None) -> Union[float, tuple]: 849 """Get the bounds `[ymin,ymax]`. Can specify upper or lower with i (0,1).""" 850 b = self.bounds() 851 if i == 0: 852 return b[2] 853 if i == 1: 854 return b[3] 855 return (b[2], b[3]) 856 857 def zbounds(self, i=None) -> Union[float, tuple]: 858 """Get the bounds `[zmin,zmax]`. Can specify upper or lower with i (0,1).""" 859 b = self.bounds() 860 if i == 0: 861 return b[4] 862 if i == 1: 863 return b[5] 864 return (b[4], b[5]) 865 866 def diagonal_size(self) -> float: 867 """Get the diagonal size of the bounding box.""" 868 b = self.bounds() 869 return np.sqrt((b[1]-b[0])**2 + (b[3]-b[2])**2 + (b[5]-b[4])**2) 870 871################################################### 872class PointsVisual(CommonVisual): 873 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a ``Points`` object.""" 874 875 def __init__(self): 876 # print("init PointsVisual") 877 super().__init__() 878 self.properties_backface = None 879 self._cmap_name = None 880 self.trail = None 881 self.trail_offset = 0 882 self.trail_points = [] 883 self._caption = None 884 885 886 def clone2d(self, size=None, offset=(), scale=None): 887 """ 888 Turn a 3D `Points` or `Mesh` into a flat 2D actor. 889 Returns a `Actor2D`. 890 891 Arguments: 892 size : (float) 893 size as scaling factor for the 2D actor 894 offset : (list) 895 2D (x, y) position of the actor in the range [-1, 1] 896 scale : (float) 897 Deprecated. Use `size` instead. 898 899 Examples: 900 - [clone2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/clone2d.py) 901 902  903 """ 904 # assembly.Assembly.clone2d() superseeds this method 905 if scale is not None: 906 vedo.logger.warning("clone2d(): use keyword size not scale") 907 size = scale 908 909 if size is None: 910 # work out a reasonable scale 911 msiz = self.diagonal_size() 912 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.window: 913 sz = vedo.plotter_instance.window.GetSize() 914 dsiz = utils.mag(sz) 915 size = dsiz / msiz / 10 916 else: 917 size = 350 / msiz 918 919 tp = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 920 transform = vtki.vtkTransform() 921 transform.Scale(size, size, size) 922 if len(offset) == 0: 923 offset = self.pos() 924 transform.Translate(-utils.make3d(offset)) 925 tp.SetTransform(transform) 926 tp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 927 tp.Update() 928 poly = tp.GetOutput() 929 930 cm = self.mapper.GetColorMode() 931 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 932 sv = self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility() 933 use_lut = self.mapper.GetUseLookupTableScalarRange() 934 vrange = self.mapper.GetScalarRange() 935 sm = self.mapper.GetScalarMode() 936 937 act2d = Actor2D(poly) 938 act2d.mapper.SetColorMode(cm) 939 act2d.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 940 act2d.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(sv) 941 act2d.mapper.SetUseLookupTableScalarRange(use_lut) 942 act2d.mapper.SetScalarRange(vrange) 943 act2d.mapper.SetScalarMode(sm) 944 945 act2d.GetPositionCoordinate().SetCoordinateSystem(4) 946 act2d.properties.SetColor(self.color()) 947 act2d.properties.SetOpacity(self.alpha()) 948 act2d.properties.SetLineWidth(self.properties.GetLineWidth()) 949 act2d.properties.SetPointSize(self.properties.GetPointSize()) 950 act2d.properties.SetDisplayLocation(0) # 0 = back, 1 = front 951 act2d.PickableOff() 952 return act2d 953 954 ################################################## 955 def copy_properties_from(self, source, deep=True, actor_related=True) -> Self: 956 """ 957 Copy properties from another ``Points`` object. 958 """ 959 pr = vtki.vtkProperty() 960 try: 961 sp = source.properties 962 mp = source.mapper 963 sa = source.actor 964 except AttributeError: 965 sp = source.GetProperty() 966 mp = source.GetMapper() 967 sa = source 968 969 if deep: 970 pr.DeepCopy(sp) 971 else: 972 pr.ShallowCopy(sp) 973 self.actor.SetProperty(pr) 974 self.properties = pr 975 976 if self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty(): 977 bfpr = vtki.vtkProperty() 978 bfpr.DeepCopy(sa.GetBackfaceProperty()) 979 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(bfpr) 980 self.properties_backface = bfpr 981 982 if not actor_related: 983 return self 984 985 # mapper related: 986 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(mp.GetScalarVisibility()) 987 self.mapper.SetScalarMode(mp.GetScalarMode()) 988 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(mp.GetScalarRange()) 989 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(mp.GetLookupTable()) 990 self.mapper.SetColorMode(mp.GetColorMode()) 991 self.mapper.SetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping( 992 mp.GetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping() 993 ) 994 self.mapper.SetUseLookupTableScalarRange( 995 mp.GetUseLookupTableScalarRange() 996 ) 997 998 self.actor.SetPickable(sa.GetPickable()) 999 self.actor.SetDragable(sa.GetDragable()) 1000 self.actor.SetTexture(sa.GetTexture()) 1001 self.actor.SetVisibility(sa.GetVisibility()) 1002 return self 1003 1004 def color(self, c=False, alpha=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 1005 """ 1006 Set/get mesh's color. 1007 If None is passed as input, will use colors from active scalars. 1008 Same as `mesh.c()`. 1009 """ 1010 if c is False: 1011 return np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1012 if c is None: 1013 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1014 return self 1015 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 1016 cc = colors.get_color(c) 1017 self.properties.SetColor(cc) 1018 if self.trail: 1019 self.trail.properties.SetColor(cc) 1020 if alpha is not None: 1021 self.alpha(alpha) 1022 return self 1023 1024 def c(self, color=False, alpha=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 1025 """ 1026 Shortcut for `color()`. 1027 If None is passed as input, will use colors from current active scalars. 1028 """ 1029 return self.color(color, alpha) 1030 1031 def alpha(self, opacity=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 1032 """Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as `mesh.opacity()`.""" 1033 if opacity is None: 1034 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 1035 1036 self.properties.SetOpacity(opacity) 1037 bfp = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 1038 if bfp: 1039 if opacity < 1: 1040 self.properties_backface = bfp 1041 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(None) 1042 else: 1043 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(self.properties_backface) 1044 return self 1045 1046 def lut_color_at(self, value) -> np.ndarray: 1047 """ 1048 Return the color and alpha in the lookup table at given value. 1049 """ 1050 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1051 if not lut: 1052 return None 1053 rgb = [0,0,0] 1054 lut.GetColor(value, rgb) 1055 alpha = lut.GetOpacity(value) 1056 return np.array(rgb + [alpha]) 1057 1058 def opacity(self, alpha=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 1059 """Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as `mesh.alpha()`.""" 1060 return self.alpha(alpha) 1061 1062 def force_opaque(self, value=True) -> Self: 1063 """ Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as opaque""" 1064 ## force the opaque pass, fixes picking in vtk9 1065 # but causes other bad troubles with lines.. 1066 self.actor.SetForceOpaque(value) 1067 return self 1068 1069 def force_translucent(self, value=True) -> Self: 1070 """ Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as translucent""" 1071 self.actor.SetForceTranslucent(value) 1072 return self 1073 1074 def point_size(self, value=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 1075 """Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as `mesh.ps()`""" 1076 if value is None: 1077 return self.properties.GetPointSize() 1078 # self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 1079 else: 1080 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 1081 self.properties.SetPointSize(value) 1082 return self 1083 1084 def ps(self, pointsize=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 1085 """Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as `mesh.point_size()`""" 1086 return self.point_size(pointsize) 1087 1088 def render_points_as_spheres(self, value=True) -> Self: 1089 """Make points look spheric or else make them look as squares.""" 1090 self.properties.SetRenderPointsAsSpheres(value) 1091 return self 1092 1093 def lighting( 1094 self, 1095 style="", 1096 ambient=None, 1097 diffuse=None, 1098 specular=None, 1099 specular_power=None, 1100 specular_color=None, 1101 metallicity=None, 1102 roughness=None, 1103 ) -> Self: 1104 """ 1105 Set the ambient, diffuse, specular and specular_power lighting constants. 1106 1107 Arguments: 1108 style : (str) 1109 preset style, options are `[metallic, plastic, shiny, glossy, ambient, off]` 1110 ambient : (float) 1111 ambient fraction of emission [0-1] 1112 diffuse : (float) 1113 emission of diffused light in fraction [0-1] 1114 specular : (float) 1115 fraction of reflected light [0-1] 1116 specular_power : (float) 1117 precision of reflection [1-100] 1118 specular_color : (color) 1119 color that is being reflected by the surface 1120 1121 <img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Phong_components_version_4.png" alt="", width=700px> 1122 1123 Examples: 1124 - [specular.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/specular.py) 1125 """ 1126 pr = self.properties 1127 1128 if style: 1129 1130 if style != "off": 1131 pr.LightingOn() 1132 1133 if style == "off": 1134 pr.SetInterpolationToFlat() 1135 pr.LightingOff() 1136 return self ############## 1137 1138 if hasattr(pr, "GetColor"): # could be Volume 1139 c = pr.GetColor() 1140 else: 1141 c = (1, 1, 0.99) 1142 mpr = self.mapper 1143 if hasattr(mpr, 'GetScalarVisibility') and mpr.GetScalarVisibility(): 1144 c = (1,1,0.99) 1145 if style=='metallic': pars = [0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 10, c] 1146 elif style=='plastic' : pars = [0.3, 0.4, 0.3, 5, c] 1147 elif style=='shiny' : pars = [0.2, 0.6, 0.8, 50, c] 1148 elif style=='glossy' : pars = [0.1, 0.7, 0.9, 90, (1,1,0.99)] 1149 elif style=='ambient' : pars = [0.8, 0.1, 0.0, 1, (1,1,1)] 1150 elif style=='default' : pars = [0.1, 1.0, 0.05, 5, c] 1151 else: 1152 vedo.logger.error("in lighting(): Available styles are") 1153 vedo.logger.error("[default, metallic, plastic, shiny, glossy, ambient, off]") 1154 raise RuntimeError() 1155 pr.SetAmbient(pars[0]) 1156 pr.SetDiffuse(pars[1]) 1157 pr.SetSpecular(pars[2]) 1158 pr.SetSpecularPower(pars[3]) 1159 if hasattr(pr, "GetColor"): 1160 pr.SetSpecularColor(pars[4]) 1161 1162 if ambient is not None: pr.SetAmbient(ambient) 1163 if diffuse is not None: pr.SetDiffuse(diffuse) 1164 if specular is not None: pr.SetSpecular(specular) 1165 if specular_power is not None: pr.SetSpecularPower(specular_power) 1166 if specular_color is not None: pr.SetSpecularColor(colors.get_color(specular_color)) 1167 if metallicity is not None: 1168 pr.SetInterpolationToPBR() 1169 pr.SetMetallic(metallicity) 1170 if roughness is not None: 1171 pr.SetInterpolationToPBR() 1172 pr.SetRoughness(roughness) 1173 1174 return self 1175 1176 def point_blurring(self, r=1, alpha=1.0, emissive=False) -> Self: 1177 """Set point blurring. 1178 Apply a gaussian convolution filter to the points. 1179 In this case the radius `r` is in absolute units of the mesh coordinates. 1180 With emissive set, the halo of point becomes light-emissive. 1181 """ 1182 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 1183 if emissive: 1184 self.mapper.SetEmissive(bool(emissive)) 1185 self.mapper.SetScaleFactor(r * 1.4142) 1186 1187 # https://kitware.github.io/vtk-examples/site/Python/Meshes/PointInterpolator/ 1188 if alpha < 1: 1189 self.mapper.SetSplatShaderCode( 1190 "//VTK::Color::Impl\n" 1191 "float dist = dot(offsetVCVSOutput.xy,offsetVCVSOutput.xy);\n" 1192 "if (dist > 1.0) {\n" 1193 " discard;\n" 1194 "} else {\n" 1195 f" float scale = ({alpha} - dist);\n" 1196 " ambientColor *= scale;\n" 1197 " diffuseColor *= scale;\n" 1198 "}\n" 1199 ) 1200 alpha = 1 1201 1202 self.mapper.Modified() 1203 self.actor.Modified() 1204 self.properties.SetOpacity(alpha) 1205 self.actor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 1206 return self 1207 1208 @property 1209 def cellcolors(self): 1210 """ 1211 Colorize each cell (face) of a mesh by passing 1212 a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. 1213 Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255]. 1214 1215 A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA. 1216 1217 A cell array named "CellsRGBA" is automatically created. 1218 1219 Examples: 1220 - [color_mesh_cells1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/color_mesh_cells1.py) 1221 - [color_mesh_cells2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/color_mesh_cells2.py) 1222 1223  1224 """ 1225 if "CellsRGBA" not in self.celldata.keys(): 1226 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1227 vscalars = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 1228 if vscalars is None or lut is None: 1229 arr = np.zeros([self.ncells, 4], dtype=np.uint8) 1230 col = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1231 col = np.round(col * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1232 alf = self.properties.GetOpacity() 1233 alf = np.round(alf * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1234 arr[:, (0, 1, 2)] = col 1235 arr[:, 3] = alf 1236 else: 1237 cols = lut.MapScalars(vscalars, 0, 0) 1238 arr = utils.vtk2numpy(cols) 1239 self.celldata["CellsRGBA"] = arr 1240 self.celldata.select("CellsRGBA") 1241 return self.celldata["CellsRGBA"] 1242 1243 @cellcolors.setter 1244 def cellcolors(self, value): 1245 if isinstance(value, str): 1246 c = colors.get_color(value) 1247 value = np.array([*c, 1]) * 255 1248 value = np.round(value) 1249 1250 value = np.asarray(value) 1251 n = self.ncells 1252 1253 if value.ndim == 1: 1254 value = np.repeat([value], n, axis=0) 1255 1256 if value.shape[1] == 3: 1257 z = np.zeros((n, 1), dtype=np.uint8) 1258 value = np.append(value, z + 255, axis=1) 1259 1260 assert n == value.shape[0] 1261 1262 self.celldata["CellsRGBA"] = value.astype(np.uint8) 1263 # self.mapper.SetColorModeToDirectScalars() # done in select() 1264 self.celldata.select("CellsRGBA") 1265 1266 @property 1267 def pointcolors(self): 1268 """ 1269 Colorize each point (or vertex of a mesh) by passing 1270 a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. 1271 Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255]. 1272 1273 A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA. 1274 1275 A point array named "PointsRGBA" is automatically created. 1276 """ 1277 if "PointsRGBA" not in self.pointdata.keys(): 1278 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1279 vscalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 1280 if vscalars is None or lut is None: 1281 # create a constant array 1282 arr = np.zeros([self.npoints, 4], dtype=np.uint8) 1283 col = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1284 col = np.round(col * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1285 alf = self.properties.GetOpacity() 1286 alf = np.round(alf * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1287 arr[:, (0, 1, 2)] = col 1288 arr[:, 3] = alf 1289 else: 1290 cols = lut.MapScalars(vscalars, 0, 0) 1291 arr = utils.vtk2numpy(cols) 1292 self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"] = arr 1293 self.pointdata.select("PointsRGBA") 1294 return self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"] 1295 1296 @pointcolors.setter 1297 def pointcolors(self, value): 1298 if isinstance(value, str): 1299 c = colors.get_color(value) 1300 value = np.array([*c, 1]) * 255 1301 value = np.round(value) 1302 1303 value = np.asarray(value) 1304 n = self.npoints 1305 1306 if value.ndim == 1: 1307 value = np.repeat([value], n, axis=0) 1308 1309 if value.shape[1] == 3: 1310 z = np.zeros((n, 1), dtype=np.uint8) 1311 value = np.append(value, z + 255, axis=1) 1312 1313 assert n == value.shape[0] 1314 1315 self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"] = value.astype(np.uint8) 1316 self.mapper.SetColorModeToDirectScalars() # also done in select() 1317 self.pointdata.select("PointsRGBA") 1318 1319 ##################################################################################### 1320 def cmap( 1321 self, 1322 input_cmap, 1323 input_array=None, 1324 on="", 1325 name="Scalars", 1326 vmin=None, 1327 vmax=None, 1328 n_colors=256, 1329 alpha=1.0, 1330 logscale=False, 1331 ) -> Self: 1332 """ 1333 Set individual point/cell colors by providing a list of scalar values and a color map. 1334 1335 Arguments: 1336 input_cmap : (str, list, vtkLookupTable, matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap) 1337 color map scheme to transform a real number into a color. 1338 input_array : (str, list, vtkArray) 1339 can be the string name of an existing array, a new array or a `vtkArray`. 1340 on : (str) 1341 either 'points' or 'cells' or blank (automatic). 1342 Apply the color map to data which is defined on either points or cells. 1343 name : (str) 1344 give a name to the provided array (if input_array is an array) 1345 vmin : (float) 1346 clip scalars to this minimum value 1347 vmax : (float) 1348 clip scalars to this maximum value 1349 n_colors : (int) 1350 number of distinct colors to be used in colormap table. 1351 alpha : (float, list) 1352 Mesh transparency. Can be a `list` of values one for each vertex. 1353 logscale : (bool) 1354 Use logscale 1355 1356 Examples: 1357 - [mesh_coloring.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_coloring.py) 1358 - [mesh_alphas.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_alphas.py) 1359 - [mesh_custom.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_custom.py) 1360 - (and many others) 1361 1362  1363 """ 1364 self._cmap_name = input_cmap 1365 1366 if on == "": 1367 try: 1368 on = self.mapper.GetScalarModeAsString().replace("Use", "") 1369 if on not in ["PointData", "CellData"]: # can be "Default" 1370 on = "points" 1371 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1372 except AttributeError: 1373 on = "points" 1374 elif on == "Default": 1375 on = "points" 1376 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1377 1378 if input_array is None: 1379 if not self.pointdata.keys() and self.celldata.keys(): 1380 on = "cells" 1381 if not self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 1382 input_array = 0 # pick the first at hand 1383 1384 if "point" in on.lower(): 1385 data = self.dataset.GetPointData() 1386 n = self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints() 1387 elif "cell" in on.lower(): 1388 data = self.dataset.GetCellData() 1389 n = self.dataset.GetNumberOfCells() 1390 else: 1391 vedo.logger.error( 1392 f"Must specify in cmap(on=...) to either 'cells' or 'points', not {on}") 1393 raise RuntimeError() 1394 1395 if input_array is None: # if None try to fetch the active scalars 1396 arr = data.GetScalars() 1397 if not arr: 1398 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find any {on} active array ...skip coloring.") 1399 return self 1400 1401 if not arr.GetName(): # sometimes arrays dont have a name.. 1402 arr.SetName(name) 1403 1404 elif isinstance(input_array, str): # if a string is passed 1405 arr = data.GetArray(input_array) 1406 if not arr: 1407 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find {on} array {input_array} ...skip coloring.") 1408 return self 1409 1410 elif isinstance(input_array, int): # if an int is passed 1411 if input_array < data.GetNumberOfArrays(): 1412 arr = data.GetArray(input_array) 1413 else: 1414 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find {on} array at {input_array} ...skip coloring.") 1415 return self 1416 1417 elif utils.is_sequence(input_array): # if a numpy array is passed 1418 npts = len(input_array) 1419 if npts != n: 1420 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), nr. of input {on} scalars {npts} != {n} ...skip coloring.") 1421 return self 1422 arr = utils.numpy2vtk(input_array, name=name, dtype=float) 1423 data.AddArray(arr) 1424 data.Modified() 1425 1426 elif isinstance(input_array, vtki.vtkArray): # if a vtkArray is passed 1427 arr = input_array 1428 data.AddArray(arr) 1429 data.Modified() 1430 1431 else: 1432 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot understand input type {type(input_array)}") 1433 raise RuntimeError() 1434 1435 # Now we have array "arr" 1436 array_name = arr.GetName() 1437 1438 if arr.GetNumberOfComponents() == 1: 1439 if vmin is None: 1440 vmin = arr.GetRange()[0] 1441 if vmax is None: 1442 vmax = arr.GetRange()[1] 1443 else: 1444 if vmin is None or vmax is None: 1445 vn = utils.mag(utils.vtk2numpy(arr)) 1446 if vmin is None: 1447 vmin = vn.min() 1448 if vmax is None: 1449 vmax = vn.max() 1450 1451 # interpolate alphas if they are not constant 1452 if not utils.is_sequence(alpha): 1453 alpha = [alpha] * n_colors 1454 else: 1455 v = np.linspace(0, 1, n_colors, endpoint=True) 1456 xp = np.linspace(0, 1, len(alpha), endpoint=True) 1457 alpha = np.interp(v, xp, alpha) 1458 1459 ########################### build the look-up table 1460 if isinstance(input_cmap, vtki.vtkLookupTable): # vtkLookupTable 1461 lut = input_cmap 1462 1463 elif utils.is_sequence(input_cmap): # manual sequence of colors 1464 lut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 1465 if logscale: 1466 lut.SetScaleToLog10() 1467 lut.SetRange(vmin, vmax) 1468 ncols = len(input_cmap) 1469 lut.SetNumberOfTableValues(ncols) 1470 1471 for i, c in enumerate(input_cmap): 1472 r, g, b = colors.get_color(c) 1473 lut.SetTableValue(i, r, g, b, alpha[i]) 1474 lut.Build() 1475 1476 else: 1477 # assume string cmap name OR matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap 1478 lut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 1479 if logscale: 1480 lut.SetScaleToLog10() 1481 lut.SetVectorModeToMagnitude() 1482 lut.SetRange(vmin, vmax) 1483 lut.SetNumberOfTableValues(n_colors) 1484 mycols = colors.color_map(range(n_colors), input_cmap, 0, n_colors) 1485 for i, c in enumerate(mycols): 1486 r, g, b = c 1487 lut.SetTableValue(i, r, g, b, alpha[i]) 1488 lut.Build() 1489 1490 # TEST NEW WAY 1491 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 1492 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1493 self.mapper.SetColorModeToMapScalars() 1494 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(lut.GetRange()) 1495 if "point" in on.lower(): 1496 self.pointdata.select(array_name) 1497 else: 1498 self.celldata.select(array_name) 1499 return self 1500 1501 # # TEST this is the old way: 1502 # # arr.SetLookupTable(lut) # wrong! causes weird instabilities with LUT 1503 # # if data.GetScalars(): 1504 # # data.GetScalars().SetLookupTable(lut) 1505 # # data.GetScalars().Modified() 1506 1507 # data.SetActiveScalars(array_name) 1508 # # data.SetScalars(arr) # wrong! it deletes array in position 0, never use SetScalars 1509 # # data.SetActiveAttribute(array_name, 0) # boh! 1510 1511 # self.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 1512 # self.mapper.SetColorModeToMapScalars() # so we dont need to convert uint8 scalars 1513 1514 # self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1515 # self.mapper.SetScalarRange(lut.GetRange()) 1516 1517 # if on.startswith("point"): 1518 # self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1519 # else: 1520 # self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUseCellData() 1521 # if hasattr(self.mapper, "SetArrayName"): 1522 # self.mapper.SetArrayName(array_name) 1523 # return self 1524 1525 def add_trail(self, offset=(0, 0, 0), n=50, c=None, alpha=1.0, lw=2) -> Self: 1526 """ 1527 Add a trailing line to mesh. 1528 This new mesh is accessible through `mesh.trail`. 1529 1530 Arguments: 1531 offset : (float) 1532 set an offset vector from the object center. 1533 n : (int) 1534 number of segments 1535 lw : (float) 1536 line width of the trail 1537 1538 Examples: 1539 - [trail.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/trail.py) 1540 1541  1542 1543 - [airplane1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane1.py) 1544 - [airplane2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane2.py) 1545 """ 1546 if self.trail is None: 1547 pos = self.pos() 1548 self.trail_offset = np.asarray(offset) 1549 self.trail_points = [pos] * n 1550 1551 if c is None: 1552 col = self.properties.GetColor() 1553 else: 1554 col = colors.get_color(c) 1555 1556 tline = vedo.shapes.Line(pos, pos, res=n, c=col, alpha=alpha, lw=lw) 1557 self.trail = tline # holds the Line 1558 self.trail.initilized = False # so the first update will be a reset 1559 return self 1560 1561 def update_trail(self) -> Self: 1562 """ 1563 Update the trailing line of a moving object. 1564 """ 1565 currentpos = self.pos() 1566 if not self.trail.initilized: 1567 self.trail_points = [currentpos] * self.trail.npoints 1568 self.trail.initilized = True 1569 return self 1570 self.trail_points.append(currentpos) # cycle 1571 self.trail_points.pop(0) 1572 1573 data = np.array(self.trail_points) + self.trail_offset 1574 tpoly = self.trail.dataset 1575 tpoly.GetPoints().SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(data, dtype=np.float32)) 1576 return self 1577 1578 def _compute_shadow(self, plane, point, direction): 1579 shad = self.clone() 1580 shad.name = "Shadow" 1581 1582 tarr = shad.dataset.GetPointData().GetTCoords() 1583 if tarr: # remove any texture coords 1584 tname = tarr.GetName() 1585 shad.pointdata.remove(tname) 1586 shad.dataset.GetPointData().SetTCoords(None) 1587 shad.actor.SetTexture(None) 1588 1589 pts = shad.vertices 1590 if plane == "x": 1591 # shad = shad.project_on_plane('x') 1592 # instead do it manually so in case of alpha<1 1593 # we dont see glitches due to coplanar points 1594 # we leave a small tolerance of 0.1% in thickness 1595 x0, x1 = self.xbounds() 1596 pts[:, 0] = (pts[:, 0] - (x0 + x1) / 2) / 1000 + self.actor.GetOrigin()[0] 1597 shad.vertices = pts 1598 shad.x(point) 1599 elif plane == "y": 1600 x0, x1 = self.ybounds() 1601 pts[:, 1] = (pts[:, 1] - (x0 + x1) / 2) / 1000 + self.actor.GetOrigin()[1] 1602 shad.vertices = pts 1603 shad.y(point) 1604 elif plane == "z": 1605 x0, x1 = self.zbounds() 1606 pts[:, 2] = (pts[:, 2] - (x0 + x1) / 2) / 1000 + self.actor.GetOrigin()[2] 1607 shad.vertices = pts 1608 shad.z(point) 1609 else: 1610 shad = shad.project_on_plane(plane, point, direction) 1611 return shad 1612 1613 def add_shadow(self, plane, point, direction=None, c=(0.6, 0.6, 0.6), alpha=1, culling=0) -> Self: 1614 """ 1615 Generate a shadow out of an `Mesh` on one of the three Cartesian planes. 1616 The output is a new `Mesh` representing the shadow. 1617 This new mesh is accessible through `mesh.shadow`. 1618 By default the shadow mesh is placed on the bottom wall of the bounding box. 1619 1620 See also `pointcloud.project_on_plane()`. 1621 1622 Arguments: 1623 plane : (str, Plane) 1624 if plane is `str`, plane can be one of `['x', 'y', 'z']`, 1625 represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. 1626 Otherwise, plane should be an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane` 1627 point : (float, array) 1628 if plane is `str`, point should be a float represents the intercept. 1629 Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection 1630 direction : (list) 1631 direction of oblique projection 1632 culling : (int) 1633 choose between front [1] or backface [-1] culling or None. 1634 1635 Examples: 1636 - [shadow1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/shadow1.py) 1637 - [airplane1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane1.py) 1638 - [airplane2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane2.py) 1639 1640  1641 """ 1642 shad = self._compute_shadow(plane, point, direction) 1643 shad.c(c).alpha(alpha) 1644 1645 try: 1646 # Points dont have these methods 1647 shad.flat() 1648 if culling in (1, True): 1649 shad.frontface_culling() 1650 elif culling == -1: 1651 shad.backface_culling() 1652 except AttributeError: 1653 pass 1654 1655 shad.properties.LightingOff() 1656 shad.actor.SetPickable(False) 1657 shad.actor.SetUseBounds(True) 1658 1659 if shad not in self.shadows: 1660 self.shadows.append(shad) 1661 shad.info = dict(plane=plane, point=point, direction=direction) 1662 # shad.metadata["plane"] = plane 1663 # shad.metadata["point"] = point 1664 # print("AAAA", direction, plane, point) 1665 # if direction is None: 1666 # direction = [0,0,0] 1667 # shad.metadata["direction"] = direction 1668 return self 1669 1670 def update_shadows(self) -> Self: 1671 """Update the shadows of a moving object.""" 1672 for sha in self.shadows: 1673 plane = sha.info["plane"] 1674 point = sha.info["point"] 1675 direction = sha.info["direction"] 1676 # print("update_shadows direction", direction,plane,point ) 1677 # plane = sha.metadata["plane"] 1678 # point = sha.metadata["point"] 1679 # direction = sha.metadata["direction"] 1680 # if direction[0]==0 and direction[1]==0 and direction[2]==0: 1681 # direction = None 1682 # print("BBBB", sha.metadata["direction"], 1683 # sha.metadata["plane"], sha.metadata["point"]) 1684 new_sha = self._compute_shadow(plane, point, direction) 1685 sha._update(new_sha.dataset) 1686 if self.trail: 1687 self.trail.update_shadows() 1688 return self 1689 1690 def labels( 1691 self, 1692 content=None, 1693 on="points", 1694 scale=None, 1695 xrot=0.0, 1696 yrot=0.0, 1697 zrot=0.0, 1698 ratio=1, 1699 precision=None, 1700 italic=False, 1701 font="", 1702 justify="", 1703 c="black", 1704 alpha=1.0, 1705 ) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", None]: 1706 """ 1707 Generate value or ID labels for mesh cells or points. 1708 For large nr. of labels use `font="VTK"` which is much faster. 1709 1710 See also: 1711 `labels2d()`, `flagpole()`, `caption()` and `legend()`. 1712 1713 Arguments: 1714 content : (list,int,str) 1715 either 'id', 'cellid', array name or array number. 1716 A array can also be passed (must match the nr. of points or cells). 1717 on : (str) 1718 generate labels for "cells" instead of "points" 1719 scale : (float) 1720 absolute size of labels, if left as None it is automatic 1721 zrot : (float) 1722 local rotation angle of label in degrees 1723 ratio : (int) 1724 skipping ratio, to reduce nr of labels for large meshes 1725 precision : (int) 1726 numeric precision of labels 1727 1728 ```python 1729 from vedo import * 1730 s = Sphere(res=10).linewidth(1).c("orange").compute_normals() 1731 point_ids = s.labels('id', on="points").c('green') 1732 cell_ids = s.labels('id', on="cells" ).c('black') 1733 show(s, point_ids, cell_ids) 1734 ``` 1735  1736 1737 Examples: 1738 - [boundaries.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/boundaries.py) 1739 1740  1741 """ 1742 1743 cells = False 1744 if "cell" in on or "face" in on: 1745 cells = True 1746 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1747 1748 if isinstance(content, str): 1749 if content in ("pointid", "pointsid"): 1750 cells = False 1751 content = "id" 1752 justify = "bottom-left" if justify == "" else justify 1753 if content in ("cellid", "cellsid"): 1754 cells = True 1755 content = "id" 1756 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1757 1758 try: 1759 if cells: 1760 ns = np.sqrt(self.ncells) 1761 elems = self.cell_centers().points 1762 norms = self.cell_normals 1763 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1764 else: 1765 ns = np.sqrt(self.npoints) 1766 elems = self.vertices 1767 norms = self.vertex_normals 1768 except AttributeError: 1769 norms = [] 1770 1771 if not justify: 1772 justify = "bottom-left" 1773 1774 hasnorms = False 1775 if len(norms) > 0: 1776 hasnorms = True 1777 1778 if scale is None: 1779 if not ns: 1780 ns = 100 1781 scale = self.diagonal_size() / ns / 10 1782 1783 arr = None 1784 mode = 0 1785 if content is None: 1786 mode = 0 1787 if cells: 1788 if self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 1789 name = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars().GetName() 1790 arr = self.celldata[name] 1791 else: 1792 if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 1793 name = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars().GetName() 1794 arr = self.pointdata[name] 1795 elif isinstance(content, (str, int)): 1796 if content == "id": 1797 mode = 1 1798 elif cells: 1799 mode = 0 1800 arr = self.celldata[content] 1801 else: 1802 mode = 0 1803 arr = self.pointdata[content] 1804 elif utils.is_sequence(content): 1805 mode = 0 1806 arr = content 1807 1808 if arr is None and mode == 0: 1809 vedo.logger.error("in labels(), array not found in point or cell data") 1810 return None 1811 1812 ratio = int(ratio+0.5) 1813 tapp = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1814 has_inputs = False 1815 1816 for i, e in enumerate(elems): 1817 if i % ratio: 1818 continue 1819 1820 if mode == 1: 1821 txt_lab = str(i) 1822 else: 1823 if precision: 1824 txt_lab = utils.precision(arr[i], precision) 1825 else: 1826 txt_lab = str(arr[i]) 1827 1828 if not txt_lab: 1829 continue 1830 1831 if font == "VTK": 1832 tx = vtki.new("VectorText") 1833 tx.SetText(txt_lab) 1834 tx.Update() 1835 tx_poly = tx.GetOutput() 1836 else: 1837 tx_poly = vedo.shapes.Text3D(txt_lab, font=font, justify=justify).dataset 1838 1839 if tx_poly.GetNumberOfPoints() == 0: 1840 continue ###################### 1841 1842 T = vtki.vtkTransform() 1843 T.PostMultiply() 1844 if italic: 1845 T.Concatenate([1, 0.2, 0, 0, 1846 0, 1 , 0, 0, 1847 0, 0 , 1, 0, 1848 0, 0 , 0, 1]) 1849 if hasnorms: 1850 ni = norms[i] 1851 if cells and font=="VTK": # center-justify 1852 bb = tx_poly.GetBounds() 1853 dx, dy = (bb[1] - bb[0]) / 2, (bb[3] - bb[2]) / 2 1854 T.Translate(-dx, -dy, 0) 1855 if xrot: T.RotateX(xrot) 1856 if yrot: T.RotateY(yrot) 1857 if zrot: T.RotateZ(zrot) 1858 crossvec = np.cross([0, 0, 1], ni) 1859 angle = np.arccos(np.dot([0, 0, 1], ni)) * 57.3 1860 T.RotateWXYZ(float(angle), crossvec.tolist()) 1861 T.Translate(ni / 100) 1862 else: 1863 if xrot: T.RotateX(xrot) 1864 if yrot: T.RotateY(yrot) 1865 if zrot: T.RotateZ(zrot) 1866 T.Scale(scale, scale, scale) 1867 T.Translate(e) 1868 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 1869 tf.SetInputData(tx_poly) 1870 tf.SetTransform(T) 1871 tf.Update() 1872 tapp.AddInputData(tf.GetOutput()) 1873 has_inputs = True 1874 1875 if has_inputs: 1876 tapp.Update() 1877 lpoly = tapp.GetOutput() 1878 else: 1879 lpoly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1880 ids = vedo.Mesh(lpoly, c=c, alpha=alpha) 1881 ids.properties.LightingOff() 1882 ids.actor.PickableOff() 1883 ids.actor.SetUseBounds(False) 1884 ids.name = "Labels" 1885 return ids 1886 1887 def labels2d( 1888 self, 1889 content="id", 1890 on="points", 1891 scale=1.0, 1892 precision=4, 1893 font="Calco", 1894 justify="bottom-left", 1895 angle=0.0, 1896 frame=False, 1897 c="black", 1898 bc=None, 1899 alpha=1.0, 1900 ) -> Union["Actor2D", None]: 1901 """ 1902 Generate value or ID bi-dimensional labels for mesh cells or points. 1903 1904 See also: `labels()`, `flagpole()`, `caption()` and `legend()`. 1905 1906 Arguments: 1907 content : (str) 1908 either 'id', 'cellid', or array name 1909 on : (str) 1910 generate labels for "cells" instead of "points" (the default) 1911 scale : (float) 1912 size scaling of labels 1913 precision : (int) 1914 precision of numeric labels 1915 angle : (float) 1916 local rotation angle of label in degrees 1917 frame : (bool) 1918 draw a frame around the label 1919 bc : (str) 1920 background color of the label 1921 1922 ```python 1923 from vedo import Sphere, show 1924 sph = Sphere(quads=True, res=4).compute_normals().wireframe() 1925 sph.celldata["zvals"] = sph.cell_centers().coordinates[:,2] 1926 l2d = sph.labels("zvals", on="cells", precision=2).backcolor('orange9') 1927 show(sph, l2d, axes=1).close() 1928 ``` 1929  1930 """ 1931 cells = False 1932 if "cell" in on: 1933 cells = True 1934 1935 if isinstance(content, str): 1936 if content in ("id", "pointid", "pointsid"): 1937 cells = False 1938 content = "id" 1939 if content in ("cellid", "cellsid"): 1940 cells = True 1941 content = "id" 1942 1943 if cells: 1944 if content != "id" and content not in self.celldata.keys(): 1945 vedo.logger.error(f"In labels2d: cell array {content} does not exist.") 1946 return None 1947 arr = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 1948 poly = self.cell_centers().dataset 1949 poly.GetPointData().SetScalars(arr) 1950 else: 1951 arr = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 1952 poly = self.dataset 1953 if content != "id" and content not in self.pointdata.keys(): 1954 vedo.logger.error(f"In labels2d: point array {content} does not exist.") 1955 return None 1956 1957 mp = vtki.new("LabeledDataMapper") 1958 1959 if content == "id": 1960 mp.SetLabelModeToLabelIds() 1961 else: 1962 mp.SetLabelModeToLabelScalars() 1963 if precision is not None: 1964 dtype = arr.GetDataType() 1965 if dtype in (vtki.VTK_FLOAT, vtki.VTK_DOUBLE): 1966 mp.SetLabelFormat(f"%-#.{precision}g") 1967 1968 pr = mp.GetLabelTextProperty() 1969 c = colors.get_color(c) 1970 pr.SetColor(c) 1971 pr.SetOpacity(alpha) 1972 pr.SetFrame(frame) 1973 pr.SetFrameColor(c) 1974 pr.SetItalic(False) 1975 pr.BoldOff() 1976 pr.ShadowOff() 1977 pr.UseTightBoundingBoxOn() 1978 pr.SetOrientation(angle) 1979 pr.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 1980 fl = utils.get_font_path(font) 1981 pr.SetFontFile(fl) 1982 pr.SetFontSize(int(20 * scale)) 1983 1984 if "cent" in justify or "mid" in justify: 1985 pr.SetJustificationToCentered() 1986 elif "rig" in justify: 1987 pr.SetJustificationToRight() 1988 elif "left" in justify: 1989 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 1990 # ------ 1991 if "top" in justify: 1992 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 1993 else: 1994 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 1995 1996 if bc is not None: 1997 bc = colors.get_color(bc) 1998 pr.SetBackgroundColor(bc) 1999 pr.SetBackgroundOpacity(alpha) 2000 2001 mp.SetInputData(poly) 2002 a2d = Actor2D() 2003 a2d.PickableOff() 2004 a2d.SetMapper(mp) 2005 return a2d 2006 2007 def legend(self, txt) -> Self: 2008 """Book a legend text.""" 2009 self.info["legend"] = txt 2010 # self.metadata["legend"] = txt 2011 return self 2012 2013 def flagpole( 2014 self, 2015 txt=None, 2016 point=None, 2017 offset=None, 2018 s=None, 2019 font="Calco", 2020 rounded=True, 2021 c=None, 2022 alpha=1.0, 2023 lw=2, 2024 italic=0.0, 2025 padding=0.1, 2026 ) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", None]: 2027 """ 2028 Generate a flag pole style element to describe an object. 2029 Returns a `Mesh` object. 2030 2031 Use flagpole.follow_camera() to make it face the camera in the scene. 2032 2033 Consider using `settings.use_parallel_projection = True` 2034 to avoid perspective distortions. 2035 2036 See also `flagpost()`. 2037 2038 Arguments: 2039 txt : (str) 2040 Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name. 2041 point : (list) 2042 position of the flagpole pointer. 2043 offset : (list) 2044 text offset wrt the application point. 2045 s : (float) 2046 size of the flagpole. 2047 font : (str) 2048 font face. Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2049 rounded : (bool) 2050 draw a rounded or squared box around the text. 2051 c : (list) 2052 text and box color. 2053 alpha : (float) 2054 opacity of text and box. 2055 lw : (float) 2056 line with of box frame. 2057 italic : (float) 2058 italicness of text. 2059 2060 Examples: 2061 - [intersect2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/intersect2d.py) 2062 2063 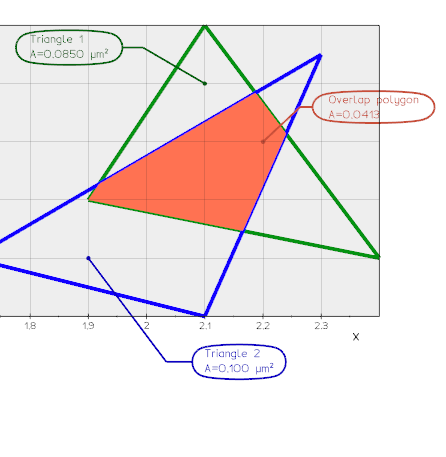 2064 2065 - [goniometer.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/goniometer.py) 2066 - [flag_labels1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels1.py) 2067 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2068 """ 2069 objs = [] 2070 2071 if txt is None: 2072 if self.filename: 2073 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2074 elif self.name: 2075 txt = self.name 2076 else: 2077 return None 2078 2079 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2080 d = self.diagonal_size() 2081 if point is None: 2082 if d: 2083 point = self.closest_point([(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1]) 2084 # point = self.closest_point([x1, y0, z1]) 2085 else: # it's a Point 2086 point = self.transform.position 2087 2088 pt = utils.make3d(point) 2089 2090 if offset is None: 2091 offset = [(x1 - x0) / 1.75, (y1 - y0) / 5, 0] 2092 offset = utils.make3d(offset) 2093 2094 if s is None: 2095 s = d / 20 2096 2097 sph = None 2098 if d and (z1 - z0) / d > 0.1: 2099 sph = vedo.shapes.Sphere(pt, r=s * 0.4, res=6) 2100 2101 if c is None: 2102 c = np.array(self.color()) / 1.4 2103 2104 lab = vedo.shapes.Text3D( 2105 txt, pos=pt + offset, s=s, font=font, italic=italic, justify="center" 2106 ) 2107 objs.append(lab) 2108 2109 if d and not sph: 2110 sph = vedo.shapes.Circle(pt, r=s / 3, res=16) 2111 objs.append(sph) 2112 2113 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = lab.bounds() 2114 aline = [(x0,y0,z0), (x1,y0,z0), (x1,y1,z0), (x0,y1,z0)] 2115 if rounded: 2116 box = vedo.shapes.KSpline(aline, closed=True) 2117 else: 2118 box = vedo.shapes.Line(aline, closed=True) 2119 2120 cnt = [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, (z0 + z1) / 2] 2121 2122 # box.actor.SetOrigin(cnt) 2123 box.scale([1 + padding, 1 + 2 * padding, 1], origin=cnt) 2124 objs.append(box) 2125 2126 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = box.bounds() 2127 if x0 < pt[0] < x1: 2128 c0 = box.closest_point(pt) 2129 c1 = [c0[0], c0[1] + (pt[1] - y0) / 4, pt[2]] 2130 elif (pt[0] - x0) < (x1 - pt[0]): 2131 c0 = [x0, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2132 c1 = [x0 + (pt[0] - x0) / 4, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2133 else: 2134 c0 = [x1, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2135 c1 = [x1 + (pt[0] - x1) / 4, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2136 2137 con = vedo.shapes.Line([c0, c1, pt]) 2138 objs.append(con) 2139 2140 mobjs = vedo.merge(objs).c(c).alpha(alpha) 2141 mobjs.name = "FlagPole" 2142 mobjs.bc("tomato").pickable(False) 2143 mobjs.properties.LightingOff() 2144 mobjs.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2145 mobjs.actor.UseBoundsOff() 2146 mobjs.actor.SetPosition([0,0,0]) 2147 mobjs.actor.SetOrigin(pt) 2148 return mobjs 2149 2150 # mobjs = vedo.Assembly(objs)#.c(c).alpha(alpha) 2151 # mobjs.name = "FlagPole" 2152 # # mobjs.bc("tomato").pickable(False) 2153 # # mobjs.properties.LightingOff() 2154 # # mobjs.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2155 # # mobjs.actor.UseBoundsOff() 2156 # # mobjs.actor.SetPosition([0,0,0]) 2157 # # mobjs.actor.SetOrigin(pt) 2158 # # print(pt) 2159 # return mobjs 2160 2161 def flagpost( 2162 self, 2163 txt=None, 2164 point=None, 2165 offset=None, 2166 s=1.0, 2167 c="k9", 2168 bc="k1", 2169 alpha=1, 2170 lw=0, 2171 font="Calco", 2172 justify="center-left", 2173 vspacing=1.0, 2174 ) -> Union["vedo.addons.Flagpost", None]: 2175 """ 2176 Generate a flag post style element to describe an object. 2177 2178 Arguments: 2179 txt : (str) 2180 Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name. 2181 point : (list) 2182 position of the flag anchor point. The default is None. 2183 offset : (list) 2184 a 3D displacement or offset. The default is None. 2185 s : (float) 2186 size of the text to be shown 2187 c : (list) 2188 color of text and line 2189 bc : (list) 2190 color of the flag background 2191 alpha : (float) 2192 opacity of text and box. 2193 lw : (int) 2194 line with of box frame. The default is 0. 2195 font : (str) 2196 font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "Calco". 2197 Type `vedo -r fonts` for a font demo. 2198 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2199 justify : (str) 2200 internal text justification. The default is "center-left". 2201 vspacing : (float) 2202 vertical spacing between lines. 2203 2204 Examples: 2205 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2206 2207 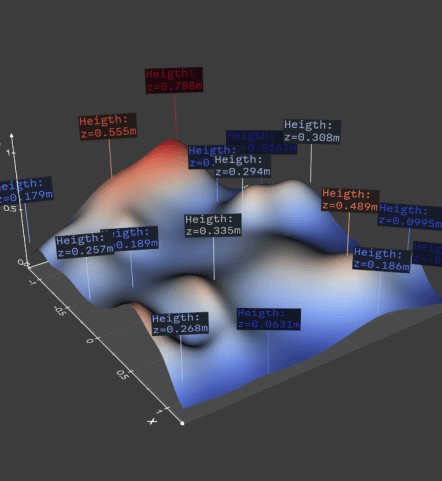 2208 """ 2209 if txt is None: 2210 if self.filename: 2211 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2212 elif self.name: 2213 txt = self.name 2214 else: 2215 return None 2216 2217 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2218 d = self.diagonal_size() 2219 if point is None: 2220 if d: 2221 point = self.closest_point([(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1]) 2222 else: # it's a Point 2223 point = self.transform.position 2224 2225 point = utils.make3d(point) 2226 2227 if offset is None: 2228 offset = [0, 0, (z1 - z0) / 2] 2229 offset = utils.make3d(offset) 2230 2231 fpost = vedo.addons.Flagpost( 2232 txt, point, point + offset, s, c, bc, alpha, lw, font, justify, vspacing 2233 ) 2234 self._caption = fpost 2235 return fpost 2236 2237 def caption( 2238 self, 2239 txt=None, 2240 point=None, 2241 size=(0.30, 0.15), 2242 padding=5, 2243 font="Calco", 2244 justify="center-right", 2245 vspacing=1.0, 2246 c=None, 2247 alpha=1.0, 2248 lw=1, 2249 ontop=True, 2250 ) -> Union["vtki.vtkCaptionActor2D", None]: 2251 """ 2252 Create a 2D caption to an object which follows the camera movements. 2253 Latex is not supported. Returns the same input object for concatenation. 2254 2255 See also `flagpole()`, `flagpost()`, `labels()` and `legend()` 2256 with similar functionality. 2257 2258 Arguments: 2259 txt : (str) 2260 text to be rendered. The default is the file name. 2261 point : (list) 2262 anchoring point. The default is None. 2263 size : (list) 2264 (width, height) of the caption box. The default is (0.30, 0.15). 2265 padding : (float) 2266 padding space of the caption box in pixels. The default is 5. 2267 font : (str) 2268 font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "VictorMono". 2269 Type `vedo -r fonts` for a font demo. 2270 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2271 justify : (str) 2272 internal text justification. The default is "center-right". 2273 vspacing : (float) 2274 vertical spacing between lines. The default is 1. 2275 c : (str) 2276 text and box color. The default is 'lb'. 2277 alpha : (float) 2278 text and box transparency. The default is 1. 2279 lw : (int) 2280 line width in pixels. The default is 1. 2281 ontop : (bool) 2282 keep the 2d caption always on top. The default is True. 2283 2284 Examples: 2285 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 2286 2287  2288 2289 - [flag_labels1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels1.py) 2290 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2291 """ 2292 if txt is None: 2293 if self.filename: 2294 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2295 elif self.name: 2296 txt = self.name 2297 2298 if not txt: # disable it 2299 self._caption = None 2300 return None 2301 2302 for r in vedo.shapes._reps: 2303 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 2304 2305 if c is None: 2306 c = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) / 2 2307 else: 2308 c = colors.get_color(c) 2309 2310 if point is None: 2311 x0, x1, y0, y1, _, z1 = self.dataset.GetBounds() 2312 pt = [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1] 2313 point = self.closest_point(pt) 2314 2315 capt = vtki.vtkCaptionActor2D() 2316 capt.SetAttachmentPoint(point) 2317 capt.SetBorder(True) 2318 capt.SetLeader(True) 2319 sph = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2320 sph.Update() 2321 capt.SetLeaderGlyphData(sph.GetOutput()) 2322 capt.SetMaximumLeaderGlyphSize(5) 2323 capt.SetPadding(int(padding)) 2324 capt.SetCaption(txt) 2325 capt.SetWidth(size[0]) 2326 capt.SetHeight(size[1]) 2327 capt.SetThreeDimensionalLeader(not ontop) 2328 2329 pra = capt.GetProperty() 2330 pra.SetColor(c) 2331 pra.SetOpacity(alpha) 2332 pra.SetLineWidth(lw) 2333 2334 pr = capt.GetCaptionTextProperty() 2335 pr.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 2336 fl = utils.get_font_path(font) 2337 pr.SetFontFile(fl) 2338 pr.ShadowOff() 2339 pr.BoldOff() 2340 pr.FrameOff() 2341 pr.SetColor(c) 2342 pr.SetOpacity(alpha) 2343 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 2344 if "top" in justify: 2345 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 2346 if "bottom" in justify: 2347 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 2348 if "cent" in justify: 2349 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToCentered() 2350 pr.SetJustificationToCentered() 2351 if "left" in justify: 2352 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 2353 if "right" in justify: 2354 pr.SetJustificationToRight() 2355 pr.SetLineSpacing(vspacing) 2356 return capt 2357 2358 2359##################################################################### 2360class MeshVisual(PointsVisual): 2361 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a `Mesh` object.""" 2362 2363 def __init__(self) -> None: 2364 # print("INIT MeshVisual", super()) 2365 super().__init__() 2366 2367 def follow_camera(self, camera=None, origin=None) -> Self: 2368 """ 2369 Return an object that will follow camera movements and stay locked to it. 2370 Use `mesh.follow_camera(False)` to disable it. 2371 2372 A `vtkCamera` object can also be passed. 2373 """ 2374 if camera is False: 2375 try: 2376 self.SetCamera(None) 2377 return self 2378 except AttributeError: 2379 return self 2380 2381 factor = vtki.vtkFollower() 2382 factor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 2383 factor.SetProperty(self.properties) 2384 factor.SetBackfaceProperty(self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty()) 2385 factor.SetTexture(self.actor.GetTexture()) 2386 factor.SetScale(self.actor.GetScale()) 2387 # factor.SetOrientation(self.actor.GetOrientation()) 2388 factor.SetPosition(self.actor.GetPosition()) 2389 factor.SetUseBounds(self.actor.GetUseBounds()) 2390 2391 if origin is None: 2392 factor.SetOrigin(self.actor.GetOrigin()) 2393 else: 2394 factor.SetOrigin(origin) 2395 2396 factor.PickableOff() 2397 2398 if isinstance(camera, vtki.vtkCamera): 2399 factor.SetCamera(camera) 2400 else: 2401 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 2402 if plt and plt.renderer and plt.renderer.GetActiveCamera(): 2403 factor.SetCamera(plt.renderer.GetActiveCamera()) 2404 2405 self.actor = None 2406 factor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 2407 self.actor = factor 2408 return self 2409 2410 def wireframe(self, value=True) -> Self: 2411 """Set mesh's representation as wireframe or solid surface.""" 2412 if value: 2413 self.properties.SetRepresentationToWireframe() 2414 else: 2415 self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 2416 return self 2417 2418 def flat(self) -> Self: 2419 """Set surface interpolation to flat. 2420 2421 <img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Phong_components_version_4.png" width="700"> 2422 """ 2423 self.properties.SetInterpolationToFlat() 2424 return self 2425 2426 def phong(self) -> Self: 2427 """Set surface interpolation to "phong".""" 2428 self.properties.SetInterpolationToPhong() 2429 return self 2430 2431 def backface_culling(self, value=True) -> Self: 2432 """Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.""" 2433 self.properties.SetBackfaceCulling(value) 2434 return self 2435 2436 def render_lines_as_tubes(self, value=True) -> Self: 2437 """Wrap a fake tube around a simple line for visualization""" 2438 self.properties.SetRenderLinesAsTubes(value) 2439 return self 2440 2441 def frontface_culling(self, value=True) -> Self: 2442 """Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.""" 2443 self.properties.SetFrontfaceCulling(value) 2444 return self 2445 2446 def backcolor(self, bc=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2447 """ 2448 Set/get mesh's backface color. 2449 """ 2450 back_prop = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 2451 2452 if bc is None: 2453 if back_prop: 2454 return back_prop.GetDiffuseColor() 2455 return self 2456 2457 if self.properties.GetOpacity() < 1: 2458 return self 2459 2460 if not back_prop: 2461 back_prop = vtki.vtkProperty() 2462 2463 back_prop.SetDiffuseColor(colors.get_color(bc)) 2464 back_prop.SetOpacity(self.properties.GetOpacity()) 2465 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(back_prop) 2466 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2467 return self 2468 2469 def bc(self, backcolor=False) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2470 """Shortcut for `mesh.backcolor()`.""" 2471 return self.backcolor(backcolor) 2472 2473 def linewidth(self, lw=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2474 """Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as `lw()`.""" 2475 if lw is not None: 2476 if lw == 0: 2477 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOff() 2478 self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 2479 return self 2480 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOn() 2481 self.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2482 else: 2483 return self.properties.GetLineWidth() 2484 return self 2485 2486 def lw(self, linewidth=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2487 """Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as `linewidth()`.""" 2488 return self.linewidth(linewidth) 2489 2490 def linecolor(self, lc=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2491 """Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as `lc()`.""" 2492 if lc is None: 2493 return np.array(self.properties.GetEdgeColor()) 2494 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOn() 2495 self.properties.SetEdgeColor(colors.get_color(lc)) 2496 return self 2497 2498 def lc(self, linecolor=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2499 """Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as `linecolor()`.""" 2500 return self.linecolor(linecolor) 2501 2502 def texture( 2503 self, 2504 tname, 2505 tcoords=None, 2506 interpolate=True, 2507 repeat=True, 2508 edge_clamp=False, 2509 scale=None, 2510 ushift=None, 2511 vshift=None, 2512 ) -> Self: 2513 """ 2514 Assign a texture to mesh from image file or predefined texture `tname`. 2515 If tname is set to `None` texture is disabled. 2516 Input tname can also be an array or a `vtkTexture`. 2517 2518 Arguments: 2519 tname : (numpy.array, str, Image, vtkTexture, None) 2520 the input texture to be applied. Can be a numpy array, a path to an image file, 2521 a vedo Image. The None value disables texture. 2522 tcoords : (numpy.array, str) 2523 this is the (u,v) texture coordinate array. Can also be a string of an existing array 2524 in the mesh. 2525 interpolate : (bool) 2526 turn on/off linear interpolation of the texture map when rendering. 2527 repeat : (bool) 2528 repeat of the texture when tcoords extend beyond the [0,1] range. 2529 edge_clamp : (bool) 2530 turn on/off the clamping of the texture map when 2531 the texture coords extend beyond the [0,1] range. 2532 Only used when repeat is False, and edge clamping is supported by the graphics card. 2533 scale : (bool) 2534 scale the texture image by this factor 2535 ushift : (bool) 2536 shift u-coordinates of texture by this amount 2537 vshift : (bool) 2538 shift v-coordinates of texture by this amount 2539 2540 Examples: 2541 - [texturecubes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/texturecubes.py) 2542 2543  2544 """ 2545 pd = self.dataset 2546 out_img = None 2547 2548 if tname is None: # disable texture 2549 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(None) 2550 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2551 return self ###################################### 2552 2553 if isinstance(tname, vtki.vtkTexture): 2554 tu = tname 2555 2556 elif isinstance(tname, vedo.Image): 2557 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2558 out_img = tname.dataset 2559 2560 elif utils.is_sequence(tname): 2561 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2562 out_img = vedo.image._get_img(tname) 2563 2564 elif isinstance(tname, str): 2565 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2566 2567 if "https://" in tname: 2568 try: 2569 tname = vedo.file_io.download(tname, verbose=False) 2570 except: 2571 vedo.logger.error(f"texture {tname} could not be downloaded") 2572 return self 2573 2574 fn = tname + ".jpg" 2575 if os.path.exists(tname): 2576 fn = tname 2577 else: 2578 vedo.logger.error(f"texture file {tname} does not exist") 2579 return self 2580 2581 fnl = fn.lower() 2582 if ".jpg" in fnl or ".jpeg" in fnl: 2583 reader = vtki.new("JPEGReader") 2584 elif ".png" in fnl: 2585 reader = vtki.new("PNGReader") 2586 elif ".bmp" in fnl: 2587 reader = vtki.new("BMPReader") 2588 else: 2589 vedo.logger.error("in texture() supported files are only PNG, BMP or JPG") 2590 return self 2591 reader.SetFileName(fn) 2592 reader.Update() 2593 out_img = reader.GetOutput() 2594 2595 else: 2596 vedo.logger.error(f"in texture() cannot understand input {type(tname)}") 2597 return self 2598 2599 if tcoords is not None: 2600 2601 if isinstance(tcoords, str): 2602 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(tcoords) 2603 2604 else: 2605 tcoords = np.asarray(tcoords) 2606 if tcoords.ndim != 2: 2607 vedo.logger.error("tcoords must be a 2-dimensional array") 2608 return self 2609 if tcoords.shape[0] != pd.GetNumberOfPoints(): 2610 vedo.logger.error("nr of texture coords must match nr of points") 2611 return self 2612 if tcoords.shape[1] != 2: 2613 vedo.logger.error("tcoords texture vector must have 2 components") 2614 vtarr = utils.numpy2vtk(tcoords) 2615 vtarr.SetName("TCoordinates") 2616 2617 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtarr) 2618 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2619 2620 elif not pd.GetPointData().GetTCoords(): 2621 2622 # TCoords still void.. 2623 # check that there are no texture-like arrays: 2624 names = self.pointdata.keys() 2625 candidate_arr = "" 2626 for name in names: 2627 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(name) 2628 if vtarr.GetNumberOfComponents() != 2: 2629 continue 2630 t0, t1 = vtarr.GetRange() 2631 if t0 >= 0 and t1 <= 1: 2632 candidate_arr = name 2633 2634 if candidate_arr: 2635 2636 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(candidate_arr) 2637 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtarr) 2638 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2639 2640 else: 2641 # last resource is automatic mapping 2642 tmapper = vtki.new("TextureMapToPlane") 2643 tmapper.AutomaticPlaneGenerationOn() 2644 tmapper.SetInputData(pd) 2645 tmapper.Update() 2646 tc = tmapper.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetTCoords() 2647 if scale or ushift or vshift: 2648 ntc = utils.vtk2numpy(tc) 2649 if scale: 2650 ntc *= scale 2651 if ushift: 2652 ntc[:, 0] += ushift 2653 if vshift: 2654 ntc[:, 1] += vshift 2655 tc = utils.numpy2vtk(tc) 2656 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(tc) 2657 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2658 2659 if out_img: 2660 tu.SetInputData(out_img) 2661 tu.SetInterpolate(interpolate) 2662 tu.SetRepeat(repeat) 2663 tu.SetEdgeClamp(edge_clamp) 2664 2665 self.properties.SetColor(1, 1, 1) 2666 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2667 self.actor.SetTexture(tu) 2668 2669 # if seam_threshold is not None: 2670 # tname = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetTCoords().GetName() 2671 # grad = self.gradient(tname) 2672 # ugrad, vgrad = np.split(grad, 2, axis=1) 2673 # ugradm, vgradm = utils.mag2(ugrad), utils.mag2(vgrad) 2674 # gradm = np.log(ugradm + vgradm) 2675 # largegrad_ids = np.arange(len(grad))[gradm > seam_threshold * 4] 2676 # uvmap = self.pointdata[tname] 2677 # # collapse triangles that have large gradient 2678 # new_points = self.points.copy() 2679 # for f in self.cells: 2680 # if np.isin(f, largegrad_ids).all(): 2681 # id1, id2, id3 = f 2682 # uv1, uv2, uv3 = uvmap[f] 2683 # d12 = utils.mag2(uv1 - uv2) 2684 # d23 = utils.mag2(uv2 - uv3) 2685 # d31 = utils.mag2(uv3 - uv1) 2686 # idm = np.argmin([d12, d23, d31]) 2687 # if idm == 0: 2688 # new_points[id1] = new_points[id3] 2689 # new_points[id2] = new_points[id3] 2690 # elif idm == 1: 2691 # new_points[id2] = new_points[id1] 2692 # new_points[id3] = new_points[id1] 2693 # self.points = new_points 2694 2695 self.dataset.Modified() 2696 return self 2697 2698######################################################################################## 2699class VolumeVisual(CommonVisual): 2700 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a ``Volume`` object.""" 2701 2702 # def __init__(self) -> None: 2703 # # print("INIT VolumeVisual") 2704 # super().__init__() 2705 2706 def alpha_unit(self, u=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2707 """ 2708 Defines light attenuation per unit length. Default is 1. 2709 The larger the unit length, the further light has to travel to attenuate the same amount. 2710 2711 E.g., if you set the unit distance to 0, you will get full opacity. 2712 It means that when light travels 0 distance it's already attenuated a finite amount. 2713 Thus, any finite distance should attenuate all light. 2714 The larger you make the unit distance, the more transparent the rendering becomes. 2715 """ 2716 if u is None: 2717 return self.properties.GetScalarOpacityUnitDistance() 2718 self.properties.SetScalarOpacityUnitDistance(u) 2719 return self 2720 2721 def alpha_gradient(self, alpha_grad, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 2722 """ 2723 Assign a set of tranparencies to a volume's gradient 2724 along the range of the scalar value. 2725 A single constant value can also be assigned. 2726 The gradient function is used to decrease the opacity 2727 in the "flat" regions of the volume while maintaining the opacity 2728 at the boundaries between material types. The gradient is measured 2729 as the amount by which the intensity changes over unit distance. 2730 2731 The format for alpha_grad is the same as for method `volume.alpha()`. 2732 """ 2733 if vmin is None: 2734 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 2735 if vmax is None: 2736 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 2737 2738 if alpha_grad is None: 2739 self.properties.DisableGradientOpacityOn() 2740 return self 2741 2742 self.properties.DisableGradientOpacityOff() 2743 2744 gotf = self.properties.GetGradientOpacity() 2745 if utils.is_sequence(alpha_grad): 2746 alpha_grad = np.array(alpha_grad) 2747 if len(alpha_grad.shape) == 1: # user passing a flat list e.g. (0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1) 2748 for i, al in enumerate(alpha_grad): 2749 xalpha = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(alpha_grad) - 1) 2750 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to gradient opacity 2751 gotf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 2752 elif len(alpha_grad.shape) == 2: # user passing [(x0,alpha0), ...] 2753 gotf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha_grad[0][1]) 2754 for xalpha, al in alpha_grad: 2755 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 2756 gotf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 2757 gotf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha_grad[-1][1]) 2758 # print("alpha_grad at", round(xalpha, 1), "\tset to", al) 2759 else: 2760 gotf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha_grad) # constant alpha_grad 2761 gotf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha_grad) 2762 return self 2763 2764 def cmap(self, c, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 2765 """Same as `color()`. 2766 2767 Arguments: 2768 alpha : (list) 2769 use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range 2770 vmin : (float) 2771 force the min of the scalar range to be this value 2772 vmax : (float) 2773 force the max of the scalar range to be this value 2774 """ 2775 return self.color(c, alpha, vmin, vmax) 2776 2777 def jittering(self, status=None) -> Union[Self, bool]: 2778 """ 2779 If `True`, each ray traversal direction will be perturbed slightly 2780 using a noise-texture to get rid of wood-grain effects. 2781 """ 2782 if hasattr(self.mapper, "SetUseJittering"): # tetmesh doesnt have it 2783 if status is None: 2784 return self.mapper.GetUseJittering() 2785 self.mapper.SetUseJittering(status) 2786 return self 2787 2788 def hide_voxels(self, ids) -> Self: 2789 """ 2790 Hide voxels (cells) from visualization. 2791 2792 Example: 2793 ```python 2794 from vedo import * 2795 embryo = Volume(dataurl+'embryo.tif') 2796 embryo.hide_voxels(list(range(400000))) 2797 show(embryo, axes=1).close() 2798 ``` 2799 2800 See also: 2801 `volume.mask()` 2802 """ 2803 ghost_mask = np.zeros(self.ncells, dtype=np.uint8) 2804 ghost_mask[ids] = vtki.vtkDataSetAttributes.HIDDENCELL 2805 name = vtki.vtkDataSetAttributes.GhostArrayName() 2806 garr = utils.numpy2vtk(ghost_mask, name=name, dtype=np.uint8) 2807 self.dataset.GetCellData().AddArray(garr) 2808 self.dataset.GetCellData().Modified() 2809 return self 2810 2811 def mask(self, data) -> Self: 2812 """ 2813 Mask a volume visualization with a binary value. 2814 Needs to specify `volume.mapper = "gpu"`. 2815 2816 Example: 2817 ```python 2818 from vedo import np, Volume, show 2819 data_matrix = np.zeros([75, 75, 75], dtype=np.uint8) 2820 # all voxels have value zero except: 2821 data_matrix[ 0:35, 0:35, 0:35] = 1 2822 data_matrix[35:55, 35:55, 35:55] = 2 2823 data_matrix[55:74, 55:74, 55:74] = 3 2824 vol = Volume(data_matrix).cmap('Blues') 2825 vol.mapper = "gpu" 2826 data_mask = np.zeros_like(data_matrix) 2827 data_mask[10:65, 10:60, 20:70] = 1 2828 vol.mask(data_mask) 2829 show(vol, axes=1).close() 2830 ``` 2831 See also: 2832 `volume.hide_voxels()` 2833 """ 2834 rdata = data.astype(np.uint8).ravel(order="F") 2835 varr = utils.numpy2vtk(rdata, name="input_mask") 2836 2837 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 2838 img.SetDimensions(self.dimensions()) 2839 img.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 2840 img.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(varr.GetName()) 2841 2842 try: 2843 self.mapper.SetMaskTypeToBinary() 2844 self.mapper.SetMaskInput(img) 2845 except AttributeError: 2846 vedo.logger.error("volume.mask() must specify volume.mapper = 'gpu'") 2847 return self 2848 2849 2850 def mode(self, mode=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2851 """ 2852 Define the volumetric rendering mode following this: 2853 - 0, composite rendering 2854 - 1, maximum projection rendering 2855 - 2, minimum projection rendering 2856 - 3, average projection rendering 2857 - 4, additive mode 2858 2859 The default mode is "composite" where the scalar values are sampled through 2860 the volume and composited in a front-to-back scheme through alpha blending. 2861 The final color and opacity is determined using the color and opacity transfer 2862 functions specified in alpha keyword. 2863 2864 Maximum and minimum intensity blend modes use the maximum and minimum 2865 scalar values, respectively, along the sampling ray. 2866 The final color and opacity is determined by passing the resultant value 2867 through the color and opacity transfer functions. 2868 2869 Additive blend mode accumulates scalar values by passing each value 2870 through the opacity transfer function and then adding up the product 2871 of the value and its opacity. In other words, the scalar values are scaled 2872 using the opacity transfer function and summed to derive the final color. 2873 Note that the resulting image is always grayscale i.e. aggregated values 2874 are not passed through the color transfer function. 2875 This is because the final value is a derived value and not a real data value 2876 along the sampling ray. 2877 2878 Average intensity blend mode works similar to the additive blend mode where 2879 the scalar values are multiplied by opacity calculated from the opacity 2880 transfer function and then added. 2881 The additional step here is to divide the sum by the number of samples 2882 taken through the volume. 2883 As is the case with the additive intensity projection, the final image will 2884 always be grayscale i.e. the aggregated values are not passed through the 2885 color transfer function. 2886 """ 2887 if mode is None: 2888 return self.mapper.GetBlendMode() 2889 2890 if isinstance(mode, str): 2891 if "comp" in mode: 2892 mode = 0 2893 elif "proj" in mode: 2894 if "max" in mode: 2895 mode = 1 2896 elif "min" in mode: 2897 mode = 2 2898 elif "ave" in mode: 2899 mode = 3 2900 else: 2901 vedo.logger.warning(f"unknown mode {mode}") 2902 mode = 0 2903 elif "add" in mode: 2904 mode = 4 2905 else: 2906 vedo.logger.warning(f"unknown mode {mode}") 2907 mode = 0 2908 2909 self.mapper.SetBlendMode(mode) 2910 return self 2911 2912 def shade(self, status=None) -> Union[Self, bool]: 2913 """ 2914 Set/Get the shading of a Volume. 2915 Shading can be further controlled with `volume.lighting()` method. 2916 2917 If shading is turned on, the mapper may perform shading calculations. 2918 In some cases shading does not apply 2919 (for example, in maximum intensity projection mode). 2920 """ 2921 if status is None: 2922 return self.properties.GetShade() 2923 self.properties.SetShade(status) 2924 return self 2925 2926 def interpolation(self, itype) -> Self: 2927 """ 2928 Set interpolation type. 2929 2930 0=nearest neighbour, 1=linear 2931 """ 2932 self.properties.SetInterpolationType(itype) 2933 return self 2934 2935 2936######################################################################################## 2937class ImageVisual(CommonVisual, Actor3DHelper): 2938 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a ``Image`` object.""" 2939 2940 # def __init__(self) -> None: 2941 # # print("init ImageVisual") 2942 # super().__init__() 2943 2944 def memory_size(self) -> int: 2945 """Return the size in bytes of the object in memory.""" 2946 return self.dataset.GetActualMemorySize() 2947 2948 def scalar_range(self) -> np.ndarray: 2949 """Return the scalar range of the image.""" 2950 return np.array(self.dataset.GetScalarRange()) 2951 2952 def alpha(self, a=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2953 """Set/get image's transparency in the rendering scene.""" 2954 if a is not None: 2955 self.properties.SetOpacity(a) 2956 return self 2957 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 2958 2959 def level(self, value=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2960 """Get/Set the image color level (brightness) in the rendering scene.""" 2961 if value is None: 2962 return self.properties.GetColorLevel() 2963 self.properties.SetColorLevel(value) 2964 return self 2965 2966 def window(self, value=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2967 """Get/Set the image color window (contrast) in the rendering scene.""" 2968 if value is None: 2969 return self.properties.GetColorWindow() 2970 self.properties.SetColorWindow(value) 2971 return self 2972 2973 2974class LightKit: 2975 """ 2976 A LightKit consists of three lights, a 'key light', a 'fill light', and a 'head light'. 2977 2978 The main light is the key light. It is usually positioned so that it appears like 2979 an overhead light (like the sun, or a ceiling light). 2980 It is generally positioned to shine down on the scene from about a 45 degree angle vertically 2981 and at least a little offset side to side. The key light usually at least about twice as bright 2982 as the total of all other lights in the scene to provide good modeling of object features. 2983 2984 The other lights in the kit (the fill light, headlight, and a pair of back lights) 2985 are weaker sources that provide extra illumination to fill in the spots that the key light misses. 2986 The fill light is usually positioned across from or opposite from the key light 2987 (though still on the same side of the object as the camera) in order to simulate diffuse reflections 2988 from other objects in the scene. 2989 2990 The headlight, always located at the position of the camera, reduces the contrast between areas lit 2991 by the key and fill light. The two back lights, one on the left of the object as seen from the observer 2992 and one on the right, fill on the high-contrast areas behind the object. 2993 To enforce the relationship between the different lights, the intensity of the fill, back and headlights 2994 are set as a ratio to the key light brightness. 2995 Thus, the brightness of all the lights in the scene can be changed by changing the key light intensity. 2996 2997 All lights are directional lights, infinitely far away with no falloff. Lights move with the camera. 2998 2999 For simplicity, the position of lights in the LightKit can only be specified using angles: 3000 the elevation (latitude) and azimuth (longitude) of each light with respect to the camera, in degrees. 3001 For example, a light at (elevation=0, azimuth=0) is located at the camera (a headlight). 3002 A light at (elevation=90, azimuth=0) is above the lookat point, shining down. 3003 Negative azimuth values move the lights clockwise as seen above, positive values counter-clockwise. 3004 So, a light at (elevation=45, azimuth=-20) is above and in front of the object and shining 3005 slightly from the left side. 3006 3007 LightKit limits the colors that can be assigned to any light to those of incandescent sources such as 3008 light bulbs and sunlight. It defines a special color spectrum called "warmth" from which light colors 3009 can be chosen, where 0 is cold blue, 0.5 is neutral white, and 1 is deep sunset red. 3010 Colors close to 0.5 are "cool whites" and "warm whites," respectively. 3011 3012 Since colors far from white on the warmth scale appear less bright, key-to-fill and key-to-headlight 3013 ratios are skewed by key, fill, and headlight colors. If `maintain_luminance` is set, LightKit will 3014 attempt to compensate for these perceptual differences by increasing the brightness of more saturated colors. 3015 3016 To specify the color of a light, positioning etc you can pass a dictionary with the following keys: 3017 - `intensity` : (float) The intensity of the key light. Default is 1. 3018 - `ratio` : (float) The ratio of the light intensity wrt key light. 3019 - `warmth` : (float) The warmth of the light. Default is 0.5. 3020 - `elevation` : (float) The elevation of the light in degrees. 3021 - `azimuth` : (float) The azimuth of the light in degrees. 3022 3023 Example: 3024 ```python 3025 from vedo import * 3026 lightkit = LightKit(head={"warmth":0.6}) 3027 mesh = Mesh(dataurl+"bunny.obj") 3028 plt = Plotter() 3029 plt.remove_lights().add(mesh, lightkit) 3030 plt.show().close() 3031 ``` 3032 """ 3033 def __init__(self, key=(), fill=(), back=(), head=(), maintain_luminance=False) -> None: 3034 3035 self.lightkit = vtki.new("LightKit") 3036 self.lightkit.SetMaintainLuminance(maintain_luminance) 3037 self.key = dict(key) 3038 self.head = dict(head) 3039 self.fill = dict(fill) 3040 self.back = dict(back) 3041 self.update() 3042 3043 def update(self) -> None: 3044 """Update the LightKit properties.""" 3045 if "warmth" in self.key: 3046 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightWarmth(self.key["warmth"]) 3047 if "warmth" in self.fill: 3048 self.lightkit.SetFillLightWarmth(self.fill["warmth"]) 3049 if "warmth" in self.head: 3050 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightWarmth(self.head["warmth"]) 3051 if "warmth" in self.back: 3052 self.lightkit.SetBackLightWarmth(self.back["warmth"]) 3053 3054 if "intensity" in self.key: 3055 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightIntensity(self.key["intensity"]) 3056 if "ratio" in self.fill: 3057 self.lightkit.SetKeyToFillRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3058 if "ratio" in self.head: 3059 self.lightkit.SetKeyToHeadRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3060 if "ratio" in self.back: 3061 self.lightkit.SetKeyToBackRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3062 3063 if "elevation" in self.key: 3064 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightElevation(self.key["elevation"]) 3065 if "elevation" in self.fill: 3066 self.lightkit.SetFillLightElevation(self.fill["elevation"]) 3067 if "elevation" in self.head: 3068 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightElevation(self.head["elevation"]) 3069 if "elevation" in self.back: 3070 self.lightkit.SetBackLightElevation(self.back["elevation"]) 3071 3072 if "azimuth" in self.key: 3073 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightAzimuth(self.key["azimuth"]) 3074 if "azimuth" in self.fill: 3075 self.lightkit.SetFillLightAzimuth(self.fill["azimuth"]) 3076 if "azimuth" in self.head: 3077 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightAzimuth(self.head["azimuth"]) 3078 if "azimuth" in self.back: 3079 self.lightkit.SetBackLightAzimuth(self.back["azimuth"])
36class CommonVisual: 37 """Class to manage the visual aspects common to all objects.""" 38 39 def __init__(self): 40 # print("init CommonVisual", type(self)) 41 42 self.properties = None 43 44 self.scalarbar = None 45 self.pipeline = None 46 47 self.trail = None 48 self.trail_points = [] 49 self.trail_segment_size = 0 50 self.trail_offset = None 51 52 self.shadows = [] 53 54 self.axes = None 55 self.picked3d = None 56 57 self.rendered_at = set() 58 59 self._ligthingnr = 0 # index of the lighting mode changed from CLI 60 self._cmap_name = "" # remember the cmap name for self._keypress 61 self._caption = None 62 63 self.actor = None 64 65 66 def print(self): 67 """Print object info.""" 68 print(self.__str__()) 69 return self 70 71 @property 72 def LUT(self) -> np.ndarray: 73 """Return the lookup table of the object as a numpy object.""" 74 try: 75 _lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 76 values = [] 77 for i in range(_lut.GetTable().GetNumberOfTuples()): 78 # print("LUT i =", i, "value =", _lut.GetTableValue(i)) 79 values.append(_lut.GetTableValue(i)) 80 return np.array(values) 81 except AttributeError: 82 return np.array([], dtype=float) 83 84 @LUT.setter 85 def LUT(self, arr): 86 """ 87 Set the lookup table of the object from a numpy or `vtkLookupTable` object. 88 Consider using `cmap()` or `build_lut()` instead as it allows 89 to set the range of the LUT and to use a string name for the color map. 90 """ 91 if isinstance(arr, vtki.vtkLookupTable): 92 newlut = arr 93 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(newlut.GetRange()) 94 else: 95 newlut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 96 newlut.SetNumberOfTableValues(len(arr)) 97 if len(arr[0]) == 3: 98 arr = np.insert(arr, 3, 1, axis=1) 99 for i, v in enumerate(arr): 100 newlut.SetTableValue(i, v) 101 newlut.SetRange(self.mapper.GetScalarRange()) 102 # print("newlut.GetRange() =", newlut.GetRange()) 103 # print("self.mapper.GetScalarRange() =", self.mapper.GetScalarRange()) 104 newlut.Build() 105 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(newlut) 106 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 107 108 def scalar_range(self, vmin=None, vmax=None): 109 """Set the range of the scalar value for visualization.""" 110 if vmin is None and vmax is None: 111 return np.array(self.mapper.GetScalarRange()) 112 if vmax is None: 113 vmin, vmax = vmin # assume it is a list 114 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(float(vmin), float(vmax)) 115 return self 116 117 def add_observer(self, event_name, func, priority=0) -> int: 118 """Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.""" 119 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 120 idd = self.actor.AddObserver(event_name, func, priority) 121 return idd 122 123 def invoke_event(self, event_name) -> Self: 124 """Invoke an event.""" 125 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 126 self.actor.InvokeEvent(event_name) 127 return self 128 129 # def abort_event(self, obs_id): 130 # """Abort an event.""" 131 # cmd = self.actor.GetCommand(obs_id) # vtkCommand 132 # if cmd: 133 # cmd.AbortFlagOn() 134 # return self 135 136 def show(self, **options) -> Union["vedo.Plotter", None]: 137 """ 138 Create on the fly an instance of class `Plotter` or use the last existing one to 139 show one single object. 140 141 This method is meant as a shortcut. If more than one object needs to be visualised 142 please use the syntax `show(mesh1, mesh2, volume, ..., options)`. 143 144 Returns the `Plotter` class instance. 145 """ 146 return vedo.plotter.show(self, **options) 147 148 def thumbnail(self, zoom=1.25, size=(200, 200), bg="white", azimuth=0, elevation=0, axes=False) -> np.ndarray: 149 """Build a thumbnail of the object and return it as an array.""" 150 # speed is about 20Hz for size=[200,200] 151 ren = vtki.vtkRenderer() 152 153 actor = self.actor 154 if isinstance(self, vedo.UnstructuredGrid): 155 geo = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 156 geo.SetInputData(self.dataset) 157 geo.Update() 158 actor = vedo.Mesh(geo.GetOutput()).cmap("rainbow").actor 159 160 ren.AddActor(actor) 161 if axes: 162 axes = vedo.addons.Axes(self) 163 ren.AddActor(axes.actor) 164 ren.ResetCamera() 165 cam = ren.GetActiveCamera() 166 cam.Zoom(zoom) 167 cam.Elevation(elevation) 168 cam.Azimuth(azimuth) 169 170 ren_win = vtki.vtkRenderWindow() 171 ren_win.SetOffScreenRendering(True) 172 ren_win.SetSize(size) 173 ren.SetBackground(colors.get_color(bg)) 174 ren_win.AddRenderer(ren) 175 ren.ResetCameraClippingRange() 176 ren_win.Render() 177 178 nx, ny = ren_win.GetSize() 179 arr = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 180 ren_win.GetRGBACharPixelData(0, 0, nx - 1, ny - 1, 0, arr) 181 narr = utils.vtk2numpy(arr).T[:3].T.reshape([ny, nx, 3]) 182 narr = np.ascontiguousarray(np.flip(narr, axis=0)) 183 184 ren.RemoveActor(actor) 185 if axes: 186 ren.RemoveActor(axes.actor) 187 ren_win.Finalize() 188 del ren_win 189 return narr 190 191 def pickable(self, value=None) -> Self: 192 """Set/get the pickability property of an object.""" 193 if value is None: 194 return self.actor.GetPickable() 195 self.actor.SetPickable(value) 196 return self 197 198 def use_bounds(self, value=True) -> Self: 199 """ 200 Instruct the current camera to either take into account or ignore 201 the object bounds when resetting. 202 """ 203 self.actor.SetUseBounds(value) 204 return self 205 206 def draggable(self, value=None) -> Self: # NOT FUNCTIONAL? 207 """Set/get the draggability property of an object.""" 208 if value is None: 209 return self.actor.GetDragable() 210 self.actor.SetDragable(value) 211 return self 212 213 def on(self) -> Self: 214 """Switch on object visibility. Object is not removed.""" 215 self.actor.VisibilityOn() 216 try: 217 self.scalarbar.actor.VisibilityOn() 218 except AttributeError: 219 pass 220 try: 221 self.trail.actor.VisibilityOn() 222 except AttributeError: 223 pass 224 try: 225 for sh in self.shadows: 226 sh.actor.VisibilityOn() 227 except AttributeError: 228 pass 229 return self 230 231 def off(self) -> Self: 232 """Switch off object visibility. Object is not removed.""" 233 self.actor.VisibilityOff() 234 try: 235 self.scalarbar.actor.VisibilityOff() 236 except AttributeError: 237 pass 238 try: 239 self.trail.actor.VisibilityOff() 240 except AttributeError: 241 pass 242 try: 243 for sh in self.shadows: 244 sh.actor.VisibilityOff() 245 except AttributeError: 246 pass 247 return self 248 249 def toggle(self) -> Self: 250 """Toggle object visibility on/off.""" 251 v = self.actor.GetVisibility() 252 if v: 253 self.off() 254 else: 255 self.on() 256 return self 257 258 def add_scalarbar( 259 self, 260 title="", 261 pos=(), 262 size=(80, 400), 263 font_size=14, 264 title_yoffset=15, 265 nlabels=None, 266 c=None, 267 horizontal=False, 268 use_alpha=True, 269 label_format=":6.3g", 270 ) -> Self: 271 """ 272 Add a 2D scalar bar for the specified object. 273 274 Arguments: 275 title : (str) 276 scalar bar title 277 pos : (list) 278 position coordinates of the bottom left corner. 279 Can also be a pair of (x,y) values in the range [0,1] 280 to indicate the position of the bottom left and top right corners. 281 size : (float,float) 282 size of the scalarbar in number of pixels (width, height) 283 font_size : (float) 284 size of font for title and numeric labels 285 title_yoffset : (float) 286 vertical space offset between title and color scalarbar 287 nlabels : (int) 288 number of numeric labels 289 c : (list) 290 color of the scalar bar text 291 horizontal : (bool) 292 lay the scalarbar horizontally 293 use_alpha : (bool) 294 render transparency in the color bar itself 295 label_format : (str) 296 c-style format string for numeric labels 297 298 Examples: 299 - [mesh_coloring.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_coloring.py) 300 - [scalarbars.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/scalarbars.py) 301 """ 302 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 303 304 if plt and plt.renderer: 305 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 306 if np.sum(plt.renderer.GetBackground()) > 1.5: 307 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 308 if isinstance(self.scalarbar, vtki.vtkActor): 309 plt.renderer.RemoveActor(self.scalarbar) 310 elif isinstance(self.scalarbar, vedo.Assembly): 311 for a in self.scalarbar.unpack(): 312 plt.renderer.RemoveActor(a) 313 if c is None: 314 c = "gray" 315 316 sb = vedo.addons.ScalarBar( 317 self, 318 title, 319 pos, 320 size, 321 font_size, 322 title_yoffset, 323 nlabels, 324 c, 325 horizontal, 326 use_alpha, 327 label_format, 328 ) 329 self.scalarbar = sb 330 return self 331 332 def add_scalarbar3d( 333 self, 334 title="", 335 pos=None, 336 size=(0, 0), 337 title_font="", 338 title_xoffset=-1.2, 339 title_yoffset=0.0, 340 title_size=1.5, 341 title_rotation=0.0, 342 nlabels=9, 343 label_font="", 344 label_size=1, 345 label_offset=0.375, 346 label_rotation=0, 347 label_format="", 348 italic=0, 349 c=None, 350 draw_box=True, 351 above_text=None, 352 below_text=None, 353 nan_text="NaN", 354 categories=None, 355 ) -> Self: 356 """ 357 Associate a 3D scalar bar to the object and add it to the scene. 358 The new scalarbar object (Assembly) will be accessible as obj.scalarbar 359 360 Arguments: 361 size : (list) 362 (thickness, length) of scalarbar 363 title : (str) 364 scalar bar title 365 title_xoffset : (float) 366 horizontal space btw title and color scalarbar 367 title_yoffset : (float) 368 vertical space offset 369 title_size : (float) 370 size of title wrt numeric labels 371 title_rotation : (float) 372 title rotation in degrees 373 nlabels : (int) 374 number of numeric labels 375 label_font : (str) 376 font type for labels 377 label_size : (float) 378 label scale factor 379 label_offset : (float) 380 space btw numeric labels and scale 381 label_rotation : (float) 382 label rotation in degrees 383 label_format : (str) 384 label format for floats and integers (e.g. `':.2f'`) 385 draw_box : (bool) 386 draw a box around the colorbar 387 categories : (list) 388 make a categorical scalarbar, 389 the input list will have the format `[value, color, alpha, textlabel]` 390 391 Examples: 392 - [scalarbars.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/scalarbars.py) 393 """ 394 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 395 if plt and c is None: # automatic black or white 396 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 397 if np.sum(vedo.get_color(plt.backgrcol)) > 1.5: 398 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 399 if c is None: 400 c = (0, 0, 0) 401 c = vedo.get_color(c) 402 403 self.scalarbar = vedo.addons.ScalarBar3D( 404 self, 405 title, 406 pos, 407 size, 408 title_font, 409 title_xoffset, 410 title_yoffset, 411 title_size, 412 title_rotation, 413 nlabels, 414 label_font, 415 label_size, 416 label_offset, 417 label_rotation, 418 label_format, 419 italic, 420 c, 421 draw_box, 422 above_text, 423 below_text, 424 nan_text, 425 categories, 426 ) 427 return self 428 429 def color(self, col, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None): 430 """ 431 Assign a color or a set of colors along the range of the scalar value. 432 A single constant color can also be assigned. 433 Any matplotlib color map name is also accepted, e.g. `volume.color('jet')`. 434 435 E.g.: say that your cells scalar runs from -3 to 6, 436 and you want -3 to show red and 1.5 violet and 6 green, then just set: 437 438 `volume.color(['red', 'violet', 'green'])` 439 440 You can also assign a specific color to a aspecific value with eg.: 441 442 `volume.color([(0,'red'), (0.5,'violet'), (1,'green')])` 443 444 Arguments: 445 alpha : (list) 446 use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range 447 vmin : (float) 448 force the min of the scalar range to be this value 449 vmax : (float) 450 force the max of the scalar range to be this value 451 """ 452 # supersedes method in Points, Mesh 453 454 if col is None: 455 return self 456 457 if vmin is None: 458 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 459 if vmax is None: 460 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 461 ctf = self.properties.GetRGBTransferFunction() 462 ctf.RemoveAllPoints() 463 464 if utils.is_sequence(col): 465 if utils.is_sequence(col[0]) and len(col[0]) == 2: 466 # user passing [(value1, color1), ...] 467 for x, ci in col: 468 r, g, b = colors.get_color(ci) 469 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 470 # colors.printc('color at', round(x, 1), 471 # 'set to', colors.get_color_name((r, g, b)), bold=0) 472 else: 473 # user passing [color1, color2, ..] 474 for i, ci in enumerate(col): 475 r, g, b = colors.get_color(ci) 476 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(col) - 1) 477 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 478 elif isinstance(col, str): 479 if col in colors.colors.keys() or col in colors.color_nicks.keys(): 480 r, g, b = colors.get_color(col) 481 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmin, r, g, b) # constant color 482 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmax, r, g, b) 483 else: # assume it's a colormap 484 for x in np.linspace(vmin, vmax, num=64, endpoint=True): 485 r, g, b = colors.color_map(x, name=col, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax) 486 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 487 elif isinstance(col, int): 488 r, g, b = colors.get_color(col) 489 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmin, r, g, b) # constant color 490 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmax, r, g, b) 491 elif isinstance(col, vtki.vtkLookupTable): 492 alpha=[] 493 nt = col.GetNumberOfTableValues() 494 for i in range(nt): 495 r, g, b, a = col.GetTableValue(i) 496 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (nt - 1) 497 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 498 alpha.append(a) 499 elif hasattr(col, "resampled"): # cover the case of LinearSegmentedColormap 500 N = col.N 501 cs = np.array([col(i/N) for i in range(N)]) 502 alpha = cs[:,3].copy() 503 for i, v in enumerate(cs): 504 r, g, b, _ = v 505 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (N - 1) 506 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 507 elif hasattr(col, "to_rgba"): # col is a matplotlib colormap 508 for i in range(256): 509 r, g, b, a = col(i / 255) 510 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / 255 511 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 512 alpha.append(a) 513 else: 514 vedo.logger.warning(f"in color() unknown input type {type(col)}") 515 516 if alpha is not None: 517 self.alpha(alpha, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax) 518 return self 519 520 def alpha(self, alpha, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 521 """ 522 Assign a set of tranparencies along the range of the scalar value. 523 A single constant value can also be assigned. 524 525 E.g.: say `alpha=(0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1)` and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150. 526 Then all cells with a value close to -10 will be completely transparent, cells at 1/4 527 of the range will get an alpha equal to 0.3 and voxels with value close to 150 528 will be completely opaque. 529 530 As a second option one can set explicit (x, alpha_x) pairs to define the transfer function. 531 532 E.g.: say `alpha=[(-5, 0), (35, 0.4) (123,0.9)]` and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150. 533 Then all cells below -5 will be completely transparent, cells with a scalar value of 35 534 will get an opacity of 40% and above 123 alpha is set to 90%. 535 """ 536 if vmin is None: 537 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 538 if vmax is None: 539 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 540 otf = self.properties.GetScalarOpacity() 541 otf.RemoveAllPoints() 542 543 if utils.is_sequence(alpha): 544 alpha = np.array(alpha) 545 if len(alpha.shape) == 1: # user passing a flat list e.g. (0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1) 546 for i, al in enumerate(alpha): 547 xalpha = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(alpha) - 1) 548 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 549 otf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 550 # print("alpha at", round(xalpha, 1), "\tset to", al) 551 elif len(alpha.shape) == 2: # user passing [(x0,alpha0), ...] 552 otf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha[0][1]) 553 for xalpha, al in alpha: 554 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 555 otf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 556 otf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha[-1][1]) 557 558 else: 559 560 otf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha) # constant alpha 561 otf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha) 562 563 return self
Class to manage the visual aspects common to all objects.
39 def __init__(self): 40 # print("init CommonVisual", type(self)) 41 42 self.properties = None 43 44 self.scalarbar = None 45 self.pipeline = None 46 47 self.trail = None 48 self.trail_points = [] 49 self.trail_segment_size = 0 50 self.trail_offset = None 51 52 self.shadows = [] 53 54 self.axes = None 55 self.picked3d = None 56 57 self.rendered_at = set() 58 59 self._ligthingnr = 0 # index of the lighting mode changed from CLI 60 self._cmap_name = "" # remember the cmap name for self._keypress 61 self._caption = None 62 63 self.actor = None
71 @property 72 def LUT(self) -> np.ndarray: 73 """Return the lookup table of the object as a numpy object.""" 74 try: 75 _lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 76 values = [] 77 for i in range(_lut.GetTable().GetNumberOfTuples()): 78 # print("LUT i =", i, "value =", _lut.GetTableValue(i)) 79 values.append(_lut.GetTableValue(i)) 80 return np.array(values) 81 except AttributeError: 82 return np.array([], dtype=float)
Return the lookup table of the object as a numpy object.
108 def scalar_range(self, vmin=None, vmax=None): 109 """Set the range of the scalar value for visualization.""" 110 if vmin is None and vmax is None: 111 return np.array(self.mapper.GetScalarRange()) 112 if vmax is None: 113 vmin, vmax = vmin # assume it is a list 114 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(float(vmin), float(vmax)) 115 return self
Set the range of the scalar value for visualization.
117 def add_observer(self, event_name, func, priority=0) -> int: 118 """Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.""" 119 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 120 idd = self.actor.AddObserver(event_name, func, priority) 121 return idd
Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.
123 def invoke_event(self, event_name) -> Self: 124 """Invoke an event.""" 125 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 126 self.actor.InvokeEvent(event_name) 127 return self
Invoke an event.
136 def show(self, **options) -> Union["vedo.Plotter", None]: 137 """ 138 Create on the fly an instance of class `Plotter` or use the last existing one to 139 show one single object. 140 141 This method is meant as a shortcut. If more than one object needs to be visualised 142 please use the syntax `show(mesh1, mesh2, volume, ..., options)`. 143 144 Returns the `Plotter` class instance. 145 """ 146 return vedo.plotter.show(self, **options)
Create on the fly an instance of class Plotter or use the last existing one to
show one single object.
This method is meant as a shortcut. If more than one object needs to be visualised
please use the syntax show(mesh1, mesh2, volume, ..., options).
Returns the Plotter class instance.
148 def thumbnail(self, zoom=1.25, size=(200, 200), bg="white", azimuth=0, elevation=0, axes=False) -> np.ndarray: 149 """Build a thumbnail of the object and return it as an array.""" 150 # speed is about 20Hz for size=[200,200] 151 ren = vtki.vtkRenderer() 152 153 actor = self.actor 154 if isinstance(self, vedo.UnstructuredGrid): 155 geo = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 156 geo.SetInputData(self.dataset) 157 geo.Update() 158 actor = vedo.Mesh(geo.GetOutput()).cmap("rainbow").actor 159 160 ren.AddActor(actor) 161 if axes: 162 axes = vedo.addons.Axes(self) 163 ren.AddActor(axes.actor) 164 ren.ResetCamera() 165 cam = ren.GetActiveCamera() 166 cam.Zoom(zoom) 167 cam.Elevation(elevation) 168 cam.Azimuth(azimuth) 169 170 ren_win = vtki.vtkRenderWindow() 171 ren_win.SetOffScreenRendering(True) 172 ren_win.SetSize(size) 173 ren.SetBackground(colors.get_color(bg)) 174 ren_win.AddRenderer(ren) 175 ren.ResetCameraClippingRange() 176 ren_win.Render() 177 178 nx, ny = ren_win.GetSize() 179 arr = vtki.vtkUnsignedCharArray() 180 ren_win.GetRGBACharPixelData(0, 0, nx - 1, ny - 1, 0, arr) 181 narr = utils.vtk2numpy(arr).T[:3].T.reshape([ny, nx, 3]) 182 narr = np.ascontiguousarray(np.flip(narr, axis=0)) 183 184 ren.RemoveActor(actor) 185 if axes: 186 ren.RemoveActor(axes.actor) 187 ren_win.Finalize() 188 del ren_win 189 return narr
Build a thumbnail of the object and return it as an array.
191 def pickable(self, value=None) -> Self: 192 """Set/get the pickability property of an object.""" 193 if value is None: 194 return self.actor.GetPickable() 195 self.actor.SetPickable(value) 196 return self
Set/get the pickability property of an object.
198 def use_bounds(self, value=True) -> Self: 199 """ 200 Instruct the current camera to either take into account or ignore 201 the object bounds when resetting. 202 """ 203 self.actor.SetUseBounds(value) 204 return self
Instruct the current camera to either take into account or ignore the object bounds when resetting.
206 def draggable(self, value=None) -> Self: # NOT FUNCTIONAL? 207 """Set/get the draggability property of an object.""" 208 if value is None: 209 return self.actor.GetDragable() 210 self.actor.SetDragable(value) 211 return self
Set/get the draggability property of an object.
213 def on(self) -> Self: 214 """Switch on object visibility. Object is not removed.""" 215 self.actor.VisibilityOn() 216 try: 217 self.scalarbar.actor.VisibilityOn() 218 except AttributeError: 219 pass 220 try: 221 self.trail.actor.VisibilityOn() 222 except AttributeError: 223 pass 224 try: 225 for sh in self.shadows: 226 sh.actor.VisibilityOn() 227 except AttributeError: 228 pass 229 return self
Switch on object visibility. Object is not removed.
231 def off(self) -> Self: 232 """Switch off object visibility. Object is not removed.""" 233 self.actor.VisibilityOff() 234 try: 235 self.scalarbar.actor.VisibilityOff() 236 except AttributeError: 237 pass 238 try: 239 self.trail.actor.VisibilityOff() 240 except AttributeError: 241 pass 242 try: 243 for sh in self.shadows: 244 sh.actor.VisibilityOff() 245 except AttributeError: 246 pass 247 return self
Switch off object visibility. Object is not removed.
249 def toggle(self) -> Self: 250 """Toggle object visibility on/off.""" 251 v = self.actor.GetVisibility() 252 if v: 253 self.off() 254 else: 255 self.on() 256 return self
Toggle object visibility on/off.
258 def add_scalarbar( 259 self, 260 title="", 261 pos=(), 262 size=(80, 400), 263 font_size=14, 264 title_yoffset=15, 265 nlabels=None, 266 c=None, 267 horizontal=False, 268 use_alpha=True, 269 label_format=":6.3g", 270 ) -> Self: 271 """ 272 Add a 2D scalar bar for the specified object. 273 274 Arguments: 275 title : (str) 276 scalar bar title 277 pos : (list) 278 position coordinates of the bottom left corner. 279 Can also be a pair of (x,y) values in the range [0,1] 280 to indicate the position of the bottom left and top right corners. 281 size : (float,float) 282 size of the scalarbar in number of pixels (width, height) 283 font_size : (float) 284 size of font for title and numeric labels 285 title_yoffset : (float) 286 vertical space offset between title and color scalarbar 287 nlabels : (int) 288 number of numeric labels 289 c : (list) 290 color of the scalar bar text 291 horizontal : (bool) 292 lay the scalarbar horizontally 293 use_alpha : (bool) 294 render transparency in the color bar itself 295 label_format : (str) 296 c-style format string for numeric labels 297 298 Examples: 299 - [mesh_coloring.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_coloring.py) 300 - [scalarbars.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/scalarbars.py) 301 """ 302 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 303 304 if plt and plt.renderer: 305 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 306 if np.sum(plt.renderer.GetBackground()) > 1.5: 307 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 308 if isinstance(self.scalarbar, vtki.vtkActor): 309 plt.renderer.RemoveActor(self.scalarbar) 310 elif isinstance(self.scalarbar, vedo.Assembly): 311 for a in self.scalarbar.unpack(): 312 plt.renderer.RemoveActor(a) 313 if c is None: 314 c = "gray" 315 316 sb = vedo.addons.ScalarBar( 317 self, 318 title, 319 pos, 320 size, 321 font_size, 322 title_yoffset, 323 nlabels, 324 c, 325 horizontal, 326 use_alpha, 327 label_format, 328 ) 329 self.scalarbar = sb 330 return self
Add a 2D scalar bar for the specified object.
Arguments:
- title : (str) scalar bar title
- pos : (list) position coordinates of the bottom left corner. Can also be a pair of (x,y) values in the range [0,1] to indicate the position of the bottom left and top right corners.
- size : (float,float) size of the scalarbar in number of pixels (width, height)
- font_size : (float) size of font for title and numeric labels
- title_yoffset : (float) vertical space offset between title and color scalarbar
- nlabels : (int) number of numeric labels
- c : (list) color of the scalar bar text
- horizontal : (bool) lay the scalarbar horizontally
- use_alpha : (bool) render transparency in the color bar itself
- label_format : (str) c-style format string for numeric labels
Examples:
332 def add_scalarbar3d( 333 self, 334 title="", 335 pos=None, 336 size=(0, 0), 337 title_font="", 338 title_xoffset=-1.2, 339 title_yoffset=0.0, 340 title_size=1.5, 341 title_rotation=0.0, 342 nlabels=9, 343 label_font="", 344 label_size=1, 345 label_offset=0.375, 346 label_rotation=0, 347 label_format="", 348 italic=0, 349 c=None, 350 draw_box=True, 351 above_text=None, 352 below_text=None, 353 nan_text="NaN", 354 categories=None, 355 ) -> Self: 356 """ 357 Associate a 3D scalar bar to the object and add it to the scene. 358 The new scalarbar object (Assembly) will be accessible as obj.scalarbar 359 360 Arguments: 361 size : (list) 362 (thickness, length) of scalarbar 363 title : (str) 364 scalar bar title 365 title_xoffset : (float) 366 horizontal space btw title and color scalarbar 367 title_yoffset : (float) 368 vertical space offset 369 title_size : (float) 370 size of title wrt numeric labels 371 title_rotation : (float) 372 title rotation in degrees 373 nlabels : (int) 374 number of numeric labels 375 label_font : (str) 376 font type for labels 377 label_size : (float) 378 label scale factor 379 label_offset : (float) 380 space btw numeric labels and scale 381 label_rotation : (float) 382 label rotation in degrees 383 label_format : (str) 384 label format for floats and integers (e.g. `':.2f'`) 385 draw_box : (bool) 386 draw a box around the colorbar 387 categories : (list) 388 make a categorical scalarbar, 389 the input list will have the format `[value, color, alpha, textlabel]` 390 391 Examples: 392 - [scalarbars.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/scalarbars.py) 393 """ 394 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 395 if plt and c is None: # automatic black or white 396 c = (0.9, 0.9, 0.9) 397 if np.sum(vedo.get_color(plt.backgrcol)) > 1.5: 398 c = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) 399 if c is None: 400 c = (0, 0, 0) 401 c = vedo.get_color(c) 402 403 self.scalarbar = vedo.addons.ScalarBar3D( 404 self, 405 title, 406 pos, 407 size, 408 title_font, 409 title_xoffset, 410 title_yoffset, 411 title_size, 412 title_rotation, 413 nlabels, 414 label_font, 415 label_size, 416 label_offset, 417 label_rotation, 418 label_format, 419 italic, 420 c, 421 draw_box, 422 above_text, 423 below_text, 424 nan_text, 425 categories, 426 ) 427 return self
Associate a 3D scalar bar to the object and add it to the scene. The new scalarbar object (Assembly) will be accessible as obj.scalarbar
Arguments:
- size : (list) (thickness, length) of scalarbar
- title : (str) scalar bar title
- title_xoffset : (float) horizontal space btw title and color scalarbar
- title_yoffset : (float) vertical space offset
- title_size : (float) size of title wrt numeric labels
- title_rotation : (float) title rotation in degrees
- nlabels : (int) number of numeric labels
- label_font : (str) font type for labels
- label_size : (float) label scale factor
- label_offset : (float) space btw numeric labels and scale
- label_rotation : (float) label rotation in degrees
- label_format : (str)
label format for floats and integers (e.g.
':.2f') - draw_box : (bool) draw a box around the colorbar
- categories : (list)
make a categorical scalarbar,
the input list will have the format
[value, color, alpha, textlabel]
Examples:
429 def color(self, col, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None): 430 """ 431 Assign a color or a set of colors along the range of the scalar value. 432 A single constant color can also be assigned. 433 Any matplotlib color map name is also accepted, e.g. `volume.color('jet')`. 434 435 E.g.: say that your cells scalar runs from -3 to 6, 436 and you want -3 to show red and 1.5 violet and 6 green, then just set: 437 438 `volume.color(['red', 'violet', 'green'])` 439 440 You can also assign a specific color to a aspecific value with eg.: 441 442 `volume.color([(0,'red'), (0.5,'violet'), (1,'green')])` 443 444 Arguments: 445 alpha : (list) 446 use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range 447 vmin : (float) 448 force the min of the scalar range to be this value 449 vmax : (float) 450 force the max of the scalar range to be this value 451 """ 452 # supersedes method in Points, Mesh 453 454 if col is None: 455 return self 456 457 if vmin is None: 458 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 459 if vmax is None: 460 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 461 ctf = self.properties.GetRGBTransferFunction() 462 ctf.RemoveAllPoints() 463 464 if utils.is_sequence(col): 465 if utils.is_sequence(col[0]) and len(col[0]) == 2: 466 # user passing [(value1, color1), ...] 467 for x, ci in col: 468 r, g, b = colors.get_color(ci) 469 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 470 # colors.printc('color at', round(x, 1), 471 # 'set to', colors.get_color_name((r, g, b)), bold=0) 472 else: 473 # user passing [color1, color2, ..] 474 for i, ci in enumerate(col): 475 r, g, b = colors.get_color(ci) 476 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(col) - 1) 477 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 478 elif isinstance(col, str): 479 if col in colors.colors.keys() or col in colors.color_nicks.keys(): 480 r, g, b = colors.get_color(col) 481 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmin, r, g, b) # constant color 482 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmax, r, g, b) 483 else: # assume it's a colormap 484 for x in np.linspace(vmin, vmax, num=64, endpoint=True): 485 r, g, b = colors.color_map(x, name=col, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax) 486 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 487 elif isinstance(col, int): 488 r, g, b = colors.get_color(col) 489 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmin, r, g, b) # constant color 490 ctf.AddRGBPoint(vmax, r, g, b) 491 elif isinstance(col, vtki.vtkLookupTable): 492 alpha=[] 493 nt = col.GetNumberOfTableValues() 494 for i in range(nt): 495 r, g, b, a = col.GetTableValue(i) 496 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (nt - 1) 497 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 498 alpha.append(a) 499 elif hasattr(col, "resampled"): # cover the case of LinearSegmentedColormap 500 N = col.N 501 cs = np.array([col(i/N) for i in range(N)]) 502 alpha = cs[:,3].copy() 503 for i, v in enumerate(cs): 504 r, g, b, _ = v 505 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (N - 1) 506 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 507 elif hasattr(col, "to_rgba"): # col is a matplotlib colormap 508 for i in range(256): 509 r, g, b, a = col(i / 255) 510 x = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / 255 511 ctf.AddRGBPoint(x, r, g, b) 512 alpha.append(a) 513 else: 514 vedo.logger.warning(f"in color() unknown input type {type(col)}") 515 516 if alpha is not None: 517 self.alpha(alpha, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax) 518 return self
Assign a color or a set of colors along the range of the scalar value.
A single constant color can also be assigned.
Any matplotlib color map name is also accepted, e.g. volume.color('jet').
E.g.: say that your cells scalar runs from -3 to 6, and you want -3 to show red and 1.5 violet and 6 green, then just set:
volume.color(['red', 'violet', 'green'])
You can also assign a specific color to a aspecific value with eg.:
volume.color([(0,'red'), (0.5,'violet'), (1,'green')])
Arguments:
- alpha : (list) use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range
- vmin : (float) force the min of the scalar range to be this value
- vmax : (float) force the max of the scalar range to be this value
520 def alpha(self, alpha, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 521 """ 522 Assign a set of tranparencies along the range of the scalar value. 523 A single constant value can also be assigned. 524 525 E.g.: say `alpha=(0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1)` and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150. 526 Then all cells with a value close to -10 will be completely transparent, cells at 1/4 527 of the range will get an alpha equal to 0.3 and voxels with value close to 150 528 will be completely opaque. 529 530 As a second option one can set explicit (x, alpha_x) pairs to define the transfer function. 531 532 E.g.: say `alpha=[(-5, 0), (35, 0.4) (123,0.9)]` and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150. 533 Then all cells below -5 will be completely transparent, cells with a scalar value of 35 534 will get an opacity of 40% and above 123 alpha is set to 90%. 535 """ 536 if vmin is None: 537 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 538 if vmax is None: 539 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 540 otf = self.properties.GetScalarOpacity() 541 otf.RemoveAllPoints() 542 543 if utils.is_sequence(alpha): 544 alpha = np.array(alpha) 545 if len(alpha.shape) == 1: # user passing a flat list e.g. (0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1) 546 for i, al in enumerate(alpha): 547 xalpha = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(alpha) - 1) 548 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 549 otf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 550 # print("alpha at", round(xalpha, 1), "\tset to", al) 551 elif len(alpha.shape) == 2: # user passing [(x0,alpha0), ...] 552 otf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha[0][1]) 553 for xalpha, al in alpha: 554 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 555 otf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 556 otf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha[-1][1]) 557 558 else: 559 560 otf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha) # constant alpha 561 otf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha) 562 563 return self
Assign a set of tranparencies along the range of the scalar value. A single constant value can also be assigned.
E.g.: say alpha=(0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1) and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150.
Then all cells with a value close to -10 will be completely transparent, cells at 1/4
of the range will get an alpha equal to 0.3 and voxels with value close to 150
will be completely opaque.
As a second option one can set explicit (x, alpha_x) pairs to define the transfer function.
E.g.: say alpha=[(-5, 0), (35, 0.4) (123,0.9)] and the scalar range goes from -10 to 150.
Then all cells below -5 will be completely transparent, cells with a scalar value of 35
will get an opacity of 40% and above 123 alpha is set to 90%.
873class PointsVisual(CommonVisual): 874 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a ``Points`` object.""" 875 876 def __init__(self): 877 # print("init PointsVisual") 878 super().__init__() 879 self.properties_backface = None 880 self._cmap_name = None 881 self.trail = None 882 self.trail_offset = 0 883 self.trail_points = [] 884 self._caption = None 885 886 887 def clone2d(self, size=None, offset=(), scale=None): 888 """ 889 Turn a 3D `Points` or `Mesh` into a flat 2D actor. 890 Returns a `Actor2D`. 891 892 Arguments: 893 size : (float) 894 size as scaling factor for the 2D actor 895 offset : (list) 896 2D (x, y) position of the actor in the range [-1, 1] 897 scale : (float) 898 Deprecated. Use `size` instead. 899 900 Examples: 901 - [clone2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/clone2d.py) 902 903  904 """ 905 # assembly.Assembly.clone2d() superseeds this method 906 if scale is not None: 907 vedo.logger.warning("clone2d(): use keyword size not scale") 908 size = scale 909 910 if size is None: 911 # work out a reasonable scale 912 msiz = self.diagonal_size() 913 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.window: 914 sz = vedo.plotter_instance.window.GetSize() 915 dsiz = utils.mag(sz) 916 size = dsiz / msiz / 10 917 else: 918 size = 350 / msiz 919 920 tp = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 921 transform = vtki.vtkTransform() 922 transform.Scale(size, size, size) 923 if len(offset) == 0: 924 offset = self.pos() 925 transform.Translate(-utils.make3d(offset)) 926 tp.SetTransform(transform) 927 tp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 928 tp.Update() 929 poly = tp.GetOutput() 930 931 cm = self.mapper.GetColorMode() 932 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 933 sv = self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility() 934 use_lut = self.mapper.GetUseLookupTableScalarRange() 935 vrange = self.mapper.GetScalarRange() 936 sm = self.mapper.GetScalarMode() 937 938 act2d = Actor2D(poly) 939 act2d.mapper.SetColorMode(cm) 940 act2d.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 941 act2d.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(sv) 942 act2d.mapper.SetUseLookupTableScalarRange(use_lut) 943 act2d.mapper.SetScalarRange(vrange) 944 act2d.mapper.SetScalarMode(sm) 945 946 act2d.GetPositionCoordinate().SetCoordinateSystem(4) 947 act2d.properties.SetColor(self.color()) 948 act2d.properties.SetOpacity(self.alpha()) 949 act2d.properties.SetLineWidth(self.properties.GetLineWidth()) 950 act2d.properties.SetPointSize(self.properties.GetPointSize()) 951 act2d.properties.SetDisplayLocation(0) # 0 = back, 1 = front 952 act2d.PickableOff() 953 return act2d 954 955 ################################################## 956 def copy_properties_from(self, source, deep=True, actor_related=True) -> Self: 957 """ 958 Copy properties from another ``Points`` object. 959 """ 960 pr = vtki.vtkProperty() 961 try: 962 sp = source.properties 963 mp = source.mapper 964 sa = source.actor 965 except AttributeError: 966 sp = source.GetProperty() 967 mp = source.GetMapper() 968 sa = source 969 970 if deep: 971 pr.DeepCopy(sp) 972 else: 973 pr.ShallowCopy(sp) 974 self.actor.SetProperty(pr) 975 self.properties = pr 976 977 if self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty(): 978 bfpr = vtki.vtkProperty() 979 bfpr.DeepCopy(sa.GetBackfaceProperty()) 980 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(bfpr) 981 self.properties_backface = bfpr 982 983 if not actor_related: 984 return self 985 986 # mapper related: 987 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(mp.GetScalarVisibility()) 988 self.mapper.SetScalarMode(mp.GetScalarMode()) 989 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(mp.GetScalarRange()) 990 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(mp.GetLookupTable()) 991 self.mapper.SetColorMode(mp.GetColorMode()) 992 self.mapper.SetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping( 993 mp.GetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping() 994 ) 995 self.mapper.SetUseLookupTableScalarRange( 996 mp.GetUseLookupTableScalarRange() 997 ) 998 999 self.actor.SetPickable(sa.GetPickable()) 1000 self.actor.SetDragable(sa.GetDragable()) 1001 self.actor.SetTexture(sa.GetTexture()) 1002 self.actor.SetVisibility(sa.GetVisibility()) 1003 return self 1004 1005 def color(self, c=False, alpha=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 1006 """ 1007 Set/get mesh's color. 1008 If None is passed as input, will use colors from active scalars. 1009 Same as `mesh.c()`. 1010 """ 1011 if c is False: 1012 return np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1013 if c is None: 1014 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1015 return self 1016 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 1017 cc = colors.get_color(c) 1018 self.properties.SetColor(cc) 1019 if self.trail: 1020 self.trail.properties.SetColor(cc) 1021 if alpha is not None: 1022 self.alpha(alpha) 1023 return self 1024 1025 def c(self, color=False, alpha=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 1026 """ 1027 Shortcut for `color()`. 1028 If None is passed as input, will use colors from current active scalars. 1029 """ 1030 return self.color(color, alpha) 1031 1032 def alpha(self, opacity=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 1033 """Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as `mesh.opacity()`.""" 1034 if opacity is None: 1035 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 1036 1037 self.properties.SetOpacity(opacity) 1038 bfp = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 1039 if bfp: 1040 if opacity < 1: 1041 self.properties_backface = bfp 1042 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(None) 1043 else: 1044 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(self.properties_backface) 1045 return self 1046 1047 def lut_color_at(self, value) -> np.ndarray: 1048 """ 1049 Return the color and alpha in the lookup table at given value. 1050 """ 1051 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1052 if not lut: 1053 return None 1054 rgb = [0,0,0] 1055 lut.GetColor(value, rgb) 1056 alpha = lut.GetOpacity(value) 1057 return np.array(rgb + [alpha]) 1058 1059 def opacity(self, alpha=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 1060 """Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as `mesh.alpha()`.""" 1061 return self.alpha(alpha) 1062 1063 def force_opaque(self, value=True) -> Self: 1064 """ Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as opaque""" 1065 ## force the opaque pass, fixes picking in vtk9 1066 # but causes other bad troubles with lines.. 1067 self.actor.SetForceOpaque(value) 1068 return self 1069 1070 def force_translucent(self, value=True) -> Self: 1071 """ Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as translucent""" 1072 self.actor.SetForceTranslucent(value) 1073 return self 1074 1075 def point_size(self, value=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 1076 """Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as `mesh.ps()`""" 1077 if value is None: 1078 return self.properties.GetPointSize() 1079 # self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 1080 else: 1081 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 1082 self.properties.SetPointSize(value) 1083 return self 1084 1085 def ps(self, pointsize=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 1086 """Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as `mesh.point_size()`""" 1087 return self.point_size(pointsize) 1088 1089 def render_points_as_spheres(self, value=True) -> Self: 1090 """Make points look spheric or else make them look as squares.""" 1091 self.properties.SetRenderPointsAsSpheres(value) 1092 return self 1093 1094 def lighting( 1095 self, 1096 style="", 1097 ambient=None, 1098 diffuse=None, 1099 specular=None, 1100 specular_power=None, 1101 specular_color=None, 1102 metallicity=None, 1103 roughness=None, 1104 ) -> Self: 1105 """ 1106 Set the ambient, diffuse, specular and specular_power lighting constants. 1107 1108 Arguments: 1109 style : (str) 1110 preset style, options are `[metallic, plastic, shiny, glossy, ambient, off]` 1111 ambient : (float) 1112 ambient fraction of emission [0-1] 1113 diffuse : (float) 1114 emission of diffused light in fraction [0-1] 1115 specular : (float) 1116 fraction of reflected light [0-1] 1117 specular_power : (float) 1118 precision of reflection [1-100] 1119 specular_color : (color) 1120 color that is being reflected by the surface 1121 1122 <img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Phong_components_version_4.png" alt="", width=700px> 1123 1124 Examples: 1125 - [specular.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/specular.py) 1126 """ 1127 pr = self.properties 1128 1129 if style: 1130 1131 if style != "off": 1132 pr.LightingOn() 1133 1134 if style == "off": 1135 pr.SetInterpolationToFlat() 1136 pr.LightingOff() 1137 return self ############## 1138 1139 if hasattr(pr, "GetColor"): # could be Volume 1140 c = pr.GetColor() 1141 else: 1142 c = (1, 1, 0.99) 1143 mpr = self.mapper 1144 if hasattr(mpr, 'GetScalarVisibility') and mpr.GetScalarVisibility(): 1145 c = (1,1,0.99) 1146 if style=='metallic': pars = [0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 10, c] 1147 elif style=='plastic' : pars = [0.3, 0.4, 0.3, 5, c] 1148 elif style=='shiny' : pars = [0.2, 0.6, 0.8, 50, c] 1149 elif style=='glossy' : pars = [0.1, 0.7, 0.9, 90, (1,1,0.99)] 1150 elif style=='ambient' : pars = [0.8, 0.1, 0.0, 1, (1,1,1)] 1151 elif style=='default' : pars = [0.1, 1.0, 0.05, 5, c] 1152 else: 1153 vedo.logger.error("in lighting(): Available styles are") 1154 vedo.logger.error("[default, metallic, plastic, shiny, glossy, ambient, off]") 1155 raise RuntimeError() 1156 pr.SetAmbient(pars[0]) 1157 pr.SetDiffuse(pars[1]) 1158 pr.SetSpecular(pars[2]) 1159 pr.SetSpecularPower(pars[3]) 1160 if hasattr(pr, "GetColor"): 1161 pr.SetSpecularColor(pars[4]) 1162 1163 if ambient is not None: pr.SetAmbient(ambient) 1164 if diffuse is not None: pr.SetDiffuse(diffuse) 1165 if specular is not None: pr.SetSpecular(specular) 1166 if specular_power is not None: pr.SetSpecularPower(specular_power) 1167 if specular_color is not None: pr.SetSpecularColor(colors.get_color(specular_color)) 1168 if metallicity is not None: 1169 pr.SetInterpolationToPBR() 1170 pr.SetMetallic(metallicity) 1171 if roughness is not None: 1172 pr.SetInterpolationToPBR() 1173 pr.SetRoughness(roughness) 1174 1175 return self 1176 1177 def point_blurring(self, r=1, alpha=1.0, emissive=False) -> Self: 1178 """Set point blurring. 1179 Apply a gaussian convolution filter to the points. 1180 In this case the radius `r` is in absolute units of the mesh coordinates. 1181 With emissive set, the halo of point becomes light-emissive. 1182 """ 1183 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 1184 if emissive: 1185 self.mapper.SetEmissive(bool(emissive)) 1186 self.mapper.SetScaleFactor(r * 1.4142) 1187 1188 # https://kitware.github.io/vtk-examples/site/Python/Meshes/PointInterpolator/ 1189 if alpha < 1: 1190 self.mapper.SetSplatShaderCode( 1191 "//VTK::Color::Impl\n" 1192 "float dist = dot(offsetVCVSOutput.xy,offsetVCVSOutput.xy);\n" 1193 "if (dist > 1.0) {\n" 1194 " discard;\n" 1195 "} else {\n" 1196 f" float scale = ({alpha} - dist);\n" 1197 " ambientColor *= scale;\n" 1198 " diffuseColor *= scale;\n" 1199 "}\n" 1200 ) 1201 alpha = 1 1202 1203 self.mapper.Modified() 1204 self.actor.Modified() 1205 self.properties.SetOpacity(alpha) 1206 self.actor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 1207 return self 1208 1209 @property 1210 def cellcolors(self): 1211 """ 1212 Colorize each cell (face) of a mesh by passing 1213 a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. 1214 Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255]. 1215 1216 A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA. 1217 1218 A cell array named "CellsRGBA" is automatically created. 1219 1220 Examples: 1221 - [color_mesh_cells1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/color_mesh_cells1.py) 1222 - [color_mesh_cells2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/color_mesh_cells2.py) 1223 1224  1225 """ 1226 if "CellsRGBA" not in self.celldata.keys(): 1227 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1228 vscalars = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 1229 if vscalars is None or lut is None: 1230 arr = np.zeros([self.ncells, 4], dtype=np.uint8) 1231 col = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1232 col = np.round(col * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1233 alf = self.properties.GetOpacity() 1234 alf = np.round(alf * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1235 arr[:, (0, 1, 2)] = col 1236 arr[:, 3] = alf 1237 else: 1238 cols = lut.MapScalars(vscalars, 0, 0) 1239 arr = utils.vtk2numpy(cols) 1240 self.celldata["CellsRGBA"] = arr 1241 self.celldata.select("CellsRGBA") 1242 return self.celldata["CellsRGBA"] 1243 1244 @cellcolors.setter 1245 def cellcolors(self, value): 1246 if isinstance(value, str): 1247 c = colors.get_color(value) 1248 value = np.array([*c, 1]) * 255 1249 value = np.round(value) 1250 1251 value = np.asarray(value) 1252 n = self.ncells 1253 1254 if value.ndim == 1: 1255 value = np.repeat([value], n, axis=0) 1256 1257 if value.shape[1] == 3: 1258 z = np.zeros((n, 1), dtype=np.uint8) 1259 value = np.append(value, z + 255, axis=1) 1260 1261 assert n == value.shape[0] 1262 1263 self.celldata["CellsRGBA"] = value.astype(np.uint8) 1264 # self.mapper.SetColorModeToDirectScalars() # done in select() 1265 self.celldata.select("CellsRGBA") 1266 1267 @property 1268 def pointcolors(self): 1269 """ 1270 Colorize each point (or vertex of a mesh) by passing 1271 a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. 1272 Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255]. 1273 1274 A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA. 1275 1276 A point array named "PointsRGBA" is automatically created. 1277 """ 1278 if "PointsRGBA" not in self.pointdata.keys(): 1279 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1280 vscalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 1281 if vscalars is None or lut is None: 1282 # create a constant array 1283 arr = np.zeros([self.npoints, 4], dtype=np.uint8) 1284 col = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1285 col = np.round(col * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1286 alf = self.properties.GetOpacity() 1287 alf = np.round(alf * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1288 arr[:, (0, 1, 2)] = col 1289 arr[:, 3] = alf 1290 else: 1291 cols = lut.MapScalars(vscalars, 0, 0) 1292 arr = utils.vtk2numpy(cols) 1293 self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"] = arr 1294 self.pointdata.select("PointsRGBA") 1295 return self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"] 1296 1297 @pointcolors.setter 1298 def pointcolors(self, value): 1299 if isinstance(value, str): 1300 c = colors.get_color(value) 1301 value = np.array([*c, 1]) * 255 1302 value = np.round(value) 1303 1304 value = np.asarray(value) 1305 n = self.npoints 1306 1307 if value.ndim == 1: 1308 value = np.repeat([value], n, axis=0) 1309 1310 if value.shape[1] == 3: 1311 z = np.zeros((n, 1), dtype=np.uint8) 1312 value = np.append(value, z + 255, axis=1) 1313 1314 assert n == value.shape[0] 1315 1316 self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"] = value.astype(np.uint8) 1317 self.mapper.SetColorModeToDirectScalars() # also done in select() 1318 self.pointdata.select("PointsRGBA") 1319 1320 ##################################################################################### 1321 def cmap( 1322 self, 1323 input_cmap, 1324 input_array=None, 1325 on="", 1326 name="Scalars", 1327 vmin=None, 1328 vmax=None, 1329 n_colors=256, 1330 alpha=1.0, 1331 logscale=False, 1332 ) -> Self: 1333 """ 1334 Set individual point/cell colors by providing a list of scalar values and a color map. 1335 1336 Arguments: 1337 input_cmap : (str, list, vtkLookupTable, matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap) 1338 color map scheme to transform a real number into a color. 1339 input_array : (str, list, vtkArray) 1340 can be the string name of an existing array, a new array or a `vtkArray`. 1341 on : (str) 1342 either 'points' or 'cells' or blank (automatic). 1343 Apply the color map to data which is defined on either points or cells. 1344 name : (str) 1345 give a name to the provided array (if input_array is an array) 1346 vmin : (float) 1347 clip scalars to this minimum value 1348 vmax : (float) 1349 clip scalars to this maximum value 1350 n_colors : (int) 1351 number of distinct colors to be used in colormap table. 1352 alpha : (float, list) 1353 Mesh transparency. Can be a `list` of values one for each vertex. 1354 logscale : (bool) 1355 Use logscale 1356 1357 Examples: 1358 - [mesh_coloring.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_coloring.py) 1359 - [mesh_alphas.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_alphas.py) 1360 - [mesh_custom.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_custom.py) 1361 - (and many others) 1362 1363  1364 """ 1365 self._cmap_name = input_cmap 1366 1367 if on == "": 1368 try: 1369 on = self.mapper.GetScalarModeAsString().replace("Use", "") 1370 if on not in ["PointData", "CellData"]: # can be "Default" 1371 on = "points" 1372 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1373 except AttributeError: 1374 on = "points" 1375 elif on == "Default": 1376 on = "points" 1377 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1378 1379 if input_array is None: 1380 if not self.pointdata.keys() and self.celldata.keys(): 1381 on = "cells" 1382 if not self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 1383 input_array = 0 # pick the first at hand 1384 1385 if "point" in on.lower(): 1386 data = self.dataset.GetPointData() 1387 n = self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints() 1388 elif "cell" in on.lower(): 1389 data = self.dataset.GetCellData() 1390 n = self.dataset.GetNumberOfCells() 1391 else: 1392 vedo.logger.error( 1393 f"Must specify in cmap(on=...) to either 'cells' or 'points', not {on}") 1394 raise RuntimeError() 1395 1396 if input_array is None: # if None try to fetch the active scalars 1397 arr = data.GetScalars() 1398 if not arr: 1399 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find any {on} active array ...skip coloring.") 1400 return self 1401 1402 if not arr.GetName(): # sometimes arrays dont have a name.. 1403 arr.SetName(name) 1404 1405 elif isinstance(input_array, str): # if a string is passed 1406 arr = data.GetArray(input_array) 1407 if not arr: 1408 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find {on} array {input_array} ...skip coloring.") 1409 return self 1410 1411 elif isinstance(input_array, int): # if an int is passed 1412 if input_array < data.GetNumberOfArrays(): 1413 arr = data.GetArray(input_array) 1414 else: 1415 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find {on} array at {input_array} ...skip coloring.") 1416 return self 1417 1418 elif utils.is_sequence(input_array): # if a numpy array is passed 1419 npts = len(input_array) 1420 if npts != n: 1421 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), nr. of input {on} scalars {npts} != {n} ...skip coloring.") 1422 return self 1423 arr = utils.numpy2vtk(input_array, name=name, dtype=float) 1424 data.AddArray(arr) 1425 data.Modified() 1426 1427 elif isinstance(input_array, vtki.vtkArray): # if a vtkArray is passed 1428 arr = input_array 1429 data.AddArray(arr) 1430 data.Modified() 1431 1432 else: 1433 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot understand input type {type(input_array)}") 1434 raise RuntimeError() 1435 1436 # Now we have array "arr" 1437 array_name = arr.GetName() 1438 1439 if arr.GetNumberOfComponents() == 1: 1440 if vmin is None: 1441 vmin = arr.GetRange()[0] 1442 if vmax is None: 1443 vmax = arr.GetRange()[1] 1444 else: 1445 if vmin is None or vmax is None: 1446 vn = utils.mag(utils.vtk2numpy(arr)) 1447 if vmin is None: 1448 vmin = vn.min() 1449 if vmax is None: 1450 vmax = vn.max() 1451 1452 # interpolate alphas if they are not constant 1453 if not utils.is_sequence(alpha): 1454 alpha = [alpha] * n_colors 1455 else: 1456 v = np.linspace(0, 1, n_colors, endpoint=True) 1457 xp = np.linspace(0, 1, len(alpha), endpoint=True) 1458 alpha = np.interp(v, xp, alpha) 1459 1460 ########################### build the look-up table 1461 if isinstance(input_cmap, vtki.vtkLookupTable): # vtkLookupTable 1462 lut = input_cmap 1463 1464 elif utils.is_sequence(input_cmap): # manual sequence of colors 1465 lut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 1466 if logscale: 1467 lut.SetScaleToLog10() 1468 lut.SetRange(vmin, vmax) 1469 ncols = len(input_cmap) 1470 lut.SetNumberOfTableValues(ncols) 1471 1472 for i, c in enumerate(input_cmap): 1473 r, g, b = colors.get_color(c) 1474 lut.SetTableValue(i, r, g, b, alpha[i]) 1475 lut.Build() 1476 1477 else: 1478 # assume string cmap name OR matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap 1479 lut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 1480 if logscale: 1481 lut.SetScaleToLog10() 1482 lut.SetVectorModeToMagnitude() 1483 lut.SetRange(vmin, vmax) 1484 lut.SetNumberOfTableValues(n_colors) 1485 mycols = colors.color_map(range(n_colors), input_cmap, 0, n_colors) 1486 for i, c in enumerate(mycols): 1487 r, g, b = c 1488 lut.SetTableValue(i, r, g, b, alpha[i]) 1489 lut.Build() 1490 1491 # TEST NEW WAY 1492 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 1493 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1494 self.mapper.SetColorModeToMapScalars() 1495 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(lut.GetRange()) 1496 if "point" in on.lower(): 1497 self.pointdata.select(array_name) 1498 else: 1499 self.celldata.select(array_name) 1500 return self 1501 1502 # # TEST this is the old way: 1503 # # arr.SetLookupTable(lut) # wrong! causes weird instabilities with LUT 1504 # # if data.GetScalars(): 1505 # # data.GetScalars().SetLookupTable(lut) 1506 # # data.GetScalars().Modified() 1507 1508 # data.SetActiveScalars(array_name) 1509 # # data.SetScalars(arr) # wrong! it deletes array in position 0, never use SetScalars 1510 # # data.SetActiveAttribute(array_name, 0) # boh! 1511 1512 # self.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 1513 # self.mapper.SetColorModeToMapScalars() # so we dont need to convert uint8 scalars 1514 1515 # self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1516 # self.mapper.SetScalarRange(lut.GetRange()) 1517 1518 # if on.startswith("point"): 1519 # self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1520 # else: 1521 # self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUseCellData() 1522 # if hasattr(self.mapper, "SetArrayName"): 1523 # self.mapper.SetArrayName(array_name) 1524 # return self 1525 1526 def add_trail(self, offset=(0, 0, 0), n=50, c=None, alpha=1.0, lw=2) -> Self: 1527 """ 1528 Add a trailing line to mesh. 1529 This new mesh is accessible through `mesh.trail`. 1530 1531 Arguments: 1532 offset : (float) 1533 set an offset vector from the object center. 1534 n : (int) 1535 number of segments 1536 lw : (float) 1537 line width of the trail 1538 1539 Examples: 1540 - [trail.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/trail.py) 1541 1542  1543 1544 - [airplane1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane1.py) 1545 - [airplane2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane2.py) 1546 """ 1547 if self.trail is None: 1548 pos = self.pos() 1549 self.trail_offset = np.asarray(offset) 1550 self.trail_points = [pos] * n 1551 1552 if c is None: 1553 col = self.properties.GetColor() 1554 else: 1555 col = colors.get_color(c) 1556 1557 tline = vedo.shapes.Line(pos, pos, res=n, c=col, alpha=alpha, lw=lw) 1558 self.trail = tline # holds the Line 1559 self.trail.initilized = False # so the first update will be a reset 1560 return self 1561 1562 def update_trail(self) -> Self: 1563 """ 1564 Update the trailing line of a moving object. 1565 """ 1566 currentpos = self.pos() 1567 if not self.trail.initilized: 1568 self.trail_points = [currentpos] * self.trail.npoints 1569 self.trail.initilized = True 1570 return self 1571 self.trail_points.append(currentpos) # cycle 1572 self.trail_points.pop(0) 1573 1574 data = np.array(self.trail_points) + self.trail_offset 1575 tpoly = self.trail.dataset 1576 tpoly.GetPoints().SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(data, dtype=np.float32)) 1577 return self 1578 1579 def _compute_shadow(self, plane, point, direction): 1580 shad = self.clone() 1581 shad.name = "Shadow" 1582 1583 tarr = shad.dataset.GetPointData().GetTCoords() 1584 if tarr: # remove any texture coords 1585 tname = tarr.GetName() 1586 shad.pointdata.remove(tname) 1587 shad.dataset.GetPointData().SetTCoords(None) 1588 shad.actor.SetTexture(None) 1589 1590 pts = shad.vertices 1591 if plane == "x": 1592 # shad = shad.project_on_plane('x') 1593 # instead do it manually so in case of alpha<1 1594 # we dont see glitches due to coplanar points 1595 # we leave a small tolerance of 0.1% in thickness 1596 x0, x1 = self.xbounds() 1597 pts[:, 0] = (pts[:, 0] - (x0 + x1) / 2) / 1000 + self.actor.GetOrigin()[0] 1598 shad.vertices = pts 1599 shad.x(point) 1600 elif plane == "y": 1601 x0, x1 = self.ybounds() 1602 pts[:, 1] = (pts[:, 1] - (x0 + x1) / 2) / 1000 + self.actor.GetOrigin()[1] 1603 shad.vertices = pts 1604 shad.y(point) 1605 elif plane == "z": 1606 x0, x1 = self.zbounds() 1607 pts[:, 2] = (pts[:, 2] - (x0 + x1) / 2) / 1000 + self.actor.GetOrigin()[2] 1608 shad.vertices = pts 1609 shad.z(point) 1610 else: 1611 shad = shad.project_on_plane(plane, point, direction) 1612 return shad 1613 1614 def add_shadow(self, plane, point, direction=None, c=(0.6, 0.6, 0.6), alpha=1, culling=0) -> Self: 1615 """ 1616 Generate a shadow out of an `Mesh` on one of the three Cartesian planes. 1617 The output is a new `Mesh` representing the shadow. 1618 This new mesh is accessible through `mesh.shadow`. 1619 By default the shadow mesh is placed on the bottom wall of the bounding box. 1620 1621 See also `pointcloud.project_on_plane()`. 1622 1623 Arguments: 1624 plane : (str, Plane) 1625 if plane is `str`, plane can be one of `['x', 'y', 'z']`, 1626 represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. 1627 Otherwise, plane should be an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane` 1628 point : (float, array) 1629 if plane is `str`, point should be a float represents the intercept. 1630 Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection 1631 direction : (list) 1632 direction of oblique projection 1633 culling : (int) 1634 choose between front [1] or backface [-1] culling or None. 1635 1636 Examples: 1637 - [shadow1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/shadow1.py) 1638 - [airplane1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane1.py) 1639 - [airplane2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane2.py) 1640 1641  1642 """ 1643 shad = self._compute_shadow(plane, point, direction) 1644 shad.c(c).alpha(alpha) 1645 1646 try: 1647 # Points dont have these methods 1648 shad.flat() 1649 if culling in (1, True): 1650 shad.frontface_culling() 1651 elif culling == -1: 1652 shad.backface_culling() 1653 except AttributeError: 1654 pass 1655 1656 shad.properties.LightingOff() 1657 shad.actor.SetPickable(False) 1658 shad.actor.SetUseBounds(True) 1659 1660 if shad not in self.shadows: 1661 self.shadows.append(shad) 1662 shad.info = dict(plane=plane, point=point, direction=direction) 1663 # shad.metadata["plane"] = plane 1664 # shad.metadata["point"] = point 1665 # print("AAAA", direction, plane, point) 1666 # if direction is None: 1667 # direction = [0,0,0] 1668 # shad.metadata["direction"] = direction 1669 return self 1670 1671 def update_shadows(self) -> Self: 1672 """Update the shadows of a moving object.""" 1673 for sha in self.shadows: 1674 plane = sha.info["plane"] 1675 point = sha.info["point"] 1676 direction = sha.info["direction"] 1677 # print("update_shadows direction", direction,plane,point ) 1678 # plane = sha.metadata["plane"] 1679 # point = sha.metadata["point"] 1680 # direction = sha.metadata["direction"] 1681 # if direction[0]==0 and direction[1]==0 and direction[2]==0: 1682 # direction = None 1683 # print("BBBB", sha.metadata["direction"], 1684 # sha.metadata["plane"], sha.metadata["point"]) 1685 new_sha = self._compute_shadow(plane, point, direction) 1686 sha._update(new_sha.dataset) 1687 if self.trail: 1688 self.trail.update_shadows() 1689 return self 1690 1691 def labels( 1692 self, 1693 content=None, 1694 on="points", 1695 scale=None, 1696 xrot=0.0, 1697 yrot=0.0, 1698 zrot=0.0, 1699 ratio=1, 1700 precision=None, 1701 italic=False, 1702 font="", 1703 justify="", 1704 c="black", 1705 alpha=1.0, 1706 ) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", None]: 1707 """ 1708 Generate value or ID labels for mesh cells or points. 1709 For large nr. of labels use `font="VTK"` which is much faster. 1710 1711 See also: 1712 `labels2d()`, `flagpole()`, `caption()` and `legend()`. 1713 1714 Arguments: 1715 content : (list,int,str) 1716 either 'id', 'cellid', array name or array number. 1717 A array can also be passed (must match the nr. of points or cells). 1718 on : (str) 1719 generate labels for "cells" instead of "points" 1720 scale : (float) 1721 absolute size of labels, if left as None it is automatic 1722 zrot : (float) 1723 local rotation angle of label in degrees 1724 ratio : (int) 1725 skipping ratio, to reduce nr of labels for large meshes 1726 precision : (int) 1727 numeric precision of labels 1728 1729 ```python 1730 from vedo import * 1731 s = Sphere(res=10).linewidth(1).c("orange").compute_normals() 1732 point_ids = s.labels('id', on="points").c('green') 1733 cell_ids = s.labels('id', on="cells" ).c('black') 1734 show(s, point_ids, cell_ids) 1735 ``` 1736  1737 1738 Examples: 1739 - [boundaries.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/boundaries.py) 1740 1741  1742 """ 1743 1744 cells = False 1745 if "cell" in on or "face" in on: 1746 cells = True 1747 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1748 1749 if isinstance(content, str): 1750 if content in ("pointid", "pointsid"): 1751 cells = False 1752 content = "id" 1753 justify = "bottom-left" if justify == "" else justify 1754 if content in ("cellid", "cellsid"): 1755 cells = True 1756 content = "id" 1757 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1758 1759 try: 1760 if cells: 1761 ns = np.sqrt(self.ncells) 1762 elems = self.cell_centers().points 1763 norms = self.cell_normals 1764 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1765 else: 1766 ns = np.sqrt(self.npoints) 1767 elems = self.vertices 1768 norms = self.vertex_normals 1769 except AttributeError: 1770 norms = [] 1771 1772 if not justify: 1773 justify = "bottom-left" 1774 1775 hasnorms = False 1776 if len(norms) > 0: 1777 hasnorms = True 1778 1779 if scale is None: 1780 if not ns: 1781 ns = 100 1782 scale = self.diagonal_size() / ns / 10 1783 1784 arr = None 1785 mode = 0 1786 if content is None: 1787 mode = 0 1788 if cells: 1789 if self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 1790 name = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars().GetName() 1791 arr = self.celldata[name] 1792 else: 1793 if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 1794 name = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars().GetName() 1795 arr = self.pointdata[name] 1796 elif isinstance(content, (str, int)): 1797 if content == "id": 1798 mode = 1 1799 elif cells: 1800 mode = 0 1801 arr = self.celldata[content] 1802 else: 1803 mode = 0 1804 arr = self.pointdata[content] 1805 elif utils.is_sequence(content): 1806 mode = 0 1807 arr = content 1808 1809 if arr is None and mode == 0: 1810 vedo.logger.error("in labels(), array not found in point or cell data") 1811 return None 1812 1813 ratio = int(ratio+0.5) 1814 tapp = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1815 has_inputs = False 1816 1817 for i, e in enumerate(elems): 1818 if i % ratio: 1819 continue 1820 1821 if mode == 1: 1822 txt_lab = str(i) 1823 else: 1824 if precision: 1825 txt_lab = utils.precision(arr[i], precision) 1826 else: 1827 txt_lab = str(arr[i]) 1828 1829 if not txt_lab: 1830 continue 1831 1832 if font == "VTK": 1833 tx = vtki.new("VectorText") 1834 tx.SetText(txt_lab) 1835 tx.Update() 1836 tx_poly = tx.GetOutput() 1837 else: 1838 tx_poly = vedo.shapes.Text3D(txt_lab, font=font, justify=justify).dataset 1839 1840 if tx_poly.GetNumberOfPoints() == 0: 1841 continue ###################### 1842 1843 T = vtki.vtkTransform() 1844 T.PostMultiply() 1845 if italic: 1846 T.Concatenate([1, 0.2, 0, 0, 1847 0, 1 , 0, 0, 1848 0, 0 , 1, 0, 1849 0, 0 , 0, 1]) 1850 if hasnorms: 1851 ni = norms[i] 1852 if cells and font=="VTK": # center-justify 1853 bb = tx_poly.GetBounds() 1854 dx, dy = (bb[1] - bb[0]) / 2, (bb[3] - bb[2]) / 2 1855 T.Translate(-dx, -dy, 0) 1856 if xrot: T.RotateX(xrot) 1857 if yrot: T.RotateY(yrot) 1858 if zrot: T.RotateZ(zrot) 1859 crossvec = np.cross([0, 0, 1], ni) 1860 angle = np.arccos(np.dot([0, 0, 1], ni)) * 57.3 1861 T.RotateWXYZ(float(angle), crossvec.tolist()) 1862 T.Translate(ni / 100) 1863 else: 1864 if xrot: T.RotateX(xrot) 1865 if yrot: T.RotateY(yrot) 1866 if zrot: T.RotateZ(zrot) 1867 T.Scale(scale, scale, scale) 1868 T.Translate(e) 1869 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 1870 tf.SetInputData(tx_poly) 1871 tf.SetTransform(T) 1872 tf.Update() 1873 tapp.AddInputData(tf.GetOutput()) 1874 has_inputs = True 1875 1876 if has_inputs: 1877 tapp.Update() 1878 lpoly = tapp.GetOutput() 1879 else: 1880 lpoly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1881 ids = vedo.Mesh(lpoly, c=c, alpha=alpha) 1882 ids.properties.LightingOff() 1883 ids.actor.PickableOff() 1884 ids.actor.SetUseBounds(False) 1885 ids.name = "Labels" 1886 return ids 1887 1888 def labels2d( 1889 self, 1890 content="id", 1891 on="points", 1892 scale=1.0, 1893 precision=4, 1894 font="Calco", 1895 justify="bottom-left", 1896 angle=0.0, 1897 frame=False, 1898 c="black", 1899 bc=None, 1900 alpha=1.0, 1901 ) -> Union["Actor2D", None]: 1902 """ 1903 Generate value or ID bi-dimensional labels for mesh cells or points. 1904 1905 See also: `labels()`, `flagpole()`, `caption()` and `legend()`. 1906 1907 Arguments: 1908 content : (str) 1909 either 'id', 'cellid', or array name 1910 on : (str) 1911 generate labels for "cells" instead of "points" (the default) 1912 scale : (float) 1913 size scaling of labels 1914 precision : (int) 1915 precision of numeric labels 1916 angle : (float) 1917 local rotation angle of label in degrees 1918 frame : (bool) 1919 draw a frame around the label 1920 bc : (str) 1921 background color of the label 1922 1923 ```python 1924 from vedo import Sphere, show 1925 sph = Sphere(quads=True, res=4).compute_normals().wireframe() 1926 sph.celldata["zvals"] = sph.cell_centers().coordinates[:,2] 1927 l2d = sph.labels("zvals", on="cells", precision=2).backcolor('orange9') 1928 show(sph, l2d, axes=1).close() 1929 ``` 1930  1931 """ 1932 cells = False 1933 if "cell" in on: 1934 cells = True 1935 1936 if isinstance(content, str): 1937 if content in ("id", "pointid", "pointsid"): 1938 cells = False 1939 content = "id" 1940 if content in ("cellid", "cellsid"): 1941 cells = True 1942 content = "id" 1943 1944 if cells: 1945 if content != "id" and content not in self.celldata.keys(): 1946 vedo.logger.error(f"In labels2d: cell array {content} does not exist.") 1947 return None 1948 arr = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 1949 poly = self.cell_centers().dataset 1950 poly.GetPointData().SetScalars(arr) 1951 else: 1952 arr = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 1953 poly = self.dataset 1954 if content != "id" and content not in self.pointdata.keys(): 1955 vedo.logger.error(f"In labels2d: point array {content} does not exist.") 1956 return None 1957 1958 mp = vtki.new("LabeledDataMapper") 1959 1960 if content == "id": 1961 mp.SetLabelModeToLabelIds() 1962 else: 1963 mp.SetLabelModeToLabelScalars() 1964 if precision is not None: 1965 dtype = arr.GetDataType() 1966 if dtype in (vtki.VTK_FLOAT, vtki.VTK_DOUBLE): 1967 mp.SetLabelFormat(f"%-#.{precision}g") 1968 1969 pr = mp.GetLabelTextProperty() 1970 c = colors.get_color(c) 1971 pr.SetColor(c) 1972 pr.SetOpacity(alpha) 1973 pr.SetFrame(frame) 1974 pr.SetFrameColor(c) 1975 pr.SetItalic(False) 1976 pr.BoldOff() 1977 pr.ShadowOff() 1978 pr.UseTightBoundingBoxOn() 1979 pr.SetOrientation(angle) 1980 pr.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 1981 fl = utils.get_font_path(font) 1982 pr.SetFontFile(fl) 1983 pr.SetFontSize(int(20 * scale)) 1984 1985 if "cent" in justify or "mid" in justify: 1986 pr.SetJustificationToCentered() 1987 elif "rig" in justify: 1988 pr.SetJustificationToRight() 1989 elif "left" in justify: 1990 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 1991 # ------ 1992 if "top" in justify: 1993 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 1994 else: 1995 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 1996 1997 if bc is not None: 1998 bc = colors.get_color(bc) 1999 pr.SetBackgroundColor(bc) 2000 pr.SetBackgroundOpacity(alpha) 2001 2002 mp.SetInputData(poly) 2003 a2d = Actor2D() 2004 a2d.PickableOff() 2005 a2d.SetMapper(mp) 2006 return a2d 2007 2008 def legend(self, txt) -> Self: 2009 """Book a legend text.""" 2010 self.info["legend"] = txt 2011 # self.metadata["legend"] = txt 2012 return self 2013 2014 def flagpole( 2015 self, 2016 txt=None, 2017 point=None, 2018 offset=None, 2019 s=None, 2020 font="Calco", 2021 rounded=True, 2022 c=None, 2023 alpha=1.0, 2024 lw=2, 2025 italic=0.0, 2026 padding=0.1, 2027 ) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", None]: 2028 """ 2029 Generate a flag pole style element to describe an object. 2030 Returns a `Mesh` object. 2031 2032 Use flagpole.follow_camera() to make it face the camera in the scene. 2033 2034 Consider using `settings.use_parallel_projection = True` 2035 to avoid perspective distortions. 2036 2037 See also `flagpost()`. 2038 2039 Arguments: 2040 txt : (str) 2041 Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name. 2042 point : (list) 2043 position of the flagpole pointer. 2044 offset : (list) 2045 text offset wrt the application point. 2046 s : (float) 2047 size of the flagpole. 2048 font : (str) 2049 font face. Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2050 rounded : (bool) 2051 draw a rounded or squared box around the text. 2052 c : (list) 2053 text and box color. 2054 alpha : (float) 2055 opacity of text and box. 2056 lw : (float) 2057 line with of box frame. 2058 italic : (float) 2059 italicness of text. 2060 2061 Examples: 2062 - [intersect2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/intersect2d.py) 2063 2064  2065 2066 - [goniometer.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/goniometer.py) 2067 - [flag_labels1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels1.py) 2068 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2069 """ 2070 objs = [] 2071 2072 if txt is None: 2073 if self.filename: 2074 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2075 elif self.name: 2076 txt = self.name 2077 else: 2078 return None 2079 2080 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2081 d = self.diagonal_size() 2082 if point is None: 2083 if d: 2084 point = self.closest_point([(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1]) 2085 # point = self.closest_point([x1, y0, z1]) 2086 else: # it's a Point 2087 point = self.transform.position 2088 2089 pt = utils.make3d(point) 2090 2091 if offset is None: 2092 offset = [(x1 - x0) / 1.75, (y1 - y0) / 5, 0] 2093 offset = utils.make3d(offset) 2094 2095 if s is None: 2096 s = d / 20 2097 2098 sph = None 2099 if d and (z1 - z0) / d > 0.1: 2100 sph = vedo.shapes.Sphere(pt, r=s * 0.4, res=6) 2101 2102 if c is None: 2103 c = np.array(self.color()) / 1.4 2104 2105 lab = vedo.shapes.Text3D( 2106 txt, pos=pt + offset, s=s, font=font, italic=italic, justify="center" 2107 ) 2108 objs.append(lab) 2109 2110 if d and not sph: 2111 sph = vedo.shapes.Circle(pt, r=s / 3, res=16) 2112 objs.append(sph) 2113 2114 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = lab.bounds() 2115 aline = [(x0,y0,z0), (x1,y0,z0), (x1,y1,z0), (x0,y1,z0)] 2116 if rounded: 2117 box = vedo.shapes.KSpline(aline, closed=True) 2118 else: 2119 box = vedo.shapes.Line(aline, closed=True) 2120 2121 cnt = [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, (z0 + z1) / 2] 2122 2123 # box.actor.SetOrigin(cnt) 2124 box.scale([1 + padding, 1 + 2 * padding, 1], origin=cnt) 2125 objs.append(box) 2126 2127 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = box.bounds() 2128 if x0 < pt[0] < x1: 2129 c0 = box.closest_point(pt) 2130 c1 = [c0[0], c0[1] + (pt[1] - y0) / 4, pt[2]] 2131 elif (pt[0] - x0) < (x1 - pt[0]): 2132 c0 = [x0, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2133 c1 = [x0 + (pt[0] - x0) / 4, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2134 else: 2135 c0 = [x1, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2136 c1 = [x1 + (pt[0] - x1) / 4, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2137 2138 con = vedo.shapes.Line([c0, c1, pt]) 2139 objs.append(con) 2140 2141 mobjs = vedo.merge(objs).c(c).alpha(alpha) 2142 mobjs.name = "FlagPole" 2143 mobjs.bc("tomato").pickable(False) 2144 mobjs.properties.LightingOff() 2145 mobjs.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2146 mobjs.actor.UseBoundsOff() 2147 mobjs.actor.SetPosition([0,0,0]) 2148 mobjs.actor.SetOrigin(pt) 2149 return mobjs 2150 2151 # mobjs = vedo.Assembly(objs)#.c(c).alpha(alpha) 2152 # mobjs.name = "FlagPole" 2153 # # mobjs.bc("tomato").pickable(False) 2154 # # mobjs.properties.LightingOff() 2155 # # mobjs.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2156 # # mobjs.actor.UseBoundsOff() 2157 # # mobjs.actor.SetPosition([0,0,0]) 2158 # # mobjs.actor.SetOrigin(pt) 2159 # # print(pt) 2160 # return mobjs 2161 2162 def flagpost( 2163 self, 2164 txt=None, 2165 point=None, 2166 offset=None, 2167 s=1.0, 2168 c="k9", 2169 bc="k1", 2170 alpha=1, 2171 lw=0, 2172 font="Calco", 2173 justify="center-left", 2174 vspacing=1.0, 2175 ) -> Union["vedo.addons.Flagpost", None]: 2176 """ 2177 Generate a flag post style element to describe an object. 2178 2179 Arguments: 2180 txt : (str) 2181 Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name. 2182 point : (list) 2183 position of the flag anchor point. The default is None. 2184 offset : (list) 2185 a 3D displacement or offset. The default is None. 2186 s : (float) 2187 size of the text to be shown 2188 c : (list) 2189 color of text and line 2190 bc : (list) 2191 color of the flag background 2192 alpha : (float) 2193 opacity of text and box. 2194 lw : (int) 2195 line with of box frame. The default is 0. 2196 font : (str) 2197 font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "Calco". 2198 Type `vedo -r fonts` for a font demo. 2199 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2200 justify : (str) 2201 internal text justification. The default is "center-left". 2202 vspacing : (float) 2203 vertical spacing between lines. 2204 2205 Examples: 2206 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2207 2208  2209 """ 2210 if txt is None: 2211 if self.filename: 2212 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2213 elif self.name: 2214 txt = self.name 2215 else: 2216 return None 2217 2218 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2219 d = self.diagonal_size() 2220 if point is None: 2221 if d: 2222 point = self.closest_point([(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1]) 2223 else: # it's a Point 2224 point = self.transform.position 2225 2226 point = utils.make3d(point) 2227 2228 if offset is None: 2229 offset = [0, 0, (z1 - z0) / 2] 2230 offset = utils.make3d(offset) 2231 2232 fpost = vedo.addons.Flagpost( 2233 txt, point, point + offset, s, c, bc, alpha, lw, font, justify, vspacing 2234 ) 2235 self._caption = fpost 2236 return fpost 2237 2238 def caption( 2239 self, 2240 txt=None, 2241 point=None, 2242 size=(0.30, 0.15), 2243 padding=5, 2244 font="Calco", 2245 justify="center-right", 2246 vspacing=1.0, 2247 c=None, 2248 alpha=1.0, 2249 lw=1, 2250 ontop=True, 2251 ) -> Union["vtki.vtkCaptionActor2D", None]: 2252 """ 2253 Create a 2D caption to an object which follows the camera movements. 2254 Latex is not supported. Returns the same input object for concatenation. 2255 2256 See also `flagpole()`, `flagpost()`, `labels()` and `legend()` 2257 with similar functionality. 2258 2259 Arguments: 2260 txt : (str) 2261 text to be rendered. The default is the file name. 2262 point : (list) 2263 anchoring point. The default is None. 2264 size : (list) 2265 (width, height) of the caption box. The default is (0.30, 0.15). 2266 padding : (float) 2267 padding space of the caption box in pixels. The default is 5. 2268 font : (str) 2269 font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "VictorMono". 2270 Type `vedo -r fonts` for a font demo. 2271 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2272 justify : (str) 2273 internal text justification. The default is "center-right". 2274 vspacing : (float) 2275 vertical spacing between lines. The default is 1. 2276 c : (str) 2277 text and box color. The default is 'lb'. 2278 alpha : (float) 2279 text and box transparency. The default is 1. 2280 lw : (int) 2281 line width in pixels. The default is 1. 2282 ontop : (bool) 2283 keep the 2d caption always on top. The default is True. 2284 2285 Examples: 2286 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 2287 2288  2289 2290 - [flag_labels1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels1.py) 2291 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2292 """ 2293 if txt is None: 2294 if self.filename: 2295 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2296 elif self.name: 2297 txt = self.name 2298 2299 if not txt: # disable it 2300 self._caption = None 2301 return None 2302 2303 for r in vedo.shapes._reps: 2304 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 2305 2306 if c is None: 2307 c = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) / 2 2308 else: 2309 c = colors.get_color(c) 2310 2311 if point is None: 2312 x0, x1, y0, y1, _, z1 = self.dataset.GetBounds() 2313 pt = [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1] 2314 point = self.closest_point(pt) 2315 2316 capt = vtki.vtkCaptionActor2D() 2317 capt.SetAttachmentPoint(point) 2318 capt.SetBorder(True) 2319 capt.SetLeader(True) 2320 sph = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2321 sph.Update() 2322 capt.SetLeaderGlyphData(sph.GetOutput()) 2323 capt.SetMaximumLeaderGlyphSize(5) 2324 capt.SetPadding(int(padding)) 2325 capt.SetCaption(txt) 2326 capt.SetWidth(size[0]) 2327 capt.SetHeight(size[1]) 2328 capt.SetThreeDimensionalLeader(not ontop) 2329 2330 pra = capt.GetProperty() 2331 pra.SetColor(c) 2332 pra.SetOpacity(alpha) 2333 pra.SetLineWidth(lw) 2334 2335 pr = capt.GetCaptionTextProperty() 2336 pr.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 2337 fl = utils.get_font_path(font) 2338 pr.SetFontFile(fl) 2339 pr.ShadowOff() 2340 pr.BoldOff() 2341 pr.FrameOff() 2342 pr.SetColor(c) 2343 pr.SetOpacity(alpha) 2344 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 2345 if "top" in justify: 2346 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 2347 if "bottom" in justify: 2348 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 2349 if "cent" in justify: 2350 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToCentered() 2351 pr.SetJustificationToCentered() 2352 if "left" in justify: 2353 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 2354 if "right" in justify: 2355 pr.SetJustificationToRight() 2356 pr.SetLineSpacing(vspacing) 2357 return capt
Class to manage the visual aspects of a Points object.
887 def clone2d(self, size=None, offset=(), scale=None): 888 """ 889 Turn a 3D `Points` or `Mesh` into a flat 2D actor. 890 Returns a `Actor2D`. 891 892 Arguments: 893 size : (float) 894 size as scaling factor for the 2D actor 895 offset : (list) 896 2D (x, y) position of the actor in the range [-1, 1] 897 scale : (float) 898 Deprecated. Use `size` instead. 899 900 Examples: 901 - [clone2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/clone2d.py) 902 903  904 """ 905 # assembly.Assembly.clone2d() superseeds this method 906 if scale is not None: 907 vedo.logger.warning("clone2d(): use keyword size not scale") 908 size = scale 909 910 if size is None: 911 # work out a reasonable scale 912 msiz = self.diagonal_size() 913 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.window: 914 sz = vedo.plotter_instance.window.GetSize() 915 dsiz = utils.mag(sz) 916 size = dsiz / msiz / 10 917 else: 918 size = 350 / msiz 919 920 tp = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 921 transform = vtki.vtkTransform() 922 transform.Scale(size, size, size) 923 if len(offset) == 0: 924 offset = self.pos() 925 transform.Translate(-utils.make3d(offset)) 926 tp.SetTransform(transform) 927 tp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 928 tp.Update() 929 poly = tp.GetOutput() 930 931 cm = self.mapper.GetColorMode() 932 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 933 sv = self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility() 934 use_lut = self.mapper.GetUseLookupTableScalarRange() 935 vrange = self.mapper.GetScalarRange() 936 sm = self.mapper.GetScalarMode() 937 938 act2d = Actor2D(poly) 939 act2d.mapper.SetColorMode(cm) 940 act2d.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 941 act2d.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(sv) 942 act2d.mapper.SetUseLookupTableScalarRange(use_lut) 943 act2d.mapper.SetScalarRange(vrange) 944 act2d.mapper.SetScalarMode(sm) 945 946 act2d.GetPositionCoordinate().SetCoordinateSystem(4) 947 act2d.properties.SetColor(self.color()) 948 act2d.properties.SetOpacity(self.alpha()) 949 act2d.properties.SetLineWidth(self.properties.GetLineWidth()) 950 act2d.properties.SetPointSize(self.properties.GetPointSize()) 951 act2d.properties.SetDisplayLocation(0) # 0 = back, 1 = front 952 act2d.PickableOff() 953 return act2d
Turn a 3D Points or Mesh into a flat 2D actor.
Returns a Actor2D.
Arguments:
- size : (float) size as scaling factor for the 2D actor
- offset : (list) 2D (x, y) position of the actor in the range [-1, 1]
- scale : (float)
Deprecated. Use
sizeinstead.
Examples:
956 def copy_properties_from(self, source, deep=True, actor_related=True) -> Self: 957 """ 958 Copy properties from another ``Points`` object. 959 """ 960 pr = vtki.vtkProperty() 961 try: 962 sp = source.properties 963 mp = source.mapper 964 sa = source.actor 965 except AttributeError: 966 sp = source.GetProperty() 967 mp = source.GetMapper() 968 sa = source 969 970 if deep: 971 pr.DeepCopy(sp) 972 else: 973 pr.ShallowCopy(sp) 974 self.actor.SetProperty(pr) 975 self.properties = pr 976 977 if self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty(): 978 bfpr = vtki.vtkProperty() 979 bfpr.DeepCopy(sa.GetBackfaceProperty()) 980 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(bfpr) 981 self.properties_backface = bfpr 982 983 if not actor_related: 984 return self 985 986 # mapper related: 987 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(mp.GetScalarVisibility()) 988 self.mapper.SetScalarMode(mp.GetScalarMode()) 989 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(mp.GetScalarRange()) 990 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(mp.GetLookupTable()) 991 self.mapper.SetColorMode(mp.GetColorMode()) 992 self.mapper.SetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping( 993 mp.GetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping() 994 ) 995 self.mapper.SetUseLookupTableScalarRange( 996 mp.GetUseLookupTableScalarRange() 997 ) 998 999 self.actor.SetPickable(sa.GetPickable()) 1000 self.actor.SetDragable(sa.GetDragable()) 1001 self.actor.SetTexture(sa.GetTexture()) 1002 self.actor.SetVisibility(sa.GetVisibility()) 1003 return self
Copy properties from another Points object.
1005 def color(self, c=False, alpha=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 1006 """ 1007 Set/get mesh's color. 1008 If None is passed as input, will use colors from active scalars. 1009 Same as `mesh.c()`. 1010 """ 1011 if c is False: 1012 return np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1013 if c is None: 1014 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1015 return self 1016 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 1017 cc = colors.get_color(c) 1018 self.properties.SetColor(cc) 1019 if self.trail: 1020 self.trail.properties.SetColor(cc) 1021 if alpha is not None: 1022 self.alpha(alpha) 1023 return self
Set/get mesh's color.
If None is passed as input, will use colors from active scalars.
Same as mesh.c().
1025 def c(self, color=False, alpha=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 1026 """ 1027 Shortcut for `color()`. 1028 If None is passed as input, will use colors from current active scalars. 1029 """ 1030 return self.color(color, alpha)
Shortcut for color().
If None is passed as input, will use colors from current active scalars.
1032 def alpha(self, opacity=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 1033 """Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as `mesh.opacity()`.""" 1034 if opacity is None: 1035 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 1036 1037 self.properties.SetOpacity(opacity) 1038 bfp = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 1039 if bfp: 1040 if opacity < 1: 1041 self.properties_backface = bfp 1042 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(None) 1043 else: 1044 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(self.properties_backface) 1045 return self
Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as mesh.opacity().
1047 def lut_color_at(self, value) -> np.ndarray: 1048 """ 1049 Return the color and alpha in the lookup table at given value. 1050 """ 1051 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1052 if not lut: 1053 return None 1054 rgb = [0,0,0] 1055 lut.GetColor(value, rgb) 1056 alpha = lut.GetOpacity(value) 1057 return np.array(rgb + [alpha])
Return the color and alpha in the lookup table at given value.
1059 def opacity(self, alpha=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 1060 """Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as `mesh.alpha()`.""" 1061 return self.alpha(alpha)
Set/get mesh's transparency. Same as mesh.alpha().
1063 def force_opaque(self, value=True) -> Self: 1064 """ Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as opaque""" 1065 ## force the opaque pass, fixes picking in vtk9 1066 # but causes other bad troubles with lines.. 1067 self.actor.SetForceOpaque(value) 1068 return self
Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as opaque
1070 def force_translucent(self, value=True) -> Self: 1071 """ Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as translucent""" 1072 self.actor.SetForceTranslucent(value) 1073 return self
Force the Mesh, Line or point cloud to be treated as translucent
1075 def point_size(self, value=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 1076 """Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as `mesh.ps()`""" 1077 if value is None: 1078 return self.properties.GetPointSize() 1079 # self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 1080 else: 1081 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 1082 self.properties.SetPointSize(value) 1083 return self
Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as mesh.ps()
1085 def ps(self, pointsize=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 1086 """Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as `mesh.point_size()`""" 1087 return self.point_size(pointsize)
Set/get mesh's point size of vertices. Same as mesh.point_size()
1089 def render_points_as_spheres(self, value=True) -> Self: 1090 """Make points look spheric or else make them look as squares.""" 1091 self.properties.SetRenderPointsAsSpheres(value) 1092 return self
Make points look spheric or else make them look as squares.
1094 def lighting( 1095 self, 1096 style="", 1097 ambient=None, 1098 diffuse=None, 1099 specular=None, 1100 specular_power=None, 1101 specular_color=None, 1102 metallicity=None, 1103 roughness=None, 1104 ) -> Self: 1105 """ 1106 Set the ambient, diffuse, specular and specular_power lighting constants. 1107 1108 Arguments: 1109 style : (str) 1110 preset style, options are `[metallic, plastic, shiny, glossy, ambient, off]` 1111 ambient : (float) 1112 ambient fraction of emission [0-1] 1113 diffuse : (float) 1114 emission of diffused light in fraction [0-1] 1115 specular : (float) 1116 fraction of reflected light [0-1] 1117 specular_power : (float) 1118 precision of reflection [1-100] 1119 specular_color : (color) 1120 color that is being reflected by the surface 1121 1122 <img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Phong_components_version_4.png" alt="", width=700px> 1123 1124 Examples: 1125 - [specular.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/specular.py) 1126 """ 1127 pr = self.properties 1128 1129 if style: 1130 1131 if style != "off": 1132 pr.LightingOn() 1133 1134 if style == "off": 1135 pr.SetInterpolationToFlat() 1136 pr.LightingOff() 1137 return self ############## 1138 1139 if hasattr(pr, "GetColor"): # could be Volume 1140 c = pr.GetColor() 1141 else: 1142 c = (1, 1, 0.99) 1143 mpr = self.mapper 1144 if hasattr(mpr, 'GetScalarVisibility') and mpr.GetScalarVisibility(): 1145 c = (1,1,0.99) 1146 if style=='metallic': pars = [0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 10, c] 1147 elif style=='plastic' : pars = [0.3, 0.4, 0.3, 5, c] 1148 elif style=='shiny' : pars = [0.2, 0.6, 0.8, 50, c] 1149 elif style=='glossy' : pars = [0.1, 0.7, 0.9, 90, (1,1,0.99)] 1150 elif style=='ambient' : pars = [0.8, 0.1, 0.0, 1, (1,1,1)] 1151 elif style=='default' : pars = [0.1, 1.0, 0.05, 5, c] 1152 else: 1153 vedo.logger.error("in lighting(): Available styles are") 1154 vedo.logger.error("[default, metallic, plastic, shiny, glossy, ambient, off]") 1155 raise RuntimeError() 1156 pr.SetAmbient(pars[0]) 1157 pr.SetDiffuse(pars[1]) 1158 pr.SetSpecular(pars[2]) 1159 pr.SetSpecularPower(pars[3]) 1160 if hasattr(pr, "GetColor"): 1161 pr.SetSpecularColor(pars[4]) 1162 1163 if ambient is not None: pr.SetAmbient(ambient) 1164 if diffuse is not None: pr.SetDiffuse(diffuse) 1165 if specular is not None: pr.SetSpecular(specular) 1166 if specular_power is not None: pr.SetSpecularPower(specular_power) 1167 if specular_color is not None: pr.SetSpecularColor(colors.get_color(specular_color)) 1168 if metallicity is not None: 1169 pr.SetInterpolationToPBR() 1170 pr.SetMetallic(metallicity) 1171 if roughness is not None: 1172 pr.SetInterpolationToPBR() 1173 pr.SetRoughness(roughness) 1174 1175 return self
Set the ambient, diffuse, specular and specular_power lighting constants.
Arguments:
- style : (str)
preset style, options are
[metallic, plastic, shiny, glossy, ambient, off] - ambient : (float) ambient fraction of emission [0-1]
- diffuse : (float) emission of diffused light in fraction [0-1]
- specular : (float) fraction of reflected light [0-1]
- specular_power : (float) precision of reflection [1-100]
- specular_color : (color) color that is being reflected by the surface

Examples:
1177 def point_blurring(self, r=1, alpha=1.0, emissive=False) -> Self: 1178 """Set point blurring. 1179 Apply a gaussian convolution filter to the points. 1180 In this case the radius `r` is in absolute units of the mesh coordinates. 1181 With emissive set, the halo of point becomes light-emissive. 1182 """ 1183 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 1184 if emissive: 1185 self.mapper.SetEmissive(bool(emissive)) 1186 self.mapper.SetScaleFactor(r * 1.4142) 1187 1188 # https://kitware.github.io/vtk-examples/site/Python/Meshes/PointInterpolator/ 1189 if alpha < 1: 1190 self.mapper.SetSplatShaderCode( 1191 "//VTK::Color::Impl\n" 1192 "float dist = dot(offsetVCVSOutput.xy,offsetVCVSOutput.xy);\n" 1193 "if (dist > 1.0) {\n" 1194 " discard;\n" 1195 "} else {\n" 1196 f" float scale = ({alpha} - dist);\n" 1197 " ambientColor *= scale;\n" 1198 " diffuseColor *= scale;\n" 1199 "}\n" 1200 ) 1201 alpha = 1 1202 1203 self.mapper.Modified() 1204 self.actor.Modified() 1205 self.properties.SetOpacity(alpha) 1206 self.actor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 1207 return self
Set point blurring.
Apply a gaussian convolution filter to the points.
In this case the radius r is in absolute units of the mesh coordinates.
With emissive set, the halo of point becomes light-emissive.
1209 @property 1210 def cellcolors(self): 1211 """ 1212 Colorize each cell (face) of a mesh by passing 1213 a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. 1214 Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255]. 1215 1216 A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA. 1217 1218 A cell array named "CellsRGBA" is automatically created. 1219 1220 Examples: 1221 - [color_mesh_cells1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/color_mesh_cells1.py) 1222 - [color_mesh_cells2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/color_mesh_cells2.py) 1223 1224  1225 """ 1226 if "CellsRGBA" not in self.celldata.keys(): 1227 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1228 vscalars = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 1229 if vscalars is None or lut is None: 1230 arr = np.zeros([self.ncells, 4], dtype=np.uint8) 1231 col = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1232 col = np.round(col * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1233 alf = self.properties.GetOpacity() 1234 alf = np.round(alf * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1235 arr[:, (0, 1, 2)] = col 1236 arr[:, 3] = alf 1237 else: 1238 cols = lut.MapScalars(vscalars, 0, 0) 1239 arr = utils.vtk2numpy(cols) 1240 self.celldata["CellsRGBA"] = arr 1241 self.celldata.select("CellsRGBA") 1242 return self.celldata["CellsRGBA"]
Colorize each cell (face) of a mesh by passing a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255].
A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA.
A cell array named "CellsRGBA" is automatically created.
Examples:
1267 @property 1268 def pointcolors(self): 1269 """ 1270 Colorize each point (or vertex of a mesh) by passing 1271 a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. 1272 Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255]. 1273 1274 A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA. 1275 1276 A point array named "PointsRGBA" is automatically created. 1277 """ 1278 if "PointsRGBA" not in self.pointdata.keys(): 1279 lut = self.mapper.GetLookupTable() 1280 vscalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 1281 if vscalars is None or lut is None: 1282 # create a constant array 1283 arr = np.zeros([self.npoints, 4], dtype=np.uint8) 1284 col = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) 1285 col = np.round(col * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1286 alf = self.properties.GetOpacity() 1287 alf = np.round(alf * 255).astype(np.uint8) 1288 arr[:, (0, 1, 2)] = col 1289 arr[:, 3] = alf 1290 else: 1291 cols = lut.MapScalars(vscalars, 0, 0) 1292 arr = utils.vtk2numpy(cols) 1293 self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"] = arr 1294 self.pointdata.select("PointsRGBA") 1295 return self.pointdata["PointsRGBA"]
Colorize each point (or vertex of a mesh) by passing a 1-to-1 list of colors in format [R,G,B] or [R,G,B,A]. Colors levels and opacities must be in the range [0,255].
A single constant color can also be passed as string or RGBA.
A point array named "PointsRGBA" is automatically created.
1321 def cmap( 1322 self, 1323 input_cmap, 1324 input_array=None, 1325 on="", 1326 name="Scalars", 1327 vmin=None, 1328 vmax=None, 1329 n_colors=256, 1330 alpha=1.0, 1331 logscale=False, 1332 ) -> Self: 1333 """ 1334 Set individual point/cell colors by providing a list of scalar values and a color map. 1335 1336 Arguments: 1337 input_cmap : (str, list, vtkLookupTable, matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap) 1338 color map scheme to transform a real number into a color. 1339 input_array : (str, list, vtkArray) 1340 can be the string name of an existing array, a new array or a `vtkArray`. 1341 on : (str) 1342 either 'points' or 'cells' or blank (automatic). 1343 Apply the color map to data which is defined on either points or cells. 1344 name : (str) 1345 give a name to the provided array (if input_array is an array) 1346 vmin : (float) 1347 clip scalars to this minimum value 1348 vmax : (float) 1349 clip scalars to this maximum value 1350 n_colors : (int) 1351 number of distinct colors to be used in colormap table. 1352 alpha : (float, list) 1353 Mesh transparency. Can be a `list` of values one for each vertex. 1354 logscale : (bool) 1355 Use logscale 1356 1357 Examples: 1358 - [mesh_coloring.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_coloring.py) 1359 - [mesh_alphas.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_alphas.py) 1360 - [mesh_custom.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_custom.py) 1361 - (and many others) 1362 1363  1364 """ 1365 self._cmap_name = input_cmap 1366 1367 if on == "": 1368 try: 1369 on = self.mapper.GetScalarModeAsString().replace("Use", "") 1370 if on not in ["PointData", "CellData"]: # can be "Default" 1371 on = "points" 1372 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1373 except AttributeError: 1374 on = "points" 1375 elif on == "Default": 1376 on = "points" 1377 self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1378 1379 if input_array is None: 1380 if not self.pointdata.keys() and self.celldata.keys(): 1381 on = "cells" 1382 if not self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 1383 input_array = 0 # pick the first at hand 1384 1385 if "point" in on.lower(): 1386 data = self.dataset.GetPointData() 1387 n = self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints() 1388 elif "cell" in on.lower(): 1389 data = self.dataset.GetCellData() 1390 n = self.dataset.GetNumberOfCells() 1391 else: 1392 vedo.logger.error( 1393 f"Must specify in cmap(on=...) to either 'cells' or 'points', not {on}") 1394 raise RuntimeError() 1395 1396 if input_array is None: # if None try to fetch the active scalars 1397 arr = data.GetScalars() 1398 if not arr: 1399 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find any {on} active array ...skip coloring.") 1400 return self 1401 1402 if not arr.GetName(): # sometimes arrays dont have a name.. 1403 arr.SetName(name) 1404 1405 elif isinstance(input_array, str): # if a string is passed 1406 arr = data.GetArray(input_array) 1407 if not arr: 1408 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find {on} array {input_array} ...skip coloring.") 1409 return self 1410 1411 elif isinstance(input_array, int): # if an int is passed 1412 if input_array < data.GetNumberOfArrays(): 1413 arr = data.GetArray(input_array) 1414 else: 1415 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot find {on} array at {input_array} ...skip coloring.") 1416 return self 1417 1418 elif utils.is_sequence(input_array): # if a numpy array is passed 1419 npts = len(input_array) 1420 if npts != n: 1421 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), nr. of input {on} scalars {npts} != {n} ...skip coloring.") 1422 return self 1423 arr = utils.numpy2vtk(input_array, name=name, dtype=float) 1424 data.AddArray(arr) 1425 data.Modified() 1426 1427 elif isinstance(input_array, vtki.vtkArray): # if a vtkArray is passed 1428 arr = input_array 1429 data.AddArray(arr) 1430 data.Modified() 1431 1432 else: 1433 vedo.logger.error(f"in cmap(), cannot understand input type {type(input_array)}") 1434 raise RuntimeError() 1435 1436 # Now we have array "arr" 1437 array_name = arr.GetName() 1438 1439 if arr.GetNumberOfComponents() == 1: 1440 if vmin is None: 1441 vmin = arr.GetRange()[0] 1442 if vmax is None: 1443 vmax = arr.GetRange()[1] 1444 else: 1445 if vmin is None or vmax is None: 1446 vn = utils.mag(utils.vtk2numpy(arr)) 1447 if vmin is None: 1448 vmin = vn.min() 1449 if vmax is None: 1450 vmax = vn.max() 1451 1452 # interpolate alphas if they are not constant 1453 if not utils.is_sequence(alpha): 1454 alpha = [alpha] * n_colors 1455 else: 1456 v = np.linspace(0, 1, n_colors, endpoint=True) 1457 xp = np.linspace(0, 1, len(alpha), endpoint=True) 1458 alpha = np.interp(v, xp, alpha) 1459 1460 ########################### build the look-up table 1461 if isinstance(input_cmap, vtki.vtkLookupTable): # vtkLookupTable 1462 lut = input_cmap 1463 1464 elif utils.is_sequence(input_cmap): # manual sequence of colors 1465 lut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 1466 if logscale: 1467 lut.SetScaleToLog10() 1468 lut.SetRange(vmin, vmax) 1469 ncols = len(input_cmap) 1470 lut.SetNumberOfTableValues(ncols) 1471 1472 for i, c in enumerate(input_cmap): 1473 r, g, b = colors.get_color(c) 1474 lut.SetTableValue(i, r, g, b, alpha[i]) 1475 lut.Build() 1476 1477 else: 1478 # assume string cmap name OR matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap 1479 lut = vtki.vtkLookupTable() 1480 if logscale: 1481 lut.SetScaleToLog10() 1482 lut.SetVectorModeToMagnitude() 1483 lut.SetRange(vmin, vmax) 1484 lut.SetNumberOfTableValues(n_colors) 1485 mycols = colors.color_map(range(n_colors), input_cmap, 0, n_colors) 1486 for i, c in enumerate(mycols): 1487 r, g, b = c 1488 lut.SetTableValue(i, r, g, b, alpha[i]) 1489 lut.Build() 1490 1491 # TEST NEW WAY 1492 self.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 1493 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1494 self.mapper.SetColorModeToMapScalars() 1495 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(lut.GetRange()) 1496 if "point" in on.lower(): 1497 self.pointdata.select(array_name) 1498 else: 1499 self.celldata.select(array_name) 1500 return self 1501 1502 # # TEST this is the old way: 1503 # # arr.SetLookupTable(lut) # wrong! causes weird instabilities with LUT 1504 # # if data.GetScalars(): 1505 # # data.GetScalars().SetLookupTable(lut) 1506 # # data.GetScalars().Modified() 1507 1508 # data.SetActiveScalars(array_name) 1509 # # data.SetScalars(arr) # wrong! it deletes array in position 0, never use SetScalars 1510 # # data.SetActiveAttribute(array_name, 0) # boh! 1511 1512 # self.mapper.SetLookupTable(lut) 1513 # self.mapper.SetColorModeToMapScalars() # so we dont need to convert uint8 scalars 1514 1515 # self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1516 # self.mapper.SetScalarRange(lut.GetRange()) 1517 1518 # if on.startswith("point"): 1519 # self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUsePointData() 1520 # else: 1521 # self.mapper.SetScalarModeToUseCellData() 1522 # if hasattr(self.mapper, "SetArrayName"): 1523 # self.mapper.SetArrayName(array_name) 1524 # return self
Set individual point/cell colors by providing a list of scalar values and a color map.
Arguments:
- input_cmap : (str, list, vtkLookupTable, matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap) color map scheme to transform a real number into a color.
- input_array : (str, list, vtkArray)
can be the string name of an existing array, a new array or a
vtkArray. - on : (str) either 'points' or 'cells' or blank (automatic). Apply the color map to data which is defined on either points or cells.
- name : (str) give a name to the provided array (if input_array is an array)
- vmin : (float) clip scalars to this minimum value
- vmax : (float) clip scalars to this maximum value
- n_colors : (int) number of distinct colors to be used in colormap table.
- alpha : (float, list)
Mesh transparency. Can be a
listof values one for each vertex. - logscale : (bool) Use logscale
Examples:
- mesh_coloring.py
- mesh_alphas.py
- mesh_custom.py
(and many others)
1526 def add_trail(self, offset=(0, 0, 0), n=50, c=None, alpha=1.0, lw=2) -> Self: 1527 """ 1528 Add a trailing line to mesh. 1529 This new mesh is accessible through `mesh.trail`. 1530 1531 Arguments: 1532 offset : (float) 1533 set an offset vector from the object center. 1534 n : (int) 1535 number of segments 1536 lw : (float) 1537 line width of the trail 1538 1539 Examples: 1540 - [trail.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/trail.py) 1541 1542  1543 1544 - [airplane1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane1.py) 1545 - [airplane2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane2.py) 1546 """ 1547 if self.trail is None: 1548 pos = self.pos() 1549 self.trail_offset = np.asarray(offset) 1550 self.trail_points = [pos] * n 1551 1552 if c is None: 1553 col = self.properties.GetColor() 1554 else: 1555 col = colors.get_color(c) 1556 1557 tline = vedo.shapes.Line(pos, pos, res=n, c=col, alpha=alpha, lw=lw) 1558 self.trail = tline # holds the Line 1559 self.trail.initilized = False # so the first update will be a reset 1560 return self
Add a trailing line to mesh.
This new mesh is accessible through mesh.trail.
Arguments:
- offset : (float) set an offset vector from the object center.
- n : (int) number of segments
- lw : (float) line width of the trail
Examples:
1562 def update_trail(self) -> Self: 1563 """ 1564 Update the trailing line of a moving object. 1565 """ 1566 currentpos = self.pos() 1567 if not self.trail.initilized: 1568 self.trail_points = [currentpos] * self.trail.npoints 1569 self.trail.initilized = True 1570 return self 1571 self.trail_points.append(currentpos) # cycle 1572 self.trail_points.pop(0) 1573 1574 data = np.array(self.trail_points) + self.trail_offset 1575 tpoly = self.trail.dataset 1576 tpoly.GetPoints().SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(data, dtype=np.float32)) 1577 return self
Update the trailing line of a moving object.
1614 def add_shadow(self, plane, point, direction=None, c=(0.6, 0.6, 0.6), alpha=1, culling=0) -> Self: 1615 """ 1616 Generate a shadow out of an `Mesh` on one of the three Cartesian planes. 1617 The output is a new `Mesh` representing the shadow. 1618 This new mesh is accessible through `mesh.shadow`. 1619 By default the shadow mesh is placed on the bottom wall of the bounding box. 1620 1621 See also `pointcloud.project_on_plane()`. 1622 1623 Arguments: 1624 plane : (str, Plane) 1625 if plane is `str`, plane can be one of `['x', 'y', 'z']`, 1626 represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. 1627 Otherwise, plane should be an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane` 1628 point : (float, array) 1629 if plane is `str`, point should be a float represents the intercept. 1630 Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection 1631 direction : (list) 1632 direction of oblique projection 1633 culling : (int) 1634 choose between front [1] or backface [-1] culling or None. 1635 1636 Examples: 1637 - [shadow1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/shadow1.py) 1638 - [airplane1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane1.py) 1639 - [airplane2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/airplane2.py) 1640 1641  1642 """ 1643 shad = self._compute_shadow(plane, point, direction) 1644 shad.c(c).alpha(alpha) 1645 1646 try: 1647 # Points dont have these methods 1648 shad.flat() 1649 if culling in (1, True): 1650 shad.frontface_culling() 1651 elif culling == -1: 1652 shad.backface_culling() 1653 except AttributeError: 1654 pass 1655 1656 shad.properties.LightingOff() 1657 shad.actor.SetPickable(False) 1658 shad.actor.SetUseBounds(True) 1659 1660 if shad not in self.shadows: 1661 self.shadows.append(shad) 1662 shad.info = dict(plane=plane, point=point, direction=direction) 1663 # shad.metadata["plane"] = plane 1664 # shad.metadata["point"] = point 1665 # print("AAAA", direction, plane, point) 1666 # if direction is None: 1667 # direction = [0,0,0] 1668 # shad.metadata["direction"] = direction 1669 return self
Generate a shadow out of an Mesh on one of the three Cartesian planes.
The output is a new Mesh representing the shadow.
This new mesh is accessible through mesh.shadow.
By default the shadow mesh is placed on the bottom wall of the bounding box.
See also pointcloud.project_on_plane().
Arguments:
- plane : (str, Plane)
if plane is
str, plane can be one of['x', 'y', 'z'], represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. Otherwise, plane should be an instance ofvedo.shapes.Plane - point : (float, array)
if plane is
str, point should be a float represents the intercept. Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection - direction : (list) direction of oblique projection
- culling : (int) choose between front [1] or backface [-1] culling or None.
Examples:
1671 def update_shadows(self) -> Self: 1672 """Update the shadows of a moving object.""" 1673 for sha in self.shadows: 1674 plane = sha.info["plane"] 1675 point = sha.info["point"] 1676 direction = sha.info["direction"] 1677 # print("update_shadows direction", direction,plane,point ) 1678 # plane = sha.metadata["plane"] 1679 # point = sha.metadata["point"] 1680 # direction = sha.metadata["direction"] 1681 # if direction[0]==0 and direction[1]==0 and direction[2]==0: 1682 # direction = None 1683 # print("BBBB", sha.metadata["direction"], 1684 # sha.metadata["plane"], sha.metadata["point"]) 1685 new_sha = self._compute_shadow(plane, point, direction) 1686 sha._update(new_sha.dataset) 1687 if self.trail: 1688 self.trail.update_shadows() 1689 return self
Update the shadows of a moving object.
1691 def labels( 1692 self, 1693 content=None, 1694 on="points", 1695 scale=None, 1696 xrot=0.0, 1697 yrot=0.0, 1698 zrot=0.0, 1699 ratio=1, 1700 precision=None, 1701 italic=False, 1702 font="", 1703 justify="", 1704 c="black", 1705 alpha=1.0, 1706 ) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", None]: 1707 """ 1708 Generate value or ID labels for mesh cells or points. 1709 For large nr. of labels use `font="VTK"` which is much faster. 1710 1711 See also: 1712 `labels2d()`, `flagpole()`, `caption()` and `legend()`. 1713 1714 Arguments: 1715 content : (list,int,str) 1716 either 'id', 'cellid', array name or array number. 1717 A array can also be passed (must match the nr. of points or cells). 1718 on : (str) 1719 generate labels for "cells" instead of "points" 1720 scale : (float) 1721 absolute size of labels, if left as None it is automatic 1722 zrot : (float) 1723 local rotation angle of label in degrees 1724 ratio : (int) 1725 skipping ratio, to reduce nr of labels for large meshes 1726 precision : (int) 1727 numeric precision of labels 1728 1729 ```python 1730 from vedo import * 1731 s = Sphere(res=10).linewidth(1).c("orange").compute_normals() 1732 point_ids = s.labels('id', on="points").c('green') 1733 cell_ids = s.labels('id', on="cells" ).c('black') 1734 show(s, point_ids, cell_ids) 1735 ``` 1736  1737 1738 Examples: 1739 - [boundaries.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/boundaries.py) 1740 1741  1742 """ 1743 1744 cells = False 1745 if "cell" in on or "face" in on: 1746 cells = True 1747 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1748 1749 if isinstance(content, str): 1750 if content in ("pointid", "pointsid"): 1751 cells = False 1752 content = "id" 1753 justify = "bottom-left" if justify == "" else justify 1754 if content in ("cellid", "cellsid"): 1755 cells = True 1756 content = "id" 1757 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1758 1759 try: 1760 if cells: 1761 ns = np.sqrt(self.ncells) 1762 elems = self.cell_centers().points 1763 norms = self.cell_normals 1764 justify = "centered" if justify == "" else justify 1765 else: 1766 ns = np.sqrt(self.npoints) 1767 elems = self.vertices 1768 norms = self.vertex_normals 1769 except AttributeError: 1770 norms = [] 1771 1772 if not justify: 1773 justify = "bottom-left" 1774 1775 hasnorms = False 1776 if len(norms) > 0: 1777 hasnorms = True 1778 1779 if scale is None: 1780 if not ns: 1781 ns = 100 1782 scale = self.diagonal_size() / ns / 10 1783 1784 arr = None 1785 mode = 0 1786 if content is None: 1787 mode = 0 1788 if cells: 1789 if self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 1790 name = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars().GetName() 1791 arr = self.celldata[name] 1792 else: 1793 if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 1794 name = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars().GetName() 1795 arr = self.pointdata[name] 1796 elif isinstance(content, (str, int)): 1797 if content == "id": 1798 mode = 1 1799 elif cells: 1800 mode = 0 1801 arr = self.celldata[content] 1802 else: 1803 mode = 0 1804 arr = self.pointdata[content] 1805 elif utils.is_sequence(content): 1806 mode = 0 1807 arr = content 1808 1809 if arr is None and mode == 0: 1810 vedo.logger.error("in labels(), array not found in point or cell data") 1811 return None 1812 1813 ratio = int(ratio+0.5) 1814 tapp = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 1815 has_inputs = False 1816 1817 for i, e in enumerate(elems): 1818 if i % ratio: 1819 continue 1820 1821 if mode == 1: 1822 txt_lab = str(i) 1823 else: 1824 if precision: 1825 txt_lab = utils.precision(arr[i], precision) 1826 else: 1827 txt_lab = str(arr[i]) 1828 1829 if not txt_lab: 1830 continue 1831 1832 if font == "VTK": 1833 tx = vtki.new("VectorText") 1834 tx.SetText(txt_lab) 1835 tx.Update() 1836 tx_poly = tx.GetOutput() 1837 else: 1838 tx_poly = vedo.shapes.Text3D(txt_lab, font=font, justify=justify).dataset 1839 1840 if tx_poly.GetNumberOfPoints() == 0: 1841 continue ###################### 1842 1843 T = vtki.vtkTransform() 1844 T.PostMultiply() 1845 if italic: 1846 T.Concatenate([1, 0.2, 0, 0, 1847 0, 1 , 0, 0, 1848 0, 0 , 1, 0, 1849 0, 0 , 0, 1]) 1850 if hasnorms: 1851 ni = norms[i] 1852 if cells and font=="VTK": # center-justify 1853 bb = tx_poly.GetBounds() 1854 dx, dy = (bb[1] - bb[0]) / 2, (bb[3] - bb[2]) / 2 1855 T.Translate(-dx, -dy, 0) 1856 if xrot: T.RotateX(xrot) 1857 if yrot: T.RotateY(yrot) 1858 if zrot: T.RotateZ(zrot) 1859 crossvec = np.cross([0, 0, 1], ni) 1860 angle = np.arccos(np.dot([0, 0, 1], ni)) * 57.3 1861 T.RotateWXYZ(float(angle), crossvec.tolist()) 1862 T.Translate(ni / 100) 1863 else: 1864 if xrot: T.RotateX(xrot) 1865 if yrot: T.RotateY(yrot) 1866 if zrot: T.RotateZ(zrot) 1867 T.Scale(scale, scale, scale) 1868 T.Translate(e) 1869 tf = vtki.new("TransformPolyDataFilter") 1870 tf.SetInputData(tx_poly) 1871 tf.SetTransform(T) 1872 tf.Update() 1873 tapp.AddInputData(tf.GetOutput()) 1874 has_inputs = True 1875 1876 if has_inputs: 1877 tapp.Update() 1878 lpoly = tapp.GetOutput() 1879 else: 1880 lpoly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 1881 ids = vedo.Mesh(lpoly, c=c, alpha=alpha) 1882 ids.properties.LightingOff() 1883 ids.actor.PickableOff() 1884 ids.actor.SetUseBounds(False) 1885 ids.name = "Labels" 1886 return ids
Generate value or ID labels for mesh cells or points.
For large nr. of labels use font="VTK" which is much faster.
See also:
labels2d(),flagpole(),caption()andlegend().
Arguments:
- content : (list,int,str) either 'id', 'cellid', array name or array number. A array can also be passed (must match the nr. of points or cells).
- on : (str) generate labels for "cells" instead of "points"
- scale : (float) absolute size of labels, if left as None it is automatic
- zrot : (float) local rotation angle of label in degrees
- ratio : (int) skipping ratio, to reduce nr of labels for large meshes
- precision : (int) numeric precision of labels
from vedo import *
s = Sphere(res=10).linewidth(1).c("orange").compute_normals()
point_ids = s.labels('id', on="points").c('green')
cell_ids = s.labels('id', on="cells" ).c('black')
show(s, point_ids, cell_ids)

Examples:
1888 def labels2d( 1889 self, 1890 content="id", 1891 on="points", 1892 scale=1.0, 1893 precision=4, 1894 font="Calco", 1895 justify="bottom-left", 1896 angle=0.0, 1897 frame=False, 1898 c="black", 1899 bc=None, 1900 alpha=1.0, 1901 ) -> Union["Actor2D", None]: 1902 """ 1903 Generate value or ID bi-dimensional labels for mesh cells or points. 1904 1905 See also: `labels()`, `flagpole()`, `caption()` and `legend()`. 1906 1907 Arguments: 1908 content : (str) 1909 either 'id', 'cellid', or array name 1910 on : (str) 1911 generate labels for "cells" instead of "points" (the default) 1912 scale : (float) 1913 size scaling of labels 1914 precision : (int) 1915 precision of numeric labels 1916 angle : (float) 1917 local rotation angle of label in degrees 1918 frame : (bool) 1919 draw a frame around the label 1920 bc : (str) 1921 background color of the label 1922 1923 ```python 1924 from vedo import Sphere, show 1925 sph = Sphere(quads=True, res=4).compute_normals().wireframe() 1926 sph.celldata["zvals"] = sph.cell_centers().coordinates[:,2] 1927 l2d = sph.labels("zvals", on="cells", precision=2).backcolor('orange9') 1928 show(sph, l2d, axes=1).close() 1929 ``` 1930  1931 """ 1932 cells = False 1933 if "cell" in on: 1934 cells = True 1935 1936 if isinstance(content, str): 1937 if content in ("id", "pointid", "pointsid"): 1938 cells = False 1939 content = "id" 1940 if content in ("cellid", "cellsid"): 1941 cells = True 1942 content = "id" 1943 1944 if cells: 1945 if content != "id" and content not in self.celldata.keys(): 1946 vedo.logger.error(f"In labels2d: cell array {content} does not exist.") 1947 return None 1948 arr = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 1949 poly = self.cell_centers().dataset 1950 poly.GetPointData().SetScalars(arr) 1951 else: 1952 arr = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 1953 poly = self.dataset 1954 if content != "id" and content not in self.pointdata.keys(): 1955 vedo.logger.error(f"In labels2d: point array {content} does not exist.") 1956 return None 1957 1958 mp = vtki.new("LabeledDataMapper") 1959 1960 if content == "id": 1961 mp.SetLabelModeToLabelIds() 1962 else: 1963 mp.SetLabelModeToLabelScalars() 1964 if precision is not None: 1965 dtype = arr.GetDataType() 1966 if dtype in (vtki.VTK_FLOAT, vtki.VTK_DOUBLE): 1967 mp.SetLabelFormat(f"%-#.{precision}g") 1968 1969 pr = mp.GetLabelTextProperty() 1970 c = colors.get_color(c) 1971 pr.SetColor(c) 1972 pr.SetOpacity(alpha) 1973 pr.SetFrame(frame) 1974 pr.SetFrameColor(c) 1975 pr.SetItalic(False) 1976 pr.BoldOff() 1977 pr.ShadowOff() 1978 pr.UseTightBoundingBoxOn() 1979 pr.SetOrientation(angle) 1980 pr.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 1981 fl = utils.get_font_path(font) 1982 pr.SetFontFile(fl) 1983 pr.SetFontSize(int(20 * scale)) 1984 1985 if "cent" in justify or "mid" in justify: 1986 pr.SetJustificationToCentered() 1987 elif "rig" in justify: 1988 pr.SetJustificationToRight() 1989 elif "left" in justify: 1990 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 1991 # ------ 1992 if "top" in justify: 1993 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 1994 else: 1995 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 1996 1997 if bc is not None: 1998 bc = colors.get_color(bc) 1999 pr.SetBackgroundColor(bc) 2000 pr.SetBackgroundOpacity(alpha) 2001 2002 mp.SetInputData(poly) 2003 a2d = Actor2D() 2004 a2d.PickableOff() 2005 a2d.SetMapper(mp) 2006 return a2d
Generate value or ID bi-dimensional labels for mesh cells or points.
See also: labels(), flagpole(), caption() and legend().
Arguments:
- content : (str) either 'id', 'cellid', or array name
- on : (str) generate labels for "cells" instead of "points" (the default)
- scale : (float) size scaling of labels
- precision : (int) precision of numeric labels
- angle : (float) local rotation angle of label in degrees
- frame : (bool) draw a frame around the label
- bc : (str) background color of the label
from vedo import Sphere, show
sph = Sphere(quads=True, res=4).compute_normals().wireframe()
sph.celldata["zvals"] = sph.cell_centers().coordinates[:,2]
l2d = sph.labels("zvals", on="cells", precision=2).backcolor('orange9')
show(sph, l2d, axes=1).close()

2008 def legend(self, txt) -> Self: 2009 """Book a legend text.""" 2010 self.info["legend"] = txt 2011 # self.metadata["legend"] = txt 2012 return self
Book a legend text.
2014 def flagpole( 2015 self, 2016 txt=None, 2017 point=None, 2018 offset=None, 2019 s=None, 2020 font="Calco", 2021 rounded=True, 2022 c=None, 2023 alpha=1.0, 2024 lw=2, 2025 italic=0.0, 2026 padding=0.1, 2027 ) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", None]: 2028 """ 2029 Generate a flag pole style element to describe an object. 2030 Returns a `Mesh` object. 2031 2032 Use flagpole.follow_camera() to make it face the camera in the scene. 2033 2034 Consider using `settings.use_parallel_projection = True` 2035 to avoid perspective distortions. 2036 2037 See also `flagpost()`. 2038 2039 Arguments: 2040 txt : (str) 2041 Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name. 2042 point : (list) 2043 position of the flagpole pointer. 2044 offset : (list) 2045 text offset wrt the application point. 2046 s : (float) 2047 size of the flagpole. 2048 font : (str) 2049 font face. Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2050 rounded : (bool) 2051 draw a rounded or squared box around the text. 2052 c : (list) 2053 text and box color. 2054 alpha : (float) 2055 opacity of text and box. 2056 lw : (float) 2057 line with of box frame. 2058 italic : (float) 2059 italicness of text. 2060 2061 Examples: 2062 - [intersect2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/intersect2d.py) 2063 2064  2065 2066 - [goniometer.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/goniometer.py) 2067 - [flag_labels1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels1.py) 2068 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2069 """ 2070 objs = [] 2071 2072 if txt is None: 2073 if self.filename: 2074 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2075 elif self.name: 2076 txt = self.name 2077 else: 2078 return None 2079 2080 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2081 d = self.diagonal_size() 2082 if point is None: 2083 if d: 2084 point = self.closest_point([(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1]) 2085 # point = self.closest_point([x1, y0, z1]) 2086 else: # it's a Point 2087 point = self.transform.position 2088 2089 pt = utils.make3d(point) 2090 2091 if offset is None: 2092 offset = [(x1 - x0) / 1.75, (y1 - y0) / 5, 0] 2093 offset = utils.make3d(offset) 2094 2095 if s is None: 2096 s = d / 20 2097 2098 sph = None 2099 if d and (z1 - z0) / d > 0.1: 2100 sph = vedo.shapes.Sphere(pt, r=s * 0.4, res=6) 2101 2102 if c is None: 2103 c = np.array(self.color()) / 1.4 2104 2105 lab = vedo.shapes.Text3D( 2106 txt, pos=pt + offset, s=s, font=font, italic=italic, justify="center" 2107 ) 2108 objs.append(lab) 2109 2110 if d and not sph: 2111 sph = vedo.shapes.Circle(pt, r=s / 3, res=16) 2112 objs.append(sph) 2113 2114 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = lab.bounds() 2115 aline = [(x0,y0,z0), (x1,y0,z0), (x1,y1,z0), (x0,y1,z0)] 2116 if rounded: 2117 box = vedo.shapes.KSpline(aline, closed=True) 2118 else: 2119 box = vedo.shapes.Line(aline, closed=True) 2120 2121 cnt = [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, (z0 + z1) / 2] 2122 2123 # box.actor.SetOrigin(cnt) 2124 box.scale([1 + padding, 1 + 2 * padding, 1], origin=cnt) 2125 objs.append(box) 2126 2127 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = box.bounds() 2128 if x0 < pt[0] < x1: 2129 c0 = box.closest_point(pt) 2130 c1 = [c0[0], c0[1] + (pt[1] - y0) / 4, pt[2]] 2131 elif (pt[0] - x0) < (x1 - pt[0]): 2132 c0 = [x0, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2133 c1 = [x0 + (pt[0] - x0) / 4, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2134 else: 2135 c0 = [x1, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2136 c1 = [x1 + (pt[0] - x1) / 4, (y0 + y1) / 2, pt[2]] 2137 2138 con = vedo.shapes.Line([c0, c1, pt]) 2139 objs.append(con) 2140 2141 mobjs = vedo.merge(objs).c(c).alpha(alpha) 2142 mobjs.name = "FlagPole" 2143 mobjs.bc("tomato").pickable(False) 2144 mobjs.properties.LightingOff() 2145 mobjs.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2146 mobjs.actor.UseBoundsOff() 2147 mobjs.actor.SetPosition([0,0,0]) 2148 mobjs.actor.SetOrigin(pt) 2149 return mobjs 2150 2151 # mobjs = vedo.Assembly(objs)#.c(c).alpha(alpha) 2152 # mobjs.name = "FlagPole" 2153 # # mobjs.bc("tomato").pickable(False) 2154 # # mobjs.properties.LightingOff() 2155 # # mobjs.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2156 # # mobjs.actor.UseBoundsOff() 2157 # # mobjs.actor.SetPosition([0,0,0]) 2158 # # mobjs.actor.SetOrigin(pt) 2159 # # print(pt) 2160 # return mobjs
Generate a flag pole style element to describe an object.
Returns a Mesh object.
Use flagpole.follow_camera() to make it face the camera in the scene.
Consider using settings.use_parallel_projection = True
to avoid perspective distortions.
See also flagpost().
Arguments:
- txt : (str) Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name.
- point : (list) position of the flagpole pointer.
- offset : (list) text offset wrt the application point.
- s : (float) size of the flagpole.
- font : (str) font face. Check available fonts here.
- rounded : (bool) draw a rounded or squared box around the text.
- c : (list) text and box color.
- alpha : (float) opacity of text and box.
- lw : (float) line with of box frame.
- italic : (float) italicness of text.
Examples:
2162 def flagpost( 2163 self, 2164 txt=None, 2165 point=None, 2166 offset=None, 2167 s=1.0, 2168 c="k9", 2169 bc="k1", 2170 alpha=1, 2171 lw=0, 2172 font="Calco", 2173 justify="center-left", 2174 vspacing=1.0, 2175 ) -> Union["vedo.addons.Flagpost", None]: 2176 """ 2177 Generate a flag post style element to describe an object. 2178 2179 Arguments: 2180 txt : (str) 2181 Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name. 2182 point : (list) 2183 position of the flag anchor point. The default is None. 2184 offset : (list) 2185 a 3D displacement or offset. The default is None. 2186 s : (float) 2187 size of the text to be shown 2188 c : (list) 2189 color of text and line 2190 bc : (list) 2191 color of the flag background 2192 alpha : (float) 2193 opacity of text and box. 2194 lw : (int) 2195 line with of box frame. The default is 0. 2196 font : (str) 2197 font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "Calco". 2198 Type `vedo -r fonts` for a font demo. 2199 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2200 justify : (str) 2201 internal text justification. The default is "center-left". 2202 vspacing : (float) 2203 vertical spacing between lines. 2204 2205 Examples: 2206 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2207 2208  2209 """ 2210 if txt is None: 2211 if self.filename: 2212 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2213 elif self.name: 2214 txt = self.name 2215 else: 2216 return None 2217 2218 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2219 d = self.diagonal_size() 2220 if point is None: 2221 if d: 2222 point = self.closest_point([(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1]) 2223 else: # it's a Point 2224 point = self.transform.position 2225 2226 point = utils.make3d(point) 2227 2228 if offset is None: 2229 offset = [0, 0, (z1 - z0) / 2] 2230 offset = utils.make3d(offset) 2231 2232 fpost = vedo.addons.Flagpost( 2233 txt, point, point + offset, s, c, bc, alpha, lw, font, justify, vspacing 2234 ) 2235 self._caption = fpost 2236 return fpost
Generate a flag post style element to describe an object.
Arguments:
- txt : (str) Text to display. The default is the filename or the object name.
- point : (list) position of the flag anchor point. The default is None.
- offset : (list) a 3D displacement or offset. The default is None.
- s : (float) size of the text to be shown
- c : (list) color of text and line
- bc : (list) color of the flag background
- alpha : (float) opacity of text and box.
- lw : (int) line with of box frame. The default is 0.
- font : (str)
font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "Calco".
Type
vedo -r fontsfor a font demo. Check available fonts here. - justify : (str) internal text justification. The default is "center-left".
- vspacing : (float) vertical spacing between lines.
Examples:
2238 def caption( 2239 self, 2240 txt=None, 2241 point=None, 2242 size=(0.30, 0.15), 2243 padding=5, 2244 font="Calco", 2245 justify="center-right", 2246 vspacing=1.0, 2247 c=None, 2248 alpha=1.0, 2249 lw=1, 2250 ontop=True, 2251 ) -> Union["vtki.vtkCaptionActor2D", None]: 2252 """ 2253 Create a 2D caption to an object which follows the camera movements. 2254 Latex is not supported. Returns the same input object for concatenation. 2255 2256 See also `flagpole()`, `flagpost()`, `labels()` and `legend()` 2257 with similar functionality. 2258 2259 Arguments: 2260 txt : (str) 2261 text to be rendered. The default is the file name. 2262 point : (list) 2263 anchoring point. The default is None. 2264 size : (list) 2265 (width, height) of the caption box. The default is (0.30, 0.15). 2266 padding : (float) 2267 padding space of the caption box in pixels. The default is 5. 2268 font : (str) 2269 font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "VictorMono". 2270 Type `vedo -r fonts` for a font demo. 2271 Check [available fonts here](https://vedo.embl.es/fonts). 2272 justify : (str) 2273 internal text justification. The default is "center-right". 2274 vspacing : (float) 2275 vertical spacing between lines. The default is 1. 2276 c : (str) 2277 text and box color. The default is 'lb'. 2278 alpha : (float) 2279 text and box transparency. The default is 1. 2280 lw : (int) 2281 line width in pixels. The default is 1. 2282 ontop : (bool) 2283 keep the 2d caption always on top. The default is True. 2284 2285 Examples: 2286 - [caption.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/caption.py) 2287 2288  2289 2290 - [flag_labels1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels1.py) 2291 - [flag_labels2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/other/flag_labels2.py) 2292 """ 2293 if txt is None: 2294 if self.filename: 2295 txt = self.filename.split("/")[-1] 2296 elif self.name: 2297 txt = self.name 2298 2299 if not txt: # disable it 2300 self._caption = None 2301 return None 2302 2303 for r in vedo.shapes._reps: 2304 txt = txt.replace(r[0], r[1]) 2305 2306 if c is None: 2307 c = np.array(self.properties.GetColor()) / 2 2308 else: 2309 c = colors.get_color(c) 2310 2311 if point is None: 2312 x0, x1, y0, y1, _, z1 = self.dataset.GetBounds() 2313 pt = [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, z1] 2314 point = self.closest_point(pt) 2315 2316 capt = vtki.vtkCaptionActor2D() 2317 capt.SetAttachmentPoint(point) 2318 capt.SetBorder(True) 2319 capt.SetLeader(True) 2320 sph = vtki.new("SphereSource") 2321 sph.Update() 2322 capt.SetLeaderGlyphData(sph.GetOutput()) 2323 capt.SetMaximumLeaderGlyphSize(5) 2324 capt.SetPadding(int(padding)) 2325 capt.SetCaption(txt) 2326 capt.SetWidth(size[0]) 2327 capt.SetHeight(size[1]) 2328 capt.SetThreeDimensionalLeader(not ontop) 2329 2330 pra = capt.GetProperty() 2331 pra.SetColor(c) 2332 pra.SetOpacity(alpha) 2333 pra.SetLineWidth(lw) 2334 2335 pr = capt.GetCaptionTextProperty() 2336 pr.SetFontFamily(vtki.VTK_FONT_FILE) 2337 fl = utils.get_font_path(font) 2338 pr.SetFontFile(fl) 2339 pr.ShadowOff() 2340 pr.BoldOff() 2341 pr.FrameOff() 2342 pr.SetColor(c) 2343 pr.SetOpacity(alpha) 2344 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 2345 if "top" in justify: 2346 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToTop() 2347 if "bottom" in justify: 2348 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToBottom() 2349 if "cent" in justify: 2350 pr.SetVerticalJustificationToCentered() 2351 pr.SetJustificationToCentered() 2352 if "left" in justify: 2353 pr.SetJustificationToLeft() 2354 if "right" in justify: 2355 pr.SetJustificationToRight() 2356 pr.SetLineSpacing(vspacing) 2357 return capt
Create a 2D caption to an object which follows the camera movements. Latex is not supported. Returns the same input object for concatenation.
See also flagpole(), flagpost(), labels() and legend()
with similar functionality.
Arguments:
- txt : (str) text to be rendered. The default is the file name.
- point : (list) anchoring point. The default is None.
- size : (list) (width, height) of the caption box. The default is (0.30, 0.15).
- padding : (float) padding space of the caption box in pixels. The default is 5.
- font : (str)
font name. Use a monospace font for better rendering. The default is "VictorMono".
Type
vedo -r fontsfor a font demo. Check available fonts here. - justify : (str) internal text justification. The default is "center-right".
- vspacing : (float) vertical spacing between lines. The default is 1.
- c : (str) text and box color. The default is 'lb'.
- alpha : (float) text and box transparency. The default is 1.
- lw : (int) line width in pixels. The default is 1.
- ontop : (bool) keep the 2d caption always on top. The default is True.
Examples:
2700class VolumeVisual(CommonVisual): 2701 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a ``Volume`` object.""" 2702 2703 # def __init__(self) -> None: 2704 # # print("INIT VolumeVisual") 2705 # super().__init__() 2706 2707 def alpha_unit(self, u=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2708 """ 2709 Defines light attenuation per unit length. Default is 1. 2710 The larger the unit length, the further light has to travel to attenuate the same amount. 2711 2712 E.g., if you set the unit distance to 0, you will get full opacity. 2713 It means that when light travels 0 distance it's already attenuated a finite amount. 2714 Thus, any finite distance should attenuate all light. 2715 The larger you make the unit distance, the more transparent the rendering becomes. 2716 """ 2717 if u is None: 2718 return self.properties.GetScalarOpacityUnitDistance() 2719 self.properties.SetScalarOpacityUnitDistance(u) 2720 return self 2721 2722 def alpha_gradient(self, alpha_grad, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 2723 """ 2724 Assign a set of tranparencies to a volume's gradient 2725 along the range of the scalar value. 2726 A single constant value can also be assigned. 2727 The gradient function is used to decrease the opacity 2728 in the "flat" regions of the volume while maintaining the opacity 2729 at the boundaries between material types. The gradient is measured 2730 as the amount by which the intensity changes over unit distance. 2731 2732 The format for alpha_grad is the same as for method `volume.alpha()`. 2733 """ 2734 if vmin is None: 2735 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 2736 if vmax is None: 2737 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 2738 2739 if alpha_grad is None: 2740 self.properties.DisableGradientOpacityOn() 2741 return self 2742 2743 self.properties.DisableGradientOpacityOff() 2744 2745 gotf = self.properties.GetGradientOpacity() 2746 if utils.is_sequence(alpha_grad): 2747 alpha_grad = np.array(alpha_grad) 2748 if len(alpha_grad.shape) == 1: # user passing a flat list e.g. (0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1) 2749 for i, al in enumerate(alpha_grad): 2750 xalpha = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(alpha_grad) - 1) 2751 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to gradient opacity 2752 gotf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 2753 elif len(alpha_grad.shape) == 2: # user passing [(x0,alpha0), ...] 2754 gotf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha_grad[0][1]) 2755 for xalpha, al in alpha_grad: 2756 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 2757 gotf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 2758 gotf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha_grad[-1][1]) 2759 # print("alpha_grad at", round(xalpha, 1), "\tset to", al) 2760 else: 2761 gotf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha_grad) # constant alpha_grad 2762 gotf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha_grad) 2763 return self 2764 2765 def cmap(self, c, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 2766 """Same as `color()`. 2767 2768 Arguments: 2769 alpha : (list) 2770 use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range 2771 vmin : (float) 2772 force the min of the scalar range to be this value 2773 vmax : (float) 2774 force the max of the scalar range to be this value 2775 """ 2776 return self.color(c, alpha, vmin, vmax) 2777 2778 def jittering(self, status=None) -> Union[Self, bool]: 2779 """ 2780 If `True`, each ray traversal direction will be perturbed slightly 2781 using a noise-texture to get rid of wood-grain effects. 2782 """ 2783 if hasattr(self.mapper, "SetUseJittering"): # tetmesh doesnt have it 2784 if status is None: 2785 return self.mapper.GetUseJittering() 2786 self.mapper.SetUseJittering(status) 2787 return self 2788 2789 def hide_voxels(self, ids) -> Self: 2790 """ 2791 Hide voxels (cells) from visualization. 2792 2793 Example: 2794 ```python 2795 from vedo import * 2796 embryo = Volume(dataurl+'embryo.tif') 2797 embryo.hide_voxels(list(range(400000))) 2798 show(embryo, axes=1).close() 2799 ``` 2800 2801 See also: 2802 `volume.mask()` 2803 """ 2804 ghost_mask = np.zeros(self.ncells, dtype=np.uint8) 2805 ghost_mask[ids] = vtki.vtkDataSetAttributes.HIDDENCELL 2806 name = vtki.vtkDataSetAttributes.GhostArrayName() 2807 garr = utils.numpy2vtk(ghost_mask, name=name, dtype=np.uint8) 2808 self.dataset.GetCellData().AddArray(garr) 2809 self.dataset.GetCellData().Modified() 2810 return self 2811 2812 def mask(self, data) -> Self: 2813 """ 2814 Mask a volume visualization with a binary value. 2815 Needs to specify `volume.mapper = "gpu"`. 2816 2817 Example: 2818 ```python 2819 from vedo import np, Volume, show 2820 data_matrix = np.zeros([75, 75, 75], dtype=np.uint8) 2821 # all voxels have value zero except: 2822 data_matrix[ 0:35, 0:35, 0:35] = 1 2823 data_matrix[35:55, 35:55, 35:55] = 2 2824 data_matrix[55:74, 55:74, 55:74] = 3 2825 vol = Volume(data_matrix).cmap('Blues') 2826 vol.mapper = "gpu" 2827 data_mask = np.zeros_like(data_matrix) 2828 data_mask[10:65, 10:60, 20:70] = 1 2829 vol.mask(data_mask) 2830 show(vol, axes=1).close() 2831 ``` 2832 See also: 2833 `volume.hide_voxels()` 2834 """ 2835 rdata = data.astype(np.uint8).ravel(order="F") 2836 varr = utils.numpy2vtk(rdata, name="input_mask") 2837 2838 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 2839 img.SetDimensions(self.dimensions()) 2840 img.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 2841 img.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(varr.GetName()) 2842 2843 try: 2844 self.mapper.SetMaskTypeToBinary() 2845 self.mapper.SetMaskInput(img) 2846 except AttributeError: 2847 vedo.logger.error("volume.mask() must specify volume.mapper = 'gpu'") 2848 return self 2849 2850 2851 def mode(self, mode=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2852 """ 2853 Define the volumetric rendering mode following this: 2854 - 0, composite rendering 2855 - 1, maximum projection rendering 2856 - 2, minimum projection rendering 2857 - 3, average projection rendering 2858 - 4, additive mode 2859 2860 The default mode is "composite" where the scalar values are sampled through 2861 the volume and composited in a front-to-back scheme through alpha blending. 2862 The final color and opacity is determined using the color and opacity transfer 2863 functions specified in alpha keyword. 2864 2865 Maximum and minimum intensity blend modes use the maximum and minimum 2866 scalar values, respectively, along the sampling ray. 2867 The final color and opacity is determined by passing the resultant value 2868 through the color and opacity transfer functions. 2869 2870 Additive blend mode accumulates scalar values by passing each value 2871 through the opacity transfer function and then adding up the product 2872 of the value and its opacity. In other words, the scalar values are scaled 2873 using the opacity transfer function and summed to derive the final color. 2874 Note that the resulting image is always grayscale i.e. aggregated values 2875 are not passed through the color transfer function. 2876 This is because the final value is a derived value and not a real data value 2877 along the sampling ray. 2878 2879 Average intensity blend mode works similar to the additive blend mode where 2880 the scalar values are multiplied by opacity calculated from the opacity 2881 transfer function and then added. 2882 The additional step here is to divide the sum by the number of samples 2883 taken through the volume. 2884 As is the case with the additive intensity projection, the final image will 2885 always be grayscale i.e. the aggregated values are not passed through the 2886 color transfer function. 2887 """ 2888 if mode is None: 2889 return self.mapper.GetBlendMode() 2890 2891 if isinstance(mode, str): 2892 if "comp" in mode: 2893 mode = 0 2894 elif "proj" in mode: 2895 if "max" in mode: 2896 mode = 1 2897 elif "min" in mode: 2898 mode = 2 2899 elif "ave" in mode: 2900 mode = 3 2901 else: 2902 vedo.logger.warning(f"unknown mode {mode}") 2903 mode = 0 2904 elif "add" in mode: 2905 mode = 4 2906 else: 2907 vedo.logger.warning(f"unknown mode {mode}") 2908 mode = 0 2909 2910 self.mapper.SetBlendMode(mode) 2911 return self 2912 2913 def shade(self, status=None) -> Union[Self, bool]: 2914 """ 2915 Set/Get the shading of a Volume. 2916 Shading can be further controlled with `volume.lighting()` method. 2917 2918 If shading is turned on, the mapper may perform shading calculations. 2919 In some cases shading does not apply 2920 (for example, in maximum intensity projection mode). 2921 """ 2922 if status is None: 2923 return self.properties.GetShade() 2924 self.properties.SetShade(status) 2925 return self 2926 2927 def interpolation(self, itype) -> Self: 2928 """ 2929 Set interpolation type. 2930 2931 0=nearest neighbour, 1=linear 2932 """ 2933 self.properties.SetInterpolationType(itype) 2934 return self
Class to manage the visual aspects of a Volume object.
2707 def alpha_unit(self, u=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2708 """ 2709 Defines light attenuation per unit length. Default is 1. 2710 The larger the unit length, the further light has to travel to attenuate the same amount. 2711 2712 E.g., if you set the unit distance to 0, you will get full opacity. 2713 It means that when light travels 0 distance it's already attenuated a finite amount. 2714 Thus, any finite distance should attenuate all light. 2715 The larger you make the unit distance, the more transparent the rendering becomes. 2716 """ 2717 if u is None: 2718 return self.properties.GetScalarOpacityUnitDistance() 2719 self.properties.SetScalarOpacityUnitDistance(u) 2720 return self
Defines light attenuation per unit length. Default is 1. The larger the unit length, the further light has to travel to attenuate the same amount.
E.g., if you set the unit distance to 0, you will get full opacity. It means that when light travels 0 distance it's already attenuated a finite amount. Thus, any finite distance should attenuate all light. The larger you make the unit distance, the more transparent the rendering becomes.
2722 def alpha_gradient(self, alpha_grad, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 2723 """ 2724 Assign a set of tranparencies to a volume's gradient 2725 along the range of the scalar value. 2726 A single constant value can also be assigned. 2727 The gradient function is used to decrease the opacity 2728 in the "flat" regions of the volume while maintaining the opacity 2729 at the boundaries between material types. The gradient is measured 2730 as the amount by which the intensity changes over unit distance. 2731 2732 The format for alpha_grad is the same as for method `volume.alpha()`. 2733 """ 2734 if vmin is None: 2735 vmin, _ = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 2736 if vmax is None: 2737 _, vmax = self.dataset.GetScalarRange() 2738 2739 if alpha_grad is None: 2740 self.properties.DisableGradientOpacityOn() 2741 return self 2742 2743 self.properties.DisableGradientOpacityOff() 2744 2745 gotf = self.properties.GetGradientOpacity() 2746 if utils.is_sequence(alpha_grad): 2747 alpha_grad = np.array(alpha_grad) 2748 if len(alpha_grad.shape) == 1: # user passing a flat list e.g. (0.0, 0.3, 0.9, 1) 2749 for i, al in enumerate(alpha_grad): 2750 xalpha = vmin + (vmax - vmin) * i / (len(alpha_grad) - 1) 2751 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to gradient opacity 2752 gotf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 2753 elif len(alpha_grad.shape) == 2: # user passing [(x0,alpha0), ...] 2754 gotf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha_grad[0][1]) 2755 for xalpha, al in alpha_grad: 2756 # Create transfer mapping scalar value to opacity 2757 gotf.AddPoint(xalpha, al) 2758 gotf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha_grad[-1][1]) 2759 # print("alpha_grad at", round(xalpha, 1), "\tset to", al) 2760 else: 2761 gotf.AddPoint(vmin, alpha_grad) # constant alpha_grad 2762 gotf.AddPoint(vmax, alpha_grad) 2763 return self
Assign a set of tranparencies to a volume's gradient along the range of the scalar value. A single constant value can also be assigned. The gradient function is used to decrease the opacity in the "flat" regions of the volume while maintaining the opacity at the boundaries between material types. The gradient is measured as the amount by which the intensity changes over unit distance.
The format for alpha_grad is the same as for method volume.alpha().
2765 def cmap(self, c, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None) -> Self: 2766 """Same as `color()`. 2767 2768 Arguments: 2769 alpha : (list) 2770 use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range 2771 vmin : (float) 2772 force the min of the scalar range to be this value 2773 vmax : (float) 2774 force the max of the scalar range to be this value 2775 """ 2776 return self.color(c, alpha, vmin, vmax)
Same as color().
Arguments:
- alpha : (list) use a list to specify transparencies along the scalar range
- vmin : (float) force the min of the scalar range to be this value
- vmax : (float) force the max of the scalar range to be this value
2778 def jittering(self, status=None) -> Union[Self, bool]: 2779 """ 2780 If `True`, each ray traversal direction will be perturbed slightly 2781 using a noise-texture to get rid of wood-grain effects. 2782 """ 2783 if hasattr(self.mapper, "SetUseJittering"): # tetmesh doesnt have it 2784 if status is None: 2785 return self.mapper.GetUseJittering() 2786 self.mapper.SetUseJittering(status) 2787 return self
If True, each ray traversal direction will be perturbed slightly
using a noise-texture to get rid of wood-grain effects.
2789 def hide_voxels(self, ids) -> Self: 2790 """ 2791 Hide voxels (cells) from visualization. 2792 2793 Example: 2794 ```python 2795 from vedo import * 2796 embryo = Volume(dataurl+'embryo.tif') 2797 embryo.hide_voxels(list(range(400000))) 2798 show(embryo, axes=1).close() 2799 ``` 2800 2801 See also: 2802 `volume.mask()` 2803 """ 2804 ghost_mask = np.zeros(self.ncells, dtype=np.uint8) 2805 ghost_mask[ids] = vtki.vtkDataSetAttributes.HIDDENCELL 2806 name = vtki.vtkDataSetAttributes.GhostArrayName() 2807 garr = utils.numpy2vtk(ghost_mask, name=name, dtype=np.uint8) 2808 self.dataset.GetCellData().AddArray(garr) 2809 self.dataset.GetCellData().Modified() 2810 return self
Hide voxels (cells) from visualization.
Example:
from vedo import * embryo = Volume(dataurl+'embryo.tif') embryo.hide_voxels(list(range(400000))) show(embryo, axes=1).close()
See also:
volume.mask()
2812 def mask(self, data) -> Self: 2813 """ 2814 Mask a volume visualization with a binary value. 2815 Needs to specify `volume.mapper = "gpu"`. 2816 2817 Example: 2818 ```python 2819 from vedo import np, Volume, show 2820 data_matrix = np.zeros([75, 75, 75], dtype=np.uint8) 2821 # all voxels have value zero except: 2822 data_matrix[ 0:35, 0:35, 0:35] = 1 2823 data_matrix[35:55, 35:55, 35:55] = 2 2824 data_matrix[55:74, 55:74, 55:74] = 3 2825 vol = Volume(data_matrix).cmap('Blues') 2826 vol.mapper = "gpu" 2827 data_mask = np.zeros_like(data_matrix) 2828 data_mask[10:65, 10:60, 20:70] = 1 2829 vol.mask(data_mask) 2830 show(vol, axes=1).close() 2831 ``` 2832 See also: 2833 `volume.hide_voxels()` 2834 """ 2835 rdata = data.astype(np.uint8).ravel(order="F") 2836 varr = utils.numpy2vtk(rdata, name="input_mask") 2837 2838 img = vtki.vtkImageData() 2839 img.SetDimensions(self.dimensions()) 2840 img.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 2841 img.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(varr.GetName()) 2842 2843 try: 2844 self.mapper.SetMaskTypeToBinary() 2845 self.mapper.SetMaskInput(img) 2846 except AttributeError: 2847 vedo.logger.error("volume.mask() must specify volume.mapper = 'gpu'") 2848 return self
Mask a volume visualization with a binary value.
Needs to specify volume.mapper = "gpu".
Example:
from vedo import np, Volume, show
data_matrix = np.zeros([75, 75, 75], dtype=np.uint8)
# all voxels have value zero except:
data_matrix[ 0:35, 0:35, 0:35] = 1
data_matrix[35:55, 35:55, 35:55] = 2
data_matrix[55:74, 55:74, 55:74] = 3
vol = Volume(data_matrix).cmap('Blues')
vol.mapper = "gpu"
data_mask = np.zeros_like(data_matrix)
data_mask[10:65, 10:60, 20:70] = 1
vol.mask(data_mask)
show(vol, axes=1).close()
See also:
volume.hide_voxels()
2851 def mode(self, mode=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2852 """ 2853 Define the volumetric rendering mode following this: 2854 - 0, composite rendering 2855 - 1, maximum projection rendering 2856 - 2, minimum projection rendering 2857 - 3, average projection rendering 2858 - 4, additive mode 2859 2860 The default mode is "composite" where the scalar values are sampled through 2861 the volume and composited in a front-to-back scheme through alpha blending. 2862 The final color and opacity is determined using the color and opacity transfer 2863 functions specified in alpha keyword. 2864 2865 Maximum and minimum intensity blend modes use the maximum and minimum 2866 scalar values, respectively, along the sampling ray. 2867 The final color and opacity is determined by passing the resultant value 2868 through the color and opacity transfer functions. 2869 2870 Additive blend mode accumulates scalar values by passing each value 2871 through the opacity transfer function and then adding up the product 2872 of the value and its opacity. In other words, the scalar values are scaled 2873 using the opacity transfer function and summed to derive the final color. 2874 Note that the resulting image is always grayscale i.e. aggregated values 2875 are not passed through the color transfer function. 2876 This is because the final value is a derived value and not a real data value 2877 along the sampling ray. 2878 2879 Average intensity blend mode works similar to the additive blend mode where 2880 the scalar values are multiplied by opacity calculated from the opacity 2881 transfer function and then added. 2882 The additional step here is to divide the sum by the number of samples 2883 taken through the volume. 2884 As is the case with the additive intensity projection, the final image will 2885 always be grayscale i.e. the aggregated values are not passed through the 2886 color transfer function. 2887 """ 2888 if mode is None: 2889 return self.mapper.GetBlendMode() 2890 2891 if isinstance(mode, str): 2892 if "comp" in mode: 2893 mode = 0 2894 elif "proj" in mode: 2895 if "max" in mode: 2896 mode = 1 2897 elif "min" in mode: 2898 mode = 2 2899 elif "ave" in mode: 2900 mode = 3 2901 else: 2902 vedo.logger.warning(f"unknown mode {mode}") 2903 mode = 0 2904 elif "add" in mode: 2905 mode = 4 2906 else: 2907 vedo.logger.warning(f"unknown mode {mode}") 2908 mode = 0 2909 2910 self.mapper.SetBlendMode(mode) 2911 return self
Define the volumetric rendering mode following this:
- 0, composite rendering
- 1, maximum projection rendering
- 2, minimum projection rendering
- 3, average projection rendering
- 4, additive mode
The default mode is "composite" where the scalar values are sampled through the volume and composited in a front-to-back scheme through alpha blending. The final color and opacity is determined using the color and opacity transfer functions specified in alpha keyword.
Maximum and minimum intensity blend modes use the maximum and minimum scalar values, respectively, along the sampling ray. The final color and opacity is determined by passing the resultant value through the color and opacity transfer functions.
Additive blend mode accumulates scalar values by passing each value through the opacity transfer function and then adding up the product of the value and its opacity. In other words, the scalar values are scaled using the opacity transfer function and summed to derive the final color. Note that the resulting image is always grayscale i.e. aggregated values are not passed through the color transfer function. This is because the final value is a derived value and not a real data value along the sampling ray.
Average intensity blend mode works similar to the additive blend mode where the scalar values are multiplied by opacity calculated from the opacity transfer function and then added. The additional step here is to divide the sum by the number of samples taken through the volume. As is the case with the additive intensity projection, the final image will always be grayscale i.e. the aggregated values are not passed through the color transfer function.
2913 def shade(self, status=None) -> Union[Self, bool]: 2914 """ 2915 Set/Get the shading of a Volume. 2916 Shading can be further controlled with `volume.lighting()` method. 2917 2918 If shading is turned on, the mapper may perform shading calculations. 2919 In some cases shading does not apply 2920 (for example, in maximum intensity projection mode). 2921 """ 2922 if status is None: 2923 return self.properties.GetShade() 2924 self.properties.SetShade(status) 2925 return self
Set/Get the shading of a Volume.
Shading can be further controlled with volume.lighting() method.
If shading is turned on, the mapper may perform shading calculations. In some cases shading does not apply (for example, in maximum intensity projection mode).
2361class MeshVisual(PointsVisual): 2362 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a `Mesh` object.""" 2363 2364 def __init__(self) -> None: 2365 # print("INIT MeshVisual", super()) 2366 super().__init__() 2367 2368 def follow_camera(self, camera=None, origin=None) -> Self: 2369 """ 2370 Return an object that will follow camera movements and stay locked to it. 2371 Use `mesh.follow_camera(False)` to disable it. 2372 2373 A `vtkCamera` object can also be passed. 2374 """ 2375 if camera is False: 2376 try: 2377 self.SetCamera(None) 2378 return self 2379 except AttributeError: 2380 return self 2381 2382 factor = vtki.vtkFollower() 2383 factor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 2384 factor.SetProperty(self.properties) 2385 factor.SetBackfaceProperty(self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty()) 2386 factor.SetTexture(self.actor.GetTexture()) 2387 factor.SetScale(self.actor.GetScale()) 2388 # factor.SetOrientation(self.actor.GetOrientation()) 2389 factor.SetPosition(self.actor.GetPosition()) 2390 factor.SetUseBounds(self.actor.GetUseBounds()) 2391 2392 if origin is None: 2393 factor.SetOrigin(self.actor.GetOrigin()) 2394 else: 2395 factor.SetOrigin(origin) 2396 2397 factor.PickableOff() 2398 2399 if isinstance(camera, vtki.vtkCamera): 2400 factor.SetCamera(camera) 2401 else: 2402 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 2403 if plt and plt.renderer and plt.renderer.GetActiveCamera(): 2404 factor.SetCamera(plt.renderer.GetActiveCamera()) 2405 2406 self.actor = None 2407 factor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 2408 self.actor = factor 2409 return self 2410 2411 def wireframe(self, value=True) -> Self: 2412 """Set mesh's representation as wireframe or solid surface.""" 2413 if value: 2414 self.properties.SetRepresentationToWireframe() 2415 else: 2416 self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 2417 return self 2418 2419 def flat(self) -> Self: 2420 """Set surface interpolation to flat. 2421 2422 <img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Phong_components_version_4.png" width="700"> 2423 """ 2424 self.properties.SetInterpolationToFlat() 2425 return self 2426 2427 def phong(self) -> Self: 2428 """Set surface interpolation to "phong".""" 2429 self.properties.SetInterpolationToPhong() 2430 return self 2431 2432 def backface_culling(self, value=True) -> Self: 2433 """Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.""" 2434 self.properties.SetBackfaceCulling(value) 2435 return self 2436 2437 def render_lines_as_tubes(self, value=True) -> Self: 2438 """Wrap a fake tube around a simple line for visualization""" 2439 self.properties.SetRenderLinesAsTubes(value) 2440 return self 2441 2442 def frontface_culling(self, value=True) -> Self: 2443 """Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.""" 2444 self.properties.SetFrontfaceCulling(value) 2445 return self 2446 2447 def backcolor(self, bc=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2448 """ 2449 Set/get mesh's backface color. 2450 """ 2451 back_prop = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 2452 2453 if bc is None: 2454 if back_prop: 2455 return back_prop.GetDiffuseColor() 2456 return self 2457 2458 if self.properties.GetOpacity() < 1: 2459 return self 2460 2461 if not back_prop: 2462 back_prop = vtki.vtkProperty() 2463 2464 back_prop.SetDiffuseColor(colors.get_color(bc)) 2465 back_prop.SetOpacity(self.properties.GetOpacity()) 2466 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(back_prop) 2467 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2468 return self 2469 2470 def bc(self, backcolor=False) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2471 """Shortcut for `mesh.backcolor()`.""" 2472 return self.backcolor(backcolor) 2473 2474 def linewidth(self, lw=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2475 """Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as `lw()`.""" 2476 if lw is not None: 2477 if lw == 0: 2478 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOff() 2479 self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 2480 return self 2481 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOn() 2482 self.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2483 else: 2484 return self.properties.GetLineWidth() 2485 return self 2486 2487 def lw(self, linewidth=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2488 """Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as `linewidth()`.""" 2489 return self.linewidth(linewidth) 2490 2491 def linecolor(self, lc=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2492 """Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as `lc()`.""" 2493 if lc is None: 2494 return np.array(self.properties.GetEdgeColor()) 2495 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOn() 2496 self.properties.SetEdgeColor(colors.get_color(lc)) 2497 return self 2498 2499 def lc(self, linecolor=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2500 """Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as `linecolor()`.""" 2501 return self.linecolor(linecolor) 2502 2503 def texture( 2504 self, 2505 tname, 2506 tcoords=None, 2507 interpolate=True, 2508 repeat=True, 2509 edge_clamp=False, 2510 scale=None, 2511 ushift=None, 2512 vshift=None, 2513 ) -> Self: 2514 """ 2515 Assign a texture to mesh from image file or predefined texture `tname`. 2516 If tname is set to `None` texture is disabled. 2517 Input tname can also be an array or a `vtkTexture`. 2518 2519 Arguments: 2520 tname : (numpy.array, str, Image, vtkTexture, None) 2521 the input texture to be applied. Can be a numpy array, a path to an image file, 2522 a vedo Image. The None value disables texture. 2523 tcoords : (numpy.array, str) 2524 this is the (u,v) texture coordinate array. Can also be a string of an existing array 2525 in the mesh. 2526 interpolate : (bool) 2527 turn on/off linear interpolation of the texture map when rendering. 2528 repeat : (bool) 2529 repeat of the texture when tcoords extend beyond the [0,1] range. 2530 edge_clamp : (bool) 2531 turn on/off the clamping of the texture map when 2532 the texture coords extend beyond the [0,1] range. 2533 Only used when repeat is False, and edge clamping is supported by the graphics card. 2534 scale : (bool) 2535 scale the texture image by this factor 2536 ushift : (bool) 2537 shift u-coordinates of texture by this amount 2538 vshift : (bool) 2539 shift v-coordinates of texture by this amount 2540 2541 Examples: 2542 - [texturecubes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/texturecubes.py) 2543 2544  2545 """ 2546 pd = self.dataset 2547 out_img = None 2548 2549 if tname is None: # disable texture 2550 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(None) 2551 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2552 return self ###################################### 2553 2554 if isinstance(tname, vtki.vtkTexture): 2555 tu = tname 2556 2557 elif isinstance(tname, vedo.Image): 2558 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2559 out_img = tname.dataset 2560 2561 elif utils.is_sequence(tname): 2562 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2563 out_img = vedo.image._get_img(tname) 2564 2565 elif isinstance(tname, str): 2566 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2567 2568 if "https://" in tname: 2569 try: 2570 tname = vedo.file_io.download(tname, verbose=False) 2571 except: 2572 vedo.logger.error(f"texture {tname} could not be downloaded") 2573 return self 2574 2575 fn = tname + ".jpg" 2576 if os.path.exists(tname): 2577 fn = tname 2578 else: 2579 vedo.logger.error(f"texture file {tname} does not exist") 2580 return self 2581 2582 fnl = fn.lower() 2583 if ".jpg" in fnl or ".jpeg" in fnl: 2584 reader = vtki.new("JPEGReader") 2585 elif ".png" in fnl: 2586 reader = vtki.new("PNGReader") 2587 elif ".bmp" in fnl: 2588 reader = vtki.new("BMPReader") 2589 else: 2590 vedo.logger.error("in texture() supported files are only PNG, BMP or JPG") 2591 return self 2592 reader.SetFileName(fn) 2593 reader.Update() 2594 out_img = reader.GetOutput() 2595 2596 else: 2597 vedo.logger.error(f"in texture() cannot understand input {type(tname)}") 2598 return self 2599 2600 if tcoords is not None: 2601 2602 if isinstance(tcoords, str): 2603 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(tcoords) 2604 2605 else: 2606 tcoords = np.asarray(tcoords) 2607 if tcoords.ndim != 2: 2608 vedo.logger.error("tcoords must be a 2-dimensional array") 2609 return self 2610 if tcoords.shape[0] != pd.GetNumberOfPoints(): 2611 vedo.logger.error("nr of texture coords must match nr of points") 2612 return self 2613 if tcoords.shape[1] != 2: 2614 vedo.logger.error("tcoords texture vector must have 2 components") 2615 vtarr = utils.numpy2vtk(tcoords) 2616 vtarr.SetName("TCoordinates") 2617 2618 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtarr) 2619 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2620 2621 elif not pd.GetPointData().GetTCoords(): 2622 2623 # TCoords still void.. 2624 # check that there are no texture-like arrays: 2625 names = self.pointdata.keys() 2626 candidate_arr = "" 2627 for name in names: 2628 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(name) 2629 if vtarr.GetNumberOfComponents() != 2: 2630 continue 2631 t0, t1 = vtarr.GetRange() 2632 if t0 >= 0 and t1 <= 1: 2633 candidate_arr = name 2634 2635 if candidate_arr: 2636 2637 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(candidate_arr) 2638 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtarr) 2639 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2640 2641 else: 2642 # last resource is automatic mapping 2643 tmapper = vtki.new("TextureMapToPlane") 2644 tmapper.AutomaticPlaneGenerationOn() 2645 tmapper.SetInputData(pd) 2646 tmapper.Update() 2647 tc = tmapper.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetTCoords() 2648 if scale or ushift or vshift: 2649 ntc = utils.vtk2numpy(tc) 2650 if scale: 2651 ntc *= scale 2652 if ushift: 2653 ntc[:, 0] += ushift 2654 if vshift: 2655 ntc[:, 1] += vshift 2656 tc = utils.numpy2vtk(tc) 2657 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(tc) 2658 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2659 2660 if out_img: 2661 tu.SetInputData(out_img) 2662 tu.SetInterpolate(interpolate) 2663 tu.SetRepeat(repeat) 2664 tu.SetEdgeClamp(edge_clamp) 2665 2666 self.properties.SetColor(1, 1, 1) 2667 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2668 self.actor.SetTexture(tu) 2669 2670 # if seam_threshold is not None: 2671 # tname = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetTCoords().GetName() 2672 # grad = self.gradient(tname) 2673 # ugrad, vgrad = np.split(grad, 2, axis=1) 2674 # ugradm, vgradm = utils.mag2(ugrad), utils.mag2(vgrad) 2675 # gradm = np.log(ugradm + vgradm) 2676 # largegrad_ids = np.arange(len(grad))[gradm > seam_threshold * 4] 2677 # uvmap = self.pointdata[tname] 2678 # # collapse triangles that have large gradient 2679 # new_points = self.points.copy() 2680 # for f in self.cells: 2681 # if np.isin(f, largegrad_ids).all(): 2682 # id1, id2, id3 = f 2683 # uv1, uv2, uv3 = uvmap[f] 2684 # d12 = utils.mag2(uv1 - uv2) 2685 # d23 = utils.mag2(uv2 - uv3) 2686 # d31 = utils.mag2(uv3 - uv1) 2687 # idm = np.argmin([d12, d23, d31]) 2688 # if idm == 0: 2689 # new_points[id1] = new_points[id3] 2690 # new_points[id2] = new_points[id3] 2691 # elif idm == 1: 2692 # new_points[id2] = new_points[id1] 2693 # new_points[id3] = new_points[id1] 2694 # self.points = new_points 2695 2696 self.dataset.Modified() 2697 return self
Class to manage the visual aspects of a Mesh object.
2368 def follow_camera(self, camera=None, origin=None) -> Self: 2369 """ 2370 Return an object that will follow camera movements and stay locked to it. 2371 Use `mesh.follow_camera(False)` to disable it. 2372 2373 A `vtkCamera` object can also be passed. 2374 """ 2375 if camera is False: 2376 try: 2377 self.SetCamera(None) 2378 return self 2379 except AttributeError: 2380 return self 2381 2382 factor = vtki.vtkFollower() 2383 factor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 2384 factor.SetProperty(self.properties) 2385 factor.SetBackfaceProperty(self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty()) 2386 factor.SetTexture(self.actor.GetTexture()) 2387 factor.SetScale(self.actor.GetScale()) 2388 # factor.SetOrientation(self.actor.GetOrientation()) 2389 factor.SetPosition(self.actor.GetPosition()) 2390 factor.SetUseBounds(self.actor.GetUseBounds()) 2391 2392 if origin is None: 2393 factor.SetOrigin(self.actor.GetOrigin()) 2394 else: 2395 factor.SetOrigin(origin) 2396 2397 factor.PickableOff() 2398 2399 if isinstance(camera, vtki.vtkCamera): 2400 factor.SetCamera(camera) 2401 else: 2402 plt = vedo.plotter_instance 2403 if plt and plt.renderer and plt.renderer.GetActiveCamera(): 2404 factor.SetCamera(plt.renderer.GetActiveCamera()) 2405 2406 self.actor = None 2407 factor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 2408 self.actor = factor 2409 return self
Return an object that will follow camera movements and stay locked to it.
Use mesh.follow_camera(False) to disable it.
A vtkCamera object can also be passed.
2411 def wireframe(self, value=True) -> Self: 2412 """Set mesh's representation as wireframe or solid surface.""" 2413 if value: 2414 self.properties.SetRepresentationToWireframe() 2415 else: 2416 self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 2417 return self
Set mesh's representation as wireframe or solid surface.
2419 def flat(self) -> Self: 2420 """Set surface interpolation to flat. 2421 2422 <img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Phong_components_version_4.png" width="700"> 2423 """ 2424 self.properties.SetInterpolationToFlat() 2425 return self
Set surface interpolation to flat.

2427 def phong(self) -> Self: 2428 """Set surface interpolation to "phong".""" 2429 self.properties.SetInterpolationToPhong() 2430 return self
Set surface interpolation to "phong".
2432 def backface_culling(self, value=True) -> Self: 2433 """Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.""" 2434 self.properties.SetBackfaceCulling(value) 2435 return self
Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.
2437 def render_lines_as_tubes(self, value=True) -> Self: 2438 """Wrap a fake tube around a simple line for visualization""" 2439 self.properties.SetRenderLinesAsTubes(value) 2440 return self
Wrap a fake tube around a simple line for visualization
2442 def frontface_culling(self, value=True) -> Self: 2443 """Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.""" 2444 self.properties.SetFrontfaceCulling(value) 2445 return self
Set culling of polygons based on orientation of normal with respect to camera.
2447 def backcolor(self, bc=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2448 """ 2449 Set/get mesh's backface color. 2450 """ 2451 back_prop = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 2452 2453 if bc is None: 2454 if back_prop: 2455 return back_prop.GetDiffuseColor() 2456 return self 2457 2458 if self.properties.GetOpacity() < 1: 2459 return self 2460 2461 if not back_prop: 2462 back_prop = vtki.vtkProperty() 2463 2464 back_prop.SetDiffuseColor(colors.get_color(bc)) 2465 back_prop.SetOpacity(self.properties.GetOpacity()) 2466 self.actor.SetBackfaceProperty(back_prop) 2467 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2468 return self
Set/get mesh's backface color.
2470 def bc(self, backcolor=False) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2471 """Shortcut for `mesh.backcolor()`.""" 2472 return self.backcolor(backcolor)
Shortcut for mesh.backcolor().
2474 def linewidth(self, lw=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2475 """Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as `lw()`.""" 2476 if lw is not None: 2477 if lw == 0: 2478 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOff() 2479 self.properties.SetRepresentationToSurface() 2480 return self 2481 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOn() 2482 self.properties.SetLineWidth(lw) 2483 else: 2484 return self.properties.GetLineWidth() 2485 return self
Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as lw().
2487 def lw(self, linewidth=None) -> Union[Self, int]: 2488 """Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as `linewidth()`.""" 2489 return self.linewidth(linewidth)
Set/get width of mesh edges. Same as linewidth().
2491 def linecolor(self, lc=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2492 """Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as `lc()`.""" 2493 if lc is None: 2494 return np.array(self.properties.GetEdgeColor()) 2495 self.properties.EdgeVisibilityOn() 2496 self.properties.SetEdgeColor(colors.get_color(lc)) 2497 return self
Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as lc().
2499 def lc(self, linecolor=None) -> Union[Self, np.ndarray]: 2500 """Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as `linecolor()`.""" 2501 return self.linecolor(linecolor)
Set/get color of mesh edges. Same as linecolor().
2503 def texture( 2504 self, 2505 tname, 2506 tcoords=None, 2507 interpolate=True, 2508 repeat=True, 2509 edge_clamp=False, 2510 scale=None, 2511 ushift=None, 2512 vshift=None, 2513 ) -> Self: 2514 """ 2515 Assign a texture to mesh from image file or predefined texture `tname`. 2516 If tname is set to `None` texture is disabled. 2517 Input tname can also be an array or a `vtkTexture`. 2518 2519 Arguments: 2520 tname : (numpy.array, str, Image, vtkTexture, None) 2521 the input texture to be applied. Can be a numpy array, a path to an image file, 2522 a vedo Image. The None value disables texture. 2523 tcoords : (numpy.array, str) 2524 this is the (u,v) texture coordinate array. Can also be a string of an existing array 2525 in the mesh. 2526 interpolate : (bool) 2527 turn on/off linear interpolation of the texture map when rendering. 2528 repeat : (bool) 2529 repeat of the texture when tcoords extend beyond the [0,1] range. 2530 edge_clamp : (bool) 2531 turn on/off the clamping of the texture map when 2532 the texture coords extend beyond the [0,1] range. 2533 Only used when repeat is False, and edge clamping is supported by the graphics card. 2534 scale : (bool) 2535 scale the texture image by this factor 2536 ushift : (bool) 2537 shift u-coordinates of texture by this amount 2538 vshift : (bool) 2539 shift v-coordinates of texture by this amount 2540 2541 Examples: 2542 - [texturecubes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/texturecubes.py) 2543 2544  2545 """ 2546 pd = self.dataset 2547 out_img = None 2548 2549 if tname is None: # disable texture 2550 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(None) 2551 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2552 return self ###################################### 2553 2554 if isinstance(tname, vtki.vtkTexture): 2555 tu = tname 2556 2557 elif isinstance(tname, vedo.Image): 2558 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2559 out_img = tname.dataset 2560 2561 elif utils.is_sequence(tname): 2562 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2563 out_img = vedo.image._get_img(tname) 2564 2565 elif isinstance(tname, str): 2566 tu = vtki.vtkTexture() 2567 2568 if "https://" in tname: 2569 try: 2570 tname = vedo.file_io.download(tname, verbose=False) 2571 except: 2572 vedo.logger.error(f"texture {tname} could not be downloaded") 2573 return self 2574 2575 fn = tname + ".jpg" 2576 if os.path.exists(tname): 2577 fn = tname 2578 else: 2579 vedo.logger.error(f"texture file {tname} does not exist") 2580 return self 2581 2582 fnl = fn.lower() 2583 if ".jpg" in fnl or ".jpeg" in fnl: 2584 reader = vtki.new("JPEGReader") 2585 elif ".png" in fnl: 2586 reader = vtki.new("PNGReader") 2587 elif ".bmp" in fnl: 2588 reader = vtki.new("BMPReader") 2589 else: 2590 vedo.logger.error("in texture() supported files are only PNG, BMP or JPG") 2591 return self 2592 reader.SetFileName(fn) 2593 reader.Update() 2594 out_img = reader.GetOutput() 2595 2596 else: 2597 vedo.logger.error(f"in texture() cannot understand input {type(tname)}") 2598 return self 2599 2600 if tcoords is not None: 2601 2602 if isinstance(tcoords, str): 2603 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(tcoords) 2604 2605 else: 2606 tcoords = np.asarray(tcoords) 2607 if tcoords.ndim != 2: 2608 vedo.logger.error("tcoords must be a 2-dimensional array") 2609 return self 2610 if tcoords.shape[0] != pd.GetNumberOfPoints(): 2611 vedo.logger.error("nr of texture coords must match nr of points") 2612 return self 2613 if tcoords.shape[1] != 2: 2614 vedo.logger.error("tcoords texture vector must have 2 components") 2615 vtarr = utils.numpy2vtk(tcoords) 2616 vtarr.SetName("TCoordinates") 2617 2618 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtarr) 2619 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2620 2621 elif not pd.GetPointData().GetTCoords(): 2622 2623 # TCoords still void.. 2624 # check that there are no texture-like arrays: 2625 names = self.pointdata.keys() 2626 candidate_arr = "" 2627 for name in names: 2628 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(name) 2629 if vtarr.GetNumberOfComponents() != 2: 2630 continue 2631 t0, t1 = vtarr.GetRange() 2632 if t0 >= 0 and t1 <= 1: 2633 candidate_arr = name 2634 2635 if candidate_arr: 2636 2637 vtarr = pd.GetPointData().GetArray(candidate_arr) 2638 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(vtarr) 2639 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2640 2641 else: 2642 # last resource is automatic mapping 2643 tmapper = vtki.new("TextureMapToPlane") 2644 tmapper.AutomaticPlaneGenerationOn() 2645 tmapper.SetInputData(pd) 2646 tmapper.Update() 2647 tc = tmapper.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetTCoords() 2648 if scale or ushift or vshift: 2649 ntc = utils.vtk2numpy(tc) 2650 if scale: 2651 ntc *= scale 2652 if ushift: 2653 ntc[:, 0] += ushift 2654 if vshift: 2655 ntc[:, 1] += vshift 2656 tc = utils.numpy2vtk(tc) 2657 pd.GetPointData().SetTCoords(tc) 2658 pd.GetPointData().Modified() 2659 2660 if out_img: 2661 tu.SetInputData(out_img) 2662 tu.SetInterpolate(interpolate) 2663 tu.SetRepeat(repeat) 2664 tu.SetEdgeClamp(edge_clamp) 2665 2666 self.properties.SetColor(1, 1, 1) 2667 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOff() 2668 self.actor.SetTexture(tu) 2669 2670 # if seam_threshold is not None: 2671 # tname = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetTCoords().GetName() 2672 # grad = self.gradient(tname) 2673 # ugrad, vgrad = np.split(grad, 2, axis=1) 2674 # ugradm, vgradm = utils.mag2(ugrad), utils.mag2(vgrad) 2675 # gradm = np.log(ugradm + vgradm) 2676 # largegrad_ids = np.arange(len(grad))[gradm > seam_threshold * 4] 2677 # uvmap = self.pointdata[tname] 2678 # # collapse triangles that have large gradient 2679 # new_points = self.points.copy() 2680 # for f in self.cells: 2681 # if np.isin(f, largegrad_ids).all(): 2682 # id1, id2, id3 = f 2683 # uv1, uv2, uv3 = uvmap[f] 2684 # d12 = utils.mag2(uv1 - uv2) 2685 # d23 = utils.mag2(uv2 - uv3) 2686 # d31 = utils.mag2(uv3 - uv1) 2687 # idm = np.argmin([d12, d23, d31]) 2688 # if idm == 0: 2689 # new_points[id1] = new_points[id3] 2690 # new_points[id2] = new_points[id3] 2691 # elif idm == 1: 2692 # new_points[id2] = new_points[id1] 2693 # new_points[id3] = new_points[id1] 2694 # self.points = new_points 2695 2696 self.dataset.Modified() 2697 return self
Assign a texture to mesh from image file or predefined texture tname.
If tname is set to None texture is disabled.
Input tname can also be an array or a vtkTexture.
Arguments:
- tname : (numpy.array, str, Image, vtkTexture, None) the input texture to be applied. Can be a numpy array, a path to an image file, a vedo Image. The None value disables texture.
- tcoords : (numpy.array, str) this is the (u,v) texture coordinate array. Can also be a string of an existing array in the mesh.
- interpolate : (bool) turn on/off linear interpolation of the texture map when rendering.
- repeat : (bool) repeat of the texture when tcoords extend beyond the [0,1] range.
- edge_clamp : (bool) turn on/off the clamping of the texture map when the texture coords extend beyond the [0,1] range. Only used when repeat is False, and edge clamping is supported by the graphics card.
- scale : (bool) scale the texture image by this factor
- ushift : (bool) shift u-coordinates of texture by this amount
- vshift : (bool) shift v-coordinates of texture by this amount
Examples:
Inherited Members
2938class ImageVisual(CommonVisual, Actor3DHelper): 2939 """Class to manage the visual aspects of a ``Image`` object.""" 2940 2941 # def __init__(self) -> None: 2942 # # print("init ImageVisual") 2943 # super().__init__() 2944 2945 def memory_size(self) -> int: 2946 """Return the size in bytes of the object in memory.""" 2947 return self.dataset.GetActualMemorySize() 2948 2949 def scalar_range(self) -> np.ndarray: 2950 """Return the scalar range of the image.""" 2951 return np.array(self.dataset.GetScalarRange()) 2952 2953 def alpha(self, a=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2954 """Set/get image's transparency in the rendering scene.""" 2955 if a is not None: 2956 self.properties.SetOpacity(a) 2957 return self 2958 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 2959 2960 def level(self, value=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2961 """Get/Set the image color level (brightness) in the rendering scene.""" 2962 if value is None: 2963 return self.properties.GetColorLevel() 2964 self.properties.SetColorLevel(value) 2965 return self 2966 2967 def window(self, value=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2968 """Get/Set the image color window (contrast) in the rendering scene.""" 2969 if value is None: 2970 return self.properties.GetColorWindow() 2971 self.properties.SetColorWindow(value) 2972 return self
Class to manage the visual aspects of a Image object.
2945 def memory_size(self) -> int: 2946 """Return the size in bytes of the object in memory.""" 2947 return self.dataset.GetActualMemorySize()
Return the size in bytes of the object in memory.
2949 def scalar_range(self) -> np.ndarray: 2950 """Return the scalar range of the image.""" 2951 return np.array(self.dataset.GetScalarRange())
Return the scalar range of the image.
2953 def alpha(self, a=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2954 """Set/get image's transparency in the rendering scene.""" 2955 if a is not None: 2956 self.properties.SetOpacity(a) 2957 return self 2958 return self.properties.GetOpacity()
Set/get image's transparency in the rendering scene.
2960 def level(self, value=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2961 """Get/Set the image color level (brightness) in the rendering scene.""" 2962 if value is None: 2963 return self.properties.GetColorLevel() 2964 self.properties.SetColorLevel(value) 2965 return self
Get/Set the image color level (brightness) in the rendering scene.
2967 def window(self, value=None) -> Union[Self, float]: 2968 """Get/Set the image color window (contrast) in the rendering scene.""" 2969 if value is None: 2970 return self.properties.GetColorWindow() 2971 self.properties.SetColorWindow(value) 2972 return self
Get/Set the image color window (contrast) in the rendering scene.
Inherited Members
567class Actor2D(vtki.vtkActor2D): 568 """Wrapping of `vtkActor2D` class.""" 569 570 def __init__(self, dataset=None): 571 """Manage 2D objects.""" 572 super().__init__() 573 574 self.dataset = None 575 self.name = "Actor2D" 576 self.filename = "" 577 self.file_size = 0 578 self.pipeline = None 579 self.shape = [] # for images 580 self.coordinate = None 581 582 if dataset is not None: 583 mapper = vtki.new("PolyDataMapper2D") 584 mapper.SetInputData(dataset) 585 self.SetMapper(mapper) 586 587 self.dataset = dataset 588 self.properties = self.GetProperty() 589 590 591 @property 592 def mapper(self): 593 """Get the internal vtkMapper.""" 594 return self.GetMapper() 595 596 # not usable 597 # @property 598 # def properties(self): 599 # """Get the internal vtkProperty.""" 600 # return self.GetProperty() 601 602 # @properties.setter 603 # def properties(self, prop): 604 # """Set the internal vtkProperty.""" 605 # self.SetProperty(prop) 606 607 @mapper.setter 608 def mapper(self, amapper): 609 """Set the internal vtkMapper.""" 610 self.SetMapper(amapper) 611 612 def layer(self, value=None): 613 """Set/Get the layer number in the overlay planes into which to render.""" 614 if value is None: 615 return self.GetLayerNumber() 616 self.SetLayerNumber(value) 617 return self 618 619 def pos(self, px=None, py=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 620 """Set/Get the screen-coordinate position.""" 621 if isinstance(px, str): 622 vedo.logger.error("Use string descriptors only inside the constructor") 623 return self 624 if px is None: 625 return np.array(self.GetPosition(), dtype=int) 626 if py is not None: 627 p = [px, py] 628 else: 629 p = px 630 assert len(p) == 2, "Error: len(pos) must be 2 for Actor2D" 631 self.SetPosition(p) 632 return self 633 634 def coordinate_system(self, value=None) -> Self: 635 """ 636 Set/get the coordinate system which this coordinate is defined in. 637 638 The options are: 639 0. Display 640 1. Normalized Display 641 2. Viewport 642 3. Normalized Viewport 643 4. View 644 5. Pose 645 6. World 646 """ 647 coor = self.GetPositionCoordinate() 648 if value is None: 649 return coor.GetCoordinateSystem() 650 coor.SetCoordinateSystem(value) 651 return self 652 653 def set_position_coordinates(self, p1, p2): 654 """Set the position coordinates.""" 655 self.GetPositionCoordinate().SetValue(*p1) 656 self.GetPosition2Coordinate().SetValue(*p2) 657 return self 658 659 def on(self) -> Self: 660 """Set object visibility.""" 661 self.VisibilityOn() 662 return self 663 664 def off(self) -> Self: 665 """Set object visibility.""" 666 self.VisibilityOn() 667 return self 668 669 def toggle(self) -> Self: 670 """Toggle object visibility.""" 671 self.SetVisibility(not self.GetVisibility()) 672 return self 673 674 def visibility(self, value=None) -> bool: 675 """Get/Set object visibility.""" 676 if value is not None: 677 self.SetVisibility(value) 678 return self.GetVisibility() 679 680 def pickable(self, value=True) -> Self: 681 """Set object pickability.""" 682 self.SetPickable(value) 683 return self 684 685 def color(self, value=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 686 """Set/Get the object color.""" 687 if value is None: 688 return self.properties.GetColor() 689 self.properties.SetColor(colors.get_color(value)) 690 return self 691 692 def c(self, value=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 693 """Set/Get the object color.""" 694 return self.color(value) 695 696 def alpha(self, value=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 697 """Set/Get the object opacity.""" 698 if value is None: 699 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 700 self.properties.SetOpacity(value) 701 return self 702 703 def ps(self, point_size=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 704 """Set/Get the point size of the object. Same as `point_size()`.""" 705 if point_size is None: 706 return self.properties.GetPointSize() 707 self.properties.SetPointSize(point_size) 708 return self 709 710 def lw(self, line_width=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 711 """Set/Get the line width of the object. Same as `line_width()`.""" 712 if line_width is None: 713 return self.properties.GetLineWidth() 714 self.properties.SetLineWidth(line_width) 715 return self 716 717 def ontop(self, value=True) -> Self: 718 """Keep the object always on top of everything else.""" 719 if value: 720 self.properties.SetDisplayLocationToForeground() 721 else: 722 self.properties.SetDisplayLocationToBackground() 723 return self 724 725 def add_observer(self, event_name, func, priority=0) -> int: 726 """Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.""" 727 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 728 idd = self.AddObserver(event_name, func, priority) 729 return idd
Wrapping of vtkActor2D class.
570 def __init__(self, dataset=None): 571 """Manage 2D objects.""" 572 super().__init__() 573 574 self.dataset = None 575 self.name = "Actor2D" 576 self.filename = "" 577 self.file_size = 0 578 self.pipeline = None 579 self.shape = [] # for images 580 self.coordinate = None 581 582 if dataset is not None: 583 mapper = vtki.new("PolyDataMapper2D") 584 mapper.SetInputData(dataset) 585 self.SetMapper(mapper) 586 587 self.dataset = dataset 588 self.properties = self.GetProperty()
Manage 2D objects.
591 @property 592 def mapper(self): 593 """Get the internal vtkMapper.""" 594 return self.GetMapper()
Get the internal vtkMapper.
612 def layer(self, value=None): 613 """Set/Get the layer number in the overlay planes into which to render.""" 614 if value is None: 615 return self.GetLayerNumber() 616 self.SetLayerNumber(value) 617 return self
Set/Get the layer number in the overlay planes into which to render.
619 def pos(self, px=None, py=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 620 """Set/Get the screen-coordinate position.""" 621 if isinstance(px, str): 622 vedo.logger.error("Use string descriptors only inside the constructor") 623 return self 624 if px is None: 625 return np.array(self.GetPosition(), dtype=int) 626 if py is not None: 627 p = [px, py] 628 else: 629 p = px 630 assert len(p) == 2, "Error: len(pos) must be 2 for Actor2D" 631 self.SetPosition(p) 632 return self
Set/Get the screen-coordinate position.
634 def coordinate_system(self, value=None) -> Self: 635 """ 636 Set/get the coordinate system which this coordinate is defined in. 637 638 The options are: 639 0. Display 640 1. Normalized Display 641 2. Viewport 642 3. Normalized Viewport 643 4. View 644 5. Pose 645 6. World 646 """ 647 coor = self.GetPositionCoordinate() 648 if value is None: 649 return coor.GetCoordinateSystem() 650 coor.SetCoordinateSystem(value) 651 return self
Set/get the coordinate system which this coordinate is defined in.
The options are:
- Display
- Normalized Display
- Viewport
- Normalized Viewport
- View
- Pose
- World
653 def set_position_coordinates(self, p1, p2): 654 """Set the position coordinates.""" 655 self.GetPositionCoordinate().SetValue(*p1) 656 self.GetPosition2Coordinate().SetValue(*p2) 657 return self
Set the position coordinates.
669 def toggle(self) -> Self: 670 """Toggle object visibility.""" 671 self.SetVisibility(not self.GetVisibility()) 672 return self
Toggle object visibility.
674 def visibility(self, value=None) -> bool: 675 """Get/Set object visibility.""" 676 if value is not None: 677 self.SetVisibility(value) 678 return self.GetVisibility()
Get/Set object visibility.
680 def pickable(self, value=True) -> Self: 681 """Set object pickability.""" 682 self.SetPickable(value) 683 return self
Set object pickability.
685 def color(self, value=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 686 """Set/Get the object color.""" 687 if value is None: 688 return self.properties.GetColor() 689 self.properties.SetColor(colors.get_color(value)) 690 return self
Set/Get the object color.
692 def c(self, value=None) -> Union[np.ndarray, Self]: 693 """Set/Get the object color.""" 694 return self.color(value)
Set/Get the object color.
696 def alpha(self, value=None) -> Union[float, Self]: 697 """Set/Get the object opacity.""" 698 if value is None: 699 return self.properties.GetOpacity() 700 self.properties.SetOpacity(value) 701 return self
Set/Get the object opacity.
703 def ps(self, point_size=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 704 """Set/Get the point size of the object. Same as `point_size()`.""" 705 if point_size is None: 706 return self.properties.GetPointSize() 707 self.properties.SetPointSize(point_size) 708 return self
Set/Get the point size of the object. Same as point_size().
710 def lw(self, line_width=None) -> Union[int, Self]: 711 """Set/Get the line width of the object. Same as `line_width()`.""" 712 if line_width is None: 713 return self.properties.GetLineWidth() 714 self.properties.SetLineWidth(line_width) 715 return self
Set/Get the line width of the object. Same as line_width().
717 def ontop(self, value=True) -> Self: 718 """Keep the object always on top of everything else.""" 719 if value: 720 self.properties.SetDisplayLocationToForeground() 721 else: 722 self.properties.SetDisplayLocationToBackground() 723 return self
Keep the object always on top of everything else.
725 def add_observer(self, event_name, func, priority=0) -> int: 726 """Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.""" 727 event_name = utils.get_vtk_name_event(event_name) 728 idd = self.AddObserver(event_name, func, priority) 729 return idd
Add a callback function that will be called when an event occurs.
2975class LightKit: 2976 """ 2977 A LightKit consists of three lights, a 'key light', a 'fill light', and a 'head light'. 2978 2979 The main light is the key light. It is usually positioned so that it appears like 2980 an overhead light (like the sun, or a ceiling light). 2981 It is generally positioned to shine down on the scene from about a 45 degree angle vertically 2982 and at least a little offset side to side. The key light usually at least about twice as bright 2983 as the total of all other lights in the scene to provide good modeling of object features. 2984 2985 The other lights in the kit (the fill light, headlight, and a pair of back lights) 2986 are weaker sources that provide extra illumination to fill in the spots that the key light misses. 2987 The fill light is usually positioned across from or opposite from the key light 2988 (though still on the same side of the object as the camera) in order to simulate diffuse reflections 2989 from other objects in the scene. 2990 2991 The headlight, always located at the position of the camera, reduces the contrast between areas lit 2992 by the key and fill light. The two back lights, one on the left of the object as seen from the observer 2993 and one on the right, fill on the high-contrast areas behind the object. 2994 To enforce the relationship between the different lights, the intensity of the fill, back and headlights 2995 are set as a ratio to the key light brightness. 2996 Thus, the brightness of all the lights in the scene can be changed by changing the key light intensity. 2997 2998 All lights are directional lights, infinitely far away with no falloff. Lights move with the camera. 2999 3000 For simplicity, the position of lights in the LightKit can only be specified using angles: 3001 the elevation (latitude) and azimuth (longitude) of each light with respect to the camera, in degrees. 3002 For example, a light at (elevation=0, azimuth=0) is located at the camera (a headlight). 3003 A light at (elevation=90, azimuth=0) is above the lookat point, shining down. 3004 Negative azimuth values move the lights clockwise as seen above, positive values counter-clockwise. 3005 So, a light at (elevation=45, azimuth=-20) is above and in front of the object and shining 3006 slightly from the left side. 3007 3008 LightKit limits the colors that can be assigned to any light to those of incandescent sources such as 3009 light bulbs and sunlight. It defines a special color spectrum called "warmth" from which light colors 3010 can be chosen, where 0 is cold blue, 0.5 is neutral white, and 1 is deep sunset red. 3011 Colors close to 0.5 are "cool whites" and "warm whites," respectively. 3012 3013 Since colors far from white on the warmth scale appear less bright, key-to-fill and key-to-headlight 3014 ratios are skewed by key, fill, and headlight colors. If `maintain_luminance` is set, LightKit will 3015 attempt to compensate for these perceptual differences by increasing the brightness of more saturated colors. 3016 3017 To specify the color of a light, positioning etc you can pass a dictionary with the following keys: 3018 - `intensity` : (float) The intensity of the key light. Default is 1. 3019 - `ratio` : (float) The ratio of the light intensity wrt key light. 3020 - `warmth` : (float) The warmth of the light. Default is 0.5. 3021 - `elevation` : (float) The elevation of the light in degrees. 3022 - `azimuth` : (float) The azimuth of the light in degrees. 3023 3024 Example: 3025 ```python 3026 from vedo import * 3027 lightkit = LightKit(head={"warmth":0.6}) 3028 mesh = Mesh(dataurl+"bunny.obj") 3029 plt = Plotter() 3030 plt.remove_lights().add(mesh, lightkit) 3031 plt.show().close() 3032 ``` 3033 """ 3034 def __init__(self, key=(), fill=(), back=(), head=(), maintain_luminance=False) -> None: 3035 3036 self.lightkit = vtki.new("LightKit") 3037 self.lightkit.SetMaintainLuminance(maintain_luminance) 3038 self.key = dict(key) 3039 self.head = dict(head) 3040 self.fill = dict(fill) 3041 self.back = dict(back) 3042 self.update() 3043 3044 def update(self) -> None: 3045 """Update the LightKit properties.""" 3046 if "warmth" in self.key: 3047 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightWarmth(self.key["warmth"]) 3048 if "warmth" in self.fill: 3049 self.lightkit.SetFillLightWarmth(self.fill["warmth"]) 3050 if "warmth" in self.head: 3051 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightWarmth(self.head["warmth"]) 3052 if "warmth" in self.back: 3053 self.lightkit.SetBackLightWarmth(self.back["warmth"]) 3054 3055 if "intensity" in self.key: 3056 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightIntensity(self.key["intensity"]) 3057 if "ratio" in self.fill: 3058 self.lightkit.SetKeyToFillRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3059 if "ratio" in self.head: 3060 self.lightkit.SetKeyToHeadRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3061 if "ratio" in self.back: 3062 self.lightkit.SetKeyToBackRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3063 3064 if "elevation" in self.key: 3065 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightElevation(self.key["elevation"]) 3066 if "elevation" in self.fill: 3067 self.lightkit.SetFillLightElevation(self.fill["elevation"]) 3068 if "elevation" in self.head: 3069 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightElevation(self.head["elevation"]) 3070 if "elevation" in self.back: 3071 self.lightkit.SetBackLightElevation(self.back["elevation"]) 3072 3073 if "azimuth" in self.key: 3074 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightAzimuth(self.key["azimuth"]) 3075 if "azimuth" in self.fill: 3076 self.lightkit.SetFillLightAzimuth(self.fill["azimuth"]) 3077 if "azimuth" in self.head: 3078 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightAzimuth(self.head["azimuth"]) 3079 if "azimuth" in self.back: 3080 self.lightkit.SetBackLightAzimuth(self.back["azimuth"])
A LightKit consists of three lights, a 'key light', a 'fill light', and a 'head light'.
The main light is the key light. It is usually positioned so that it appears like an overhead light (like the sun, or a ceiling light). It is generally positioned to shine down on the scene from about a 45 degree angle vertically and at least a little offset side to side. The key light usually at least about twice as bright as the total of all other lights in the scene to provide good modeling of object features.
The other lights in the kit (the fill light, headlight, and a pair of back lights) are weaker sources that provide extra illumination to fill in the spots that the key light misses. The fill light is usually positioned across from or opposite from the key light (though still on the same side of the object as the camera) in order to simulate diffuse reflections from other objects in the scene.
The headlight, always located at the position of the camera, reduces the contrast between areas lit by the key and fill light. The two back lights, one on the left of the object as seen from the observer and one on the right, fill on the high-contrast areas behind the object. To enforce the relationship between the different lights, the intensity of the fill, back and headlights are set as a ratio to the key light brightness. Thus, the brightness of all the lights in the scene can be changed by changing the key light intensity.
All lights are directional lights, infinitely far away with no falloff. Lights move with the camera.
For simplicity, the position of lights in the LightKit can only be specified using angles: the elevation (latitude) and azimuth (longitude) of each light with respect to the camera, in degrees. For example, a light at (elevation=0, azimuth=0) is located at the camera (a headlight). A light at (elevation=90, azimuth=0) is above the lookat point, shining down. Negative azimuth values move the lights clockwise as seen above, positive values counter-clockwise. So, a light at (elevation=45, azimuth=-20) is above and in front of the object and shining slightly from the left side.
LightKit limits the colors that can be assigned to any light to those of incandescent sources such as light bulbs and sunlight. It defines a special color spectrum called "warmth" from which light colors can be chosen, where 0 is cold blue, 0.5 is neutral white, and 1 is deep sunset red. Colors close to 0.5 are "cool whites" and "warm whites," respectively.
Since colors far from white on the warmth scale appear less bright, key-to-fill and key-to-headlight
ratios are skewed by key, fill, and headlight colors. If maintain_luminance is set, LightKit will
attempt to compensate for these perceptual differences by increasing the brightness of more saturated colors.
To specify the color of a light, positioning etc you can pass a dictionary with the following keys:
- intensity : (float) The intensity of the key light. Default is 1.
- ratio : (float) The ratio of the light intensity wrt key light.
- warmth : (float) The warmth of the light. Default is 0.5.
- elevation : (float) The elevation of the light in degrees.
- azimuth : (float) The azimuth of the light in degrees.
Example:
from vedo import * lightkit = LightKit(head={"warmth":0.6}) mesh = Mesh(dataurl+"bunny.obj") plt = Plotter() plt.remove_lights().add(mesh, lightkit) plt.show().close()
3034 def __init__(self, key=(), fill=(), back=(), head=(), maintain_luminance=False) -> None: 3035 3036 self.lightkit = vtki.new("LightKit") 3037 self.lightkit.SetMaintainLuminance(maintain_luminance) 3038 self.key = dict(key) 3039 self.head = dict(head) 3040 self.fill = dict(fill) 3041 self.back = dict(back) 3042 self.update()
3044 def update(self) -> None: 3045 """Update the LightKit properties.""" 3046 if "warmth" in self.key: 3047 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightWarmth(self.key["warmth"]) 3048 if "warmth" in self.fill: 3049 self.lightkit.SetFillLightWarmth(self.fill["warmth"]) 3050 if "warmth" in self.head: 3051 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightWarmth(self.head["warmth"]) 3052 if "warmth" in self.back: 3053 self.lightkit.SetBackLightWarmth(self.back["warmth"]) 3054 3055 if "intensity" in self.key: 3056 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightIntensity(self.key["intensity"]) 3057 if "ratio" in self.fill: 3058 self.lightkit.SetKeyToFillRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3059 if "ratio" in self.head: 3060 self.lightkit.SetKeyToHeadRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3061 if "ratio" in self.back: 3062 self.lightkit.SetKeyToBackRatio(self.key["ratio"]) 3063 3064 if "elevation" in self.key: 3065 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightElevation(self.key["elevation"]) 3066 if "elevation" in self.fill: 3067 self.lightkit.SetFillLightElevation(self.fill["elevation"]) 3068 if "elevation" in self.head: 3069 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightElevation(self.head["elevation"]) 3070 if "elevation" in self.back: 3071 self.lightkit.SetBackLightElevation(self.back["elevation"]) 3072 3073 if "azimuth" in self.key: 3074 self.lightkit.SetKeyLightAzimuth(self.key["azimuth"]) 3075 if "azimuth" in self.fill: 3076 self.lightkit.SetFillLightAzimuth(self.fill["azimuth"]) 3077 if "azimuth" in self.head: 3078 self.lightkit.SetHeadLightAzimuth(self.head["azimuth"]) 3079 if "azimuth" in self.back: 3080 self.lightkit.SetBackLightAzimuth(self.back["azimuth"])
Update the LightKit properties.









