vedo.pointcloud
Submodule to work with point clouds.
1#!/usr/bin/env python3 2# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3import time 4from weakref import ref as weak_ref_to 5 6from typing import Union, List 7from typing_extensions import Self 8 9import numpy as np 10 11import vedo.vtkclasses as vtki 12 13import vedo 14from vedo import colors 15from vedo import utils 16from vedo.transformations import LinearTransform, NonLinearTransform 17from vedo.core import PointAlgorithms 18from vedo.visual import PointsVisual 19 20__docformat__ = "google" 21 22__doc__ = """ 23Submodule to work with point clouds. 24 25 26""" 27 28__all__ = [ 29 "Points", 30 "Point", 31 "merge", 32 "fit_line", 33 "fit_circle", 34 "fit_plane", 35 "fit_sphere", 36 "pca_ellipse", 37 "pca_ellipsoid", 38] 39 40 41#################################################### 42def merge(*meshs, flag=False) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", "vedo.Points", None]: 43 """ 44 Build a new Mesh (or Points) formed by the fusion of the inputs. 45 46 Similar to Assembly, but in this case the input objects become a single entity. 47 48 To keep track of the original identities of the inputs you can set `flag=True`. 49 In this case a `pointdata` array of ids is added to the output with name "OriginalMeshID". 50 51 Examples: 52 - [warp1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp1.py) 53 54  55 56 - [value_iteration.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/value_iteration.py) 57 58 """ 59 objs = [a for a in utils.flatten(meshs) if a] 60 61 if not objs: 62 return None 63 64 idarr = [] 65 polyapp = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 66 for i, ob in enumerate(objs): 67 polyapp.AddInputData(ob.dataset) 68 if flag: 69 idarr += [i] * ob.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints() 70 polyapp.Update() 71 mpoly = polyapp.GetOutput() 72 73 if flag: 74 varr = utils.numpy2vtk(idarr, dtype=np.uint16, name="OriginalMeshID") 75 mpoly.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 76 77 has_mesh = False 78 for ob in objs: 79 if isinstance(ob, vedo.Mesh): 80 has_mesh = True 81 break 82 83 if has_mesh: 84 msh = vedo.Mesh(mpoly) 85 else: 86 msh = Points(mpoly) # type: ignore 87 88 msh.copy_properties_from(objs[0]) 89 90 msh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 91 "merge", parents=objs, comment=f"#pts {msh.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 92 ) 93 return msh 94 95 96def _rotate_points(points, n0=None, n1=(0, 0, 1)) -> Union[np.ndarray, tuple]: 97 # Rotate a set of 3D points from direction n0 to direction n1. 98 # Return the rotated points and the normal to the fitting plane (if n0 is None). 99 # The pointing direction of the normal in this case is arbitrary. 100 points = np.asarray(points) 101 102 if points.ndim == 1: 103 points = points[np.newaxis, :] 104 105 if len(points[0]) == 2: 106 return points, (0, 0, 1) 107 108 if n0 is None: # fit plane 109 datamean = points.mean(axis=0) 110 vv = np.linalg.svd(points - datamean)[2] 111 n0 = np.cross(vv[0], vv[1]) 112 113 n0 = n0 / np.linalg.norm(n0) 114 n1 = n1 / np.linalg.norm(n1) 115 k = np.cross(n0, n1) 116 l = np.linalg.norm(k) 117 if not l: 118 k = n0 119 k /= np.linalg.norm(k) 120 121 ct = np.dot(n0, n1) 122 theta = np.arccos(ct) 123 st = np.sin(theta) 124 v = k * (1 - ct) 125 126 rpoints = [] 127 for p in points: 128 a = p * ct 129 b = np.cross(k, p) * st 130 c = v * np.dot(k, p) 131 rpoints.append(a + b + c) 132 133 return np.array(rpoints), n0 134 135 136def fit_line(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"]) -> "vedo.shapes.Line": 137 """ 138 Fits a line through points. 139 140 Extra info is stored in `Line.slope`, `Line.center`, `Line.variances`. 141 142 Examples: 143 - [fitline.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/fitline.py) 144 145  146 """ 147 if isinstance(points, Points): 148 points = points.coordinates 149 data = np.asarray(points) 150 datamean = data.mean(axis=0) 151 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(data - datamean) 152 vv = vv[0] / np.linalg.norm(vv[0]) 153 # vv contains the first principal component, i.e. the direction 154 # vector of the best fit line in the least squares sense. 155 xyz_min = data.min(axis=0) 156 xyz_max = data.max(axis=0) 157 a = np.linalg.norm(xyz_min - datamean) 158 b = np.linalg.norm(xyz_max - datamean) 159 p1 = datamean - a * vv 160 p2 = datamean + b * vv 161 line = vedo.shapes.Line(p1, p2, lw=1) 162 line.slope = vv 163 line.center = datamean 164 line.variances = dd 165 return line 166 167 168def fit_circle(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"]) -> tuple: 169 """ 170 Fits a circle through a set of 3D points, with a very fast non-iterative method. 171 172 Returns the tuple `(center, radius, normal_to_circle)`. 173 174 .. warning:: 175 trying to fit s-shaped points will inevitably lead to instabilities and 176 circles of small radius. 177 178 References: 179 *J.F. Crawford, Nucl. Instr. Meth. 211, 1983, 223-225.* 180 """ 181 if isinstance(points, Points): 182 points = points.coordinates 183 data = np.asarray(points) 184 185 offs = data.mean(axis=0) 186 data, n0 = _rotate_points(data - offs) 187 188 xi = data[:, 0] 189 yi = data[:, 1] 190 191 x = sum(xi) 192 xi2 = xi * xi 193 xx = sum(xi2) 194 xxx = sum(xi2 * xi) 195 196 y = sum(yi) 197 yi2 = yi * yi 198 yy = sum(yi2) 199 yyy = sum(yi2 * yi) 200 201 xiyi = xi * yi 202 xy = sum(xiyi) 203 xyy = sum(xiyi * yi) 204 xxy = sum(xi * xiyi) 205 206 N = len(xi) 207 k = (xx + yy) / N 208 209 a1 = xx - x * x / N 210 b1 = xy - x * y / N 211 c1 = 0.5 * (xxx + xyy - x * k) 212 213 a2 = xy - x * y / N 214 b2 = yy - y * y / N 215 c2 = 0.5 * (xxy + yyy - y * k) 216 217 d = a2 * b1 - a1 * b2 218 if not d: 219 return offs, 0, n0 220 x0 = (b1 * c2 - b2 * c1) / d 221 y0 = (c1 - a1 * x0) / b1 222 223 R = np.sqrt(x0 * x0 + y0 * y0 - 1 / N * (2 * x0 * x + 2 * y0 * y - xx - yy)) 224 225 c, _ = _rotate_points([x0, y0, 0], (0, 0, 1), n0) 226 227 return c[0] + offs, R, n0 228 229 230def fit_plane(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"], signed=False) -> "vedo.shapes.Plane": 231 """ 232 Fits a plane to a set of points. 233 234 Extra info is stored in `Plane.normal`, `Plane.center`, `Plane.variance`. 235 236 Arguments: 237 signed : (bool) 238 if True flip sign of the normal based on the ordering of the points 239 240 Examples: 241 - [fitline.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/fitline.py) 242 243  244 """ 245 if isinstance(points, Points): 246 points = points.coordinates 247 data = np.asarray(points) 248 datamean = data.mean(axis=0) 249 pts = data - datamean 250 res = np.linalg.svd(pts) 251 dd, vv = res[1], res[2] 252 n = np.cross(vv[0], vv[1]) 253 if signed: 254 v = np.zeros_like(pts) 255 for i in range(len(pts) - 1): 256 vi = np.cross(pts[i], pts[i + 1]) 257 v[i] = vi / np.linalg.norm(vi) 258 ns = np.mean(v, axis=0) # normal to the points plane 259 if np.dot(n, ns) < 0: 260 n = -n 261 xyz_min = data.min(axis=0) 262 xyz_max = data.max(axis=0) 263 s = np.linalg.norm(xyz_max - xyz_min) 264 pla = vedo.shapes.Plane(datamean, n, s=[s, s]) 265 pla.variance = dd[2] 266 pla.name = "FitPlane" 267 return pla 268 269 270def fit_sphere(coords: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"]) -> "vedo.shapes.Sphere": 271 """ 272 Fits a sphere to a set of points. 273 274 Extra info is stored in `Sphere.radius`, `Sphere.center`, `Sphere.residue`. 275 276 Examples: 277 - [fitspheres1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/fitspheres1.py) 278 279  280 """ 281 if isinstance(coords, Points): 282 coords = coords.coordinates 283 coords = np.array(coords) 284 n = len(coords) 285 A = np.zeros((n, 4)) 286 A[:, :-1] = coords * 2 287 A[:, 3] = 1 288 f = np.zeros((n, 1)) 289 x = coords[:, 0] 290 y = coords[:, 1] 291 z = coords[:, 2] 292 f[:, 0] = x * x + y * y + z * z 293 try: 294 C, residue, rank, _ = np.linalg.lstsq(A, f, rcond=-1) # solve AC=f 295 except: 296 C, residue, rank, _ = np.linalg.lstsq(A, f) # solve AC=f 297 if rank < 4: 298 return None 299 t = (C[0] * C[0]) + (C[1] * C[1]) + (C[2] * C[2]) + C[3] 300 radius = np.sqrt(t)[0] 301 center = np.array([C[0][0], C[1][0], C[2][0]]) 302 if len(residue) > 0: 303 residue = np.sqrt(residue[0]) / n 304 else: 305 residue = 0 306 sph = vedo.shapes.Sphere(center, radius, c=(1, 0, 0)).wireframe(1) 307 sph.radius = radius 308 sph.center = center 309 sph.residue = residue 310 sph.name = "FitSphere" 311 return sph 312 313 314def pca_ellipse(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"], pvalue=0.673, res=60) -> Union["vedo.shapes.Circle", None]: 315 """ 316 Create the oriented 2D ellipse that contains the fraction `pvalue` of points. 317 PCA (Principal Component Analysis) is used to compute the ellipse orientation. 318 319 Parameter `pvalue` sets the specified fraction of points inside the ellipse. 320 Normalized directions are stored in `ellipse.axis1`, `ellipse.axis2`. 321 Axes sizes are stored in `ellipse.va`, `ellipse.vb` 322 323 Arguments: 324 pvalue : (float) 325 ellipse will include this fraction of points 326 res : (int) 327 resolution of the ellipse 328 329 Examples: 330 - [pca_ellipse.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/pca_ellipse.py) 331 - [histo_pca.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/histo_pca.py) 332 333  334 """ 335 from scipy.stats import f 336 337 if isinstance(points, Points): 338 coords = points.coordinates 339 else: 340 coords = points 341 if len(coords) < 4: 342 vedo.logger.warning("in pca_ellipse(), there are not enough points!") 343 return None 344 345 P = np.array(coords, dtype=float)[:, (0, 1)] 346 cov = np.cov(P, rowvar=0) # type: ignore 347 _, s, R = np.linalg.svd(cov) # singular value decomposition 348 p, n = s.size, P.shape[0] 349 fppf = f.ppf(pvalue, p, n - p) # f % point function 350 u = np.sqrt(s * fppf / 2) * 2 # semi-axes (largest first) 351 ua, ub = u 352 center = utils.make3d(np.mean(P, axis=0)) # centroid of the ellipse 353 354 t = LinearTransform(R.T * u).translate(center) 355 elli = vedo.shapes.Circle(alpha=0.75, res=res) 356 elli.apply_transform(t) 357 elli.properties.LightingOff() 358 359 elli.pvalue = pvalue 360 elli.center = np.array([center[0], center[1], 0]) 361 elli.nr_of_points = n 362 elli.va = ua 363 elli.vb = ub 364 365 # we subtract center because it's in t 366 elli.axis1 = t.move([1, 0, 0]) - center 367 elli.axis2 = t.move([0, 1, 0]) - center 368 369 elli.axis1 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis1) 370 elli.axis2 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis2) 371 elli.name = "PCAEllipse" 372 return elli 373 374 375def pca_ellipsoid(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"], pvalue=0.673, res=24) -> Union["vedo.shapes.Ellipsoid", None]: 376 """ 377 Create the oriented ellipsoid that contains the fraction `pvalue` of points. 378 PCA (Principal Component Analysis) is used to compute the ellipsoid orientation. 379 380 Axes sizes can be accessed in `ellips.va`, `ellips.vb`, `ellips.vc`, 381 normalized directions are stored in `ellips.axis1`, `ellips.axis2` and `ellips.axis3`. 382 Center of mass is stored in `ellips.center`. 383 384 Asphericity can be accessed in `ellips.asphericity()` and ellips.asphericity_error(). 385 A value of 0 means a perfect sphere. 386 387 Arguments: 388 pvalue : (float) 389 ellipsoid will include this fraction of points 390 391 Examples: 392 [pca_ellipsoid.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/pca_ellipsoid.py) 393 394  395 396 See also: 397 `pca_ellipse()` for a 2D ellipse. 398 """ 399 from scipy.stats import f 400 401 if isinstance(points, Points): 402 coords = points.coordinates 403 else: 404 coords = points 405 if len(coords) < 4: 406 vedo.logger.warning("in pca_ellipsoid(), not enough input points!") 407 return None 408 409 P = np.array(coords, ndmin=2, dtype=float) 410 cov = np.cov(P, rowvar=0) # type: ignore 411 _, s, R = np.linalg.svd(cov) # singular value decomposition 412 p, n = s.size, P.shape[0] 413 fppf = f.ppf(pvalue, p, n-p)*(n-1)*p*(n+1)/n/(n-p) # f % point function 414 u = np.sqrt(s*fppf) 415 ua, ub, uc = u # semi-axes (largest first) 416 center = np.mean(P, axis=0) # centroid of the hyperellipsoid 417 418 t = LinearTransform(R.T * u).translate(center) 419 elli = vedo.shapes.Ellipsoid((0,0,0), (1,0,0), (0,1,0), (0,0,1), res=res) 420 elli.apply_transform(t) 421 elli.alpha(0.25) 422 elli.properties.LightingOff() 423 424 elli.pvalue = pvalue 425 elli.nr_of_points = n 426 elli.center = center 427 elli.va = ua 428 elli.vb = ub 429 elli.vc = uc 430 # we subtract center because it's in t 431 elli.axis1 = np.array(t.move([1, 0, 0])) - center 432 elli.axis2 = np.array(t.move([0, 1, 0])) - center 433 elli.axis3 = np.array(t.move([0, 0, 1])) - center 434 elli.axis1 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis1) 435 elli.axis2 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis2) 436 elli.axis3 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis3) 437 elli.name = "PCAEllipsoid" 438 return elli 439 440 441################################################### 442def Point(pos=(0, 0, 0), r=12, c="red", alpha=1.0) -> Self: 443 """ 444 Create a simple point in space. 445 446 .. note:: if you are creating many points you should use class `Points` instead! 447 """ 448 pt = Points([[0,0,0]], r, c, alpha).pos(pos) 449 pt.name = "Point" 450 return pt 451 452 453################################################### 454class Points(PointsVisual, PointAlgorithms): 455 """Work with point clouds.""" 456 457 def __init__(self, inputobj=None, r=4, c=(0.2, 0.2, 0.2), alpha=1): 458 """ 459 Build an object made of only vertex points for a list of 2D/3D points. 460 Both shapes (N, 3) or (3, N) are accepted as input, if N>3. 461 462 Arguments: 463 inputobj : (list, tuple) 464 r : (int) 465 Point radius in units of pixels. 466 c : (str, list) 467 Color name or rgb tuple. 468 alpha : (float) 469 Transparency in range [0,1]. 470 471 Example: 472 ```python 473 from vedo import * 474 475 def fibonacci_sphere(n): 476 s = np.linspace(0, n, num=n, endpoint=False) 477 theta = s * 2.399963229728653 478 y = 1 - s * (2/(n-1)) 479 r = np.sqrt(1 - y * y) 480 x = np.cos(theta) * r 481 z = np.sin(theta) * r 482 return np._c[x,y,z] 483 484 Points(fibonacci_sphere(1000)).show(axes=1).close() 485 ``` 486  487 """ 488 # print("INIT POINTS") 489 super().__init__() 490 491 self.name = "" 492 self.filename = "" 493 self.file_size = "" 494 495 self.info = {} 496 self.time = time.time() 497 498 self.transform = LinearTransform() 499 500 self.point_locator = None 501 self.cell_locator = None 502 self.line_locator = None 503 504 self.actor = vtki.vtkActor() 505 self.properties = self.actor.GetProperty() 506 self.properties_backface = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 507 self.mapper = vtki.new("PolyDataMapper") 508 self.dataset = vtki.vtkPolyData() 509 510 # Create weakref so actor can access this object (eg to pick/remove): 511 self.actor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 512 513 try: 514 self.properties.RenderPointsAsSpheresOn() 515 except AttributeError: 516 pass 517 518 if inputobj is None: #################### 519 return 520 ########################################## 521 522 self.name = "Points" 523 524 ###### 525 if isinstance(inputobj, vtki.vtkActor): 526 self.dataset.DeepCopy(inputobj.GetMapper().GetInput()) 527 pr = vtki.vtkProperty() 528 pr.DeepCopy(inputobj.GetProperty()) 529 self.actor.SetProperty(pr) 530 self.properties = pr 531 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(inputobj.GetMapper().GetScalarVisibility()) 532 533 elif isinstance(inputobj, vtki.vtkPolyData): 534 self.dataset = inputobj 535 if self.dataset.GetNumberOfCells() == 0: 536 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 537 for i in range(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()): 538 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 539 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 540 self.dataset.SetVerts(carr) 541 542 elif isinstance(inputobj, Points): 543 self.dataset = inputobj.dataset 544 self.copy_properties_from(inputobj) 545 546 elif utils.is_sequence(inputobj): # passing point coords 547 self.dataset = utils.buildPolyData(utils.make3d(inputobj)) 548 549 elif isinstance(inputobj, str) or "PosixPath" in str(type(inputobj)): 550 verts = vedo.file_io.load(inputobj) 551 self.filename = str(inputobj) 552 self.dataset = verts.dataset 553 554 elif "meshlib" in str(type(inputobj)): 555 from meshlib import mrmeshnumpy as mn 556 self.dataset = utils.buildPolyData(mn.toNumpyArray(inputobj.points)) 557 558 else: 559 # try to extract the points from a generic VTK input data object 560 if hasattr(inputobj, "dataset"): 561 inputobj = inputobj.dataset 562 try: 563 vvpts = inputobj.GetPoints() 564 self.dataset = vtki.vtkPolyData() 565 self.dataset.SetPoints(vvpts) 566 for i in range(inputobj.GetPointData().GetNumberOfArrays()): 567 arr = inputobj.GetPointData().GetArray(i) 568 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(arr) 569 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 570 for i in range(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()): 571 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 572 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 573 self.dataset.SetVerts(carr) 574 except: 575 vedo.logger.error(f"cannot build Points from type {type(inputobj)}") 576 raise RuntimeError() 577 578 self.actor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 579 self.mapper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 580 581 self.properties.SetColor(colors.get_color(c)) 582 self.properties.SetOpacity(alpha) 583 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 584 self.properties.SetPointSize(r) 585 self.properties.LightingOff() 586 587 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 588 self, parents=[], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 589 ) 590 591 def _update(self, polydata, reset_locators=True) -> Self: 592 """Overwrite the polygonal dataset with a new vtkPolyData.""" 593 self.dataset = polydata 594 self.mapper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 595 self.mapper.Modified() 596 if reset_locators: 597 self.point_locator = None 598 self.line_locator = None 599 self.cell_locator = None 600 return self 601 602 def __str__(self): 603 """Print a description of the Points/Mesh.""" 604 module = self.__class__.__module__ 605 name = self.__class__.__name__ 606 out = vedo.printc( 607 f"{module}.{name} at ({hex(self.memory_address())})".ljust(75), 608 c="g", bold=True, invert=True, return_string=True, 609 ) 610 out += "\x1b[0m\x1b[32;1m" 611 612 if self.name: 613 out += "name".ljust(14) + ": " + self.name 614 if "legend" in self.info.keys() and self.info["legend"]: 615 out+= f", legend='{self.info['legend']}'" 616 out += "\n" 617 618 if self.filename: 619 out+= "file name".ljust(14) + ": " + self.filename + "\n" 620 621 if not self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility(): 622 col = utils.precision(self.properties.GetColor(), 3) 623 cname = vedo.colors.get_color_name(self.properties.GetColor()) 624 out+= "color".ljust(14) + ": " + cname 625 out+= f", rgb={col}, alpha={self.properties.GetOpacity()}\n" 626 if self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty(): 627 bcol = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty().GetDiffuseColor() 628 cname = vedo.colors.get_color_name(bcol) 629 out+= "backface color".ljust(14) + ": " 630 out+= f"{cname}, rgb={utils.precision(bcol,3)}\n" 631 632 npt = self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints() 633 npo, nln = self.dataset.GetNumberOfPolys(), self.dataset.GetNumberOfLines() 634 out+= "elements".ljust(14) + f": vertices={npt:,} polygons={npo:,} lines={nln:,}" 635 if self.dataset.GetNumberOfStrips(): 636 out+= f", strips={self.dataset.GetNumberOfStrips():,}" 637 out+= "\n" 638 if self.dataset.GetNumberOfPieces() > 1: 639 out+= "pieces".ljust(14) + ": " + str(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPieces()) + "\n" 640 641 out+= "position".ljust(14) + ": " + f"{utils.precision(self.pos(), 6)}\n" 642 try: 643 sc = self.transform.get_scale() 644 out+= "scaling".ljust(14) + ": " 645 out+= utils.precision(sc, 6) + "\n" 646 except AttributeError: 647 pass 648 649 if self.npoints: 650 out+="size".ljust(14)+ ": average=" + utils.precision(self.average_size(),6) 651 out+=", diagonal="+ utils.precision(self.diagonal_size(), 6)+ "\n" 652 out+="center of mass".ljust(14) + ": " + utils.precision(self.center_of_mass(),6)+"\n" 653 654 bnds = self.bounds() 655 bx1, bx2 = utils.precision(bnds[0], 3), utils.precision(bnds[1], 3) 656 by1, by2 = utils.precision(bnds[2], 3), utils.precision(bnds[3], 3) 657 bz1, bz2 = utils.precision(bnds[4], 3), utils.precision(bnds[5], 3) 658 out+= "bounds".ljust(14) + ":" 659 out+= " x=(" + bx1 + ", " + bx2 + ")," 660 out+= " y=(" + by1 + ", " + by2 + ")," 661 out+= " z=(" + bz1 + ", " + bz2 + ")\n" 662 663 for key in self.pointdata.keys(): 664 arr = self.pointdata[key] 665 dim = arr.shape[1] if arr.ndim > 1 else 1 666 mark_active = "pointdata" 667 a_scalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 668 a_vectors = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetVectors() 669 a_tensors = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetTensors() 670 if a_scalars and a_scalars.GetName() == key: 671 mark_active += " *" 672 elif a_vectors and a_vectors.GetName() == key: 673 mark_active += " **" 674 elif a_tensors and a_tensors.GetName() == key: 675 mark_active += " ***" 676 out += mark_active.ljust(14) + f': "{key}" ({arr.dtype}), dim={dim}' 677 if dim == 1 and len(arr)>0: 678 rng = utils.precision(arr.min(), 3) + ", " + utils.precision(arr.max(), 3) 679 out += f", range=({rng})\n" 680 else: 681 out += "\n" 682 683 for key in self.celldata.keys(): 684 arr = self.celldata[key] 685 dim = arr.shape[1] if arr.ndim > 1 else 1 686 mark_active = "celldata" 687 a_scalars = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 688 a_vectors = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetVectors() 689 a_tensors = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetTensors() 690 if a_scalars and a_scalars.GetName() == key: 691 mark_active += " *" 692 elif a_vectors and a_vectors.GetName() == key: 693 mark_active += " **" 694 elif a_tensors and a_tensors.GetName() == key: 695 mark_active += " ***" 696 out += mark_active.ljust(14) + f': "{key}" ({arr.dtype}), dim={dim}' 697 if dim == 1 and len(arr)>0: 698 rng = utils.precision(arr.min(), 3) + ", " + utils.precision(arr.max(), 3) 699 out += f", range=({rng})\n" 700 else: 701 out += "\n" 702 703 for key in self.metadata.keys(): 704 arr = self.metadata[key] 705 if len(arr) > 3: 706 out+= "metadata".ljust(14) + ": " + f'"{key}" ({len(arr)} values)\n' 707 else: 708 out+= "metadata".ljust(14) + ": " + f'"{key}" = {arr}\n' 709 710 if self.picked3d is not None: 711 idp = self.closest_point(self.picked3d, return_point_id=True) 712 idc = self.closest_point(self.picked3d, return_cell_id=True) 713 out+= "clicked point".ljust(14) + ": " + utils.precision(self.picked3d, 6) 714 out+= f", pointID={idp}, cellID={idc}\n" 715 716 return out.rstrip() + "\x1b[0m" 717 718 def _repr_html_(self): 719 """ 720 HTML representation of the Point cloud object for Jupyter Notebooks. 721 722 Returns: 723 HTML text with the image and some properties. 724 """ 725 import io 726 import base64 727 from PIL import Image 728 729 library_name = "vedo.pointcloud.Points" 730 help_url = "https://vedo.embl.es/docs/vedo/pointcloud.html#Points" 731 732 arr = self.thumbnail() 733 im = Image.fromarray(arr) 734 buffered = io.BytesIO() 735 im.save(buffered, format="PNG", quality=100) 736 encoded = base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode("utf-8") 737 url = "data:image/png;base64," + encoded 738 image = f"<img src='{url}'></img>" 739 740 bounds = "<br/>".join( 741 [ 742 utils.precision(min_x, 4) + " ... " + utils.precision(max_x, 4) 743 for min_x, max_x in zip(self.bounds()[::2], self.bounds()[1::2]) 744 ] 745 ) 746 average_size = "{size:.3f}".format(size=self.average_size()) 747 748 help_text = "" 749 if self.name: 750 help_text += f"<b> {self.name}:   </b>" 751 help_text += '<b><a href="' + help_url + '" target="_blank">' + library_name + "</a></b>" 752 if self.filename: 753 dots = "" 754 if len(self.filename) > 30: 755 dots = "..." 756 help_text += f"<br/><code><i>({dots}{self.filename[-30:]})</i></code>" 757 758 pdata = "" 759 if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 760 if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars().GetName(): 761 name = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars().GetName() 762 pdata = "<tr><td><b> point data array </b></td><td>" + name + "</td></tr>" 763 764 cdata = "" 765 if self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 766 if self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars().GetName(): 767 name = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars().GetName() 768 cdata = "<tr><td><b> cell data array </b></td><td>" + name + "</td></tr>" 769 770 allt = [ 771 "<table>", 772 "<tr>", 773 "<td>", 774 image, 775 "</td>", 776 "<td style='text-align: center; vertical-align: center;'><br/>", 777 help_text, 778 "<table>", 779 "<tr><td><b> bounds </b> <br/> (x/y/z) </td><td>" + str(bounds) + "</td></tr>", 780 "<tr><td><b> center of mass </b></td><td>" 781 + utils.precision(self.center_of_mass(), 3) 782 + "</td></tr>", 783 "<tr><td><b> average size </b></td><td>" + str(average_size) + "</td></tr>", 784 "<tr><td><b> nr. points </b></td><td>" + str(self.npoints) + "</td></tr>", 785 pdata, 786 cdata, 787 "</table>", 788 "</table>", 789 ] 790 return "\n".join(allt) 791 792 ################################################################################## 793 def __add__(self, meshs): 794 """ 795 Add two meshes or a list of meshes together to form an `Assembly` object. 796 """ 797 if isinstance(meshs, list): 798 alist = [self] 799 for l in meshs: 800 if isinstance(l, vedo.Assembly): 801 alist += l.unpack() 802 else: 803 alist += l 804 return vedo.assembly.Assembly(alist) 805 806 if isinstance(meshs, vedo.Assembly): 807 return meshs + self # use Assembly.__add__ 808 809 return vedo.assembly.Assembly([self, meshs]) 810 811 def polydata(self): 812 """ 813 Obsolete. Use property `.dataset` instead. 814 Returns the underlying `vtkPolyData` object. 815 """ 816 colors.printc( 817 "WARNING: call to .polydata() is obsolete, use property .dataset instead.", 818 c="y") 819 return self.dataset 820 821 def __copy__(self): 822 return self.clone(deep=False) 823 824 def __deepcopy__(self, memo): 825 return self.clone(deep=memo) 826 827 def copy(self, deep=True) -> Self: 828 """Return a copy of the object. Alias of `clone()`.""" 829 return self.clone(deep=deep) 830 831 def clone(self, deep=True) -> Self: 832 """ 833 Clone a `PointCloud` or `Mesh` object to make an exact copy of it. 834 Alias of `copy()`. 835 836 Arguments: 837 deep : (bool) 838 if False return a shallow copy of the mesh without copying the points array. 839 840 Examples: 841 - [mirror.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mirror.py) 842 843  844 """ 845 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 846 if deep or isinstance(deep, dict): # if a memo object is passed this checks as True 847 poly.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 848 else: 849 poly.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 850 851 if isinstance(self, vedo.Mesh): 852 cloned = vedo.Mesh(poly) 853 else: 854 cloned = Points(poly) 855 # print([self], self.__class__) 856 # cloned = self.__class__(poly) 857 858 cloned.transform = self.transform.clone() 859 860 cloned.copy_properties_from(self) 861 862 cloned.name = str(self.name) 863 cloned.filename = str(self.filename) 864 cloned.info = dict(self.info) 865 cloned.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("clone", parents=[self], shape="diamond", c="#edede9") 866 867 if isinstance(deep, dict): 868 deep[id(self)] = cloned 869 870 return cloned 871 872 def compute_normals_with_pca(self, n=20, orientation_point=None, invert=False) -> Self: 873 """ 874 Generate point normals using PCA (principal component analysis). 875 This algorithm estimates a local tangent plane around each sample point p 876 by considering a small neighborhood of points around p, and fitting a plane 877 to the neighborhood (via PCA). 878 879 Arguments: 880 n : (int) 881 neighborhood size to calculate the normal 882 orientation_point : (list) 883 adjust the +/- sign of the normals so that 884 the normals all point towards a specified point. If None, perform a traversal 885 of the point cloud and flip neighboring normals so that they are mutually consistent. 886 invert : (bool) 887 flip all normals 888 """ 889 poly = self.dataset 890 pcan = vtki.new("PCANormalEstimation") 891 pcan.SetInputData(poly) 892 pcan.SetSampleSize(n) 893 894 if orientation_point is not None: 895 pcan.SetNormalOrientationToPoint() 896 pcan.SetOrientationPoint(orientation_point) 897 else: 898 pcan.SetNormalOrientationToGraphTraversal() 899 900 if invert: 901 pcan.FlipNormalsOn() 902 pcan.Update() 903 904 varr = pcan.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetNormals() 905 varr.SetName("Normals") 906 self.dataset.GetPointData().SetNormals(varr) 907 self.dataset.GetPointData().Modified() 908 return self 909 910 def compute_acoplanarity(self, n=25, radius=None, on="points") -> Self: 911 """ 912 Compute acoplanarity which is a measure of how much a local region of the mesh 913 differs from a plane. 914 915 The information is stored in a `pointdata` or `celldata` array with name 'Acoplanarity'. 916 917 Either `n` (number of neighbour points) or `radius` (radius of local search) can be specified. 918 If a radius value is given and not enough points fall inside it, then a -1 is stored. 919 920 Example: 921 ```python 922 from vedo import * 923 msh = ParametricShape('RandomHills') 924 msh.compute_acoplanarity(radius=0.1, on='cells') 925 msh.cmap("coolwarm", on='cells').add_scalarbar() 926 msh.show(axes=1).close() 927 ``` 928  929 """ 930 acoplanarities = [] 931 if "point" in on: 932 pts = self.coordinates 933 elif "cell" in on: 934 pts = self.cell_centers().coordinates 935 else: 936 raise ValueError(f"In compute_acoplanarity() set on to either 'cells' or 'points', not {on}") 937 938 for p in utils.progressbar(pts, delay=5, width=15, title=f"{on} acoplanarity"): 939 if n: 940 data = self.closest_point(p, n=n) 941 npts = n 942 elif radius: 943 data = self.closest_point(p, radius=radius) 944 npts = len(data) 945 946 try: 947 center = data.mean(axis=0) 948 res = np.linalg.svd(data - center) 949 acoplanarities.append(res[1][2] / npts) 950 except: 951 acoplanarities.append(-1.0) 952 953 if "point" in on: 954 self.pointdata["Acoplanarity"] = np.array(acoplanarities, dtype=float) 955 else: 956 self.celldata["Acoplanarity"] = np.array(acoplanarities, dtype=float) 957 return self 958 959 def distance_to(self, pcloud, signed=False, invert=False, name="Distance") -> np.ndarray: 960 """ 961 Computes the distance from one point cloud or mesh to another point cloud or mesh. 962 This new `pointdata` array is saved with default name "Distance". 963 964 Keywords `signed` and `invert` are used to compute signed distance, 965 but the mesh in that case must have polygonal faces (not a simple point cloud), 966 and normals must also be computed. 967 968 Examples: 969 - [distance2mesh.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/distance2mesh.py) 970 971 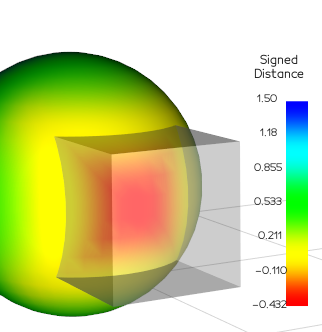 972 """ 973 if pcloud.dataset.GetNumberOfPolys(): 974 975 poly1 = self.dataset 976 poly2 = pcloud.dataset 977 df = vtki.new("DistancePolyDataFilter") 978 df.ComputeSecondDistanceOff() 979 df.SetInputData(0, poly1) 980 df.SetInputData(1, poly2) 981 df.SetSignedDistance(signed) 982 df.SetNegateDistance(invert) 983 df.Update() 984 scals = df.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetScalars() 985 dists = utils.vtk2numpy(scals) 986 987 else: # has no polygons 988 989 if signed: 990 vedo.logger.warning("distance_to() called with signed=True but input object has no polygons") 991 992 if not pcloud.point_locator: 993 pcloud.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 994 pcloud.point_locator.SetDataSet(pcloud.dataset) 995 pcloud.point_locator.BuildLocator() 996 997 ids = [] 998 ps1 = self.coordinates 999 ps2 = pcloud.coordinates 1000 for p in ps1: 1001 pid = pcloud.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1002 ids.append(pid) 1003 1004 deltas = ps2[ids] - ps1 1005 dists = np.linalg.norm(deltas, axis=1).astype(np.float32) 1006 scals = utils.numpy2vtk(dists) 1007 1008 scals.SetName(name) 1009 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(scals) 1010 self.dataset.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(scals.GetName()) 1011 rng = scals.GetRange() 1012 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(rng[0], rng[1]) 1013 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1014 1015 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1016 "distance_to", 1017 parents=[self, pcloud], 1018 shape="cylinder", 1019 comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 1020 ) 1021 return dists 1022 1023 def clean(self) -> Self: 1024 """Clean pointcloud or mesh by removing coincident points.""" 1025 cpd = vtki.new("CleanPolyData") 1026 cpd.PointMergingOn() 1027 cpd.ConvertLinesToPointsOff() 1028 cpd.ConvertPolysToLinesOff() 1029 cpd.ConvertStripsToPolysOff() 1030 cpd.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1031 cpd.Update() 1032 self._update(cpd.GetOutput()) 1033 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1034 "clean", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 1035 ) 1036 return self 1037 1038 def subsample(self, fraction: float, absolute=False) -> Self: 1039 """ 1040 Subsample a point cloud by requiring that the points 1041 or vertices are far apart at least by the specified fraction of the object size. 1042 If a Mesh is passed the polygonal faces are not removed 1043 but holes can appear as their vertices are removed. 1044 1045 Examples: 1046 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 1047 1048  1049 1050 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 1051 1052 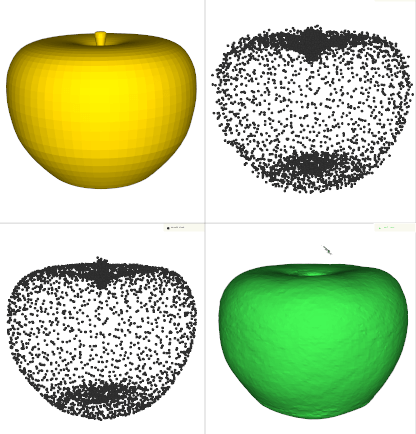 1053 """ 1054 if not absolute: 1055 if fraction > 1: 1056 vedo.logger.warning( 1057 f"subsample(fraction=...), fraction must be < 1, but is {fraction}" 1058 ) 1059 if fraction <= 0: 1060 return self 1061 1062 cpd = vtki.new("CleanPolyData") 1063 cpd.PointMergingOn() 1064 cpd.ConvertLinesToPointsOn() 1065 cpd.ConvertPolysToLinesOn() 1066 cpd.ConvertStripsToPolysOn() 1067 cpd.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1068 if absolute: 1069 cpd.SetTolerance(fraction / self.diagonal_size()) 1070 # cpd.SetToleranceIsAbsolute(absolute) 1071 else: 1072 cpd.SetTolerance(fraction) 1073 cpd.Update() 1074 1075 ps = 2 1076 if self.properties.GetRepresentation() == 0: 1077 ps = self.properties.GetPointSize() 1078 1079 self._update(cpd.GetOutput()) 1080 self.ps(ps) 1081 1082 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1083 "subsample", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 1084 ) 1085 return self 1086 1087 def threshold(self, scalars: str, above=None, below=None, on="points") -> Self: 1088 """ 1089 Extracts cells where scalar value satisfies threshold criterion. 1090 1091 Arguments: 1092 scalars : (str) 1093 name of the scalars array. 1094 above : (float) 1095 minimum value of the scalar 1096 below : (float) 1097 maximum value of the scalar 1098 on : (str) 1099 if 'cells' assume array of scalars refers to cell data. 1100 1101 Examples: 1102 - [mesh_threshold.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_threshold.py) 1103 """ 1104 thres = vtki.new("Threshold") 1105 thres.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1106 1107 if on.startswith("c"): 1108 asso = vtki.vtkDataObject.FIELD_ASSOCIATION_CELLS 1109 else: 1110 asso = vtki.vtkDataObject.FIELD_ASSOCIATION_POINTS 1111 1112 thres.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, asso, scalars) 1113 1114 if above is None and below is not None: 1115 try: # vtk 9.2 1116 thres.ThresholdByLower(below) 1117 except AttributeError: # vtk 9.3 1118 thres.SetUpperThreshold(below) 1119 1120 elif below is None and above is not None: 1121 try: 1122 thres.ThresholdByUpper(above) 1123 except AttributeError: 1124 thres.SetLowerThreshold(above) 1125 else: 1126 try: 1127 thres.ThresholdBetween(above, below) 1128 except AttributeError: 1129 thres.SetUpperThreshold(below) 1130 thres.SetLowerThreshold(above) 1131 1132 thres.Update() 1133 1134 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 1135 gf.SetInputData(thres.GetOutput()) 1136 gf.Update() 1137 self._update(gf.GetOutput()) 1138 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("threshold", parents=[self]) 1139 return self 1140 1141 def quantize(self, value: float) -> Self: 1142 """ 1143 The user should input a value and all {x,y,z} coordinates 1144 will be quantized to that absolute grain size. 1145 """ 1146 qp = vtki.new("QuantizePolyDataPoints") 1147 qp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1148 qp.SetQFactor(value) 1149 qp.Update() 1150 self._update(qp.GetOutput()) 1151 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("quantize", parents=[self]) 1152 return self 1153 1154 @property 1155 def vertex_normals(self) -> np.ndarray: 1156 """ 1157 Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as `point_normals`. 1158 If needed, normals are computed via `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1159 Check out also `compute_normals()` and `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1160 """ 1161 vtknormals = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetNormals() 1162 if vtknormals is None: 1163 self.compute_normals_with_pca() 1164 vtknormals = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetNormals() 1165 return utils.vtk2numpy(vtknormals) 1166 1167 @property 1168 def point_normals(self) -> np.ndarray: 1169 """ 1170 Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as `vertex_normals`. 1171 Check out also `compute_normals()` and `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1172 """ 1173 return self.vertex_normals 1174 1175 def align_to(self, target, iters=100, rigid=False, invert=False, use_centroids=False) -> Self: 1176 """ 1177 Aligned to target mesh through the `Iterative Closest Point` algorithm. 1178 1179 The core of the algorithm is to match each vertex in one surface with 1180 the closest surface point on the other, then apply the transformation 1181 that modify one surface to best match the other (in the least-square sense). 1182 1183 Arguments: 1184 rigid : (bool) 1185 if True do not allow scaling 1186 invert : (bool) 1187 if True start by aligning the target to the source but 1188 invert the transformation finally. Useful when the target is smaller 1189 than the source. 1190 use_centroids : (bool) 1191 start by matching the centroids of the two objects. 1192 1193 Examples: 1194 - [align1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align1.py) 1195 1196 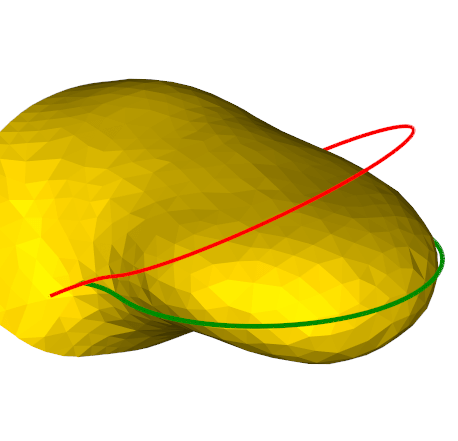 1197 1198 - [align2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align2.py) 1199 1200 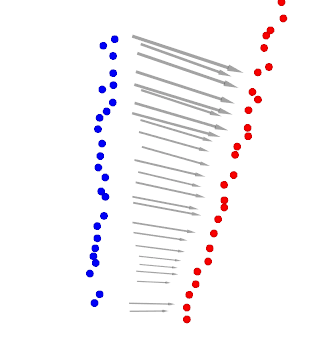 1201 """ 1202 icp = vtki.new("IterativeClosestPointTransform") 1203 icp.SetSource(self.dataset) 1204 icp.SetTarget(target.dataset) 1205 if invert: 1206 icp.Inverse() 1207 icp.SetMaximumNumberOfIterations(iters) 1208 if rigid: 1209 icp.GetLandmarkTransform().SetModeToRigidBody() 1210 icp.SetStartByMatchingCentroids(use_centroids) 1211 icp.Update() 1212 1213 self.apply_transform(icp.GetMatrix()) 1214 1215 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1216 "align_to", parents=[self, target], comment=f"rigid = {rigid}" 1217 ) 1218 return self 1219 1220 def align_to_bounding_box(self, msh, rigid=False) -> Self: 1221 """ 1222 Align the current object's bounding box to the bounding box 1223 of the input object. 1224 1225 Use `rigid=True` to disable scaling. 1226 1227 Example: 1228 [align6.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align6.py) 1229 """ 1230 lmt = vtki.vtkLandmarkTransform() 1231 ss = vtki.vtkPoints() 1232 xss0, xss1, yss0, yss1, zss0, zss1 = self.bounds() 1233 for p in [ 1234 [xss0, yss0, zss0], 1235 [xss1, yss0, zss0], 1236 [xss1, yss1, zss0], 1237 [xss0, yss1, zss0], 1238 [xss0, yss0, zss1], 1239 [xss1, yss0, zss1], 1240 [xss1, yss1, zss1], 1241 [xss0, yss1, zss1], 1242 ]: 1243 ss.InsertNextPoint(p) 1244 st = vtki.vtkPoints() 1245 xst0, xst1, yst0, yst1, zst0, zst1 = msh.bounds() 1246 for p in [ 1247 [xst0, yst0, zst0], 1248 [xst1, yst0, zst0], 1249 [xst1, yst1, zst0], 1250 [xst0, yst1, zst0], 1251 [xst0, yst0, zst1], 1252 [xst1, yst0, zst1], 1253 [xst1, yst1, zst1], 1254 [xst0, yst1, zst1], 1255 ]: 1256 st.InsertNextPoint(p) 1257 1258 lmt.SetSourceLandmarks(ss) 1259 lmt.SetTargetLandmarks(st) 1260 lmt.SetModeToAffine() 1261 if rigid: 1262 lmt.SetModeToRigidBody() 1263 lmt.Update() 1264 1265 LT = LinearTransform(lmt) 1266 self.apply_transform(LT) 1267 return self 1268 1269 def align_with_landmarks( 1270 self, 1271 source_landmarks, 1272 target_landmarks, 1273 rigid=False, 1274 affine=False, 1275 least_squares=False, 1276 ) -> Self: 1277 """ 1278 Transform mesh orientation and position based on a set of landmarks points. 1279 The algorithm finds the best matching of source points to target points 1280 in the mean least square sense, in one single step. 1281 1282 If `affine` is True the x, y and z axes can scale independently but stay collinear. 1283 With least_squares they can vary orientation. 1284 1285 Examples: 1286 - [align5.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align5.py) 1287 1288 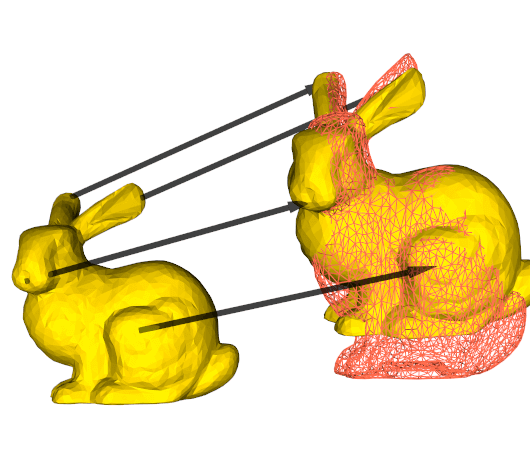 1289 """ 1290 1291 if utils.is_sequence(source_landmarks): 1292 ss = vtki.vtkPoints() 1293 for p in source_landmarks: 1294 ss.InsertNextPoint(p) 1295 else: 1296 ss = source_landmarks.dataset.GetPoints() 1297 if least_squares: 1298 source_landmarks = source_landmarks.coordinates 1299 1300 if utils.is_sequence(target_landmarks): 1301 st = vtki.vtkPoints() 1302 for p in target_landmarks: 1303 st.InsertNextPoint(p) 1304 else: 1305 st = target_landmarks.GetPoints() 1306 if least_squares: 1307 target_landmarks = target_landmarks.coordinates 1308 1309 if ss.GetNumberOfPoints() != st.GetNumberOfPoints(): 1310 n1 = ss.GetNumberOfPoints() 1311 n2 = st.GetNumberOfPoints() 1312 vedo.logger.error(f"source and target have different nr of points {n1} vs {n2}") 1313 raise RuntimeError() 1314 1315 if int(rigid) + int(affine) + int(least_squares) > 1: 1316 vedo.logger.error( 1317 "only one of rigid, affine, least_squares can be True at a time" 1318 ) 1319 raise RuntimeError() 1320 1321 lmt = vtki.vtkLandmarkTransform() 1322 lmt.SetSourceLandmarks(ss) 1323 lmt.SetTargetLandmarks(st) 1324 lmt.SetModeToSimilarity() 1325 1326 if rigid: 1327 lmt.SetModeToRigidBody() 1328 lmt.Update() 1329 1330 elif affine: 1331 lmt.SetModeToAffine() 1332 lmt.Update() 1333 1334 elif least_squares: 1335 cms = source_landmarks.mean(axis=0) 1336 cmt = target_landmarks.mean(axis=0) 1337 m = np.linalg.lstsq(source_landmarks - cms, target_landmarks - cmt, rcond=None)[0] 1338 M = vtki.vtkMatrix4x4() 1339 for i in range(3): 1340 for j in range(3): 1341 M.SetElement(j, i, m[i][j]) 1342 lmt = vtki.vtkTransform() 1343 lmt.Translate(cmt) 1344 lmt.Concatenate(M) 1345 lmt.Translate(-cms) 1346 1347 else: 1348 lmt.Update() 1349 1350 self.apply_transform(lmt) 1351 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("transform_with_landmarks", parents=[self]) 1352 return self 1353 1354 def normalize(self) -> Self: 1355 """Scale average size to unit. The scaling is performed around the center of mass.""" 1356 coords = self.coordinates 1357 if not coords.shape[0]: 1358 return self 1359 cm = np.mean(coords, axis=0) 1360 pts = coords - cm 1361 xyz2 = np.sum(pts * pts, axis=0) 1362 scale = 1 / np.sqrt(np.sum(xyz2) / len(pts)) 1363 self.scale(scale, origin=cm) 1364 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("normalize", parents=[self]) 1365 return self 1366 1367 def mirror(self, axis="x", origin=True) -> Self: 1368 """ 1369 Mirror reflect along one of the cartesian axes 1370 1371 Arguments: 1372 axis : (str) 1373 axis to use for mirroring, must be set to `x, y, z`. 1374 Or any combination of those. 1375 origin : (list) 1376 use this point as the origin of the mirroring transformation. 1377 1378 Examples: 1379 - [mirror.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mirror.py) 1380 1381  1382 """ 1383 sx, sy, sz = 1, 1, 1 1384 if "x" in axis.lower(): sx = -1 1385 if "y" in axis.lower(): sy = -1 1386 if "z" in axis.lower(): sz = -1 1387 1388 self.scale([sx, sy, sz], origin=origin) 1389 1390 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1391 "mirror", comment=f"axis = {axis}", parents=[self]) 1392 1393 if sx * sy * sz < 0: 1394 if hasattr(self, "reverse"): 1395 self.reverse() 1396 return self 1397 1398 def flip_normals(self) -> Self: 1399 """Flip all normals orientation.""" 1400 rs = vtki.new("ReverseSense") 1401 rs.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1402 rs.ReverseCellsOff() 1403 rs.ReverseNormalsOn() 1404 rs.Update() 1405 self._update(rs.GetOutput()) 1406 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("flip_normals", parents=[self]) 1407 return self 1408 1409 def add_gaussian_noise(self, sigma=1.0) -> Self: 1410 """ 1411 Add gaussian noise to point positions. 1412 An extra array is added named "GaussianNoise" with the displacements. 1413 1414 Arguments: 1415 sigma : (float) 1416 nr. of standard deviations, expressed in percent of the diagonal size of mesh. 1417 Can also be a list `[sigma_x, sigma_y, sigma_z]`. 1418 1419 Example: 1420 ```python 1421 from vedo import Sphere 1422 Sphere().add_gaussian_noise(1.0).point_size(8).show().close() 1423 ``` 1424 """ 1425 sz = self.diagonal_size() 1426 pts = self.coordinates 1427 n = len(pts) 1428 ns = (np.random.randn(n, 3) * sigma) * (sz / 100) 1429 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 1430 vpts.SetNumberOfPoints(n) 1431 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(pts + ns, dtype=np.float32)) 1432 self.dataset.SetPoints(vpts) 1433 self.dataset.GetPoints().Modified() 1434 self.pointdata["GaussianNoise"] = -ns 1435 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1436 "gaussian_noise", parents=[self], shape="egg", comment=f"sigma = {sigma}" 1437 ) 1438 return self 1439 1440 def closest_point( 1441 self, pt, n=1, radius=None, return_point_id=False, return_cell_id=False 1442 ) -> Union[List[int], int, np.ndarray]: 1443 """ 1444 Find the closest point(s) on a mesh given from the input point `pt`. 1445 1446 Arguments: 1447 n : (int) 1448 if greater than 1, return a list of n ordered closest points 1449 radius : (float) 1450 if given, get all points within that radius. Then n is ignored. 1451 return_point_id : (bool) 1452 return point ID instead of coordinates 1453 return_cell_id : (bool) 1454 return cell ID in which the closest point sits 1455 1456 Examples: 1457 - [align1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align1.py) 1458 - [fitplanes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/fitplanes.py) 1459 - [quadratic_morphing.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/quadratic_morphing.py) 1460 1461 .. note:: 1462 The appropriate tree search locator is built on the fly and cached for speed. 1463 1464 If you want to reset it use `mymesh.point_locator=None` 1465 and / or `mymesh.cell_locator=None`. 1466 """ 1467 if len(pt) != 3: 1468 pt = [pt[0], pt[1], 0] 1469 1470 # NB: every time the mesh moves or is warped the locators are set to None 1471 if ((n > 1 or radius) or (n == 1 and return_point_id)) and not return_cell_id: 1472 poly = None 1473 if not self.point_locator: 1474 poly = self.dataset 1475 self.point_locator = vtki.new("StaticPointLocator") 1476 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 1477 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1478 1479 ########## 1480 if radius: 1481 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1482 self.point_locator.FindPointsWithinRadius(radius, pt, vtklist) 1483 elif n > 1: 1484 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1485 self.point_locator.FindClosestNPoints(n, pt, vtklist) 1486 else: # n==1 hence return_point_id==True 1487 ######## 1488 return self.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(pt) 1489 ######## 1490 1491 if return_point_id: 1492 ######## 1493 return utils.vtk2numpy(vtklist) 1494 ######## 1495 1496 if not poly: 1497 poly = self.dataset 1498 trgp = [] 1499 for i in range(vtklist.GetNumberOfIds()): 1500 trgp_ = [0, 0, 0] 1501 vi = vtklist.GetId(i) 1502 poly.GetPoints().GetPoint(vi, trgp_) 1503 trgp.append(trgp_) 1504 ######## 1505 return np.array(trgp) 1506 ######## 1507 1508 else: 1509 1510 if not self.cell_locator: 1511 poly = self.dataset 1512 1513 # As per Miquel example with limbs the vtkStaticCellLocator doesnt work !! 1514 # https://discourse.vtk.org/t/vtkstaticcelllocator-problem-vtk9-0-3/7854/4 1515 if vedo.vtk_version[0] >= 9 and vedo.vtk_version[1] > 0: 1516 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("StaticCellLocator") 1517 else: 1518 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("CellLocator") 1519 1520 self.cell_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 1521 self.cell_locator.BuildLocator() 1522 1523 if radius is not None: 1524 vedo.printc("Warning: closest_point() with radius is not implemented for cells.", c='r') 1525 1526 if n != 1: 1527 vedo.printc("Warning: closest_point() with n>1 is not implemented for cells.", c='r') 1528 1529 trgp = [0, 0, 0] 1530 cid = vtki.mutable(0) 1531 dist2 = vtki.mutable(0) 1532 subid = vtki.mutable(0) 1533 self.cell_locator.FindClosestPoint(pt, trgp, cid, subid, dist2) 1534 1535 if return_cell_id: 1536 return int(cid) 1537 1538 return np.array(trgp) 1539 1540 def auto_distance(self) -> np.ndarray: 1541 """ 1542 Calculate the distance to the closest point in the same cloud of points. 1543 The output is stored in a new pointdata array called "AutoDistance", 1544 and it is also returned by the function. 1545 """ 1546 points = self.coordinates 1547 if not self.point_locator: 1548 self.point_locator = vtki.new("StaticPointLocator") 1549 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(self.dataset) 1550 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1551 qs = [] 1552 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1553 vtkpoints = self.dataset.GetPoints() 1554 for p in points: 1555 self.point_locator.FindClosestNPoints(2, p, vtklist) 1556 q = [0, 0, 0] 1557 pid = vtklist.GetId(1) 1558 vtkpoints.GetPoint(pid, q) 1559 qs.append(q) 1560 dists = np.linalg.norm(points - np.array(qs), axis=1) 1561 self.pointdata["AutoDistance"] = dists 1562 return dists 1563 1564 def hausdorff_distance(self, points) -> float: 1565 """ 1566 Compute the Hausdorff distance to the input point set. 1567 Returns a single `float`. 1568 1569 Example: 1570 ```python 1571 from vedo import * 1572 t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) 1573 x = 4/3 * sin(t)**3 1574 y = cos(t) - cos(2*t)/3 - cos(3*t)/6 - cos(4*t)/12 1575 pol1 = Line(np.c_[x,y], closed=True).triangulate() 1576 pol2 = Polygon(nsides=5).pos(2,2) 1577 d12 = pol1.distance_to(pol2) 1578 d21 = pol2.distance_to(pol1) 1579 pol1.lw(0).cmap("viridis") 1580 pol2.lw(0).cmap("viridis") 1581 print("distance d12, d21 :", min(d12), min(d21)) 1582 print("hausdorff distance:", pol1.hausdorff_distance(pol2)) 1583 print("chamfer distance :", pol1.chamfer_distance(pol2)) 1584 show(pol1, pol2, axes=1) 1585 ``` 1586 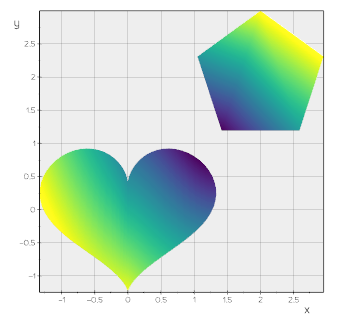 1587 """ 1588 hp = vtki.new("HausdorffDistancePointSetFilter") 1589 hp.SetInputData(0, self.dataset) 1590 hp.SetInputData(1, points.dataset) 1591 hp.SetTargetDistanceMethodToPointToCell() 1592 hp.Update() 1593 return hp.GetHausdorffDistance() 1594 1595 def chamfer_distance(self, pcloud) -> float: 1596 """ 1597 Compute the Chamfer distance to the input point set. 1598 1599 Example: 1600 ```python 1601 from vedo import * 1602 cloud1 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) 1603 cloud2 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) + [1, 2, 3] 1604 c1 = Points(cloud1, r=5, c="red") 1605 c2 = Points(cloud2, r=5, c="green") 1606 d = c1.chamfer_distance(c2) 1607 show(f"Chamfer distance = {d}", c1, c2, axes=1).close() 1608 ``` 1609 """ 1610 # Definition of Chamfer distance may vary, here we use the average 1611 if not pcloud.point_locator: 1612 pcloud.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 1613 pcloud.point_locator.SetDataSet(pcloud.dataset) 1614 pcloud.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1615 if not self.point_locator: 1616 self.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 1617 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(self.dataset) 1618 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1619 1620 ps1 = self.coordinates 1621 ps2 = pcloud.coordinates 1622 1623 ids12 = [] 1624 for p in ps1: 1625 pid12 = pcloud.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1626 ids12.append(pid12) 1627 deltav = ps2[ids12] - ps1 1628 da = np.mean(np.linalg.norm(deltav, axis=1)) 1629 1630 ids21 = [] 1631 for p in ps2: 1632 pid21 = self.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1633 ids21.append(pid21) 1634 deltav = ps1[ids21] - ps2 1635 db = np.mean(np.linalg.norm(deltav, axis=1)) 1636 return (da + db) / 2 1637 1638 def remove_outliers(self, radius: float, neighbors=5) -> Self: 1639 """ 1640 Remove outliers from a cloud of points within the specified `radius` search. 1641 1642 Arguments: 1643 radius : (float) 1644 Specify the local search radius. 1645 neighbors : (int) 1646 Specify the number of neighbors that a point must have, 1647 within the specified radius, for the point to not be considered isolated. 1648 1649 Examples: 1650 - [clustering.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/clustering.py) 1651 1652 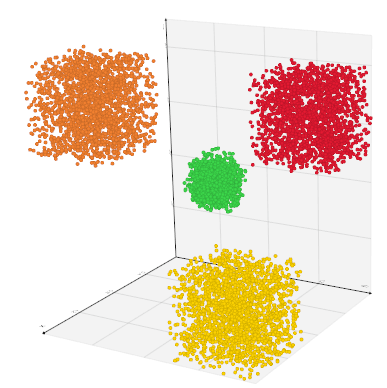 1653 """ 1654 removal = vtki.new("RadiusOutlierRemoval") 1655 removal.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1656 removal.SetRadius(radius) 1657 removal.SetNumberOfNeighbors(neighbors) 1658 removal.GenerateOutliersOff() 1659 removal.Update() 1660 inputobj = removal.GetOutput() 1661 if inputobj.GetNumberOfCells() == 0: 1662 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1663 for i in range(inputobj.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1664 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 1665 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 1666 inputobj.SetVerts(carr) 1667 self._update(removal.GetOutput()) 1668 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("remove_outliers", parents=[self]) 1669 return self 1670 1671 def relax_point_positions( 1672 self, 1673 n=10, 1674 iters=10, 1675 sub_iters=10, 1676 packing_factor=1, 1677 max_step=0, 1678 constraints=(), 1679 ) -> Self: 1680 """ 1681 Smooth mesh or points with a 1682 [Laplacian algorithm](https://vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkPointSmoothingFilter.html) 1683 variant. This modifies the coordinates of the input points by adjusting their positions 1684 to create a smooth distribution (and thereby form a pleasing packing of the points). 1685 Smoothing is performed by considering the effects of neighboring points on one another 1686 it uses a cubic cutoff function to produce repulsive forces between close points 1687 and attractive forces that are a little further away. 1688 1689 In general, the larger the neighborhood size, the greater the reduction in high frequency 1690 information. The memory and computational requirements of the algorithm may also 1691 significantly increase. 1692 1693 The algorithm incrementally adjusts the point positions through an iterative process. 1694 Basically points are moved due to the influence of neighboring points. 1695 1696 As points move, both the local connectivity and data attributes associated with each point 1697 must be updated. Rather than performing these expensive operations after every iteration, 1698 a number of sub-iterations can be specified. If so, then the neighborhood and attribute 1699 value updates occur only every sub iteration, which can improve performance significantly. 1700 1701 Arguments: 1702 n : (int) 1703 neighborhood size to calculate the Laplacian. 1704 iters : (int) 1705 number of iterations. 1706 sub_iters : (int) 1707 number of sub-iterations, i.e. the number of times the neighborhood and attribute 1708 value updates occur during each iteration. 1709 packing_factor : (float) 1710 adjust convergence speed. 1711 max_step : (float) 1712 Specify the maximum smoothing step size for each smoothing iteration. 1713 This limits the the distance over which a point can move in each iteration. 1714 As in all iterative methods, the stability of the process is sensitive to this parameter. 1715 In general, small step size and large numbers of iterations are more stable than a larger 1716 step size and a smaller numbers of iterations. 1717 constraints : (dict) 1718 dictionary of constraints. 1719 Point constraints are used to prevent points from moving, 1720 or to move only on a plane. This can prevent shrinking or growing point clouds. 1721 If enabled, a local topological analysis is performed to determine whether a point 1722 should be marked as fixed" i.e., never moves, or the point only moves on a plane, 1723 or the point can move freely. 1724 If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined by 1725 `fixed_angle`, then the point is classified as fixed. 1726 If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined by 1727 `boundary_angle`, then the point is classified as lying on a plane. 1728 Angles are expressed in degrees. 1729 1730 Example: 1731 ```py 1732 import numpy as np 1733 from vedo import Points, show 1734 from vedo.pyplot import histogram 1735 1736 vpts1 = Points(np.random.rand(10_000, 3)) 1737 dists = vpts1.auto_distance() 1738 h1 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() 1739 1740 vpts2 = vpts1.clone().relax_point_positions(n=100, iters=20, sub_iters=10) 1741 dists = vpts2.auto_distance() 1742 h2 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() 1743 1744 show([[vpts1, h1], [vpts2, h2]], N=2).close() 1745 ``` 1746 """ 1747 smooth = vtki.new("PointSmoothingFilter") 1748 smooth.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1749 smooth.SetSmoothingModeToUniform() 1750 smooth.SetNumberOfIterations(iters) 1751 smooth.SetNumberOfSubIterations(sub_iters) 1752 smooth.SetPackingFactor(packing_factor) 1753 if self.point_locator: 1754 smooth.SetLocator(self.point_locator) 1755 if not max_step: 1756 max_step = self.diagonal_size() / 100 1757 smooth.SetMaximumStepSize(max_step) 1758 smooth.SetNeighborhoodSize(n) 1759 if constraints: 1760 fixed_angle = constraints.get("fixed_angle", 45) 1761 boundary_angle = constraints.get("boundary_angle", 110) 1762 smooth.EnableConstraintsOn() 1763 smooth.SetFixedAngle(fixed_angle) 1764 smooth.SetBoundaryAngle(boundary_angle) 1765 smooth.GenerateConstraintScalarsOn() 1766 smooth.GenerateConstraintNormalsOn() 1767 smooth.Update() 1768 self._update(smooth.GetOutput()) 1769 self.metadata["PackingRadius"] = smooth.GetPackingRadius() 1770 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("relax_point_positions", parents=[self]) 1771 return self 1772 1773 def smooth_mls_1d(self, f=0.2, radius=None, n=0) -> Self: 1774 """ 1775 Smooth mesh or points with a `Moving Least Squares` variant. 1776 The point data array "Variances" will contain the residue calculated for each point. 1777 1778 Arguments: 1779 f : (float) 1780 smoothing factor - typical range is [0,2]. 1781 radius : (float) 1782 radius search in absolute units. 1783 If set then `f` is ignored. 1784 n : (int) 1785 number of neighbours to be used for the fit. 1786 If set then `f` and `radius` are ignored. 1787 1788 Examples: 1789 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 1790 - [skeletonize.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/skeletonize.py) 1791 1792  1793 """ 1794 coords = self.coordinates 1795 ncoords = len(coords) 1796 1797 if n: 1798 Ncp = n 1799 elif radius: 1800 Ncp = 1 1801 else: 1802 Ncp = int(ncoords * f / 10) 1803 if Ncp < 5: 1804 vedo.logger.warning(f"Please choose a fraction higher than {f}") 1805 Ncp = 5 1806 1807 variances, newline = [], [] 1808 for p in coords: 1809 points = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius) 1810 if len(points) < 4: 1811 continue 1812 1813 points = np.array(points) 1814 pointsmean = points.mean(axis=0) # plane center 1815 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(points - pointsmean) 1816 newp = np.dot(p - pointsmean, vv[0]) * vv[0] + pointsmean 1817 variances.append(dd[1] + dd[2]) 1818 newline.append(newp) 1819 1820 self.pointdata["Variances"] = np.array(variances).astype(np.float32) 1821 self.coordinates = newline 1822 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_mls_1d", parents=[self]) 1823 return self 1824 1825 def smooth_mls_2d(self, f=0.2, radius=None, n=0) -> Self: 1826 """ 1827 Smooth mesh or points with a `Moving Least Squares` algorithm variant. 1828 1829 The `mesh.pointdata['MLSVariance']` array will contain the residue calculated for each point. 1830 When a radius is specified, points that are isolated will not be moved and will get 1831 a 0 entry in array `mesh.pointdata['MLSValidPoint']`. 1832 1833 Arguments: 1834 f : (float) 1835 smoothing factor - typical range is [0, 2]. 1836 radius : (float | array) 1837 radius search in absolute units. Can be single value (float) or sequence 1838 for adaptive smoothing. If set then `f` is ignored. 1839 n : (int) 1840 number of neighbours to be used for the fit. 1841 If set then `f` and `radius` are ignored. 1842 1843 Examples: 1844 - [moving_least_squares2D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares2D.py) 1845 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 1846 1847  1848 """ 1849 coords = self.coordinates 1850 ncoords = len(coords) 1851 1852 if n: 1853 Ncp = n 1854 radius = None 1855 elif radius is not None: 1856 Ncp = 1 1857 else: 1858 Ncp = int(ncoords * f / 100) 1859 if Ncp < 4: 1860 vedo.logger.error(f"please choose a f-value higher than {f}") 1861 Ncp = 4 1862 1863 variances, newpts, valid = [], [], [] 1864 radius_is_sequence = utils.is_sequence(radius) 1865 1866 pb = None 1867 if ncoords > 10000: 1868 pb = utils.ProgressBar(0, ncoords, delay=3) 1869 1870 for i, p in enumerate(coords): 1871 if pb: 1872 pb.print("smooth_mls_2d working ...") 1873 1874 # if a radius was provided for each point 1875 if radius_is_sequence: 1876 pts = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius[i]) 1877 else: 1878 pts = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius) 1879 1880 if len(pts) > 3: 1881 ptsmean = pts.mean(axis=0) # plane center 1882 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(pts - ptsmean) 1883 cv = np.cross(vv[0], vv[1]) 1884 t = (np.dot(cv, ptsmean) - np.dot(cv, p)) / np.dot(cv, cv) 1885 newpts.append(p + cv * t) 1886 variances.append(dd[2]) 1887 if radius is not None: 1888 valid.append(1) 1889 else: 1890 newpts.append(p) 1891 variances.append(0) 1892 if radius is not None: 1893 valid.append(0) 1894 1895 if radius is not None: 1896 self.pointdata["MLSValidPoint"] = np.array(valid).astype(np.uint8) 1897 self.pointdata["MLSVariance"] = np.array(variances).astype(np.float32) 1898 1899 self.coordinates = newpts 1900 1901 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_mls_2d", parents=[self]) 1902 return self 1903 1904 def smooth_lloyd_2d(self, iterations=2, bounds=None, options="Qbb Qc Qx") -> Self: 1905 """ 1906 Lloyd relaxation of a 2D pointcloud. 1907 1908 Arguments: 1909 iterations : (int) 1910 number of iterations. 1911 bounds : (list) 1912 bounding box of the domain. 1913 options : (str) 1914 options for the Qhull algorithm. 1915 """ 1916 # Credits: https://hatarilabs.com/ih-en/ 1917 # tutorial-to-create-a-geospatial-voronoi-sh-mesh-with-python-scipy-and-geopandas 1918 from scipy.spatial import Voronoi as scipy_voronoi 1919 1920 def _constrain_points(points): 1921 # Update any points that have drifted beyond the boundaries of this space 1922 if bounds is not None: 1923 for point in points: 1924 if point[0] < bounds[0]: point[0] = bounds[0] 1925 if point[0] > bounds[1]: point[0] = bounds[1] 1926 if point[1] < bounds[2]: point[1] = bounds[2] 1927 if point[1] > bounds[3]: point[1] = bounds[3] 1928 return points 1929 1930 def _find_centroid(vertices): 1931 # The equation for the method used here to find the centroid of a 1932 # 2D polygon is given here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centroid#Of_a_polygon 1933 area = 0 1934 centroid_x = 0 1935 centroid_y = 0 1936 for i in range(len(vertices) - 1): 1937 step = (vertices[i, 0] * vertices[i + 1, 1]) - (vertices[i + 1, 0] * vertices[i, 1]) 1938 centroid_x += (vertices[i, 0] + vertices[i + 1, 0]) * step 1939 centroid_y += (vertices[i, 1] + vertices[i + 1, 1]) * step 1940 area += step 1941 if area: 1942 centroid_x = (1.0 / (3.0 * area)) * centroid_x 1943 centroid_y = (1.0 / (3.0 * area)) * centroid_y 1944 # prevent centroids from escaping bounding box 1945 return _constrain_points([[centroid_x, centroid_y]])[0] 1946 1947 def _relax(voron): 1948 # Moves each point to the centroid of its cell in the voronoi 1949 # map to "relax" the points (i.e. jitter the points so as 1950 # to spread them out within the space). 1951 centroids = [] 1952 for idx in voron.point_region: 1953 # the region is a series of indices into voronoi.vertices 1954 # remove point at infinity, designated by index -1 1955 region = [i for i in voron.regions[idx] if i != -1] 1956 # enclose the polygon 1957 region = region + [region[0]] 1958 verts = voron.vertices[region] 1959 # find the centroid of those vertices 1960 centroids.append(_find_centroid(verts)) 1961 return _constrain_points(centroids) 1962 1963 if bounds is None: 1964 bounds = self.bounds() 1965 1966 pts = self.vertices[:, (0, 1)] 1967 for i in range(iterations): 1968 vor = scipy_voronoi(pts, qhull_options=options) 1969 _constrain_points(vor.vertices) 1970 pts = _relax(vor) 1971 out = Points(pts) 1972 out.name = "MeshSmoothLloyd2D" 1973 out.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_lloyd", parents=[self]) 1974 return out 1975 1976 def project_on_plane(self, plane="z", point=None, direction=None) -> Self: 1977 """ 1978 Project the mesh on one of the Cartesian planes. 1979 1980 Arguments: 1981 plane : (str, Plane) 1982 if plane is `str`, plane can be one of ['x', 'y', 'z'], 1983 represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. 1984 Otherwise, plane should be an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane`. 1985 point : (float, array) 1986 if plane is `str`, point should be a float represents the intercept. 1987 Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection 1988 direction : (array) 1989 direction of oblique projection 1990 1991 Note: 1992 Parameters `point` and `direction` are only used if the given plane 1993 is an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane`. And one of these two params 1994 should be left as `None` to specify the projection type. 1995 1996 Example: 1997 ```python 1998 s.project_on_plane(plane='z') # project to z-plane 1999 plane = Plane(pos=(4, 8, -4), normal=(-1, 0, 1), s=(5,5)) 2000 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane) # orthogonal projection 2001 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, point=(6, 6, 6)) # perspective projection 2002 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, direction=(1, 2, -1)) # oblique projection 2003 ``` 2004 2005 Examples: 2006 - [silhouette2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/silhouette2.py) 2007 2008 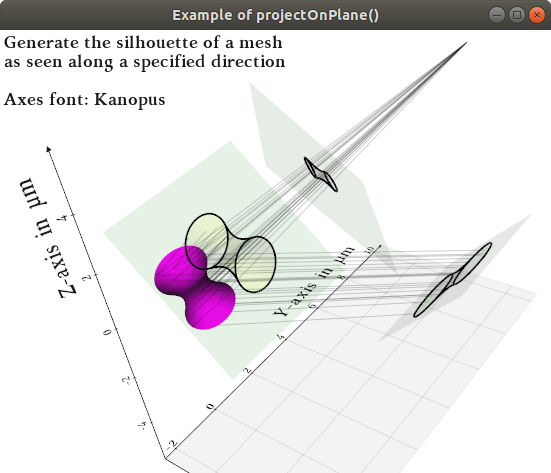 2009 """ 2010 coords = self.coordinates 2011 2012 if plane == "x": 2013 coords[:, 0] = self.transform.position[0] 2014 intercept = self.xbounds()[0] if point is None else point 2015 self.x(intercept) 2016 elif plane == "y": 2017 coords[:, 1] = self.transform.position[1] 2018 intercept = self.ybounds()[0] if point is None else point 2019 self.y(intercept) 2020 elif plane == "z": 2021 coords[:, 2] = self.transform.position[2] 2022 intercept = self.zbounds()[0] if point is None else point 2023 self.z(intercept) 2024 2025 elif isinstance(plane, vedo.shapes.Plane): 2026 normal = plane.normal / np.linalg.norm(plane.normal) 2027 pl = np.hstack((normal, -np.dot(plane.pos(), normal))).reshape(4, 1) 2028 if direction is None and point is None: 2029 # orthogonal projection 2030 pt = np.hstack((normal, [0])).reshape(4, 1) 2031 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T # python3 only 2032 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2033 2034 elif direction is None: 2035 # perspective projection 2036 pt = np.hstack((np.array(point), [1])).reshape(4, 1) 2037 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T 2038 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2039 2040 elif point is None: 2041 # oblique projection 2042 pt = np.hstack((np.array(direction), [0])).reshape(4, 1) 2043 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T 2044 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2045 2046 coords = np.concatenate([coords, np.ones((coords.shape[:-1] + (1,)))], axis=-1) 2047 # coords = coords @ proj_mat.T 2048 coords = np.matmul(coords, proj_mat.T) 2049 coords = coords[:, :3] / coords[:, 3:] 2050 2051 else: 2052 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown plane {plane}") 2053 raise RuntimeError() 2054 2055 self.alpha(0.1) 2056 self.coordinates = coords 2057 return self 2058 2059 def warp(self, source, target, sigma=1.0, mode="3d") -> Self: 2060 """ 2061 "Thin Plate Spline" transformations describe a nonlinear warp transform defined by a set 2062 of source and target landmarks. Any point on the mesh close to a source landmark will 2063 be moved to a place close to the corresponding target landmark. 2064 The points in between are interpolated smoothly using 2065 Bookstein's Thin Plate Spline algorithm. 2066 2067 Transformation object can be accessed with `mesh.transform`. 2068 2069 Arguments: 2070 sigma : (float) 2071 specify the 'stiffness' of the spline. 2072 mode : (str) 2073 set the basis function to either abs(R) (for 3d) or R2LogR (for 2d meshes) 2074 2075 Examples: 2076 - [interpolate_field.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/interpolate_field.py) 2077 - [warp1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp1.py) 2078 - [warp2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp2.py) 2079 - [warp3.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp3.py) 2080 - [warp4a.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp4a.py) 2081 - [warp4b.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp4b.py) 2082 - [warp6.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp6.py) 2083 2084  2085 """ 2086 parents = [self] 2087 2088 try: 2089 source = source.coordinates 2090 parents.append(source) 2091 except AttributeError: 2092 source = utils.make3d(source) 2093 2094 try: 2095 target = target.coordinates 2096 parents.append(target) 2097 except AttributeError: 2098 target = utils.make3d(target) 2099 2100 ns = len(source) 2101 nt = len(target) 2102 if ns != nt: 2103 vedo.logger.error(f"#source {ns} != {nt} #target points") 2104 raise RuntimeError() 2105 2106 NLT = NonLinearTransform(sigma=sigma, mode=mode) 2107 NLT.source_points = source 2108 NLT.target_points = target 2109 self.apply_transform(NLT) 2110 2111 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("warp", parents=parents) 2112 return self 2113 2114 def cut_with_plane( 2115 self, 2116 origin=(0, 0, 0), 2117 normal=(1, 0, 0), 2118 invert=False, 2119 # generate_ids=False, 2120 ) -> Self: 2121 """ 2122 Cut the mesh with the plane defined by a point and a normal. 2123 2124 Arguments: 2125 origin : (array) 2126 the cutting plane goes through this point 2127 normal : (array) 2128 normal of the cutting plane 2129 invert : (bool) 2130 select which side of the plane to keep 2131 2132 Example: 2133 ```python 2134 from vedo import Cube 2135 cube = Cube().cut_with_plane(normal=(1,1,1)) 2136 cube.back_color('pink').show().close() 2137 ``` 2138  2139 2140 Examples: 2141 - [trail.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/simulations/trail.py) 2142 2143  2144 2145 Check out also: 2146 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_cylinder()`, `cut_with_sphere()`. 2147 """ 2148 s = str(normal) 2149 if "x" in s: 2150 normal = (1, 0, 0) 2151 if "-" in s: 2152 normal = -np.array(normal) 2153 elif "y" in s: 2154 normal = (0, 1, 0) 2155 if "-" in s: 2156 normal = -np.array(normal) 2157 elif "z" in s: 2158 normal = (0, 0, 1) 2159 if "-" in s: 2160 normal = -np.array(normal) 2161 plane = vtki.vtkPlane() 2162 plane.SetOrigin(origin) 2163 plane.SetNormal(normal) 2164 2165 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2166 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2167 clipper.SetClipFunction(plane) 2168 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2169 clipper.SetGenerateClipScalars(0) 2170 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2171 clipper.SetValue(0) 2172 clipper.Update() 2173 2174 # if generate_ids: 2175 # saved_scalars = None # otherwise the scalars are lost 2176 # if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 2177 # saved_scalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 2178 # varr = clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetScalars() 2179 # if varr.GetName() is None: 2180 # varr.SetName("DistanceToCut") 2181 # arr = utils.vtk2numpy(varr) 2182 # # array of original ids 2183 # ids = np.arange(arr.shape[0]).astype(int) 2184 # ids[arr == 0] = -1 2185 # ids_arr = utils.numpy2vtk(ids, dtype=int) 2186 # ids_arr.SetName("OriginalIds") 2187 # clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().AddArray(ids_arr) 2188 # if saved_scalars: 2189 # clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().AddArray(saved_scalars) 2190 2191 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2192 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_plane", parents=[self]) 2193 return self 2194 2195 def cut_with_planes(self, origins, normals, invert=False) -> Self: 2196 """ 2197 Cut the mesh with a convex set of planes defined by points and normals. 2198 2199 Arguments: 2200 origins : (array) 2201 each cutting plane goes through this point 2202 normals : (array) 2203 normal of each of the cutting planes 2204 invert : (bool) 2205 if True, cut outside instead of inside 2206 2207 Check out also: 2208 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_cylinder()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2209 """ 2210 2211 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 2212 for p in utils.make3d(origins): 2213 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 2214 normals = utils.make3d(normals) 2215 2216 planes = vtki.vtkPlanes() 2217 planes.SetPoints(vpoints) 2218 planes.SetNormals(utils.numpy2vtk(normals, dtype=float)) 2219 2220 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2221 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2222 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2223 clipper.SetClipFunction(planes) 2224 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2225 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2226 clipper.SetValue(0) 2227 clipper.Update() 2228 2229 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2230 2231 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_planes", parents=[self]) 2232 return self 2233 2234 def cut_with_box(self, bounds, invert=False) -> Self: 2235 """ 2236 Cut the current mesh with a box or a set of boxes. 2237 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2238 2239 Input `bounds` can be either: 2240 - a Mesh or Points object 2241 - a list of 6 number representing a bounding box `[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]` 2242 - a list of bounding boxes like the above: `[[xmin1,...], [xmin2,...], ...]` 2243 2244 Example: 2245 ```python 2246 from vedo import Sphere, Cube, show 2247 mesh = Sphere(r=1, res=50) 2248 box = Cube(side=1.5).wireframe() 2249 mesh.cut_with_box(box) 2250 show(mesh, box, axes=1).close() 2251 ``` 2252  2253 2254 Check out also: 2255 `cut_with_line()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2256 """ 2257 if isinstance(bounds, Points): 2258 bounds = bounds.bounds() 2259 2260 box = vtki.new("Box") 2261 if utils.is_sequence(bounds[0]): 2262 for bs in bounds: 2263 box.AddBounds(bs) 2264 else: 2265 box.SetBounds(bounds) 2266 2267 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2268 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2269 clipper.SetClipFunction(box) 2270 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2271 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2272 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2273 clipper.SetValue(0) 2274 clipper.Update() 2275 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2276 2277 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_box", parents=[self]) 2278 return self 2279 2280 def cut_with_line(self, points, invert=False, closed=True) -> Self: 2281 """ 2282 Cut the current mesh with a line vertically in the z-axis direction like a cookie cutter. 2283 The polyline is defined by a set of points (z-coordinates are ignored). 2284 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2285 2286 Check out also: 2287 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2288 """ 2289 pplane = vtki.new("PolyPlane") 2290 if isinstance(points, Points): 2291 points = points.coordinates.tolist() 2292 2293 if closed: 2294 if isinstance(points, np.ndarray): 2295 points = points.tolist() 2296 points.append(points[0]) 2297 2298 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 2299 for p in points: 2300 if len(p) == 2: 2301 p = [p[0], p[1], 0.0] 2302 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 2303 2304 n = len(points) 2305 polyline = vtki.new("PolyLine") 2306 polyline.Initialize(n, vpoints) 2307 polyline.GetPointIds().SetNumberOfIds(n) 2308 for i in range(n): 2309 polyline.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i) 2310 pplane.SetPolyLine(polyline) 2311 2312 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2313 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2314 clipper.SetClipFunction(pplane) 2315 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2316 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2317 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2318 clipper.SetValue(0) 2319 clipper.Update() 2320 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2321 2322 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_line", parents=[self]) 2323 return self 2324 2325 def cut_with_cookiecutter(self, lines) -> Self: 2326 """ 2327 Cut the current mesh with a single line or a set of lines. 2328 2329 Input `lines` can be either: 2330 - a `Mesh` or `Points` object 2331 - a list of 3D points: `[(x1,y1,z1), (x2,y2,z2), ...]` 2332 - a list of 2D points: `[(x1,y1), (x2,y2), ...]` 2333 2334 Example: 2335 ```python 2336 from vedo import * 2337 grid = Mesh(dataurl + "dolfin_fine.vtk") 2338 grid.compute_quality().cmap("Greens") 2339 pols = merge( 2340 Polygon(nsides=10, r=0.3).pos(0.7, 0.3), 2341 Polygon(nsides=10, r=0.2).pos(0.3, 0.7), 2342 ) 2343 lines = pols.boundaries() 2344 cgrid = grid.clone().cut_with_cookiecutter(lines) 2345 grid.alpha(0.1).wireframe() 2346 show(grid, cgrid, lines, axes=8, bg='blackboard').close() 2347 ``` 2348  2349 2350 Check out also: 2351 `cut_with_line()` and `cut_with_point_loop()` 2352 2353 Note: 2354 In case of a warning message like: 2355 "Mesh and trim loop point data attributes are different" 2356 consider interpolating the mesh point data to the loop points, 2357 Eg. (in the above example): 2358 ```python 2359 lines = pols.boundaries().interpolate_data_from(grid, n=2) 2360 ``` 2361 2362 Note: 2363 trying to invert the selection by reversing the loop order 2364 will have no effect in this method, hence it does not have 2365 the `invert` option. 2366 """ 2367 if utils.is_sequence(lines): 2368 lines = utils.make3d(lines) 2369 iline = list(range(len(lines))) + [0] 2370 poly = utils.buildPolyData(lines, lines=[iline]) 2371 else: 2372 poly = lines.dataset 2373 2374 # if invert: # not working 2375 # rev = vtki.new("ReverseSense") 2376 # rev.ReverseCellsOn() 2377 # rev.SetInputData(poly) 2378 # rev.Update() 2379 # poly = rev.GetOutput() 2380 2381 # Build loops from the polyline 2382 build_loops = vtki.new("ContourLoopExtraction") 2383 build_loops.SetGlobalWarningDisplay(0) 2384 build_loops.SetInputData(poly) 2385 build_loops.Update() 2386 boundary_poly = build_loops.GetOutput() 2387 2388 ccut = vtki.new("CookieCutter") 2389 ccut.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2390 ccut.SetLoopsData(boundary_poly) 2391 ccut.SetPointInterpolationToMeshEdges() 2392 # ccut.SetPointInterpolationToLoopEdges() 2393 ccut.PassCellDataOn() 2394 ccut.PassPointDataOn() 2395 ccut.Update() 2396 self._update(ccut.GetOutput()) 2397 2398 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_cookiecutter", parents=[self]) 2399 return self 2400 2401 def cut_with_cylinder(self, center=(0, 0, 0), axis=(0, 0, 1), r=1, invert=False) -> Self: 2402 """ 2403 Cut the current mesh with an infinite cylinder. 2404 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2405 2406 Arguments: 2407 center : (array) 2408 the center of the cylinder 2409 normal : (array) 2410 direction of the cylinder axis 2411 r : (float) 2412 radius of the cylinder 2413 2414 Example: 2415 ```python 2416 from vedo import Disc, show 2417 disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) 2418 mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) 2419 mesh.cut_with_cylinder([0,0,2], r=0.4, axis='y', invert=True) 2420 show(mesh, axes=1).close() 2421 ``` 2422  2423 2424 Examples: 2425 - [optics_main1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/simulations/optics_main1.py) 2426 2427 Check out also: 2428 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2429 """ 2430 s = str(axis) 2431 if "x" in s: 2432 axis = (1, 0, 0) 2433 elif "y" in s: 2434 axis = (0, 1, 0) 2435 elif "z" in s: 2436 axis = (0, 0, 1) 2437 cyl = vtki.new("Cylinder") 2438 cyl.SetCenter(center) 2439 cyl.SetAxis(axis[0], axis[1], axis[2]) 2440 cyl.SetRadius(r) 2441 2442 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2443 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2444 clipper.SetClipFunction(cyl) 2445 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2446 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2447 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2448 clipper.SetValue(0) 2449 clipper.Update() 2450 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2451 2452 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_cylinder", parents=[self]) 2453 return self 2454 2455 def cut_with_sphere(self, center=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, invert=False) -> Self: 2456 """ 2457 Cut the current mesh with an sphere. 2458 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2459 2460 Arguments: 2461 center : (array) 2462 the center of the sphere 2463 r : (float) 2464 radius of the sphere 2465 2466 Example: 2467 ```python 2468 from vedo import Disc, show 2469 disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) 2470 mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) 2471 mesh.cut_with_sphere([1,-0.7,2], r=1.5, invert=True) 2472 show(mesh, axes=1).close() 2473 ``` 2474  2475 2476 Check out also: 2477 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2478 """ 2479 sph = vtki.new("Sphere") 2480 sph.SetCenter(center) 2481 sph.SetRadius(r) 2482 2483 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2484 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2485 clipper.SetClipFunction(sph) 2486 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2487 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2488 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2489 clipper.SetValue(0) 2490 clipper.Update() 2491 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2492 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_sphere", parents=[self]) 2493 return self 2494 2495 def cut_with_mesh(self, mesh, invert=False, keep=False) -> Union[Self, "vedo.Assembly"]: 2496 """ 2497 Cut an `Mesh` mesh with another `Mesh`. 2498 2499 Use `invert` to invert the selection. 2500 2501 Use `keep` to keep the cutoff part, in this case an `Assembly` is returned: 2502 the "cut" object and the "discarded" part of the original object. 2503 You can access both via `assembly.unpack()` method. 2504 2505 Example: 2506 ```python 2507 from vedo import * 2508 arr = np.random.randn(100000, 3)/2 2509 pts = Points(arr).c('red3').pos(5,0,0) 2510 cube = Cube().pos(4,0.5,0) 2511 assem = pts.cut_with_mesh(cube, keep=True) 2512 show(assem.unpack(), axes=1).close() 2513 ``` 2514  2515 2516 Check out also: 2517 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2518 """ 2519 polymesh = mesh.dataset 2520 poly = self.dataset 2521 2522 # Create an array to hold distance information 2523 signed_distances = vtki.vtkFloatArray() 2524 signed_distances.SetNumberOfComponents(1) 2525 signed_distances.SetName("SignedDistances") 2526 2527 # implicit function that will be used to slice the mesh 2528 ippd = vtki.new("ImplicitPolyDataDistance") 2529 ippd.SetInput(polymesh) 2530 2531 # Evaluate the signed distance function at all of the grid points 2532 for pointId in range(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()): 2533 p = poly.GetPoint(pointId) 2534 signed_distance = ippd.EvaluateFunction(p) 2535 signed_distances.InsertNextValue(signed_distance) 2536 2537 currentscals = poly.GetPointData().GetScalars() 2538 if currentscals: 2539 currentscals = currentscals.GetName() 2540 2541 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(signed_distances) 2542 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("SignedDistances") 2543 2544 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2545 clipper.SetInputData(poly) 2546 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2547 clipper.SetGenerateClippedOutput(keep) 2548 clipper.SetValue(0.0) 2549 clipper.Update() 2550 cpoly = clipper.GetOutput() 2551 2552 if keep: 2553 kpoly = clipper.GetOutput(1) 2554 2555 vis = False 2556 if currentscals: 2557 cpoly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(currentscals) 2558 vis = self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility() 2559 2560 self._update(cpoly) 2561 2562 self.pointdata.remove("SignedDistances") 2563 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(vis) 2564 if keep: 2565 if isinstance(self, vedo.Mesh): 2566 cutoff = vedo.Mesh(kpoly) 2567 else: 2568 cutoff = vedo.Points(kpoly) 2569 # cutoff = self.__class__(kpoly) # this does not work properly 2570 cutoff.properties = vtki.vtkProperty() 2571 cutoff.properties.DeepCopy(self.properties) 2572 cutoff.actor.SetProperty(cutoff.properties) 2573 cutoff.c("k5").alpha(0.2) 2574 return vedo.Assembly([self, cutoff]) 2575 2576 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_mesh", parents=[self, mesh]) 2577 return self 2578 2579 def cut_with_point_loop( 2580 self, points, invert=False, on="points", include_boundary=False 2581 ) -> Self: 2582 """ 2583 Cut an `Mesh` object with a set of points forming a closed loop. 2584 2585 Arguments: 2586 invert : (bool) 2587 invert selection (inside-out) 2588 on : (str) 2589 if 'cells' will extract the whole cells lying inside (or outside) the point loop 2590 include_boundary : (bool) 2591 include cells lying exactly on the boundary line. Only relevant on 'cells' mode 2592 2593 Examples: 2594 - [cut_with_points1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/cut_with_points1.py) 2595 2596  2597 2598 - [cut_with_points2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/cut_with_points2.py) 2599 2600 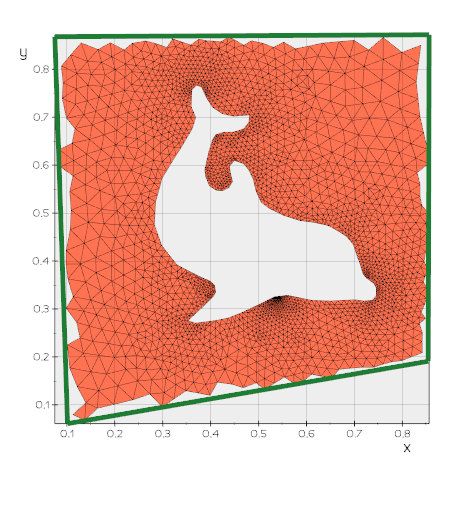 2601 """ 2602 if isinstance(points, Points): 2603 parents = [points] 2604 vpts = points.dataset.GetPoints() 2605 points = points.coordinates 2606 else: 2607 parents = [self] 2608 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 2609 points = utils.make3d(points) 2610 for p in points: 2611 vpts.InsertNextPoint(p) 2612 2613 if "cell" in on: 2614 ippd = vtki.new("ImplicitSelectionLoop") 2615 ippd.SetLoop(vpts) 2616 ippd.AutomaticNormalGenerationOn() 2617 clipper = vtki.new("ExtractPolyDataGeometry") 2618 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2619 clipper.SetImplicitFunction(ippd) 2620 clipper.SetExtractInside(not invert) 2621 clipper.SetExtractBoundaryCells(include_boundary) 2622 else: 2623 spol = vtki.new("SelectPolyData") 2624 spol.SetLoop(vpts) 2625 spol.GenerateSelectionScalarsOn() 2626 spol.GenerateUnselectedOutputOff() 2627 spol.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2628 spol.Update() 2629 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2630 clipper.SetInputData(spol.GetOutput()) 2631 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2632 clipper.SetValue(0.0) 2633 clipper.Update() 2634 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2635 2636 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_pointloop", parents=parents) 2637 return self 2638 2639 def cut_with_scalar(self, value: float, name="", invert=False) -> Self: 2640 """ 2641 Cut a mesh or point cloud with some input scalar point-data. 2642 2643 Arguments: 2644 value : (float) 2645 cutting value 2646 name : (str) 2647 array name of the scalars to be used 2648 invert : (bool) 2649 flip selection 2650 2651 Example: 2652 ```python 2653 from vedo import * 2654 s = Sphere().lw(1) 2655 pts = s.points 2656 scalars = np.sin(3*pts[:,2]) + pts[:,0] 2657 s.pointdata["somevalues"] = scalars 2658 s.cut_with_scalar(0.3) 2659 s.cmap("Spectral", "somevalues").add_scalarbar() 2660 s.show(axes=1).close() 2661 ``` 2662 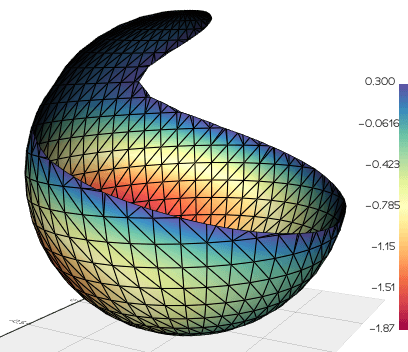 2663 """ 2664 if name: 2665 self.pointdata.select(name) 2666 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2667 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2668 clipper.SetValue(value) 2669 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2670 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2671 clipper.Update() 2672 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2673 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_scalar", parents=[self]) 2674 return self 2675 2676 def crop(self, 2677 top=None, bottom=None, right=None, left=None, front=None, back=None, 2678 bounds=()) -> Self: 2679 """ 2680 Crop an `Mesh` object. 2681 2682 Arguments: 2683 top : (float) 2684 fraction to crop from the top plane (positive z) 2685 bottom : (float) 2686 fraction to crop from the bottom plane (negative z) 2687 front : (float) 2688 fraction to crop from the front plane (positive y) 2689 back : (float) 2690 fraction to crop from the back plane (negative y) 2691 right : (float) 2692 fraction to crop from the right plane (positive x) 2693 left : (float) 2694 fraction to crop from the left plane (negative x) 2695 bounds : (list) 2696 bounding box of the crop region as `[x0,x1, y0,y1, z0,z1]` 2697 2698 Example: 2699 ```python 2700 from vedo import Sphere 2701 Sphere().crop(right=0.3, left=0.1).show() 2702 ``` 2703 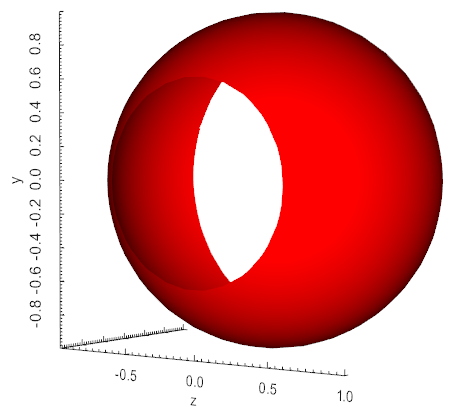 2704 """ 2705 if len(bounds) == 0: 2706 pos = np.array(self.pos()) 2707 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2708 x0, y0, z0 = [x0, y0, z0] - pos 2709 x1, y1, z1 = [x1, y1, z1] - pos 2710 2711 dx, dy, dz = x1 - x0, y1 - y0, z1 - z0 2712 if top: 2713 z1 = z1 - top * dz 2714 if bottom: 2715 z0 = z0 + bottom * dz 2716 if front: 2717 y1 = y1 - front * dy 2718 if back: 2719 y0 = y0 + back * dy 2720 if right: 2721 x1 = x1 - right * dx 2722 if left: 2723 x0 = x0 + left * dx 2724 bounds = (x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1) 2725 2726 cu = vtki.new("Box") 2727 cu.SetBounds(bounds) 2728 2729 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2730 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2731 clipper.SetClipFunction(cu) 2732 clipper.InsideOutOn() 2733 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2734 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2735 clipper.SetValue(0) 2736 clipper.Update() 2737 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2738 2739 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2740 "crop", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 2741 ) 2742 return self 2743 2744 def generate_surface_halo( 2745 self, 2746 distance=0.05, 2747 res=(50, 50, 50), 2748 bounds=(), 2749 maxdist=None, 2750 ) -> "vedo.Mesh": 2751 """ 2752 Generate the surface halo which sits at the specified distance from the input one. 2753 2754 Arguments: 2755 distance : (float) 2756 distance from the input surface 2757 res : (int) 2758 resolution of the surface 2759 bounds : (list) 2760 bounding box of the surface 2761 maxdist : (float) 2762 maximum distance to generate the surface 2763 """ 2764 if not bounds: 2765 bounds = self.bounds() 2766 2767 if not maxdist: 2768 maxdist = self.diagonal_size() / 2 2769 2770 imp = vtki.new("ImplicitModeller") 2771 imp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2772 imp.SetSampleDimensions(res) 2773 if maxdist: 2774 imp.SetMaximumDistance(maxdist) 2775 if len(bounds) == 6: 2776 imp.SetModelBounds(bounds) 2777 contour = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 2778 contour.SetInputConnection(imp.GetOutputPort()) 2779 contour.SetValue(0, distance) 2780 contour.Update() 2781 out = vedo.Mesh(contour.GetOutput()) 2782 out.c("lightblue").alpha(0.25).lighting("off") 2783 out.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("generate_surface_halo", parents=[self]) 2784 return out 2785 2786 def generate_mesh( 2787 self, 2788 line_resolution=None, 2789 mesh_resolution=None, 2790 smooth=0.0, 2791 jitter=0.001, 2792 grid=None, 2793 quads=False, 2794 invert=False, 2795 ) -> Self: 2796 """ 2797 Generate a polygonal Mesh from a closed contour line. 2798 If line is not closed it will be closed with a straight segment. 2799 2800 Check also `generate_delaunay2d()`. 2801 2802 Arguments: 2803 line_resolution : (int) 2804 resolution of the contour line. The default is None, in this case 2805 the contour is not resampled. 2806 mesh_resolution : (int) 2807 resolution of the internal triangles not touching the boundary. 2808 smooth : (float) 2809 smoothing of the contour before meshing. 2810 jitter : (float) 2811 add a small noise to the internal points. 2812 grid : (Grid) 2813 manually pass a Grid object. The default is True. 2814 quads : (bool) 2815 generate a mesh of quads instead of triangles. 2816 invert : (bool) 2817 flip the line orientation. The default is False. 2818 2819 Examples: 2820 - [line2mesh_tri.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/line2mesh_tri.py) 2821 2822 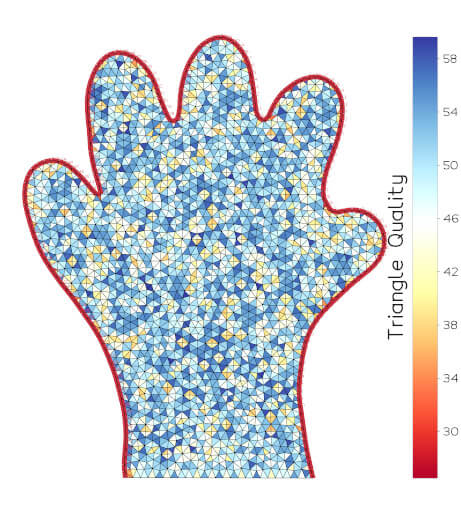 2823 2824 - [line2mesh_quads.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/line2mesh_quads.py) 2825 2826 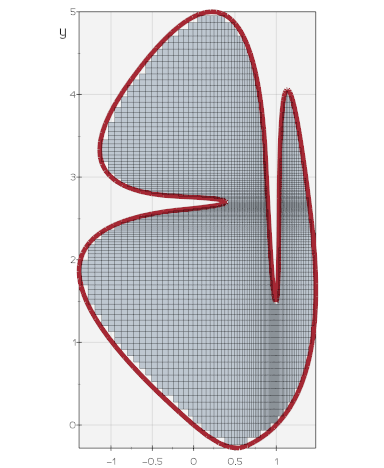 2827 """ 2828 if line_resolution is None: 2829 contour = vedo.shapes.Line(self.coordinates) 2830 else: 2831 contour = vedo.shapes.Spline(self.coordinates, smooth=smooth, res=line_resolution) 2832 contour.clean() 2833 2834 length = contour.length() 2835 density = length / contour.npoints 2836 # print(f"tomesh():\n\tline length = {length}") 2837 # print(f"\tdensity = {density} length/pt_separation") 2838 2839 x0, x1 = contour.xbounds() 2840 y0, y1 = contour.ybounds() 2841 2842 if grid is None: 2843 if mesh_resolution is None: 2844 resx = int((x1 - x0) / density + 0.5) 2845 resy = int((y1 - y0) / density + 0.5) 2846 # print(f"tmesh_resolution = {[resx, resy]}") 2847 else: 2848 if utils.is_sequence(mesh_resolution): 2849 resx, resy = mesh_resolution 2850 else: 2851 resx, resy = mesh_resolution, mesh_resolution 2852 grid = vedo.shapes.Grid( 2853 [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, 0], 2854 s=((x1 - x0) * 1.025, (y1 - y0) * 1.025), 2855 res=(resx, resy), 2856 ) 2857 else: 2858 grid = grid.clone() 2859 2860 cpts = contour.coordinates 2861 2862 # make sure it's closed 2863 p0, p1 = cpts[0], cpts[-1] 2864 nj = max(2, int(utils.mag(p1 - p0) / density + 0.5)) 2865 joinline = vedo.shapes.Line(p1, p0, res=nj) 2866 contour = vedo.merge(contour, joinline).subsample(0.0001) 2867 2868 ####################################### quads 2869 if quads: 2870 cmesh = grid.clone().cut_with_point_loop(contour, on="cells", invert=invert) 2871 cmesh.wireframe(False).lw(0.5) 2872 cmesh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2873 "generate_mesh", 2874 parents=[self, contour], 2875 comment=f"#quads {cmesh.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 2876 ) 2877 return cmesh 2878 ############################################# 2879 2880 grid_tmp = grid.coordinates.copy() 2881 2882 if jitter: 2883 np.random.seed(0) 2884 sigma = 1.0 / np.sqrt(grid.npoints) * grid.diagonal_size() * jitter 2885 # print(f"\tsigma jittering = {sigma}") 2886 grid_tmp += np.random.rand(grid.npoints, 3) * sigma 2887 grid_tmp[:, 2] = 0.0 2888 2889 todel = [] 2890 density /= np.sqrt(3) 2891 vgrid_tmp = Points(grid_tmp) 2892 2893 for p in contour.coordinates: 2894 out = vgrid_tmp.closest_point(p, radius=density, return_point_id=True) 2895 todel += out.tolist() 2896 2897 grid_tmp = grid_tmp.tolist() 2898 for index in sorted(list(set(todel)), reverse=True): 2899 del grid_tmp[index] 2900 2901 points = contour.coordinates.tolist() + grid_tmp 2902 if invert: 2903 boundary = list(reversed(range(contour.npoints))) 2904 else: 2905 boundary = list(range(contour.npoints)) 2906 2907 dln = Points(points).generate_delaunay2d(mode="xy", boundaries=[boundary]) 2908 dln.compute_normals(points=False) # fixes reversd faces 2909 dln.lw(1) 2910 2911 dln.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2912 "generate_mesh", 2913 parents=[self, contour], 2914 comment=f"#cells {dln.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 2915 ) 2916 return dln 2917 2918 def reconstruct_surface( 2919 self, 2920 dims=(100, 100, 100), 2921 radius=None, 2922 sample_size=None, 2923 hole_filling=True, 2924 bounds=(), 2925 padding=0.05, 2926 ) -> "vedo.Mesh": 2927 """ 2928 Surface reconstruction from a scattered cloud of points. 2929 2930 Arguments: 2931 dims : (int) 2932 number of voxels in x, y and z to control precision. 2933 radius : (float) 2934 radius of influence of each point. 2935 Smaller values generally improve performance markedly. 2936 Note that after the signed distance function is computed, 2937 any voxel taking on the value >= radius 2938 is presumed to be "unseen" or uninitialized. 2939 sample_size : (int) 2940 if normals are not present 2941 they will be calculated using this sample size per point. 2942 hole_filling : (bool) 2943 enables hole filling, this generates 2944 separating surfaces between the empty and unseen portions of the volume. 2945 bounds : (list) 2946 region in space in which to perform the sampling 2947 in format (xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zim, zmax) 2948 padding : (float) 2949 increase by this fraction the bounding box 2950 2951 Examples: 2952 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 2953 2954  2955 """ 2956 if not utils.is_sequence(dims): 2957 dims = (dims, dims, dims) 2958 2959 sdf = vtki.new("SignedDistance") 2960 2961 if len(bounds) == 6: 2962 sdf.SetBounds(bounds) 2963 else: 2964 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2965 sdf.SetBounds( 2966 x0 - (x1 - x0) * padding, 2967 x1 + (x1 - x0) * padding, 2968 y0 - (y1 - y0) * padding, 2969 y1 + (y1 - y0) * padding, 2970 z0 - (z1 - z0) * padding, 2971 z1 + (z1 - z0) * padding, 2972 ) 2973 2974 bb = sdf.GetBounds() 2975 if bb[0]==bb[1]: 2976 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero x-range") 2977 if bb[2]==bb[3]: 2978 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero y-range") 2979 if bb[4]==bb[5]: 2980 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero z-range") 2981 2982 pd = self.dataset 2983 2984 if pd.GetPointData().GetNormals(): 2985 sdf.SetInputData(pd) 2986 else: 2987 normals = vtki.new("PCANormalEstimation") 2988 normals.SetInputData(pd) 2989 if not sample_size: 2990 sample_size = int(pd.GetNumberOfPoints() / 50) 2991 normals.SetSampleSize(sample_size) 2992 normals.SetNormalOrientationToGraphTraversal() 2993 sdf.SetInputConnection(normals.GetOutputPort()) 2994 # print("Recalculating normals with sample size =", sample_size) 2995 2996 if radius is None: 2997 radius = self.diagonal_size() / (sum(dims) / 3) * 5 2998 # print("Calculating mesh from points with radius =", radius) 2999 3000 sdf.SetRadius(radius) 3001 sdf.SetDimensions(dims) 3002 sdf.Update() 3003 3004 surface = vtki.new("ExtractSurface") 3005 surface.SetRadius(radius * 0.99) 3006 surface.SetHoleFilling(hole_filling) 3007 surface.ComputeNormalsOff() 3008 surface.ComputeGradientsOff() 3009 surface.SetInputConnection(sdf.GetOutputPort()) 3010 surface.Update() 3011 m = vedo.mesh.Mesh(surface.GetOutput(), c=self.color()) 3012 3013 m.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3014 "reconstruct_surface", 3015 parents=[self], 3016 comment=f"#pts {m.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 3017 ) 3018 return m 3019 3020 def compute_clustering(self, radius: float) -> Self: 3021 """ 3022 Cluster points in space. The `radius` is the radius of local search. 3023 3024 An array named "ClusterId" is added to `pointdata`. 3025 3026 Examples: 3027 - [clustering.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/basic/clustering.py) 3028 3029  3030 """ 3031 cluster = vtki.new("EuclideanClusterExtraction") 3032 cluster.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3033 cluster.SetExtractionModeToAllClusters() 3034 cluster.SetRadius(radius) 3035 cluster.ColorClustersOn() 3036 cluster.Update() 3037 idsarr = cluster.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetArray("ClusterId") 3038 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(idsarr) 3039 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3040 "compute_clustering", parents=[self], comment=f"radius = {radius}" 3041 ) 3042 return self 3043 3044 def compute_connections(self, radius, mode=0, regions=(), vrange=(0, 1), seeds=(), angle=0.0) -> Self: 3045 """ 3046 Extracts and/or segments points from a point cloud based on geometric distance measures 3047 (e.g., proximity, normal alignments, etc.) and optional measures such as scalar range. 3048 The default operation is to segment the points into "connected" regions where the connection 3049 is determined by an appropriate distance measure. Each region is given a region id. 3050 3051 Optionally, the filter can output the largest connected region of points; a particular region 3052 (via id specification); those regions that are seeded using a list of input point ids; 3053 or the region of points closest to a specified position. 3054 3055 The key parameter of this filter is the radius defining a sphere around each point which defines 3056 a local neighborhood: any other points in the local neighborhood are assumed connected to the point. 3057 Note that the radius is defined in absolute terms. 3058 3059 Other parameters are used to further qualify what it means to be a neighboring point. 3060 For example, scalar range and/or point normals can be used to further constrain the neighborhood. 3061 Also the extraction mode defines how the filter operates. 3062 By default, all regions are extracted but it is possible to extract particular regions; 3063 the region closest to a seed point; seeded regions; or the largest region found while processing. 3064 By default, all regions are extracted. 3065 3066 On output, all points are labeled with a region number. 3067 However note that the number of input and output points may not be the same: 3068 if not extracting all regions then the output size may be less than the input size. 3069 3070 Arguments: 3071 radius : (float) 3072 variable specifying a local sphere used to define local point neighborhood 3073 mode : (int) 3074 - 0, Extract all regions 3075 - 1, Extract point seeded regions 3076 - 2, Extract largest region 3077 - 3, Test specified regions 3078 - 4, Extract all regions with scalar connectivity 3079 - 5, Extract point seeded regions 3080 regions : (list) 3081 a list of non-negative regions id to extract 3082 vrange : (list) 3083 scalar range to use to extract points based on scalar connectivity 3084 seeds : (list) 3085 a list of non-negative point seed ids 3086 angle : (list) 3087 points are connected if the angle between their normals is 3088 within this angle threshold (expressed in degrees). 3089 """ 3090 # https://vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkConnectedPointsFilter.html 3091 cpf = vtki.new("ConnectedPointsFilter") 3092 cpf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3093 cpf.SetRadius(radius) 3094 if mode == 0: # Extract all regions 3095 pass 3096 3097 elif mode == 1: # Extract point seeded regions 3098 cpf.SetExtractionModeToPointSeededRegions() 3099 for s in seeds: 3100 cpf.AddSeed(s) 3101 3102 elif mode == 2: # Test largest region 3103 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3104 3105 elif mode == 3: # Test specified regions 3106 cpf.SetExtractionModeToSpecifiedRegions() 3107 for r in regions: 3108 cpf.AddSpecifiedRegion(r) 3109 3110 elif mode == 4: # Extract all regions with scalar connectivity 3111 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3112 cpf.ScalarConnectivityOn() 3113 cpf.SetScalarRange(vrange[0], vrange[1]) 3114 3115 elif mode == 5: # Extract point seeded regions 3116 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3117 cpf.ScalarConnectivityOn() 3118 cpf.SetScalarRange(vrange[0], vrange[1]) 3119 cpf.AlignedNormalsOn() 3120 cpf.SetNormalAngle(angle) 3121 3122 cpf.Update() 3123 self._update(cpf.GetOutput(), reset_locators=False) 3124 return self 3125 3126 def compute_camera_distance(self) -> np.ndarray: 3127 """ 3128 Calculate the distance from points to the camera. 3129 3130 A pointdata array is created with name 'DistanceToCamera' and returned. 3131 """ 3132 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 3133 poly = self.dataset 3134 dc = vtki.new("DistanceToCamera") 3135 dc.SetInputData(poly) 3136 dc.SetRenderer(vedo.plotter_instance.renderer) 3137 dc.Update() 3138 self._update(dc.GetOutput(), reset_locators=False) 3139 return self.pointdata["DistanceToCamera"] 3140 return np.array([]) 3141 3142 def densify(self, target_distance=0.1, nclosest=6, radius=None, niter=1, nmax=None) -> Self: 3143 """ 3144 Return a copy of the cloud with new added points. 3145 The new points are created in such a way that all points in any local neighborhood are 3146 within a target distance of one another. 3147 3148 For each input point, the distance to all points in its neighborhood is computed. 3149 If any of its neighbors is further than the target distance, 3150 the edge connecting the point and its neighbor is bisected and 3151 a new point is inserted at the bisection point. 3152 A single pass is completed once all the input points are visited. 3153 Then the process repeats to the number of iterations. 3154 3155 Examples: 3156 - [densifycloud.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/densifycloud.py) 3157 3158 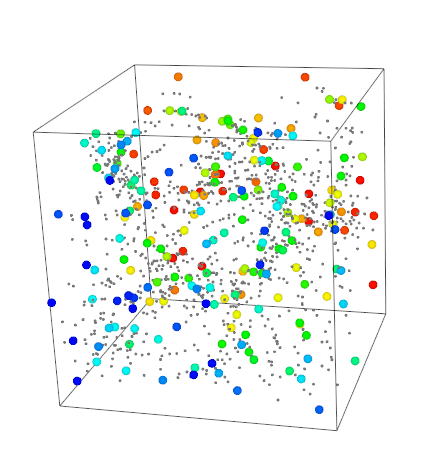 3159 3160 .. note:: 3161 Points will be created in an iterative fashion until all points in their 3162 local neighborhood are the target distance apart or less. 3163 Note that the process may terminate early due to the 3164 number of iterations. By default the target distance is set to 0.5. 3165 Note that the target_distance should be less than the radius 3166 or nothing will change on output. 3167 3168 .. warning:: 3169 This class can generate a lot of points very quickly. 3170 The maximum number of iterations is by default set to =1.0 for this reason. 3171 Increase the number of iterations very carefully. 3172 Also, `nmax` can be set to limit the explosion of points. 3173 It is also recommended that a N closest neighborhood is used. 3174 3175 """ 3176 src = vtki.new("ProgrammableSource") 3177 opts = self.coordinates 3178 # zeros = np.zeros(3) 3179 3180 def _read_points(): 3181 output = src.GetPolyDataOutput() 3182 points = vtki.vtkPoints() 3183 for p in opts: 3184 # print(p) 3185 # if not np.array_equal(p, zeros): 3186 points.InsertNextPoint(p) 3187 output.SetPoints(points) 3188 3189 src.SetExecuteMethod(_read_points) 3190 3191 dens = vtki.new("DensifyPointCloudFilter") 3192 dens.SetInputConnection(src.GetOutputPort()) 3193 # dens.SetInputData(self.dataset) # this does not work 3194 dens.InterpolateAttributeDataOn() 3195 dens.SetTargetDistance(target_distance) 3196 dens.SetMaximumNumberOfIterations(niter) 3197 if nmax: 3198 dens.SetMaximumNumberOfPoints(nmax) 3199 3200 if radius: 3201 dens.SetNeighborhoodTypeToRadius() 3202 dens.SetRadius(radius) 3203 elif nclosest: 3204 dens.SetNeighborhoodTypeToNClosest() 3205 dens.SetNumberOfClosestPoints(nclosest) 3206 else: 3207 vedo.logger.error("set either radius or nclosest") 3208 raise RuntimeError() 3209 dens.Update() 3210 3211 cld = Points(dens.GetOutput()) 3212 cld.copy_properties_from(self) 3213 cld.interpolate_data_from(self, n=nclosest, radius=radius) 3214 cld.name = "DensifiedCloud" 3215 cld.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3216 "densify", 3217 parents=[self], 3218 c="#e9c46a:", 3219 comment=f"#pts {cld.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 3220 ) 3221 return cld 3222 3223 ############################################################################### 3224 ## stuff returning a Volume 3225 ############################################################################### 3226 3227 def density( 3228 self, dims=(40, 40, 40), bounds=None, radius=None, compute_gradient=False, locator=None 3229 ) -> "vedo.Volume": 3230 """ 3231 Generate a density field from a point cloud. Input can also be a set of 3D coordinates. 3232 Output is a `Volume`. 3233 3234 The local neighborhood is specified as the `radius` around each sample position (each voxel). 3235 If left to None, the radius is automatically computed as the diagonal of the bounding box 3236 and can be accessed via `vol.metadata["radius"]`. 3237 The density is expressed as the number of counts in the radius search. 3238 3239 Arguments: 3240 dims : (int, list) 3241 number of voxels in x, y and z of the output Volume. 3242 compute_gradient : (bool) 3243 Turn on/off the generation of the gradient vector, 3244 gradient magnitude scalar, and function classification scalar. 3245 By default this is off. Note that this will increase execution time 3246 and the size of the output. (The names of these point data arrays are: 3247 "Gradient", "Gradient Magnitude", and "Classification") 3248 locator : (vtkPointLocator) 3249 can be assigned from a previous call for speed (access it via `object.point_locator`). 3250 3251 Examples: 3252 - [plot_density3d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/pyplot/plot_density3d.py) 3253 3254 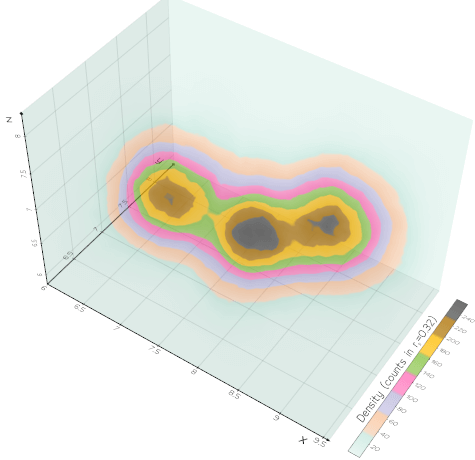 3255 """ 3256 pdf = vtki.new("PointDensityFilter") 3257 pdf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3258 3259 if not utils.is_sequence(dims): 3260 dims = [dims, dims, dims] 3261 3262 if bounds is None: 3263 bounds = list(self.bounds()) 3264 elif len(bounds) == 4: 3265 bounds = [*bounds, 0, 0] 3266 3267 if bounds[5] - bounds[4] == 0 or len(dims) == 2: # its 2D 3268 dims = list(dims) 3269 dims = [dims[0], dims[1], 2] 3270 diag = self.diagonal_size() 3271 bounds[5] = bounds[4] + diag / 1000 3272 pdf.SetModelBounds(bounds) 3273 3274 pdf.SetSampleDimensions(dims) 3275 3276 if locator: 3277 pdf.SetLocator(locator) 3278 3279 pdf.SetDensityEstimateToFixedRadius() 3280 if radius is None: 3281 radius = self.diagonal_size() / 20 3282 pdf.SetRadius(radius) 3283 pdf.SetComputeGradient(compute_gradient) 3284 pdf.Update() 3285 3286 vol = vedo.Volume(pdf.GetOutput()).mode(1) 3287 vol.name = "PointDensity" 3288 vol.metadata["radius"] = radius 3289 vol.locator = pdf.GetLocator() 3290 vol.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3291 "density", parents=[self], comment=f"dims={tuple(vol.dimensions())}" 3292 ) 3293 return vol 3294 3295 3296 def tovolume( 3297 self, 3298 kernel="shepard", 3299 radius=None, 3300 n=None, 3301 bounds=None, 3302 null_value=None, 3303 dims=(25, 25, 25), 3304 ) -> "vedo.Volume": 3305 """ 3306 Generate a `Volume` by interpolating a scalar 3307 or vector field which is only known on a scattered set of points or mesh. 3308 Available interpolation kernels are: shepard, gaussian, or linear. 3309 3310 Arguments: 3311 kernel : (str) 3312 interpolation kernel type [shepard] 3313 radius : (float) 3314 radius of the local search 3315 n : (int) 3316 number of point to use for interpolation 3317 bounds : (list) 3318 bounding box of the output Volume object 3319 dims : (list) 3320 dimensions of the output Volume object 3321 null_value : (float) 3322 value to be assigned to invalid points 3323 3324 Examples: 3325 - [interpolate_volume.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/interpolate_volume.py) 3326 3327 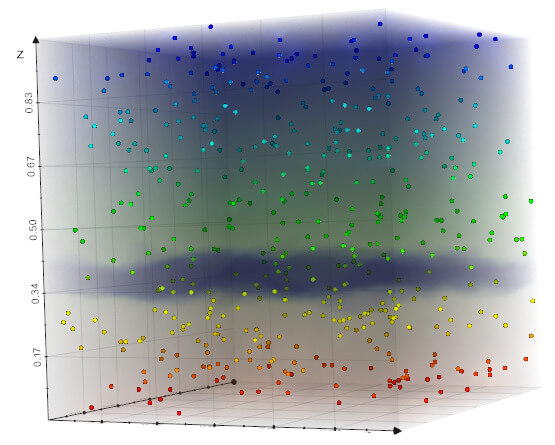 3328 """ 3329 if radius is None and not n: 3330 vedo.logger.error("please set either radius or n") 3331 raise RuntimeError 3332 3333 poly = self.dataset 3334 3335 # Create a probe volume 3336 probe = vtki.vtkImageData() 3337 probe.SetDimensions(dims) 3338 if bounds is None: 3339 bounds = self.bounds() 3340 probe.SetOrigin(bounds[0], bounds[2], bounds[4]) 3341 probe.SetSpacing( 3342 (bounds[1] - bounds[0]) / dims[0], 3343 (bounds[3] - bounds[2]) / dims[1], 3344 (bounds[5] - bounds[4]) / dims[2], 3345 ) 3346 3347 if not self.point_locator: 3348 self.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 3349 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 3350 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 3351 3352 if kernel == "shepard": 3353 kern = vtki.new("ShepardKernel") 3354 kern.SetPowerParameter(2) 3355 elif kernel == "gaussian": 3356 kern = vtki.new("GaussianKernel") 3357 elif kernel == "linear": 3358 kern = vtki.new("LinearKernel") 3359 else: 3360 vedo.logger.error("Error in tovolume(), available kernels are:") 3361 vedo.logger.error(" [shepard, gaussian, linear]") 3362 raise RuntimeError() 3363 3364 if radius: 3365 kern.SetRadius(radius) 3366 3367 interpolator = vtki.new("PointInterpolator") 3368 interpolator.SetInputData(probe) 3369 interpolator.SetSourceData(poly) 3370 interpolator.SetKernel(kern) 3371 interpolator.SetLocator(self.point_locator) 3372 3373 if n: 3374 kern.SetNumberOfPoints(n) 3375 kern.SetKernelFootprintToNClosest() 3376 else: 3377 kern.SetRadius(radius) 3378 3379 if null_value is not None: 3380 interpolator.SetNullValue(null_value) 3381 else: 3382 interpolator.SetNullPointsStrategyToClosestPoint() 3383 interpolator.Update() 3384 3385 vol = vedo.Volume(interpolator.GetOutput()) 3386 3387 vol.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3388 "signed_distance", 3389 parents=[self], 3390 comment=f"dims={tuple(vol.dimensions())}", 3391 c="#e9c46a:#0096c7", 3392 ) 3393 return vol 3394 3395 ################################################################################# 3396 def generate_segments(self, istart=0, rmax=1e30, niter=3) -> "vedo.shapes.Lines": 3397 """ 3398 Generate a line segments from a set of points. 3399 The algorithm is based on the closest point search. 3400 3401 Returns a `Line` object. 3402 This object contains the a metadata array of used vertex counts in "UsedVertexCount" 3403 and the sum of the length of the segments in "SegmentsLengthSum". 3404 3405 Arguments: 3406 istart : (int) 3407 index of the starting point 3408 rmax : (float) 3409 maximum length of a segment 3410 niter : (int) 3411 number of iterations or passes through the points 3412 3413 Examples: 3414 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 3415 """ 3416 points = self.coordinates 3417 segments = [] 3418 dists = [] 3419 n = len(points) 3420 used = np.zeros(n, dtype=int) 3421 for _ in range(niter): 3422 i = istart 3423 for _ in range(n): 3424 p = points[i] 3425 ids = self.closest_point(p, n=4, return_point_id=True) 3426 j = ids[1] 3427 if used[j] > 1 or [j, i] in segments: 3428 j = ids[2] 3429 if used[j] > 1: 3430 j = ids[3] 3431 d = np.linalg.norm(p - points[j]) 3432 if used[j] > 1 or used[i] > 1 or d > rmax: 3433 i += 1 3434 if i >= n: 3435 i = 0 3436 continue 3437 used[i] += 1 3438 used[j] += 1 3439 segments.append([i, j]) 3440 dists.append(d) 3441 i = j 3442 segments = np.array(segments, dtype=int) 3443 3444 lines = vedo.shapes.Lines(points[segments], c="k", lw=3) 3445 lines.metadata["UsedVertexCount"] = used 3446 lines.metadata["SegmentsLengthSum"] = np.sum(dists) 3447 lines.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("generate_segments", parents=[self]) 3448 lines.name = "Segments" 3449 return lines 3450 3451 def generate_delaunay2d( 3452 self, 3453 mode="scipy", 3454 boundaries=(), 3455 tol=None, 3456 alpha=0.0, 3457 offset=0.0, 3458 transform=None, 3459 ) -> "vedo.mesh.Mesh": 3460 """ 3461 Create a mesh from points in the XY plane. 3462 If `mode='fit'` then the filter computes a best fitting 3463 plane and projects the points onto it. 3464 3465 Check also `generate_mesh()`. 3466 3467 Arguments: 3468 tol : (float) 3469 specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. 3470 This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of the bounding box of the points. 3471 alpha : (float) 3472 for a non-zero alpha value, only edges or triangles contained 3473 within a sphere centered at mesh vertices will be output. 3474 Otherwise, only triangles will be output. 3475 offset : (float) 3476 multiplier to control the size of the initial, bounding Delaunay triangulation. 3477 transform: (LinearTransform, NonLinearTransform) 3478 a transformation which is applied to points to generate a 2D problem. 3479 This maps a 3D dataset into a 2D dataset where triangulation can be done on the XY plane. 3480 The points are transformed and triangulated. 3481 The topology of triangulated points is used as the output topology. 3482 3483 Examples: 3484 - [delaunay2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/delaunay2d.py) 3485 3486 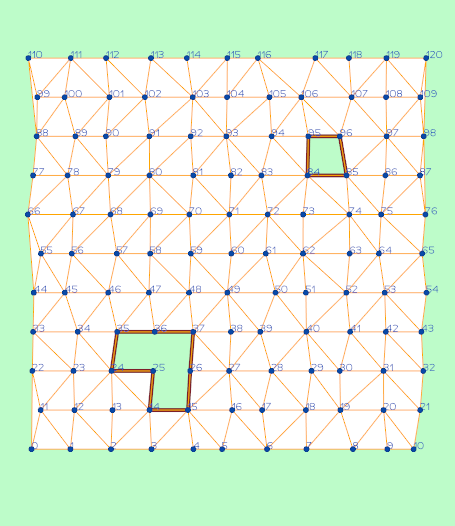 3487 """ 3488 plist = self.coordinates.copy() 3489 3490 ######################################################### 3491 if mode == "scipy": 3492 from scipy.spatial import Delaunay as scipy_delaunay 3493 3494 tri = scipy_delaunay(plist[:, 0:2]) 3495 return vedo.mesh.Mesh([plist, tri.simplices]) 3496 ########################################################## 3497 3498 pd = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3499 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 3500 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(plist, dtype=np.float32)) 3501 pd.SetPoints(vpts) 3502 3503 delny = vtki.new("Delaunay2D") 3504 delny.SetInputData(pd) 3505 if tol: 3506 delny.SetTolerance(tol) 3507 delny.SetAlpha(alpha) 3508 delny.SetOffset(offset) 3509 3510 if transform: 3511 delny.SetTransform(transform.T) 3512 elif mode == "fit": 3513 delny.SetProjectionPlaneMode(vtki.get_class("VTK_BEST_FITTING_PLANE")) 3514 elif mode == "xy" and boundaries: 3515 boundary = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3516 boundary.SetPoints(vpts) 3517 cell_array = vtki.vtkCellArray() 3518 for b in boundaries: 3519 cpolygon = vtki.vtkPolygon() 3520 for idd in b: 3521 cpolygon.GetPointIds().InsertNextId(idd) 3522 cell_array.InsertNextCell(cpolygon) 3523 boundary.SetPolys(cell_array) 3524 delny.SetSourceData(boundary) 3525 3526 delny.Update() 3527 3528 msh = vedo.mesh.Mesh(delny.GetOutput()) 3529 msh.name = "Delaunay2D" 3530 msh.clean().lighting("off") 3531 msh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3532 "delaunay2d", 3533 parents=[self], 3534 comment=f"#cells {msh.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 3535 ) 3536 return msh 3537 3538 def generate_voronoi(self, padding=0.0, fit=False, method="vtk") -> "vedo.Mesh": 3539 """ 3540 Generate the 2D Voronoi convex tiling of the input points (z is ignored). 3541 The points are assumed to lie in a plane. The output is a Mesh. Each output cell is a convex polygon. 3542 3543 A cell array named "VoronoiID" is added to the output Mesh. 3544 3545 The 2D Voronoi tessellation is a tiling of space, where each Voronoi tile represents the region nearest 3546 to one of the input points. Voronoi tessellations are important in computational geometry 3547 (and many other fields), and are the dual of Delaunay triangulations. 3548 3549 Thus the triangulation is constructed in the x-y plane, and the z coordinate is ignored 3550 (although carried through to the output). 3551 If you desire to triangulate in a different plane, you can use fit=True. 3552 3553 A brief summary is as follows. Each (generating) input point is associated with 3554 an initial Voronoi tile, which is simply the bounding box of the point set. 3555 A locator is then used to identify nearby points: each neighbor in turn generates a 3556 clipping line positioned halfway between the generating point and the neighboring point, 3557 and orthogonal to the line connecting them. Clips are readily performed by evaluationg the 3558 vertices of the convex Voronoi tile as being on either side (inside,outside) of the clip line. 3559 If two intersections of the Voronoi tile are found, the portion of the tile "outside" the clip 3560 line is discarded, resulting in a new convex, Voronoi tile. As each clip occurs, 3561 the Voronoi "Flower" error metric (the union of error spheres) is compared to the extent of the region 3562 containing the neighboring clip points. The clip region (along with the points contained in it) is grown 3563 by careful expansion (e.g., outward spiraling iterator over all candidate clip points). 3564 When the Voronoi Flower is contained within the clip region, the algorithm terminates and the Voronoi 3565 tile is output. Once complete, it is possible to construct the Delaunay triangulation from the Voronoi 3566 tessellation. Note that topological and geometric information is used to generate a valid triangulation 3567 (e.g., merging points and validating topology). 3568 3569 Arguments: 3570 pts : (list) 3571 list of input points. 3572 padding : (float) 3573 padding distance. The default is 0. 3574 fit : (bool) 3575 detect automatically the best fitting plane. The default is False. 3576 3577 Examples: 3578 - [voronoi1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/voronoi1.py) 3579 3580 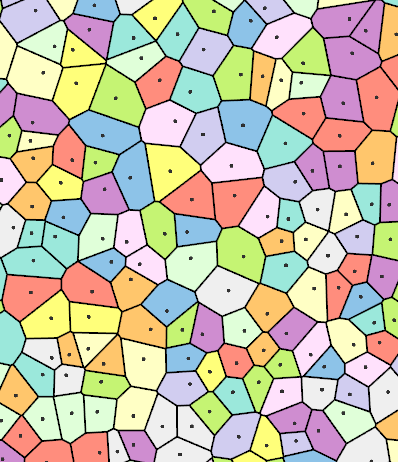 3581 3582 - [voronoi2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/voronoi2.py) 3583 3584 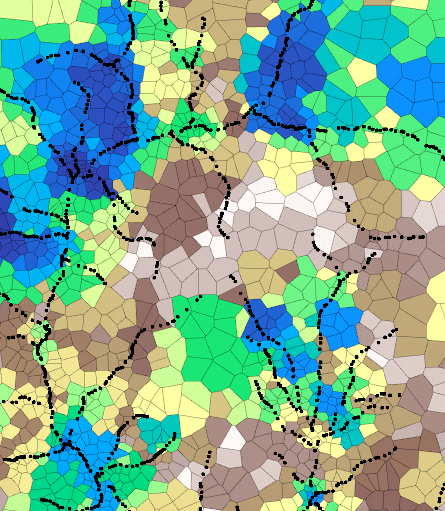 3585 """ 3586 pts = self.coordinates 3587 3588 if method == "scipy": 3589 from scipy.spatial import Voronoi as scipy_voronoi 3590 3591 pts = np.asarray(pts)[:, (0, 1)] 3592 vor = scipy_voronoi(pts) 3593 regs = [] # filter out invalid indices 3594 for r in vor.regions: 3595 flag = True 3596 for x in r: 3597 if x < 0: 3598 flag = False 3599 break 3600 if flag and len(r) > 0: 3601 regs.append(r) 3602 3603 m = vedo.Mesh([vor.vertices, regs]) 3604 m.celldata["VoronoiID"] = np.array(list(range(len(regs)))).astype(int) 3605 3606 elif method == "vtk": 3607 vor = vtki.new("Voronoi2D") 3608 if isinstance(pts, Points): 3609 vor.SetInputData(pts) 3610 else: 3611 pts = np.asarray(pts) 3612 if pts.shape[1] == 2: 3613 pts = np.c_[pts, np.zeros(len(pts))] 3614 pd = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3615 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 3616 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(pts, dtype=np.float32)) 3617 pd.SetPoints(vpts) 3618 vor.SetInputData(pd) 3619 vor.SetPadding(padding) 3620 vor.SetGenerateScalarsToPointIds() 3621 if fit: 3622 vor.SetProjectionPlaneModeToBestFittingPlane() 3623 else: 3624 vor.SetProjectionPlaneModeToXYPlane() 3625 vor.Update() 3626 poly = vor.GetOutput() 3627 arr = poly.GetCellData().GetArray(0) 3628 if arr: 3629 arr.SetName("VoronoiID") 3630 m = vedo.Mesh(poly, c="orange5") 3631 3632 else: 3633 vedo.logger.error(f"Unknown method {method} in voronoi()") 3634 raise RuntimeError 3635 3636 m.lw(2).lighting("off").wireframe() 3637 m.name = "Voronoi" 3638 return m 3639 3640 ########################################################################## 3641 def generate_delaunay3d(self, radius=0, tol=None) -> "vedo.TetMesh": 3642 """ 3643 Create 3D Delaunay triangulation of input points. 3644 3645 Arguments: 3646 radius : (float) 3647 specify distance (or "alpha") value to control output. 3648 For a non-zero values, only tetra contained within the circumsphere 3649 will be output. 3650 tol : (float) 3651 Specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. 3652 This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of 3653 the bounding box of the points. 3654 """ 3655 deln = vtki.new("Delaunay3D") 3656 deln.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3657 deln.SetAlpha(radius) 3658 deln.AlphaTetsOn() 3659 deln.AlphaTrisOff() 3660 deln.AlphaLinesOff() 3661 deln.AlphaVertsOff() 3662 deln.BoundingTriangulationOff() 3663 if tol: 3664 deln.SetTolerance(tol) 3665 deln.Update() 3666 m = vedo.TetMesh(deln.GetOutput()) 3667 m.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3668 "generate_delaunay3d", c="#e9c46a:#edabab", parents=[self], 3669 ) 3670 m.name = "Delaunay3D" 3671 return m 3672 3673 #################################################### 3674 def visible_points(self, area=(), tol=None, invert=False) -> Union[Self, None]: 3675 """ 3676 Extract points based on whether they are visible or not. 3677 Visibility is determined by accessing the z-buffer of a rendering window. 3678 The position of each input point is converted into display coordinates, 3679 and then the z-value at that point is obtained. 3680 If within the user-specified tolerance, the point is considered visible. 3681 Associated data attributes are passed to the output as well. 3682 3683 This filter also allows you to specify a rectangular window in display (pixel) 3684 coordinates in which the visible points must lie. 3685 3686 Arguments: 3687 area : (list) 3688 specify a rectangular region as (xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax) 3689 tol : (float) 3690 a tolerance in normalized display coordinate system 3691 invert : (bool) 3692 select invisible points instead. 3693 3694 Example: 3695 ```python 3696 from vedo import Ellipsoid, show 3697 s = Ellipsoid().rotate_y(30) 3698 3699 # Camera options: pos, focal_point, viewup, distance 3700 camopts = dict(pos=(0,0,25), focal_point=(0,0,0)) 3701 show(s, camera=camopts, offscreen=True) 3702 3703 m = s.visible_points() 3704 # print('visible pts:', m.vertices) # numpy array 3705 show(m, new=True, axes=1).close() # optionally draw result in a new window 3706 ``` 3707 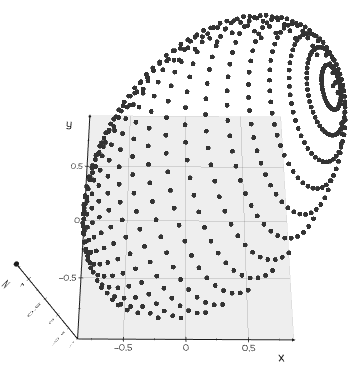 3708 """ 3709 svp = vtki.new("SelectVisiblePoints") 3710 svp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3711 3712 ren = None 3713 if vedo.plotter_instance: 3714 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 3715 ren = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer 3716 svp.SetRenderer(ren) 3717 if not ren: 3718 vedo.logger.warning( 3719 "visible_points() can only be used after a rendering step" 3720 ) 3721 return None 3722 3723 if len(area) == 2: 3724 area = utils.flatten(area) 3725 if len(area) == 4: 3726 # specify a rectangular region 3727 svp.SetSelection(area[0], area[1], area[2], area[3]) 3728 if tol is not None: 3729 svp.SetTolerance(tol) 3730 if invert: 3731 svp.SelectInvisibleOn() 3732 svp.Update() 3733 3734 m = Points(svp.GetOutput()) 3735 m.name = "VisiblePoints" 3736 return m
455class Points(PointsVisual, PointAlgorithms): 456 """Work with point clouds.""" 457 458 def __init__(self, inputobj=None, r=4, c=(0.2, 0.2, 0.2), alpha=1): 459 """ 460 Build an object made of only vertex points for a list of 2D/3D points. 461 Both shapes (N, 3) or (3, N) are accepted as input, if N>3. 462 463 Arguments: 464 inputobj : (list, tuple) 465 r : (int) 466 Point radius in units of pixels. 467 c : (str, list) 468 Color name or rgb tuple. 469 alpha : (float) 470 Transparency in range [0,1]. 471 472 Example: 473 ```python 474 from vedo import * 475 476 def fibonacci_sphere(n): 477 s = np.linspace(0, n, num=n, endpoint=False) 478 theta = s * 2.399963229728653 479 y = 1 - s * (2/(n-1)) 480 r = np.sqrt(1 - y * y) 481 x = np.cos(theta) * r 482 z = np.sin(theta) * r 483 return np._c[x,y,z] 484 485 Points(fibonacci_sphere(1000)).show(axes=1).close() 486 ``` 487  488 """ 489 # print("INIT POINTS") 490 super().__init__() 491 492 self.name = "" 493 self.filename = "" 494 self.file_size = "" 495 496 self.info = {} 497 self.time = time.time() 498 499 self.transform = LinearTransform() 500 501 self.point_locator = None 502 self.cell_locator = None 503 self.line_locator = None 504 505 self.actor = vtki.vtkActor() 506 self.properties = self.actor.GetProperty() 507 self.properties_backface = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 508 self.mapper = vtki.new("PolyDataMapper") 509 self.dataset = vtki.vtkPolyData() 510 511 # Create weakref so actor can access this object (eg to pick/remove): 512 self.actor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 513 514 try: 515 self.properties.RenderPointsAsSpheresOn() 516 except AttributeError: 517 pass 518 519 if inputobj is None: #################### 520 return 521 ########################################## 522 523 self.name = "Points" 524 525 ###### 526 if isinstance(inputobj, vtki.vtkActor): 527 self.dataset.DeepCopy(inputobj.GetMapper().GetInput()) 528 pr = vtki.vtkProperty() 529 pr.DeepCopy(inputobj.GetProperty()) 530 self.actor.SetProperty(pr) 531 self.properties = pr 532 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(inputobj.GetMapper().GetScalarVisibility()) 533 534 elif isinstance(inputobj, vtki.vtkPolyData): 535 self.dataset = inputobj 536 if self.dataset.GetNumberOfCells() == 0: 537 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 538 for i in range(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()): 539 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 540 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 541 self.dataset.SetVerts(carr) 542 543 elif isinstance(inputobj, Points): 544 self.dataset = inputobj.dataset 545 self.copy_properties_from(inputobj) 546 547 elif utils.is_sequence(inputobj): # passing point coords 548 self.dataset = utils.buildPolyData(utils.make3d(inputobj)) 549 550 elif isinstance(inputobj, str) or "PosixPath" in str(type(inputobj)): 551 verts = vedo.file_io.load(inputobj) 552 self.filename = str(inputobj) 553 self.dataset = verts.dataset 554 555 elif "meshlib" in str(type(inputobj)): 556 from meshlib import mrmeshnumpy as mn 557 self.dataset = utils.buildPolyData(mn.toNumpyArray(inputobj.points)) 558 559 else: 560 # try to extract the points from a generic VTK input data object 561 if hasattr(inputobj, "dataset"): 562 inputobj = inputobj.dataset 563 try: 564 vvpts = inputobj.GetPoints() 565 self.dataset = vtki.vtkPolyData() 566 self.dataset.SetPoints(vvpts) 567 for i in range(inputobj.GetPointData().GetNumberOfArrays()): 568 arr = inputobj.GetPointData().GetArray(i) 569 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(arr) 570 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 571 for i in range(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()): 572 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 573 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 574 self.dataset.SetVerts(carr) 575 except: 576 vedo.logger.error(f"cannot build Points from type {type(inputobj)}") 577 raise RuntimeError() 578 579 self.actor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 580 self.mapper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 581 582 self.properties.SetColor(colors.get_color(c)) 583 self.properties.SetOpacity(alpha) 584 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 585 self.properties.SetPointSize(r) 586 self.properties.LightingOff() 587 588 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 589 self, parents=[], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 590 ) 591 592 def _update(self, polydata, reset_locators=True) -> Self: 593 """Overwrite the polygonal dataset with a new vtkPolyData.""" 594 self.dataset = polydata 595 self.mapper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 596 self.mapper.Modified() 597 if reset_locators: 598 self.point_locator = None 599 self.line_locator = None 600 self.cell_locator = None 601 return self 602 603 def __str__(self): 604 """Print a description of the Points/Mesh.""" 605 module = self.__class__.__module__ 606 name = self.__class__.__name__ 607 out = vedo.printc( 608 f"{module}.{name} at ({hex(self.memory_address())})".ljust(75), 609 c="g", bold=True, invert=True, return_string=True, 610 ) 611 out += "\x1b[0m\x1b[32;1m" 612 613 if self.name: 614 out += "name".ljust(14) + ": " + self.name 615 if "legend" in self.info.keys() and self.info["legend"]: 616 out+= f", legend='{self.info['legend']}'" 617 out += "\n" 618 619 if self.filename: 620 out+= "file name".ljust(14) + ": " + self.filename + "\n" 621 622 if not self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility(): 623 col = utils.precision(self.properties.GetColor(), 3) 624 cname = vedo.colors.get_color_name(self.properties.GetColor()) 625 out+= "color".ljust(14) + ": " + cname 626 out+= f", rgb={col}, alpha={self.properties.GetOpacity()}\n" 627 if self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty(): 628 bcol = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty().GetDiffuseColor() 629 cname = vedo.colors.get_color_name(bcol) 630 out+= "backface color".ljust(14) + ": " 631 out+= f"{cname}, rgb={utils.precision(bcol,3)}\n" 632 633 npt = self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints() 634 npo, nln = self.dataset.GetNumberOfPolys(), self.dataset.GetNumberOfLines() 635 out+= "elements".ljust(14) + f": vertices={npt:,} polygons={npo:,} lines={nln:,}" 636 if self.dataset.GetNumberOfStrips(): 637 out+= f", strips={self.dataset.GetNumberOfStrips():,}" 638 out+= "\n" 639 if self.dataset.GetNumberOfPieces() > 1: 640 out+= "pieces".ljust(14) + ": " + str(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPieces()) + "\n" 641 642 out+= "position".ljust(14) + ": " + f"{utils.precision(self.pos(), 6)}\n" 643 try: 644 sc = self.transform.get_scale() 645 out+= "scaling".ljust(14) + ": " 646 out+= utils.precision(sc, 6) + "\n" 647 except AttributeError: 648 pass 649 650 if self.npoints: 651 out+="size".ljust(14)+ ": average=" + utils.precision(self.average_size(),6) 652 out+=", diagonal="+ utils.precision(self.diagonal_size(), 6)+ "\n" 653 out+="center of mass".ljust(14) + ": " + utils.precision(self.center_of_mass(),6)+"\n" 654 655 bnds = self.bounds() 656 bx1, bx2 = utils.precision(bnds[0], 3), utils.precision(bnds[1], 3) 657 by1, by2 = utils.precision(bnds[2], 3), utils.precision(bnds[3], 3) 658 bz1, bz2 = utils.precision(bnds[4], 3), utils.precision(bnds[5], 3) 659 out+= "bounds".ljust(14) + ":" 660 out+= " x=(" + bx1 + ", " + bx2 + ")," 661 out+= " y=(" + by1 + ", " + by2 + ")," 662 out+= " z=(" + bz1 + ", " + bz2 + ")\n" 663 664 for key in self.pointdata.keys(): 665 arr = self.pointdata[key] 666 dim = arr.shape[1] if arr.ndim > 1 else 1 667 mark_active = "pointdata" 668 a_scalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 669 a_vectors = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetVectors() 670 a_tensors = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetTensors() 671 if a_scalars and a_scalars.GetName() == key: 672 mark_active += " *" 673 elif a_vectors and a_vectors.GetName() == key: 674 mark_active += " **" 675 elif a_tensors and a_tensors.GetName() == key: 676 mark_active += " ***" 677 out += mark_active.ljust(14) + f': "{key}" ({arr.dtype}), dim={dim}' 678 if dim == 1 and len(arr)>0: 679 rng = utils.precision(arr.min(), 3) + ", " + utils.precision(arr.max(), 3) 680 out += f", range=({rng})\n" 681 else: 682 out += "\n" 683 684 for key in self.celldata.keys(): 685 arr = self.celldata[key] 686 dim = arr.shape[1] if arr.ndim > 1 else 1 687 mark_active = "celldata" 688 a_scalars = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars() 689 a_vectors = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetVectors() 690 a_tensors = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetTensors() 691 if a_scalars and a_scalars.GetName() == key: 692 mark_active += " *" 693 elif a_vectors and a_vectors.GetName() == key: 694 mark_active += " **" 695 elif a_tensors and a_tensors.GetName() == key: 696 mark_active += " ***" 697 out += mark_active.ljust(14) + f': "{key}" ({arr.dtype}), dim={dim}' 698 if dim == 1 and len(arr)>0: 699 rng = utils.precision(arr.min(), 3) + ", " + utils.precision(arr.max(), 3) 700 out += f", range=({rng})\n" 701 else: 702 out += "\n" 703 704 for key in self.metadata.keys(): 705 arr = self.metadata[key] 706 if len(arr) > 3: 707 out+= "metadata".ljust(14) + ": " + f'"{key}" ({len(arr)} values)\n' 708 else: 709 out+= "metadata".ljust(14) + ": " + f'"{key}" = {arr}\n' 710 711 if self.picked3d is not None: 712 idp = self.closest_point(self.picked3d, return_point_id=True) 713 idc = self.closest_point(self.picked3d, return_cell_id=True) 714 out+= "clicked point".ljust(14) + ": " + utils.precision(self.picked3d, 6) 715 out+= f", pointID={idp}, cellID={idc}\n" 716 717 return out.rstrip() + "\x1b[0m" 718 719 def _repr_html_(self): 720 """ 721 HTML representation of the Point cloud object for Jupyter Notebooks. 722 723 Returns: 724 HTML text with the image and some properties. 725 """ 726 import io 727 import base64 728 from PIL import Image 729 730 library_name = "vedo.pointcloud.Points" 731 help_url = "https://vedo.embl.es/docs/vedo/pointcloud.html#Points" 732 733 arr = self.thumbnail() 734 im = Image.fromarray(arr) 735 buffered = io.BytesIO() 736 im.save(buffered, format="PNG", quality=100) 737 encoded = base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode("utf-8") 738 url = "data:image/png;base64," + encoded 739 image = f"<img src='{url}'></img>" 740 741 bounds = "<br/>".join( 742 [ 743 utils.precision(min_x, 4) + " ... " + utils.precision(max_x, 4) 744 for min_x, max_x in zip(self.bounds()[::2], self.bounds()[1::2]) 745 ] 746 ) 747 average_size = "{size:.3f}".format(size=self.average_size()) 748 749 help_text = "" 750 if self.name: 751 help_text += f"<b> {self.name}:   </b>" 752 help_text += '<b><a href="' + help_url + '" target="_blank">' + library_name + "</a></b>" 753 if self.filename: 754 dots = "" 755 if len(self.filename) > 30: 756 dots = "..." 757 help_text += f"<br/><code><i>({dots}{self.filename[-30:]})</i></code>" 758 759 pdata = "" 760 if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 761 if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars().GetName(): 762 name = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars().GetName() 763 pdata = "<tr><td><b> point data array </b></td><td>" + name + "</td></tr>" 764 765 cdata = "" 766 if self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars(): 767 if self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars().GetName(): 768 name = self.dataset.GetCellData().GetScalars().GetName() 769 cdata = "<tr><td><b> cell data array </b></td><td>" + name + "</td></tr>" 770 771 allt = [ 772 "<table>", 773 "<tr>", 774 "<td>", 775 image, 776 "</td>", 777 "<td style='text-align: center; vertical-align: center;'><br/>", 778 help_text, 779 "<table>", 780 "<tr><td><b> bounds </b> <br/> (x/y/z) </td><td>" + str(bounds) + "</td></tr>", 781 "<tr><td><b> center of mass </b></td><td>" 782 + utils.precision(self.center_of_mass(), 3) 783 + "</td></tr>", 784 "<tr><td><b> average size </b></td><td>" + str(average_size) + "</td></tr>", 785 "<tr><td><b> nr. points </b></td><td>" + str(self.npoints) + "</td></tr>", 786 pdata, 787 cdata, 788 "</table>", 789 "</table>", 790 ] 791 return "\n".join(allt) 792 793 ################################################################################## 794 def __add__(self, meshs): 795 """ 796 Add two meshes or a list of meshes together to form an `Assembly` object. 797 """ 798 if isinstance(meshs, list): 799 alist = [self] 800 for l in meshs: 801 if isinstance(l, vedo.Assembly): 802 alist += l.unpack() 803 else: 804 alist += l 805 return vedo.assembly.Assembly(alist) 806 807 if isinstance(meshs, vedo.Assembly): 808 return meshs + self # use Assembly.__add__ 809 810 return vedo.assembly.Assembly([self, meshs]) 811 812 def polydata(self): 813 """ 814 Obsolete. Use property `.dataset` instead. 815 Returns the underlying `vtkPolyData` object. 816 """ 817 colors.printc( 818 "WARNING: call to .polydata() is obsolete, use property .dataset instead.", 819 c="y") 820 return self.dataset 821 822 def __copy__(self): 823 return self.clone(deep=False) 824 825 def __deepcopy__(self, memo): 826 return self.clone(deep=memo) 827 828 def copy(self, deep=True) -> Self: 829 """Return a copy of the object. Alias of `clone()`.""" 830 return self.clone(deep=deep) 831 832 def clone(self, deep=True) -> Self: 833 """ 834 Clone a `PointCloud` or `Mesh` object to make an exact copy of it. 835 Alias of `copy()`. 836 837 Arguments: 838 deep : (bool) 839 if False return a shallow copy of the mesh without copying the points array. 840 841 Examples: 842 - [mirror.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mirror.py) 843 844  845 """ 846 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 847 if deep or isinstance(deep, dict): # if a memo object is passed this checks as True 848 poly.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 849 else: 850 poly.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 851 852 if isinstance(self, vedo.Mesh): 853 cloned = vedo.Mesh(poly) 854 else: 855 cloned = Points(poly) 856 # print([self], self.__class__) 857 # cloned = self.__class__(poly) 858 859 cloned.transform = self.transform.clone() 860 861 cloned.copy_properties_from(self) 862 863 cloned.name = str(self.name) 864 cloned.filename = str(self.filename) 865 cloned.info = dict(self.info) 866 cloned.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("clone", parents=[self], shape="diamond", c="#edede9") 867 868 if isinstance(deep, dict): 869 deep[id(self)] = cloned 870 871 return cloned 872 873 def compute_normals_with_pca(self, n=20, orientation_point=None, invert=False) -> Self: 874 """ 875 Generate point normals using PCA (principal component analysis). 876 This algorithm estimates a local tangent plane around each sample point p 877 by considering a small neighborhood of points around p, and fitting a plane 878 to the neighborhood (via PCA). 879 880 Arguments: 881 n : (int) 882 neighborhood size to calculate the normal 883 orientation_point : (list) 884 adjust the +/- sign of the normals so that 885 the normals all point towards a specified point. If None, perform a traversal 886 of the point cloud and flip neighboring normals so that they are mutually consistent. 887 invert : (bool) 888 flip all normals 889 """ 890 poly = self.dataset 891 pcan = vtki.new("PCANormalEstimation") 892 pcan.SetInputData(poly) 893 pcan.SetSampleSize(n) 894 895 if orientation_point is not None: 896 pcan.SetNormalOrientationToPoint() 897 pcan.SetOrientationPoint(orientation_point) 898 else: 899 pcan.SetNormalOrientationToGraphTraversal() 900 901 if invert: 902 pcan.FlipNormalsOn() 903 pcan.Update() 904 905 varr = pcan.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetNormals() 906 varr.SetName("Normals") 907 self.dataset.GetPointData().SetNormals(varr) 908 self.dataset.GetPointData().Modified() 909 return self 910 911 def compute_acoplanarity(self, n=25, radius=None, on="points") -> Self: 912 """ 913 Compute acoplanarity which is a measure of how much a local region of the mesh 914 differs from a plane. 915 916 The information is stored in a `pointdata` or `celldata` array with name 'Acoplanarity'. 917 918 Either `n` (number of neighbour points) or `radius` (radius of local search) can be specified. 919 If a radius value is given and not enough points fall inside it, then a -1 is stored. 920 921 Example: 922 ```python 923 from vedo import * 924 msh = ParametricShape('RandomHills') 925 msh.compute_acoplanarity(radius=0.1, on='cells') 926 msh.cmap("coolwarm", on='cells').add_scalarbar() 927 msh.show(axes=1).close() 928 ``` 929  930 """ 931 acoplanarities = [] 932 if "point" in on: 933 pts = self.coordinates 934 elif "cell" in on: 935 pts = self.cell_centers().coordinates 936 else: 937 raise ValueError(f"In compute_acoplanarity() set on to either 'cells' or 'points', not {on}") 938 939 for p in utils.progressbar(pts, delay=5, width=15, title=f"{on} acoplanarity"): 940 if n: 941 data = self.closest_point(p, n=n) 942 npts = n 943 elif radius: 944 data = self.closest_point(p, radius=radius) 945 npts = len(data) 946 947 try: 948 center = data.mean(axis=0) 949 res = np.linalg.svd(data - center) 950 acoplanarities.append(res[1][2] / npts) 951 except: 952 acoplanarities.append(-1.0) 953 954 if "point" in on: 955 self.pointdata["Acoplanarity"] = np.array(acoplanarities, dtype=float) 956 else: 957 self.celldata["Acoplanarity"] = np.array(acoplanarities, dtype=float) 958 return self 959 960 def distance_to(self, pcloud, signed=False, invert=False, name="Distance") -> np.ndarray: 961 """ 962 Computes the distance from one point cloud or mesh to another point cloud or mesh. 963 This new `pointdata` array is saved with default name "Distance". 964 965 Keywords `signed` and `invert` are used to compute signed distance, 966 but the mesh in that case must have polygonal faces (not a simple point cloud), 967 and normals must also be computed. 968 969 Examples: 970 - [distance2mesh.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/distance2mesh.py) 971 972  973 """ 974 if pcloud.dataset.GetNumberOfPolys(): 975 976 poly1 = self.dataset 977 poly2 = pcloud.dataset 978 df = vtki.new("DistancePolyDataFilter") 979 df.ComputeSecondDistanceOff() 980 df.SetInputData(0, poly1) 981 df.SetInputData(1, poly2) 982 df.SetSignedDistance(signed) 983 df.SetNegateDistance(invert) 984 df.Update() 985 scals = df.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetScalars() 986 dists = utils.vtk2numpy(scals) 987 988 else: # has no polygons 989 990 if signed: 991 vedo.logger.warning("distance_to() called with signed=True but input object has no polygons") 992 993 if not pcloud.point_locator: 994 pcloud.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 995 pcloud.point_locator.SetDataSet(pcloud.dataset) 996 pcloud.point_locator.BuildLocator() 997 998 ids = [] 999 ps1 = self.coordinates 1000 ps2 = pcloud.coordinates 1001 for p in ps1: 1002 pid = pcloud.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1003 ids.append(pid) 1004 1005 deltas = ps2[ids] - ps1 1006 dists = np.linalg.norm(deltas, axis=1).astype(np.float32) 1007 scals = utils.numpy2vtk(dists) 1008 1009 scals.SetName(name) 1010 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(scals) 1011 self.dataset.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(scals.GetName()) 1012 rng = scals.GetRange() 1013 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(rng[0], rng[1]) 1014 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1015 1016 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1017 "distance_to", 1018 parents=[self, pcloud], 1019 shape="cylinder", 1020 comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 1021 ) 1022 return dists 1023 1024 def clean(self) -> Self: 1025 """Clean pointcloud or mesh by removing coincident points.""" 1026 cpd = vtki.new("CleanPolyData") 1027 cpd.PointMergingOn() 1028 cpd.ConvertLinesToPointsOff() 1029 cpd.ConvertPolysToLinesOff() 1030 cpd.ConvertStripsToPolysOff() 1031 cpd.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1032 cpd.Update() 1033 self._update(cpd.GetOutput()) 1034 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1035 "clean", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 1036 ) 1037 return self 1038 1039 def subsample(self, fraction: float, absolute=False) -> Self: 1040 """ 1041 Subsample a point cloud by requiring that the points 1042 or vertices are far apart at least by the specified fraction of the object size. 1043 If a Mesh is passed the polygonal faces are not removed 1044 but holes can appear as their vertices are removed. 1045 1046 Examples: 1047 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 1048 1049  1050 1051 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 1052 1053  1054 """ 1055 if not absolute: 1056 if fraction > 1: 1057 vedo.logger.warning( 1058 f"subsample(fraction=...), fraction must be < 1, but is {fraction}" 1059 ) 1060 if fraction <= 0: 1061 return self 1062 1063 cpd = vtki.new("CleanPolyData") 1064 cpd.PointMergingOn() 1065 cpd.ConvertLinesToPointsOn() 1066 cpd.ConvertPolysToLinesOn() 1067 cpd.ConvertStripsToPolysOn() 1068 cpd.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1069 if absolute: 1070 cpd.SetTolerance(fraction / self.diagonal_size()) 1071 # cpd.SetToleranceIsAbsolute(absolute) 1072 else: 1073 cpd.SetTolerance(fraction) 1074 cpd.Update() 1075 1076 ps = 2 1077 if self.properties.GetRepresentation() == 0: 1078 ps = self.properties.GetPointSize() 1079 1080 self._update(cpd.GetOutput()) 1081 self.ps(ps) 1082 1083 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1084 "subsample", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 1085 ) 1086 return self 1087 1088 def threshold(self, scalars: str, above=None, below=None, on="points") -> Self: 1089 """ 1090 Extracts cells where scalar value satisfies threshold criterion. 1091 1092 Arguments: 1093 scalars : (str) 1094 name of the scalars array. 1095 above : (float) 1096 minimum value of the scalar 1097 below : (float) 1098 maximum value of the scalar 1099 on : (str) 1100 if 'cells' assume array of scalars refers to cell data. 1101 1102 Examples: 1103 - [mesh_threshold.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_threshold.py) 1104 """ 1105 thres = vtki.new("Threshold") 1106 thres.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1107 1108 if on.startswith("c"): 1109 asso = vtki.vtkDataObject.FIELD_ASSOCIATION_CELLS 1110 else: 1111 asso = vtki.vtkDataObject.FIELD_ASSOCIATION_POINTS 1112 1113 thres.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, asso, scalars) 1114 1115 if above is None and below is not None: 1116 try: # vtk 9.2 1117 thres.ThresholdByLower(below) 1118 except AttributeError: # vtk 9.3 1119 thres.SetUpperThreshold(below) 1120 1121 elif below is None and above is not None: 1122 try: 1123 thres.ThresholdByUpper(above) 1124 except AttributeError: 1125 thres.SetLowerThreshold(above) 1126 else: 1127 try: 1128 thres.ThresholdBetween(above, below) 1129 except AttributeError: 1130 thres.SetUpperThreshold(below) 1131 thres.SetLowerThreshold(above) 1132 1133 thres.Update() 1134 1135 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 1136 gf.SetInputData(thres.GetOutput()) 1137 gf.Update() 1138 self._update(gf.GetOutput()) 1139 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("threshold", parents=[self]) 1140 return self 1141 1142 def quantize(self, value: float) -> Self: 1143 """ 1144 The user should input a value and all {x,y,z} coordinates 1145 will be quantized to that absolute grain size. 1146 """ 1147 qp = vtki.new("QuantizePolyDataPoints") 1148 qp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1149 qp.SetQFactor(value) 1150 qp.Update() 1151 self._update(qp.GetOutput()) 1152 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("quantize", parents=[self]) 1153 return self 1154 1155 @property 1156 def vertex_normals(self) -> np.ndarray: 1157 """ 1158 Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as `point_normals`. 1159 If needed, normals are computed via `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1160 Check out also `compute_normals()` and `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1161 """ 1162 vtknormals = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetNormals() 1163 if vtknormals is None: 1164 self.compute_normals_with_pca() 1165 vtknormals = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetNormals() 1166 return utils.vtk2numpy(vtknormals) 1167 1168 @property 1169 def point_normals(self) -> np.ndarray: 1170 """ 1171 Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as `vertex_normals`. 1172 Check out also `compute_normals()` and `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1173 """ 1174 return self.vertex_normals 1175 1176 def align_to(self, target, iters=100, rigid=False, invert=False, use_centroids=False) -> Self: 1177 """ 1178 Aligned to target mesh through the `Iterative Closest Point` algorithm. 1179 1180 The core of the algorithm is to match each vertex in one surface with 1181 the closest surface point on the other, then apply the transformation 1182 that modify one surface to best match the other (in the least-square sense). 1183 1184 Arguments: 1185 rigid : (bool) 1186 if True do not allow scaling 1187 invert : (bool) 1188 if True start by aligning the target to the source but 1189 invert the transformation finally. Useful when the target is smaller 1190 than the source. 1191 use_centroids : (bool) 1192 start by matching the centroids of the two objects. 1193 1194 Examples: 1195 - [align1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align1.py) 1196 1197  1198 1199 - [align2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align2.py) 1200 1201  1202 """ 1203 icp = vtki.new("IterativeClosestPointTransform") 1204 icp.SetSource(self.dataset) 1205 icp.SetTarget(target.dataset) 1206 if invert: 1207 icp.Inverse() 1208 icp.SetMaximumNumberOfIterations(iters) 1209 if rigid: 1210 icp.GetLandmarkTransform().SetModeToRigidBody() 1211 icp.SetStartByMatchingCentroids(use_centroids) 1212 icp.Update() 1213 1214 self.apply_transform(icp.GetMatrix()) 1215 1216 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1217 "align_to", parents=[self, target], comment=f"rigid = {rigid}" 1218 ) 1219 return self 1220 1221 def align_to_bounding_box(self, msh, rigid=False) -> Self: 1222 """ 1223 Align the current object's bounding box to the bounding box 1224 of the input object. 1225 1226 Use `rigid=True` to disable scaling. 1227 1228 Example: 1229 [align6.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align6.py) 1230 """ 1231 lmt = vtki.vtkLandmarkTransform() 1232 ss = vtki.vtkPoints() 1233 xss0, xss1, yss0, yss1, zss0, zss1 = self.bounds() 1234 for p in [ 1235 [xss0, yss0, zss0], 1236 [xss1, yss0, zss0], 1237 [xss1, yss1, zss0], 1238 [xss0, yss1, zss0], 1239 [xss0, yss0, zss1], 1240 [xss1, yss0, zss1], 1241 [xss1, yss1, zss1], 1242 [xss0, yss1, zss1], 1243 ]: 1244 ss.InsertNextPoint(p) 1245 st = vtki.vtkPoints() 1246 xst0, xst1, yst0, yst1, zst0, zst1 = msh.bounds() 1247 for p in [ 1248 [xst0, yst0, zst0], 1249 [xst1, yst0, zst0], 1250 [xst1, yst1, zst0], 1251 [xst0, yst1, zst0], 1252 [xst0, yst0, zst1], 1253 [xst1, yst0, zst1], 1254 [xst1, yst1, zst1], 1255 [xst0, yst1, zst1], 1256 ]: 1257 st.InsertNextPoint(p) 1258 1259 lmt.SetSourceLandmarks(ss) 1260 lmt.SetTargetLandmarks(st) 1261 lmt.SetModeToAffine() 1262 if rigid: 1263 lmt.SetModeToRigidBody() 1264 lmt.Update() 1265 1266 LT = LinearTransform(lmt) 1267 self.apply_transform(LT) 1268 return self 1269 1270 def align_with_landmarks( 1271 self, 1272 source_landmarks, 1273 target_landmarks, 1274 rigid=False, 1275 affine=False, 1276 least_squares=False, 1277 ) -> Self: 1278 """ 1279 Transform mesh orientation and position based on a set of landmarks points. 1280 The algorithm finds the best matching of source points to target points 1281 in the mean least square sense, in one single step. 1282 1283 If `affine` is True the x, y and z axes can scale independently but stay collinear. 1284 With least_squares they can vary orientation. 1285 1286 Examples: 1287 - [align5.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align5.py) 1288 1289  1290 """ 1291 1292 if utils.is_sequence(source_landmarks): 1293 ss = vtki.vtkPoints() 1294 for p in source_landmarks: 1295 ss.InsertNextPoint(p) 1296 else: 1297 ss = source_landmarks.dataset.GetPoints() 1298 if least_squares: 1299 source_landmarks = source_landmarks.coordinates 1300 1301 if utils.is_sequence(target_landmarks): 1302 st = vtki.vtkPoints() 1303 for p in target_landmarks: 1304 st.InsertNextPoint(p) 1305 else: 1306 st = target_landmarks.GetPoints() 1307 if least_squares: 1308 target_landmarks = target_landmarks.coordinates 1309 1310 if ss.GetNumberOfPoints() != st.GetNumberOfPoints(): 1311 n1 = ss.GetNumberOfPoints() 1312 n2 = st.GetNumberOfPoints() 1313 vedo.logger.error(f"source and target have different nr of points {n1} vs {n2}") 1314 raise RuntimeError() 1315 1316 if int(rigid) + int(affine) + int(least_squares) > 1: 1317 vedo.logger.error( 1318 "only one of rigid, affine, least_squares can be True at a time" 1319 ) 1320 raise RuntimeError() 1321 1322 lmt = vtki.vtkLandmarkTransform() 1323 lmt.SetSourceLandmarks(ss) 1324 lmt.SetTargetLandmarks(st) 1325 lmt.SetModeToSimilarity() 1326 1327 if rigid: 1328 lmt.SetModeToRigidBody() 1329 lmt.Update() 1330 1331 elif affine: 1332 lmt.SetModeToAffine() 1333 lmt.Update() 1334 1335 elif least_squares: 1336 cms = source_landmarks.mean(axis=0) 1337 cmt = target_landmarks.mean(axis=0) 1338 m = np.linalg.lstsq(source_landmarks - cms, target_landmarks - cmt, rcond=None)[0] 1339 M = vtki.vtkMatrix4x4() 1340 for i in range(3): 1341 for j in range(3): 1342 M.SetElement(j, i, m[i][j]) 1343 lmt = vtki.vtkTransform() 1344 lmt.Translate(cmt) 1345 lmt.Concatenate(M) 1346 lmt.Translate(-cms) 1347 1348 else: 1349 lmt.Update() 1350 1351 self.apply_transform(lmt) 1352 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("transform_with_landmarks", parents=[self]) 1353 return self 1354 1355 def normalize(self) -> Self: 1356 """Scale average size to unit. The scaling is performed around the center of mass.""" 1357 coords = self.coordinates 1358 if not coords.shape[0]: 1359 return self 1360 cm = np.mean(coords, axis=0) 1361 pts = coords - cm 1362 xyz2 = np.sum(pts * pts, axis=0) 1363 scale = 1 / np.sqrt(np.sum(xyz2) / len(pts)) 1364 self.scale(scale, origin=cm) 1365 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("normalize", parents=[self]) 1366 return self 1367 1368 def mirror(self, axis="x", origin=True) -> Self: 1369 """ 1370 Mirror reflect along one of the cartesian axes 1371 1372 Arguments: 1373 axis : (str) 1374 axis to use for mirroring, must be set to `x, y, z`. 1375 Or any combination of those. 1376 origin : (list) 1377 use this point as the origin of the mirroring transformation. 1378 1379 Examples: 1380 - [mirror.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mirror.py) 1381 1382  1383 """ 1384 sx, sy, sz = 1, 1, 1 1385 if "x" in axis.lower(): sx = -1 1386 if "y" in axis.lower(): sy = -1 1387 if "z" in axis.lower(): sz = -1 1388 1389 self.scale([sx, sy, sz], origin=origin) 1390 1391 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1392 "mirror", comment=f"axis = {axis}", parents=[self]) 1393 1394 if sx * sy * sz < 0: 1395 if hasattr(self, "reverse"): 1396 self.reverse() 1397 return self 1398 1399 def flip_normals(self) -> Self: 1400 """Flip all normals orientation.""" 1401 rs = vtki.new("ReverseSense") 1402 rs.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1403 rs.ReverseCellsOff() 1404 rs.ReverseNormalsOn() 1405 rs.Update() 1406 self._update(rs.GetOutput()) 1407 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("flip_normals", parents=[self]) 1408 return self 1409 1410 def add_gaussian_noise(self, sigma=1.0) -> Self: 1411 """ 1412 Add gaussian noise to point positions. 1413 An extra array is added named "GaussianNoise" with the displacements. 1414 1415 Arguments: 1416 sigma : (float) 1417 nr. of standard deviations, expressed in percent of the diagonal size of mesh. 1418 Can also be a list `[sigma_x, sigma_y, sigma_z]`. 1419 1420 Example: 1421 ```python 1422 from vedo import Sphere 1423 Sphere().add_gaussian_noise(1.0).point_size(8).show().close() 1424 ``` 1425 """ 1426 sz = self.diagonal_size() 1427 pts = self.coordinates 1428 n = len(pts) 1429 ns = (np.random.randn(n, 3) * sigma) * (sz / 100) 1430 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 1431 vpts.SetNumberOfPoints(n) 1432 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(pts + ns, dtype=np.float32)) 1433 self.dataset.SetPoints(vpts) 1434 self.dataset.GetPoints().Modified() 1435 self.pointdata["GaussianNoise"] = -ns 1436 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1437 "gaussian_noise", parents=[self], shape="egg", comment=f"sigma = {sigma}" 1438 ) 1439 return self 1440 1441 def closest_point( 1442 self, pt, n=1, radius=None, return_point_id=False, return_cell_id=False 1443 ) -> Union[List[int], int, np.ndarray]: 1444 """ 1445 Find the closest point(s) on a mesh given from the input point `pt`. 1446 1447 Arguments: 1448 n : (int) 1449 if greater than 1, return a list of n ordered closest points 1450 radius : (float) 1451 if given, get all points within that radius. Then n is ignored. 1452 return_point_id : (bool) 1453 return point ID instead of coordinates 1454 return_cell_id : (bool) 1455 return cell ID in which the closest point sits 1456 1457 Examples: 1458 - [align1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align1.py) 1459 - [fitplanes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/fitplanes.py) 1460 - [quadratic_morphing.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/quadratic_morphing.py) 1461 1462 .. note:: 1463 The appropriate tree search locator is built on the fly and cached for speed. 1464 1465 If you want to reset it use `mymesh.point_locator=None` 1466 and / or `mymesh.cell_locator=None`. 1467 """ 1468 if len(pt) != 3: 1469 pt = [pt[0], pt[1], 0] 1470 1471 # NB: every time the mesh moves or is warped the locators are set to None 1472 if ((n > 1 or radius) or (n == 1 and return_point_id)) and not return_cell_id: 1473 poly = None 1474 if not self.point_locator: 1475 poly = self.dataset 1476 self.point_locator = vtki.new("StaticPointLocator") 1477 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 1478 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1479 1480 ########## 1481 if radius: 1482 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1483 self.point_locator.FindPointsWithinRadius(radius, pt, vtklist) 1484 elif n > 1: 1485 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1486 self.point_locator.FindClosestNPoints(n, pt, vtklist) 1487 else: # n==1 hence return_point_id==True 1488 ######## 1489 return self.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(pt) 1490 ######## 1491 1492 if return_point_id: 1493 ######## 1494 return utils.vtk2numpy(vtklist) 1495 ######## 1496 1497 if not poly: 1498 poly = self.dataset 1499 trgp = [] 1500 for i in range(vtklist.GetNumberOfIds()): 1501 trgp_ = [0, 0, 0] 1502 vi = vtklist.GetId(i) 1503 poly.GetPoints().GetPoint(vi, trgp_) 1504 trgp.append(trgp_) 1505 ######## 1506 return np.array(trgp) 1507 ######## 1508 1509 else: 1510 1511 if not self.cell_locator: 1512 poly = self.dataset 1513 1514 # As per Miquel example with limbs the vtkStaticCellLocator doesnt work !! 1515 # https://discourse.vtk.org/t/vtkstaticcelllocator-problem-vtk9-0-3/7854/4 1516 if vedo.vtk_version[0] >= 9 and vedo.vtk_version[1] > 0: 1517 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("StaticCellLocator") 1518 else: 1519 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("CellLocator") 1520 1521 self.cell_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 1522 self.cell_locator.BuildLocator() 1523 1524 if radius is not None: 1525 vedo.printc("Warning: closest_point() with radius is not implemented for cells.", c='r') 1526 1527 if n != 1: 1528 vedo.printc("Warning: closest_point() with n>1 is not implemented for cells.", c='r') 1529 1530 trgp = [0, 0, 0] 1531 cid = vtki.mutable(0) 1532 dist2 = vtki.mutable(0) 1533 subid = vtki.mutable(0) 1534 self.cell_locator.FindClosestPoint(pt, trgp, cid, subid, dist2) 1535 1536 if return_cell_id: 1537 return int(cid) 1538 1539 return np.array(trgp) 1540 1541 def auto_distance(self) -> np.ndarray: 1542 """ 1543 Calculate the distance to the closest point in the same cloud of points. 1544 The output is stored in a new pointdata array called "AutoDistance", 1545 and it is also returned by the function. 1546 """ 1547 points = self.coordinates 1548 if not self.point_locator: 1549 self.point_locator = vtki.new("StaticPointLocator") 1550 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(self.dataset) 1551 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1552 qs = [] 1553 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1554 vtkpoints = self.dataset.GetPoints() 1555 for p in points: 1556 self.point_locator.FindClosestNPoints(2, p, vtklist) 1557 q = [0, 0, 0] 1558 pid = vtklist.GetId(1) 1559 vtkpoints.GetPoint(pid, q) 1560 qs.append(q) 1561 dists = np.linalg.norm(points - np.array(qs), axis=1) 1562 self.pointdata["AutoDistance"] = dists 1563 return dists 1564 1565 def hausdorff_distance(self, points) -> float: 1566 """ 1567 Compute the Hausdorff distance to the input point set. 1568 Returns a single `float`. 1569 1570 Example: 1571 ```python 1572 from vedo import * 1573 t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) 1574 x = 4/3 * sin(t)**3 1575 y = cos(t) - cos(2*t)/3 - cos(3*t)/6 - cos(4*t)/12 1576 pol1 = Line(np.c_[x,y], closed=True).triangulate() 1577 pol2 = Polygon(nsides=5).pos(2,2) 1578 d12 = pol1.distance_to(pol2) 1579 d21 = pol2.distance_to(pol1) 1580 pol1.lw(0).cmap("viridis") 1581 pol2.lw(0).cmap("viridis") 1582 print("distance d12, d21 :", min(d12), min(d21)) 1583 print("hausdorff distance:", pol1.hausdorff_distance(pol2)) 1584 print("chamfer distance :", pol1.chamfer_distance(pol2)) 1585 show(pol1, pol2, axes=1) 1586 ``` 1587  1588 """ 1589 hp = vtki.new("HausdorffDistancePointSetFilter") 1590 hp.SetInputData(0, self.dataset) 1591 hp.SetInputData(1, points.dataset) 1592 hp.SetTargetDistanceMethodToPointToCell() 1593 hp.Update() 1594 return hp.GetHausdorffDistance() 1595 1596 def chamfer_distance(self, pcloud) -> float: 1597 """ 1598 Compute the Chamfer distance to the input point set. 1599 1600 Example: 1601 ```python 1602 from vedo import * 1603 cloud1 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) 1604 cloud2 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) + [1, 2, 3] 1605 c1 = Points(cloud1, r=5, c="red") 1606 c2 = Points(cloud2, r=5, c="green") 1607 d = c1.chamfer_distance(c2) 1608 show(f"Chamfer distance = {d}", c1, c2, axes=1).close() 1609 ``` 1610 """ 1611 # Definition of Chamfer distance may vary, here we use the average 1612 if not pcloud.point_locator: 1613 pcloud.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 1614 pcloud.point_locator.SetDataSet(pcloud.dataset) 1615 pcloud.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1616 if not self.point_locator: 1617 self.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 1618 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(self.dataset) 1619 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1620 1621 ps1 = self.coordinates 1622 ps2 = pcloud.coordinates 1623 1624 ids12 = [] 1625 for p in ps1: 1626 pid12 = pcloud.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1627 ids12.append(pid12) 1628 deltav = ps2[ids12] - ps1 1629 da = np.mean(np.linalg.norm(deltav, axis=1)) 1630 1631 ids21 = [] 1632 for p in ps2: 1633 pid21 = self.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1634 ids21.append(pid21) 1635 deltav = ps1[ids21] - ps2 1636 db = np.mean(np.linalg.norm(deltav, axis=1)) 1637 return (da + db) / 2 1638 1639 def remove_outliers(self, radius: float, neighbors=5) -> Self: 1640 """ 1641 Remove outliers from a cloud of points within the specified `radius` search. 1642 1643 Arguments: 1644 radius : (float) 1645 Specify the local search radius. 1646 neighbors : (int) 1647 Specify the number of neighbors that a point must have, 1648 within the specified radius, for the point to not be considered isolated. 1649 1650 Examples: 1651 - [clustering.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/clustering.py) 1652 1653  1654 """ 1655 removal = vtki.new("RadiusOutlierRemoval") 1656 removal.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1657 removal.SetRadius(radius) 1658 removal.SetNumberOfNeighbors(neighbors) 1659 removal.GenerateOutliersOff() 1660 removal.Update() 1661 inputobj = removal.GetOutput() 1662 if inputobj.GetNumberOfCells() == 0: 1663 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1664 for i in range(inputobj.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1665 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 1666 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 1667 inputobj.SetVerts(carr) 1668 self._update(removal.GetOutput()) 1669 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("remove_outliers", parents=[self]) 1670 return self 1671 1672 def relax_point_positions( 1673 self, 1674 n=10, 1675 iters=10, 1676 sub_iters=10, 1677 packing_factor=1, 1678 max_step=0, 1679 constraints=(), 1680 ) -> Self: 1681 """ 1682 Smooth mesh or points with a 1683 [Laplacian algorithm](https://vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkPointSmoothingFilter.html) 1684 variant. This modifies the coordinates of the input points by adjusting their positions 1685 to create a smooth distribution (and thereby form a pleasing packing of the points). 1686 Smoothing is performed by considering the effects of neighboring points on one another 1687 it uses a cubic cutoff function to produce repulsive forces between close points 1688 and attractive forces that are a little further away. 1689 1690 In general, the larger the neighborhood size, the greater the reduction in high frequency 1691 information. The memory and computational requirements of the algorithm may also 1692 significantly increase. 1693 1694 The algorithm incrementally adjusts the point positions through an iterative process. 1695 Basically points are moved due to the influence of neighboring points. 1696 1697 As points move, both the local connectivity and data attributes associated with each point 1698 must be updated. Rather than performing these expensive operations after every iteration, 1699 a number of sub-iterations can be specified. If so, then the neighborhood and attribute 1700 value updates occur only every sub iteration, which can improve performance significantly. 1701 1702 Arguments: 1703 n : (int) 1704 neighborhood size to calculate the Laplacian. 1705 iters : (int) 1706 number of iterations. 1707 sub_iters : (int) 1708 number of sub-iterations, i.e. the number of times the neighborhood and attribute 1709 value updates occur during each iteration. 1710 packing_factor : (float) 1711 adjust convergence speed. 1712 max_step : (float) 1713 Specify the maximum smoothing step size for each smoothing iteration. 1714 This limits the the distance over which a point can move in each iteration. 1715 As in all iterative methods, the stability of the process is sensitive to this parameter. 1716 In general, small step size and large numbers of iterations are more stable than a larger 1717 step size and a smaller numbers of iterations. 1718 constraints : (dict) 1719 dictionary of constraints. 1720 Point constraints are used to prevent points from moving, 1721 or to move only on a plane. This can prevent shrinking or growing point clouds. 1722 If enabled, a local topological analysis is performed to determine whether a point 1723 should be marked as fixed" i.e., never moves, or the point only moves on a plane, 1724 or the point can move freely. 1725 If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined by 1726 `fixed_angle`, then the point is classified as fixed. 1727 If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined by 1728 `boundary_angle`, then the point is classified as lying on a plane. 1729 Angles are expressed in degrees. 1730 1731 Example: 1732 ```py 1733 import numpy as np 1734 from vedo import Points, show 1735 from vedo.pyplot import histogram 1736 1737 vpts1 = Points(np.random.rand(10_000, 3)) 1738 dists = vpts1.auto_distance() 1739 h1 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() 1740 1741 vpts2 = vpts1.clone().relax_point_positions(n=100, iters=20, sub_iters=10) 1742 dists = vpts2.auto_distance() 1743 h2 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() 1744 1745 show([[vpts1, h1], [vpts2, h2]], N=2).close() 1746 ``` 1747 """ 1748 smooth = vtki.new("PointSmoothingFilter") 1749 smooth.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1750 smooth.SetSmoothingModeToUniform() 1751 smooth.SetNumberOfIterations(iters) 1752 smooth.SetNumberOfSubIterations(sub_iters) 1753 smooth.SetPackingFactor(packing_factor) 1754 if self.point_locator: 1755 smooth.SetLocator(self.point_locator) 1756 if not max_step: 1757 max_step = self.diagonal_size() / 100 1758 smooth.SetMaximumStepSize(max_step) 1759 smooth.SetNeighborhoodSize(n) 1760 if constraints: 1761 fixed_angle = constraints.get("fixed_angle", 45) 1762 boundary_angle = constraints.get("boundary_angle", 110) 1763 smooth.EnableConstraintsOn() 1764 smooth.SetFixedAngle(fixed_angle) 1765 smooth.SetBoundaryAngle(boundary_angle) 1766 smooth.GenerateConstraintScalarsOn() 1767 smooth.GenerateConstraintNormalsOn() 1768 smooth.Update() 1769 self._update(smooth.GetOutput()) 1770 self.metadata["PackingRadius"] = smooth.GetPackingRadius() 1771 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("relax_point_positions", parents=[self]) 1772 return self 1773 1774 def smooth_mls_1d(self, f=0.2, radius=None, n=0) -> Self: 1775 """ 1776 Smooth mesh or points with a `Moving Least Squares` variant. 1777 The point data array "Variances" will contain the residue calculated for each point. 1778 1779 Arguments: 1780 f : (float) 1781 smoothing factor - typical range is [0,2]. 1782 radius : (float) 1783 radius search in absolute units. 1784 If set then `f` is ignored. 1785 n : (int) 1786 number of neighbours to be used for the fit. 1787 If set then `f` and `radius` are ignored. 1788 1789 Examples: 1790 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 1791 - [skeletonize.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/skeletonize.py) 1792 1793  1794 """ 1795 coords = self.coordinates 1796 ncoords = len(coords) 1797 1798 if n: 1799 Ncp = n 1800 elif radius: 1801 Ncp = 1 1802 else: 1803 Ncp = int(ncoords * f / 10) 1804 if Ncp < 5: 1805 vedo.logger.warning(f"Please choose a fraction higher than {f}") 1806 Ncp = 5 1807 1808 variances, newline = [], [] 1809 for p in coords: 1810 points = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius) 1811 if len(points) < 4: 1812 continue 1813 1814 points = np.array(points) 1815 pointsmean = points.mean(axis=0) # plane center 1816 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(points - pointsmean) 1817 newp = np.dot(p - pointsmean, vv[0]) * vv[0] + pointsmean 1818 variances.append(dd[1] + dd[2]) 1819 newline.append(newp) 1820 1821 self.pointdata["Variances"] = np.array(variances).astype(np.float32) 1822 self.coordinates = newline 1823 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_mls_1d", parents=[self]) 1824 return self 1825 1826 def smooth_mls_2d(self, f=0.2, radius=None, n=0) -> Self: 1827 """ 1828 Smooth mesh or points with a `Moving Least Squares` algorithm variant. 1829 1830 The `mesh.pointdata['MLSVariance']` array will contain the residue calculated for each point. 1831 When a radius is specified, points that are isolated will not be moved and will get 1832 a 0 entry in array `mesh.pointdata['MLSValidPoint']`. 1833 1834 Arguments: 1835 f : (float) 1836 smoothing factor - typical range is [0, 2]. 1837 radius : (float | array) 1838 radius search in absolute units. Can be single value (float) or sequence 1839 for adaptive smoothing. If set then `f` is ignored. 1840 n : (int) 1841 number of neighbours to be used for the fit. 1842 If set then `f` and `radius` are ignored. 1843 1844 Examples: 1845 - [moving_least_squares2D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares2D.py) 1846 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 1847 1848  1849 """ 1850 coords = self.coordinates 1851 ncoords = len(coords) 1852 1853 if n: 1854 Ncp = n 1855 radius = None 1856 elif radius is not None: 1857 Ncp = 1 1858 else: 1859 Ncp = int(ncoords * f / 100) 1860 if Ncp < 4: 1861 vedo.logger.error(f"please choose a f-value higher than {f}") 1862 Ncp = 4 1863 1864 variances, newpts, valid = [], [], [] 1865 radius_is_sequence = utils.is_sequence(radius) 1866 1867 pb = None 1868 if ncoords > 10000: 1869 pb = utils.ProgressBar(0, ncoords, delay=3) 1870 1871 for i, p in enumerate(coords): 1872 if pb: 1873 pb.print("smooth_mls_2d working ...") 1874 1875 # if a radius was provided for each point 1876 if radius_is_sequence: 1877 pts = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius[i]) 1878 else: 1879 pts = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius) 1880 1881 if len(pts) > 3: 1882 ptsmean = pts.mean(axis=0) # plane center 1883 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(pts - ptsmean) 1884 cv = np.cross(vv[0], vv[1]) 1885 t = (np.dot(cv, ptsmean) - np.dot(cv, p)) / np.dot(cv, cv) 1886 newpts.append(p + cv * t) 1887 variances.append(dd[2]) 1888 if radius is not None: 1889 valid.append(1) 1890 else: 1891 newpts.append(p) 1892 variances.append(0) 1893 if radius is not None: 1894 valid.append(0) 1895 1896 if radius is not None: 1897 self.pointdata["MLSValidPoint"] = np.array(valid).astype(np.uint8) 1898 self.pointdata["MLSVariance"] = np.array(variances).astype(np.float32) 1899 1900 self.coordinates = newpts 1901 1902 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_mls_2d", parents=[self]) 1903 return self 1904 1905 def smooth_lloyd_2d(self, iterations=2, bounds=None, options="Qbb Qc Qx") -> Self: 1906 """ 1907 Lloyd relaxation of a 2D pointcloud. 1908 1909 Arguments: 1910 iterations : (int) 1911 number of iterations. 1912 bounds : (list) 1913 bounding box of the domain. 1914 options : (str) 1915 options for the Qhull algorithm. 1916 """ 1917 # Credits: https://hatarilabs.com/ih-en/ 1918 # tutorial-to-create-a-geospatial-voronoi-sh-mesh-with-python-scipy-and-geopandas 1919 from scipy.spatial import Voronoi as scipy_voronoi 1920 1921 def _constrain_points(points): 1922 # Update any points that have drifted beyond the boundaries of this space 1923 if bounds is not None: 1924 for point in points: 1925 if point[0] < bounds[0]: point[0] = bounds[0] 1926 if point[0] > bounds[1]: point[0] = bounds[1] 1927 if point[1] < bounds[2]: point[1] = bounds[2] 1928 if point[1] > bounds[3]: point[1] = bounds[3] 1929 return points 1930 1931 def _find_centroid(vertices): 1932 # The equation for the method used here to find the centroid of a 1933 # 2D polygon is given here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centroid#Of_a_polygon 1934 area = 0 1935 centroid_x = 0 1936 centroid_y = 0 1937 for i in range(len(vertices) - 1): 1938 step = (vertices[i, 0] * vertices[i + 1, 1]) - (vertices[i + 1, 0] * vertices[i, 1]) 1939 centroid_x += (vertices[i, 0] + vertices[i + 1, 0]) * step 1940 centroid_y += (vertices[i, 1] + vertices[i + 1, 1]) * step 1941 area += step 1942 if area: 1943 centroid_x = (1.0 / (3.0 * area)) * centroid_x 1944 centroid_y = (1.0 / (3.0 * area)) * centroid_y 1945 # prevent centroids from escaping bounding box 1946 return _constrain_points([[centroid_x, centroid_y]])[0] 1947 1948 def _relax(voron): 1949 # Moves each point to the centroid of its cell in the voronoi 1950 # map to "relax" the points (i.e. jitter the points so as 1951 # to spread them out within the space). 1952 centroids = [] 1953 for idx in voron.point_region: 1954 # the region is a series of indices into voronoi.vertices 1955 # remove point at infinity, designated by index -1 1956 region = [i for i in voron.regions[idx] if i != -1] 1957 # enclose the polygon 1958 region = region + [region[0]] 1959 verts = voron.vertices[region] 1960 # find the centroid of those vertices 1961 centroids.append(_find_centroid(verts)) 1962 return _constrain_points(centroids) 1963 1964 if bounds is None: 1965 bounds = self.bounds() 1966 1967 pts = self.vertices[:, (0, 1)] 1968 for i in range(iterations): 1969 vor = scipy_voronoi(pts, qhull_options=options) 1970 _constrain_points(vor.vertices) 1971 pts = _relax(vor) 1972 out = Points(pts) 1973 out.name = "MeshSmoothLloyd2D" 1974 out.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_lloyd", parents=[self]) 1975 return out 1976 1977 def project_on_plane(self, plane="z", point=None, direction=None) -> Self: 1978 """ 1979 Project the mesh on one of the Cartesian planes. 1980 1981 Arguments: 1982 plane : (str, Plane) 1983 if plane is `str`, plane can be one of ['x', 'y', 'z'], 1984 represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. 1985 Otherwise, plane should be an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane`. 1986 point : (float, array) 1987 if plane is `str`, point should be a float represents the intercept. 1988 Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection 1989 direction : (array) 1990 direction of oblique projection 1991 1992 Note: 1993 Parameters `point` and `direction` are only used if the given plane 1994 is an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane`. And one of these two params 1995 should be left as `None` to specify the projection type. 1996 1997 Example: 1998 ```python 1999 s.project_on_plane(plane='z') # project to z-plane 2000 plane = Plane(pos=(4, 8, -4), normal=(-1, 0, 1), s=(5,5)) 2001 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane) # orthogonal projection 2002 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, point=(6, 6, 6)) # perspective projection 2003 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, direction=(1, 2, -1)) # oblique projection 2004 ``` 2005 2006 Examples: 2007 - [silhouette2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/silhouette2.py) 2008 2009  2010 """ 2011 coords = self.coordinates 2012 2013 if plane == "x": 2014 coords[:, 0] = self.transform.position[0] 2015 intercept = self.xbounds()[0] if point is None else point 2016 self.x(intercept) 2017 elif plane == "y": 2018 coords[:, 1] = self.transform.position[1] 2019 intercept = self.ybounds()[0] if point is None else point 2020 self.y(intercept) 2021 elif plane == "z": 2022 coords[:, 2] = self.transform.position[2] 2023 intercept = self.zbounds()[0] if point is None else point 2024 self.z(intercept) 2025 2026 elif isinstance(plane, vedo.shapes.Plane): 2027 normal = plane.normal / np.linalg.norm(plane.normal) 2028 pl = np.hstack((normal, -np.dot(plane.pos(), normal))).reshape(4, 1) 2029 if direction is None and point is None: 2030 # orthogonal projection 2031 pt = np.hstack((normal, [0])).reshape(4, 1) 2032 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T # python3 only 2033 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2034 2035 elif direction is None: 2036 # perspective projection 2037 pt = np.hstack((np.array(point), [1])).reshape(4, 1) 2038 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T 2039 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2040 2041 elif point is None: 2042 # oblique projection 2043 pt = np.hstack((np.array(direction), [0])).reshape(4, 1) 2044 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T 2045 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2046 2047 coords = np.concatenate([coords, np.ones((coords.shape[:-1] + (1,)))], axis=-1) 2048 # coords = coords @ proj_mat.T 2049 coords = np.matmul(coords, proj_mat.T) 2050 coords = coords[:, :3] / coords[:, 3:] 2051 2052 else: 2053 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown plane {plane}") 2054 raise RuntimeError() 2055 2056 self.alpha(0.1) 2057 self.coordinates = coords 2058 return self 2059 2060 def warp(self, source, target, sigma=1.0, mode="3d") -> Self: 2061 """ 2062 "Thin Plate Spline" transformations describe a nonlinear warp transform defined by a set 2063 of source and target landmarks. Any point on the mesh close to a source landmark will 2064 be moved to a place close to the corresponding target landmark. 2065 The points in between are interpolated smoothly using 2066 Bookstein's Thin Plate Spline algorithm. 2067 2068 Transformation object can be accessed with `mesh.transform`. 2069 2070 Arguments: 2071 sigma : (float) 2072 specify the 'stiffness' of the spline. 2073 mode : (str) 2074 set the basis function to either abs(R) (for 3d) or R2LogR (for 2d meshes) 2075 2076 Examples: 2077 - [interpolate_field.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/interpolate_field.py) 2078 - [warp1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp1.py) 2079 - [warp2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp2.py) 2080 - [warp3.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp3.py) 2081 - [warp4a.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp4a.py) 2082 - [warp4b.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp4b.py) 2083 - [warp6.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp6.py) 2084 2085  2086 """ 2087 parents = [self] 2088 2089 try: 2090 source = source.coordinates 2091 parents.append(source) 2092 except AttributeError: 2093 source = utils.make3d(source) 2094 2095 try: 2096 target = target.coordinates 2097 parents.append(target) 2098 except AttributeError: 2099 target = utils.make3d(target) 2100 2101 ns = len(source) 2102 nt = len(target) 2103 if ns != nt: 2104 vedo.logger.error(f"#source {ns} != {nt} #target points") 2105 raise RuntimeError() 2106 2107 NLT = NonLinearTransform(sigma=sigma, mode=mode) 2108 NLT.source_points = source 2109 NLT.target_points = target 2110 self.apply_transform(NLT) 2111 2112 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("warp", parents=parents) 2113 return self 2114 2115 def cut_with_plane( 2116 self, 2117 origin=(0, 0, 0), 2118 normal=(1, 0, 0), 2119 invert=False, 2120 # generate_ids=False, 2121 ) -> Self: 2122 """ 2123 Cut the mesh with the plane defined by a point and a normal. 2124 2125 Arguments: 2126 origin : (array) 2127 the cutting plane goes through this point 2128 normal : (array) 2129 normal of the cutting plane 2130 invert : (bool) 2131 select which side of the plane to keep 2132 2133 Example: 2134 ```python 2135 from vedo import Cube 2136 cube = Cube().cut_with_plane(normal=(1,1,1)) 2137 cube.back_color('pink').show().close() 2138 ``` 2139  2140 2141 Examples: 2142 - [trail.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/simulations/trail.py) 2143 2144  2145 2146 Check out also: 2147 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_cylinder()`, `cut_with_sphere()`. 2148 """ 2149 s = str(normal) 2150 if "x" in s: 2151 normal = (1, 0, 0) 2152 if "-" in s: 2153 normal = -np.array(normal) 2154 elif "y" in s: 2155 normal = (0, 1, 0) 2156 if "-" in s: 2157 normal = -np.array(normal) 2158 elif "z" in s: 2159 normal = (0, 0, 1) 2160 if "-" in s: 2161 normal = -np.array(normal) 2162 plane = vtki.vtkPlane() 2163 plane.SetOrigin(origin) 2164 plane.SetNormal(normal) 2165 2166 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2167 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2168 clipper.SetClipFunction(plane) 2169 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2170 clipper.SetGenerateClipScalars(0) 2171 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2172 clipper.SetValue(0) 2173 clipper.Update() 2174 2175 # if generate_ids: 2176 # saved_scalars = None # otherwise the scalars are lost 2177 # if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 2178 # saved_scalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 2179 # varr = clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetScalars() 2180 # if varr.GetName() is None: 2181 # varr.SetName("DistanceToCut") 2182 # arr = utils.vtk2numpy(varr) 2183 # # array of original ids 2184 # ids = np.arange(arr.shape[0]).astype(int) 2185 # ids[arr == 0] = -1 2186 # ids_arr = utils.numpy2vtk(ids, dtype=int) 2187 # ids_arr.SetName("OriginalIds") 2188 # clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().AddArray(ids_arr) 2189 # if saved_scalars: 2190 # clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().AddArray(saved_scalars) 2191 2192 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2193 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_plane", parents=[self]) 2194 return self 2195 2196 def cut_with_planes(self, origins, normals, invert=False) -> Self: 2197 """ 2198 Cut the mesh with a convex set of planes defined by points and normals. 2199 2200 Arguments: 2201 origins : (array) 2202 each cutting plane goes through this point 2203 normals : (array) 2204 normal of each of the cutting planes 2205 invert : (bool) 2206 if True, cut outside instead of inside 2207 2208 Check out also: 2209 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_cylinder()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2210 """ 2211 2212 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 2213 for p in utils.make3d(origins): 2214 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 2215 normals = utils.make3d(normals) 2216 2217 planes = vtki.vtkPlanes() 2218 planes.SetPoints(vpoints) 2219 planes.SetNormals(utils.numpy2vtk(normals, dtype=float)) 2220 2221 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2222 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2223 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2224 clipper.SetClipFunction(planes) 2225 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2226 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2227 clipper.SetValue(0) 2228 clipper.Update() 2229 2230 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2231 2232 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_planes", parents=[self]) 2233 return self 2234 2235 def cut_with_box(self, bounds, invert=False) -> Self: 2236 """ 2237 Cut the current mesh with a box or a set of boxes. 2238 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2239 2240 Input `bounds` can be either: 2241 - a Mesh or Points object 2242 - a list of 6 number representing a bounding box `[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]` 2243 - a list of bounding boxes like the above: `[[xmin1,...], [xmin2,...], ...]` 2244 2245 Example: 2246 ```python 2247 from vedo import Sphere, Cube, show 2248 mesh = Sphere(r=1, res=50) 2249 box = Cube(side=1.5).wireframe() 2250 mesh.cut_with_box(box) 2251 show(mesh, box, axes=1).close() 2252 ``` 2253  2254 2255 Check out also: 2256 `cut_with_line()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2257 """ 2258 if isinstance(bounds, Points): 2259 bounds = bounds.bounds() 2260 2261 box = vtki.new("Box") 2262 if utils.is_sequence(bounds[0]): 2263 for bs in bounds: 2264 box.AddBounds(bs) 2265 else: 2266 box.SetBounds(bounds) 2267 2268 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2269 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2270 clipper.SetClipFunction(box) 2271 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2272 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2273 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2274 clipper.SetValue(0) 2275 clipper.Update() 2276 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2277 2278 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_box", parents=[self]) 2279 return self 2280 2281 def cut_with_line(self, points, invert=False, closed=True) -> Self: 2282 """ 2283 Cut the current mesh with a line vertically in the z-axis direction like a cookie cutter. 2284 The polyline is defined by a set of points (z-coordinates are ignored). 2285 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2286 2287 Check out also: 2288 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2289 """ 2290 pplane = vtki.new("PolyPlane") 2291 if isinstance(points, Points): 2292 points = points.coordinates.tolist() 2293 2294 if closed: 2295 if isinstance(points, np.ndarray): 2296 points = points.tolist() 2297 points.append(points[0]) 2298 2299 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 2300 for p in points: 2301 if len(p) == 2: 2302 p = [p[0], p[1], 0.0] 2303 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 2304 2305 n = len(points) 2306 polyline = vtki.new("PolyLine") 2307 polyline.Initialize(n, vpoints) 2308 polyline.GetPointIds().SetNumberOfIds(n) 2309 for i in range(n): 2310 polyline.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i) 2311 pplane.SetPolyLine(polyline) 2312 2313 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2314 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2315 clipper.SetClipFunction(pplane) 2316 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2317 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2318 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2319 clipper.SetValue(0) 2320 clipper.Update() 2321 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2322 2323 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_line", parents=[self]) 2324 return self 2325 2326 def cut_with_cookiecutter(self, lines) -> Self: 2327 """ 2328 Cut the current mesh with a single line or a set of lines. 2329 2330 Input `lines` can be either: 2331 - a `Mesh` or `Points` object 2332 - a list of 3D points: `[(x1,y1,z1), (x2,y2,z2), ...]` 2333 - a list of 2D points: `[(x1,y1), (x2,y2), ...]` 2334 2335 Example: 2336 ```python 2337 from vedo import * 2338 grid = Mesh(dataurl + "dolfin_fine.vtk") 2339 grid.compute_quality().cmap("Greens") 2340 pols = merge( 2341 Polygon(nsides=10, r=0.3).pos(0.7, 0.3), 2342 Polygon(nsides=10, r=0.2).pos(0.3, 0.7), 2343 ) 2344 lines = pols.boundaries() 2345 cgrid = grid.clone().cut_with_cookiecutter(lines) 2346 grid.alpha(0.1).wireframe() 2347 show(grid, cgrid, lines, axes=8, bg='blackboard').close() 2348 ``` 2349  2350 2351 Check out also: 2352 `cut_with_line()` and `cut_with_point_loop()` 2353 2354 Note: 2355 In case of a warning message like: 2356 "Mesh and trim loop point data attributes are different" 2357 consider interpolating the mesh point data to the loop points, 2358 Eg. (in the above example): 2359 ```python 2360 lines = pols.boundaries().interpolate_data_from(grid, n=2) 2361 ``` 2362 2363 Note: 2364 trying to invert the selection by reversing the loop order 2365 will have no effect in this method, hence it does not have 2366 the `invert` option. 2367 """ 2368 if utils.is_sequence(lines): 2369 lines = utils.make3d(lines) 2370 iline = list(range(len(lines))) + [0] 2371 poly = utils.buildPolyData(lines, lines=[iline]) 2372 else: 2373 poly = lines.dataset 2374 2375 # if invert: # not working 2376 # rev = vtki.new("ReverseSense") 2377 # rev.ReverseCellsOn() 2378 # rev.SetInputData(poly) 2379 # rev.Update() 2380 # poly = rev.GetOutput() 2381 2382 # Build loops from the polyline 2383 build_loops = vtki.new("ContourLoopExtraction") 2384 build_loops.SetGlobalWarningDisplay(0) 2385 build_loops.SetInputData(poly) 2386 build_loops.Update() 2387 boundary_poly = build_loops.GetOutput() 2388 2389 ccut = vtki.new("CookieCutter") 2390 ccut.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2391 ccut.SetLoopsData(boundary_poly) 2392 ccut.SetPointInterpolationToMeshEdges() 2393 # ccut.SetPointInterpolationToLoopEdges() 2394 ccut.PassCellDataOn() 2395 ccut.PassPointDataOn() 2396 ccut.Update() 2397 self._update(ccut.GetOutput()) 2398 2399 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_cookiecutter", parents=[self]) 2400 return self 2401 2402 def cut_with_cylinder(self, center=(0, 0, 0), axis=(0, 0, 1), r=1, invert=False) -> Self: 2403 """ 2404 Cut the current mesh with an infinite cylinder. 2405 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2406 2407 Arguments: 2408 center : (array) 2409 the center of the cylinder 2410 normal : (array) 2411 direction of the cylinder axis 2412 r : (float) 2413 radius of the cylinder 2414 2415 Example: 2416 ```python 2417 from vedo import Disc, show 2418 disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) 2419 mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) 2420 mesh.cut_with_cylinder([0,0,2], r=0.4, axis='y', invert=True) 2421 show(mesh, axes=1).close() 2422 ``` 2423  2424 2425 Examples: 2426 - [optics_main1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/simulations/optics_main1.py) 2427 2428 Check out also: 2429 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2430 """ 2431 s = str(axis) 2432 if "x" in s: 2433 axis = (1, 0, 0) 2434 elif "y" in s: 2435 axis = (0, 1, 0) 2436 elif "z" in s: 2437 axis = (0, 0, 1) 2438 cyl = vtki.new("Cylinder") 2439 cyl.SetCenter(center) 2440 cyl.SetAxis(axis[0], axis[1], axis[2]) 2441 cyl.SetRadius(r) 2442 2443 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2444 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2445 clipper.SetClipFunction(cyl) 2446 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2447 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2448 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2449 clipper.SetValue(0) 2450 clipper.Update() 2451 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2452 2453 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_cylinder", parents=[self]) 2454 return self 2455 2456 def cut_with_sphere(self, center=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, invert=False) -> Self: 2457 """ 2458 Cut the current mesh with an sphere. 2459 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2460 2461 Arguments: 2462 center : (array) 2463 the center of the sphere 2464 r : (float) 2465 radius of the sphere 2466 2467 Example: 2468 ```python 2469 from vedo import Disc, show 2470 disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) 2471 mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) 2472 mesh.cut_with_sphere([1,-0.7,2], r=1.5, invert=True) 2473 show(mesh, axes=1).close() 2474 ``` 2475  2476 2477 Check out also: 2478 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2479 """ 2480 sph = vtki.new("Sphere") 2481 sph.SetCenter(center) 2482 sph.SetRadius(r) 2483 2484 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2485 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2486 clipper.SetClipFunction(sph) 2487 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2488 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2489 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2490 clipper.SetValue(0) 2491 clipper.Update() 2492 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2493 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_sphere", parents=[self]) 2494 return self 2495 2496 def cut_with_mesh(self, mesh, invert=False, keep=False) -> Union[Self, "vedo.Assembly"]: 2497 """ 2498 Cut an `Mesh` mesh with another `Mesh`. 2499 2500 Use `invert` to invert the selection. 2501 2502 Use `keep` to keep the cutoff part, in this case an `Assembly` is returned: 2503 the "cut" object and the "discarded" part of the original object. 2504 You can access both via `assembly.unpack()` method. 2505 2506 Example: 2507 ```python 2508 from vedo import * 2509 arr = np.random.randn(100000, 3)/2 2510 pts = Points(arr).c('red3').pos(5,0,0) 2511 cube = Cube().pos(4,0.5,0) 2512 assem = pts.cut_with_mesh(cube, keep=True) 2513 show(assem.unpack(), axes=1).close() 2514 ``` 2515  2516 2517 Check out also: 2518 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2519 """ 2520 polymesh = mesh.dataset 2521 poly = self.dataset 2522 2523 # Create an array to hold distance information 2524 signed_distances = vtki.vtkFloatArray() 2525 signed_distances.SetNumberOfComponents(1) 2526 signed_distances.SetName("SignedDistances") 2527 2528 # implicit function that will be used to slice the mesh 2529 ippd = vtki.new("ImplicitPolyDataDistance") 2530 ippd.SetInput(polymesh) 2531 2532 # Evaluate the signed distance function at all of the grid points 2533 for pointId in range(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()): 2534 p = poly.GetPoint(pointId) 2535 signed_distance = ippd.EvaluateFunction(p) 2536 signed_distances.InsertNextValue(signed_distance) 2537 2538 currentscals = poly.GetPointData().GetScalars() 2539 if currentscals: 2540 currentscals = currentscals.GetName() 2541 2542 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(signed_distances) 2543 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("SignedDistances") 2544 2545 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2546 clipper.SetInputData(poly) 2547 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2548 clipper.SetGenerateClippedOutput(keep) 2549 clipper.SetValue(0.0) 2550 clipper.Update() 2551 cpoly = clipper.GetOutput() 2552 2553 if keep: 2554 kpoly = clipper.GetOutput(1) 2555 2556 vis = False 2557 if currentscals: 2558 cpoly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(currentscals) 2559 vis = self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility() 2560 2561 self._update(cpoly) 2562 2563 self.pointdata.remove("SignedDistances") 2564 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(vis) 2565 if keep: 2566 if isinstance(self, vedo.Mesh): 2567 cutoff = vedo.Mesh(kpoly) 2568 else: 2569 cutoff = vedo.Points(kpoly) 2570 # cutoff = self.__class__(kpoly) # this does not work properly 2571 cutoff.properties = vtki.vtkProperty() 2572 cutoff.properties.DeepCopy(self.properties) 2573 cutoff.actor.SetProperty(cutoff.properties) 2574 cutoff.c("k5").alpha(0.2) 2575 return vedo.Assembly([self, cutoff]) 2576 2577 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_mesh", parents=[self, mesh]) 2578 return self 2579 2580 def cut_with_point_loop( 2581 self, points, invert=False, on="points", include_boundary=False 2582 ) -> Self: 2583 """ 2584 Cut an `Mesh` object with a set of points forming a closed loop. 2585 2586 Arguments: 2587 invert : (bool) 2588 invert selection (inside-out) 2589 on : (str) 2590 if 'cells' will extract the whole cells lying inside (or outside) the point loop 2591 include_boundary : (bool) 2592 include cells lying exactly on the boundary line. Only relevant on 'cells' mode 2593 2594 Examples: 2595 - [cut_with_points1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/cut_with_points1.py) 2596 2597  2598 2599 - [cut_with_points2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/cut_with_points2.py) 2600 2601  2602 """ 2603 if isinstance(points, Points): 2604 parents = [points] 2605 vpts = points.dataset.GetPoints() 2606 points = points.coordinates 2607 else: 2608 parents = [self] 2609 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 2610 points = utils.make3d(points) 2611 for p in points: 2612 vpts.InsertNextPoint(p) 2613 2614 if "cell" in on: 2615 ippd = vtki.new("ImplicitSelectionLoop") 2616 ippd.SetLoop(vpts) 2617 ippd.AutomaticNormalGenerationOn() 2618 clipper = vtki.new("ExtractPolyDataGeometry") 2619 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2620 clipper.SetImplicitFunction(ippd) 2621 clipper.SetExtractInside(not invert) 2622 clipper.SetExtractBoundaryCells(include_boundary) 2623 else: 2624 spol = vtki.new("SelectPolyData") 2625 spol.SetLoop(vpts) 2626 spol.GenerateSelectionScalarsOn() 2627 spol.GenerateUnselectedOutputOff() 2628 spol.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2629 spol.Update() 2630 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2631 clipper.SetInputData(spol.GetOutput()) 2632 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2633 clipper.SetValue(0.0) 2634 clipper.Update() 2635 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2636 2637 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_pointloop", parents=parents) 2638 return self 2639 2640 def cut_with_scalar(self, value: float, name="", invert=False) -> Self: 2641 """ 2642 Cut a mesh or point cloud with some input scalar point-data. 2643 2644 Arguments: 2645 value : (float) 2646 cutting value 2647 name : (str) 2648 array name of the scalars to be used 2649 invert : (bool) 2650 flip selection 2651 2652 Example: 2653 ```python 2654 from vedo import * 2655 s = Sphere().lw(1) 2656 pts = s.points 2657 scalars = np.sin(3*pts[:,2]) + pts[:,0] 2658 s.pointdata["somevalues"] = scalars 2659 s.cut_with_scalar(0.3) 2660 s.cmap("Spectral", "somevalues").add_scalarbar() 2661 s.show(axes=1).close() 2662 ``` 2663  2664 """ 2665 if name: 2666 self.pointdata.select(name) 2667 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2668 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2669 clipper.SetValue(value) 2670 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2671 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2672 clipper.Update() 2673 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2674 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_scalar", parents=[self]) 2675 return self 2676 2677 def crop(self, 2678 top=None, bottom=None, right=None, left=None, front=None, back=None, 2679 bounds=()) -> Self: 2680 """ 2681 Crop an `Mesh` object. 2682 2683 Arguments: 2684 top : (float) 2685 fraction to crop from the top plane (positive z) 2686 bottom : (float) 2687 fraction to crop from the bottom plane (negative z) 2688 front : (float) 2689 fraction to crop from the front plane (positive y) 2690 back : (float) 2691 fraction to crop from the back plane (negative y) 2692 right : (float) 2693 fraction to crop from the right plane (positive x) 2694 left : (float) 2695 fraction to crop from the left plane (negative x) 2696 bounds : (list) 2697 bounding box of the crop region as `[x0,x1, y0,y1, z0,z1]` 2698 2699 Example: 2700 ```python 2701 from vedo import Sphere 2702 Sphere().crop(right=0.3, left=0.1).show() 2703 ``` 2704  2705 """ 2706 if len(bounds) == 0: 2707 pos = np.array(self.pos()) 2708 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2709 x0, y0, z0 = [x0, y0, z0] - pos 2710 x1, y1, z1 = [x1, y1, z1] - pos 2711 2712 dx, dy, dz = x1 - x0, y1 - y0, z1 - z0 2713 if top: 2714 z1 = z1 - top * dz 2715 if bottom: 2716 z0 = z0 + bottom * dz 2717 if front: 2718 y1 = y1 - front * dy 2719 if back: 2720 y0 = y0 + back * dy 2721 if right: 2722 x1 = x1 - right * dx 2723 if left: 2724 x0 = x0 + left * dx 2725 bounds = (x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1) 2726 2727 cu = vtki.new("Box") 2728 cu.SetBounds(bounds) 2729 2730 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2731 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2732 clipper.SetClipFunction(cu) 2733 clipper.InsideOutOn() 2734 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2735 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2736 clipper.SetValue(0) 2737 clipper.Update() 2738 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2739 2740 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2741 "crop", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 2742 ) 2743 return self 2744 2745 def generate_surface_halo( 2746 self, 2747 distance=0.05, 2748 res=(50, 50, 50), 2749 bounds=(), 2750 maxdist=None, 2751 ) -> "vedo.Mesh": 2752 """ 2753 Generate the surface halo which sits at the specified distance from the input one. 2754 2755 Arguments: 2756 distance : (float) 2757 distance from the input surface 2758 res : (int) 2759 resolution of the surface 2760 bounds : (list) 2761 bounding box of the surface 2762 maxdist : (float) 2763 maximum distance to generate the surface 2764 """ 2765 if not bounds: 2766 bounds = self.bounds() 2767 2768 if not maxdist: 2769 maxdist = self.diagonal_size() / 2 2770 2771 imp = vtki.new("ImplicitModeller") 2772 imp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2773 imp.SetSampleDimensions(res) 2774 if maxdist: 2775 imp.SetMaximumDistance(maxdist) 2776 if len(bounds) == 6: 2777 imp.SetModelBounds(bounds) 2778 contour = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 2779 contour.SetInputConnection(imp.GetOutputPort()) 2780 contour.SetValue(0, distance) 2781 contour.Update() 2782 out = vedo.Mesh(contour.GetOutput()) 2783 out.c("lightblue").alpha(0.25).lighting("off") 2784 out.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("generate_surface_halo", parents=[self]) 2785 return out 2786 2787 def generate_mesh( 2788 self, 2789 line_resolution=None, 2790 mesh_resolution=None, 2791 smooth=0.0, 2792 jitter=0.001, 2793 grid=None, 2794 quads=False, 2795 invert=False, 2796 ) -> Self: 2797 """ 2798 Generate a polygonal Mesh from a closed contour line. 2799 If line is not closed it will be closed with a straight segment. 2800 2801 Check also `generate_delaunay2d()`. 2802 2803 Arguments: 2804 line_resolution : (int) 2805 resolution of the contour line. The default is None, in this case 2806 the contour is not resampled. 2807 mesh_resolution : (int) 2808 resolution of the internal triangles not touching the boundary. 2809 smooth : (float) 2810 smoothing of the contour before meshing. 2811 jitter : (float) 2812 add a small noise to the internal points. 2813 grid : (Grid) 2814 manually pass a Grid object. The default is True. 2815 quads : (bool) 2816 generate a mesh of quads instead of triangles. 2817 invert : (bool) 2818 flip the line orientation. The default is False. 2819 2820 Examples: 2821 - [line2mesh_tri.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/line2mesh_tri.py) 2822 2823  2824 2825 - [line2mesh_quads.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/line2mesh_quads.py) 2826 2827  2828 """ 2829 if line_resolution is None: 2830 contour = vedo.shapes.Line(self.coordinates) 2831 else: 2832 contour = vedo.shapes.Spline(self.coordinates, smooth=smooth, res=line_resolution) 2833 contour.clean() 2834 2835 length = contour.length() 2836 density = length / contour.npoints 2837 # print(f"tomesh():\n\tline length = {length}") 2838 # print(f"\tdensity = {density} length/pt_separation") 2839 2840 x0, x1 = contour.xbounds() 2841 y0, y1 = contour.ybounds() 2842 2843 if grid is None: 2844 if mesh_resolution is None: 2845 resx = int((x1 - x0) / density + 0.5) 2846 resy = int((y1 - y0) / density + 0.5) 2847 # print(f"tmesh_resolution = {[resx, resy]}") 2848 else: 2849 if utils.is_sequence(mesh_resolution): 2850 resx, resy = mesh_resolution 2851 else: 2852 resx, resy = mesh_resolution, mesh_resolution 2853 grid = vedo.shapes.Grid( 2854 [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, 0], 2855 s=((x1 - x0) * 1.025, (y1 - y0) * 1.025), 2856 res=(resx, resy), 2857 ) 2858 else: 2859 grid = grid.clone() 2860 2861 cpts = contour.coordinates 2862 2863 # make sure it's closed 2864 p0, p1 = cpts[0], cpts[-1] 2865 nj = max(2, int(utils.mag(p1 - p0) / density + 0.5)) 2866 joinline = vedo.shapes.Line(p1, p0, res=nj) 2867 contour = vedo.merge(contour, joinline).subsample(0.0001) 2868 2869 ####################################### quads 2870 if quads: 2871 cmesh = grid.clone().cut_with_point_loop(contour, on="cells", invert=invert) 2872 cmesh.wireframe(False).lw(0.5) 2873 cmesh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2874 "generate_mesh", 2875 parents=[self, contour], 2876 comment=f"#quads {cmesh.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 2877 ) 2878 return cmesh 2879 ############################################# 2880 2881 grid_tmp = grid.coordinates.copy() 2882 2883 if jitter: 2884 np.random.seed(0) 2885 sigma = 1.0 / np.sqrt(grid.npoints) * grid.diagonal_size() * jitter 2886 # print(f"\tsigma jittering = {sigma}") 2887 grid_tmp += np.random.rand(grid.npoints, 3) * sigma 2888 grid_tmp[:, 2] = 0.0 2889 2890 todel = [] 2891 density /= np.sqrt(3) 2892 vgrid_tmp = Points(grid_tmp) 2893 2894 for p in contour.coordinates: 2895 out = vgrid_tmp.closest_point(p, radius=density, return_point_id=True) 2896 todel += out.tolist() 2897 2898 grid_tmp = grid_tmp.tolist() 2899 for index in sorted(list(set(todel)), reverse=True): 2900 del grid_tmp[index] 2901 2902 points = contour.coordinates.tolist() + grid_tmp 2903 if invert: 2904 boundary = list(reversed(range(contour.npoints))) 2905 else: 2906 boundary = list(range(contour.npoints)) 2907 2908 dln = Points(points).generate_delaunay2d(mode="xy", boundaries=[boundary]) 2909 dln.compute_normals(points=False) # fixes reversd faces 2910 dln.lw(1) 2911 2912 dln.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2913 "generate_mesh", 2914 parents=[self, contour], 2915 comment=f"#cells {dln.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 2916 ) 2917 return dln 2918 2919 def reconstruct_surface( 2920 self, 2921 dims=(100, 100, 100), 2922 radius=None, 2923 sample_size=None, 2924 hole_filling=True, 2925 bounds=(), 2926 padding=0.05, 2927 ) -> "vedo.Mesh": 2928 """ 2929 Surface reconstruction from a scattered cloud of points. 2930 2931 Arguments: 2932 dims : (int) 2933 number of voxels in x, y and z to control precision. 2934 radius : (float) 2935 radius of influence of each point. 2936 Smaller values generally improve performance markedly. 2937 Note that after the signed distance function is computed, 2938 any voxel taking on the value >= radius 2939 is presumed to be "unseen" or uninitialized. 2940 sample_size : (int) 2941 if normals are not present 2942 they will be calculated using this sample size per point. 2943 hole_filling : (bool) 2944 enables hole filling, this generates 2945 separating surfaces between the empty and unseen portions of the volume. 2946 bounds : (list) 2947 region in space in which to perform the sampling 2948 in format (xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zim, zmax) 2949 padding : (float) 2950 increase by this fraction the bounding box 2951 2952 Examples: 2953 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 2954 2955  2956 """ 2957 if not utils.is_sequence(dims): 2958 dims = (dims, dims, dims) 2959 2960 sdf = vtki.new("SignedDistance") 2961 2962 if len(bounds) == 6: 2963 sdf.SetBounds(bounds) 2964 else: 2965 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2966 sdf.SetBounds( 2967 x0 - (x1 - x0) * padding, 2968 x1 + (x1 - x0) * padding, 2969 y0 - (y1 - y0) * padding, 2970 y1 + (y1 - y0) * padding, 2971 z0 - (z1 - z0) * padding, 2972 z1 + (z1 - z0) * padding, 2973 ) 2974 2975 bb = sdf.GetBounds() 2976 if bb[0]==bb[1]: 2977 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero x-range") 2978 if bb[2]==bb[3]: 2979 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero y-range") 2980 if bb[4]==bb[5]: 2981 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero z-range") 2982 2983 pd = self.dataset 2984 2985 if pd.GetPointData().GetNormals(): 2986 sdf.SetInputData(pd) 2987 else: 2988 normals = vtki.new("PCANormalEstimation") 2989 normals.SetInputData(pd) 2990 if not sample_size: 2991 sample_size = int(pd.GetNumberOfPoints() / 50) 2992 normals.SetSampleSize(sample_size) 2993 normals.SetNormalOrientationToGraphTraversal() 2994 sdf.SetInputConnection(normals.GetOutputPort()) 2995 # print("Recalculating normals with sample size =", sample_size) 2996 2997 if radius is None: 2998 radius = self.diagonal_size() / (sum(dims) / 3) * 5 2999 # print("Calculating mesh from points with radius =", radius) 3000 3001 sdf.SetRadius(radius) 3002 sdf.SetDimensions(dims) 3003 sdf.Update() 3004 3005 surface = vtki.new("ExtractSurface") 3006 surface.SetRadius(radius * 0.99) 3007 surface.SetHoleFilling(hole_filling) 3008 surface.ComputeNormalsOff() 3009 surface.ComputeGradientsOff() 3010 surface.SetInputConnection(sdf.GetOutputPort()) 3011 surface.Update() 3012 m = vedo.mesh.Mesh(surface.GetOutput(), c=self.color()) 3013 3014 m.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3015 "reconstruct_surface", 3016 parents=[self], 3017 comment=f"#pts {m.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 3018 ) 3019 return m 3020 3021 def compute_clustering(self, radius: float) -> Self: 3022 """ 3023 Cluster points in space. The `radius` is the radius of local search. 3024 3025 An array named "ClusterId" is added to `pointdata`. 3026 3027 Examples: 3028 - [clustering.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/basic/clustering.py) 3029 3030  3031 """ 3032 cluster = vtki.new("EuclideanClusterExtraction") 3033 cluster.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3034 cluster.SetExtractionModeToAllClusters() 3035 cluster.SetRadius(radius) 3036 cluster.ColorClustersOn() 3037 cluster.Update() 3038 idsarr = cluster.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetArray("ClusterId") 3039 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(idsarr) 3040 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3041 "compute_clustering", parents=[self], comment=f"radius = {radius}" 3042 ) 3043 return self 3044 3045 def compute_connections(self, radius, mode=0, regions=(), vrange=(0, 1), seeds=(), angle=0.0) -> Self: 3046 """ 3047 Extracts and/or segments points from a point cloud based on geometric distance measures 3048 (e.g., proximity, normal alignments, etc.) and optional measures such as scalar range. 3049 The default operation is to segment the points into "connected" regions where the connection 3050 is determined by an appropriate distance measure. Each region is given a region id. 3051 3052 Optionally, the filter can output the largest connected region of points; a particular region 3053 (via id specification); those regions that are seeded using a list of input point ids; 3054 or the region of points closest to a specified position. 3055 3056 The key parameter of this filter is the radius defining a sphere around each point which defines 3057 a local neighborhood: any other points in the local neighborhood are assumed connected to the point. 3058 Note that the radius is defined in absolute terms. 3059 3060 Other parameters are used to further qualify what it means to be a neighboring point. 3061 For example, scalar range and/or point normals can be used to further constrain the neighborhood. 3062 Also the extraction mode defines how the filter operates. 3063 By default, all regions are extracted but it is possible to extract particular regions; 3064 the region closest to a seed point; seeded regions; or the largest region found while processing. 3065 By default, all regions are extracted. 3066 3067 On output, all points are labeled with a region number. 3068 However note that the number of input and output points may not be the same: 3069 if not extracting all regions then the output size may be less than the input size. 3070 3071 Arguments: 3072 radius : (float) 3073 variable specifying a local sphere used to define local point neighborhood 3074 mode : (int) 3075 - 0, Extract all regions 3076 - 1, Extract point seeded regions 3077 - 2, Extract largest region 3078 - 3, Test specified regions 3079 - 4, Extract all regions with scalar connectivity 3080 - 5, Extract point seeded regions 3081 regions : (list) 3082 a list of non-negative regions id to extract 3083 vrange : (list) 3084 scalar range to use to extract points based on scalar connectivity 3085 seeds : (list) 3086 a list of non-negative point seed ids 3087 angle : (list) 3088 points are connected if the angle between their normals is 3089 within this angle threshold (expressed in degrees). 3090 """ 3091 # https://vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkConnectedPointsFilter.html 3092 cpf = vtki.new("ConnectedPointsFilter") 3093 cpf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3094 cpf.SetRadius(radius) 3095 if mode == 0: # Extract all regions 3096 pass 3097 3098 elif mode == 1: # Extract point seeded regions 3099 cpf.SetExtractionModeToPointSeededRegions() 3100 for s in seeds: 3101 cpf.AddSeed(s) 3102 3103 elif mode == 2: # Test largest region 3104 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3105 3106 elif mode == 3: # Test specified regions 3107 cpf.SetExtractionModeToSpecifiedRegions() 3108 for r in regions: 3109 cpf.AddSpecifiedRegion(r) 3110 3111 elif mode == 4: # Extract all regions with scalar connectivity 3112 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3113 cpf.ScalarConnectivityOn() 3114 cpf.SetScalarRange(vrange[0], vrange[1]) 3115 3116 elif mode == 5: # Extract point seeded regions 3117 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3118 cpf.ScalarConnectivityOn() 3119 cpf.SetScalarRange(vrange[0], vrange[1]) 3120 cpf.AlignedNormalsOn() 3121 cpf.SetNormalAngle(angle) 3122 3123 cpf.Update() 3124 self._update(cpf.GetOutput(), reset_locators=False) 3125 return self 3126 3127 def compute_camera_distance(self) -> np.ndarray: 3128 """ 3129 Calculate the distance from points to the camera. 3130 3131 A pointdata array is created with name 'DistanceToCamera' and returned. 3132 """ 3133 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 3134 poly = self.dataset 3135 dc = vtki.new("DistanceToCamera") 3136 dc.SetInputData(poly) 3137 dc.SetRenderer(vedo.plotter_instance.renderer) 3138 dc.Update() 3139 self._update(dc.GetOutput(), reset_locators=False) 3140 return self.pointdata["DistanceToCamera"] 3141 return np.array([]) 3142 3143 def densify(self, target_distance=0.1, nclosest=6, radius=None, niter=1, nmax=None) -> Self: 3144 """ 3145 Return a copy of the cloud with new added points. 3146 The new points are created in such a way that all points in any local neighborhood are 3147 within a target distance of one another. 3148 3149 For each input point, the distance to all points in its neighborhood is computed. 3150 If any of its neighbors is further than the target distance, 3151 the edge connecting the point and its neighbor is bisected and 3152 a new point is inserted at the bisection point. 3153 A single pass is completed once all the input points are visited. 3154 Then the process repeats to the number of iterations. 3155 3156 Examples: 3157 - [densifycloud.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/densifycloud.py) 3158 3159  3160 3161 .. note:: 3162 Points will be created in an iterative fashion until all points in their 3163 local neighborhood are the target distance apart or less. 3164 Note that the process may terminate early due to the 3165 number of iterations. By default the target distance is set to 0.5. 3166 Note that the target_distance should be less than the radius 3167 or nothing will change on output. 3168 3169 .. warning:: 3170 This class can generate a lot of points very quickly. 3171 The maximum number of iterations is by default set to =1.0 for this reason. 3172 Increase the number of iterations very carefully. 3173 Also, `nmax` can be set to limit the explosion of points. 3174 It is also recommended that a N closest neighborhood is used. 3175 3176 """ 3177 src = vtki.new("ProgrammableSource") 3178 opts = self.coordinates 3179 # zeros = np.zeros(3) 3180 3181 def _read_points(): 3182 output = src.GetPolyDataOutput() 3183 points = vtki.vtkPoints() 3184 for p in opts: 3185 # print(p) 3186 # if not np.array_equal(p, zeros): 3187 points.InsertNextPoint(p) 3188 output.SetPoints(points) 3189 3190 src.SetExecuteMethod(_read_points) 3191 3192 dens = vtki.new("DensifyPointCloudFilter") 3193 dens.SetInputConnection(src.GetOutputPort()) 3194 # dens.SetInputData(self.dataset) # this does not work 3195 dens.InterpolateAttributeDataOn() 3196 dens.SetTargetDistance(target_distance) 3197 dens.SetMaximumNumberOfIterations(niter) 3198 if nmax: 3199 dens.SetMaximumNumberOfPoints(nmax) 3200 3201 if radius: 3202 dens.SetNeighborhoodTypeToRadius() 3203 dens.SetRadius(radius) 3204 elif nclosest: 3205 dens.SetNeighborhoodTypeToNClosest() 3206 dens.SetNumberOfClosestPoints(nclosest) 3207 else: 3208 vedo.logger.error("set either radius or nclosest") 3209 raise RuntimeError() 3210 dens.Update() 3211 3212 cld = Points(dens.GetOutput()) 3213 cld.copy_properties_from(self) 3214 cld.interpolate_data_from(self, n=nclosest, radius=radius) 3215 cld.name = "DensifiedCloud" 3216 cld.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3217 "densify", 3218 parents=[self], 3219 c="#e9c46a:", 3220 comment=f"#pts {cld.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 3221 ) 3222 return cld 3223 3224 ############################################################################### 3225 ## stuff returning a Volume 3226 ############################################################################### 3227 3228 def density( 3229 self, dims=(40, 40, 40), bounds=None, radius=None, compute_gradient=False, locator=None 3230 ) -> "vedo.Volume": 3231 """ 3232 Generate a density field from a point cloud. Input can also be a set of 3D coordinates. 3233 Output is a `Volume`. 3234 3235 The local neighborhood is specified as the `radius` around each sample position (each voxel). 3236 If left to None, the radius is automatically computed as the diagonal of the bounding box 3237 and can be accessed via `vol.metadata["radius"]`. 3238 The density is expressed as the number of counts in the radius search. 3239 3240 Arguments: 3241 dims : (int, list) 3242 number of voxels in x, y and z of the output Volume. 3243 compute_gradient : (bool) 3244 Turn on/off the generation of the gradient vector, 3245 gradient magnitude scalar, and function classification scalar. 3246 By default this is off. Note that this will increase execution time 3247 and the size of the output. (The names of these point data arrays are: 3248 "Gradient", "Gradient Magnitude", and "Classification") 3249 locator : (vtkPointLocator) 3250 can be assigned from a previous call for speed (access it via `object.point_locator`). 3251 3252 Examples: 3253 - [plot_density3d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/pyplot/plot_density3d.py) 3254 3255  3256 """ 3257 pdf = vtki.new("PointDensityFilter") 3258 pdf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3259 3260 if not utils.is_sequence(dims): 3261 dims = [dims, dims, dims] 3262 3263 if bounds is None: 3264 bounds = list(self.bounds()) 3265 elif len(bounds) == 4: 3266 bounds = [*bounds, 0, 0] 3267 3268 if bounds[5] - bounds[4] == 0 or len(dims) == 2: # its 2D 3269 dims = list(dims) 3270 dims = [dims[0], dims[1], 2] 3271 diag = self.diagonal_size() 3272 bounds[5] = bounds[4] + diag / 1000 3273 pdf.SetModelBounds(bounds) 3274 3275 pdf.SetSampleDimensions(dims) 3276 3277 if locator: 3278 pdf.SetLocator(locator) 3279 3280 pdf.SetDensityEstimateToFixedRadius() 3281 if radius is None: 3282 radius = self.diagonal_size() / 20 3283 pdf.SetRadius(radius) 3284 pdf.SetComputeGradient(compute_gradient) 3285 pdf.Update() 3286 3287 vol = vedo.Volume(pdf.GetOutput()).mode(1) 3288 vol.name = "PointDensity" 3289 vol.metadata["radius"] = radius 3290 vol.locator = pdf.GetLocator() 3291 vol.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3292 "density", parents=[self], comment=f"dims={tuple(vol.dimensions())}" 3293 ) 3294 return vol 3295 3296 3297 def tovolume( 3298 self, 3299 kernel="shepard", 3300 radius=None, 3301 n=None, 3302 bounds=None, 3303 null_value=None, 3304 dims=(25, 25, 25), 3305 ) -> "vedo.Volume": 3306 """ 3307 Generate a `Volume` by interpolating a scalar 3308 or vector field which is only known on a scattered set of points or mesh. 3309 Available interpolation kernels are: shepard, gaussian, or linear. 3310 3311 Arguments: 3312 kernel : (str) 3313 interpolation kernel type [shepard] 3314 radius : (float) 3315 radius of the local search 3316 n : (int) 3317 number of point to use for interpolation 3318 bounds : (list) 3319 bounding box of the output Volume object 3320 dims : (list) 3321 dimensions of the output Volume object 3322 null_value : (float) 3323 value to be assigned to invalid points 3324 3325 Examples: 3326 - [interpolate_volume.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/interpolate_volume.py) 3327 3328  3329 """ 3330 if radius is None and not n: 3331 vedo.logger.error("please set either radius or n") 3332 raise RuntimeError 3333 3334 poly = self.dataset 3335 3336 # Create a probe volume 3337 probe = vtki.vtkImageData() 3338 probe.SetDimensions(dims) 3339 if bounds is None: 3340 bounds = self.bounds() 3341 probe.SetOrigin(bounds[0], bounds[2], bounds[4]) 3342 probe.SetSpacing( 3343 (bounds[1] - bounds[0]) / dims[0], 3344 (bounds[3] - bounds[2]) / dims[1], 3345 (bounds[5] - bounds[4]) / dims[2], 3346 ) 3347 3348 if not self.point_locator: 3349 self.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 3350 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 3351 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 3352 3353 if kernel == "shepard": 3354 kern = vtki.new("ShepardKernel") 3355 kern.SetPowerParameter(2) 3356 elif kernel == "gaussian": 3357 kern = vtki.new("GaussianKernel") 3358 elif kernel == "linear": 3359 kern = vtki.new("LinearKernel") 3360 else: 3361 vedo.logger.error("Error in tovolume(), available kernels are:") 3362 vedo.logger.error(" [shepard, gaussian, linear]") 3363 raise RuntimeError() 3364 3365 if radius: 3366 kern.SetRadius(radius) 3367 3368 interpolator = vtki.new("PointInterpolator") 3369 interpolator.SetInputData(probe) 3370 interpolator.SetSourceData(poly) 3371 interpolator.SetKernel(kern) 3372 interpolator.SetLocator(self.point_locator) 3373 3374 if n: 3375 kern.SetNumberOfPoints(n) 3376 kern.SetKernelFootprintToNClosest() 3377 else: 3378 kern.SetRadius(radius) 3379 3380 if null_value is not None: 3381 interpolator.SetNullValue(null_value) 3382 else: 3383 interpolator.SetNullPointsStrategyToClosestPoint() 3384 interpolator.Update() 3385 3386 vol = vedo.Volume(interpolator.GetOutput()) 3387 3388 vol.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3389 "signed_distance", 3390 parents=[self], 3391 comment=f"dims={tuple(vol.dimensions())}", 3392 c="#e9c46a:#0096c7", 3393 ) 3394 return vol 3395 3396 ################################################################################# 3397 def generate_segments(self, istart=0, rmax=1e30, niter=3) -> "vedo.shapes.Lines": 3398 """ 3399 Generate a line segments from a set of points. 3400 The algorithm is based on the closest point search. 3401 3402 Returns a `Line` object. 3403 This object contains the a metadata array of used vertex counts in "UsedVertexCount" 3404 and the sum of the length of the segments in "SegmentsLengthSum". 3405 3406 Arguments: 3407 istart : (int) 3408 index of the starting point 3409 rmax : (float) 3410 maximum length of a segment 3411 niter : (int) 3412 number of iterations or passes through the points 3413 3414 Examples: 3415 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 3416 """ 3417 points = self.coordinates 3418 segments = [] 3419 dists = [] 3420 n = len(points) 3421 used = np.zeros(n, dtype=int) 3422 for _ in range(niter): 3423 i = istart 3424 for _ in range(n): 3425 p = points[i] 3426 ids = self.closest_point(p, n=4, return_point_id=True) 3427 j = ids[1] 3428 if used[j] > 1 or [j, i] in segments: 3429 j = ids[2] 3430 if used[j] > 1: 3431 j = ids[3] 3432 d = np.linalg.norm(p - points[j]) 3433 if used[j] > 1 or used[i] > 1 or d > rmax: 3434 i += 1 3435 if i >= n: 3436 i = 0 3437 continue 3438 used[i] += 1 3439 used[j] += 1 3440 segments.append([i, j]) 3441 dists.append(d) 3442 i = j 3443 segments = np.array(segments, dtype=int) 3444 3445 lines = vedo.shapes.Lines(points[segments], c="k", lw=3) 3446 lines.metadata["UsedVertexCount"] = used 3447 lines.metadata["SegmentsLengthSum"] = np.sum(dists) 3448 lines.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("generate_segments", parents=[self]) 3449 lines.name = "Segments" 3450 return lines 3451 3452 def generate_delaunay2d( 3453 self, 3454 mode="scipy", 3455 boundaries=(), 3456 tol=None, 3457 alpha=0.0, 3458 offset=0.0, 3459 transform=None, 3460 ) -> "vedo.mesh.Mesh": 3461 """ 3462 Create a mesh from points in the XY plane. 3463 If `mode='fit'` then the filter computes a best fitting 3464 plane and projects the points onto it. 3465 3466 Check also `generate_mesh()`. 3467 3468 Arguments: 3469 tol : (float) 3470 specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. 3471 This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of the bounding box of the points. 3472 alpha : (float) 3473 for a non-zero alpha value, only edges or triangles contained 3474 within a sphere centered at mesh vertices will be output. 3475 Otherwise, only triangles will be output. 3476 offset : (float) 3477 multiplier to control the size of the initial, bounding Delaunay triangulation. 3478 transform: (LinearTransform, NonLinearTransform) 3479 a transformation which is applied to points to generate a 2D problem. 3480 This maps a 3D dataset into a 2D dataset where triangulation can be done on the XY plane. 3481 The points are transformed and triangulated. 3482 The topology of triangulated points is used as the output topology. 3483 3484 Examples: 3485 - [delaunay2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/delaunay2d.py) 3486 3487  3488 """ 3489 plist = self.coordinates.copy() 3490 3491 ######################################################### 3492 if mode == "scipy": 3493 from scipy.spatial import Delaunay as scipy_delaunay 3494 3495 tri = scipy_delaunay(plist[:, 0:2]) 3496 return vedo.mesh.Mesh([plist, tri.simplices]) 3497 ########################################################## 3498 3499 pd = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3500 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 3501 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(plist, dtype=np.float32)) 3502 pd.SetPoints(vpts) 3503 3504 delny = vtki.new("Delaunay2D") 3505 delny.SetInputData(pd) 3506 if tol: 3507 delny.SetTolerance(tol) 3508 delny.SetAlpha(alpha) 3509 delny.SetOffset(offset) 3510 3511 if transform: 3512 delny.SetTransform(transform.T) 3513 elif mode == "fit": 3514 delny.SetProjectionPlaneMode(vtki.get_class("VTK_BEST_FITTING_PLANE")) 3515 elif mode == "xy" and boundaries: 3516 boundary = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3517 boundary.SetPoints(vpts) 3518 cell_array = vtki.vtkCellArray() 3519 for b in boundaries: 3520 cpolygon = vtki.vtkPolygon() 3521 for idd in b: 3522 cpolygon.GetPointIds().InsertNextId(idd) 3523 cell_array.InsertNextCell(cpolygon) 3524 boundary.SetPolys(cell_array) 3525 delny.SetSourceData(boundary) 3526 3527 delny.Update() 3528 3529 msh = vedo.mesh.Mesh(delny.GetOutput()) 3530 msh.name = "Delaunay2D" 3531 msh.clean().lighting("off") 3532 msh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3533 "delaunay2d", 3534 parents=[self], 3535 comment=f"#cells {msh.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 3536 ) 3537 return msh 3538 3539 def generate_voronoi(self, padding=0.0, fit=False, method="vtk") -> "vedo.Mesh": 3540 """ 3541 Generate the 2D Voronoi convex tiling of the input points (z is ignored). 3542 The points are assumed to lie in a plane. The output is a Mesh. Each output cell is a convex polygon. 3543 3544 A cell array named "VoronoiID" is added to the output Mesh. 3545 3546 The 2D Voronoi tessellation is a tiling of space, where each Voronoi tile represents the region nearest 3547 to one of the input points. Voronoi tessellations are important in computational geometry 3548 (and many other fields), and are the dual of Delaunay triangulations. 3549 3550 Thus the triangulation is constructed in the x-y plane, and the z coordinate is ignored 3551 (although carried through to the output). 3552 If you desire to triangulate in a different plane, you can use fit=True. 3553 3554 A brief summary is as follows. Each (generating) input point is associated with 3555 an initial Voronoi tile, which is simply the bounding box of the point set. 3556 A locator is then used to identify nearby points: each neighbor in turn generates a 3557 clipping line positioned halfway between the generating point and the neighboring point, 3558 and orthogonal to the line connecting them. Clips are readily performed by evaluationg the 3559 vertices of the convex Voronoi tile as being on either side (inside,outside) of the clip line. 3560 If two intersections of the Voronoi tile are found, the portion of the tile "outside" the clip 3561 line is discarded, resulting in a new convex, Voronoi tile. As each clip occurs, 3562 the Voronoi "Flower" error metric (the union of error spheres) is compared to the extent of the region 3563 containing the neighboring clip points. The clip region (along with the points contained in it) is grown 3564 by careful expansion (e.g., outward spiraling iterator over all candidate clip points). 3565 When the Voronoi Flower is contained within the clip region, the algorithm terminates and the Voronoi 3566 tile is output. Once complete, it is possible to construct the Delaunay triangulation from the Voronoi 3567 tessellation. Note that topological and geometric information is used to generate a valid triangulation 3568 (e.g., merging points and validating topology). 3569 3570 Arguments: 3571 pts : (list) 3572 list of input points. 3573 padding : (float) 3574 padding distance. The default is 0. 3575 fit : (bool) 3576 detect automatically the best fitting plane. The default is False. 3577 3578 Examples: 3579 - [voronoi1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/voronoi1.py) 3580 3581  3582 3583 - [voronoi2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/voronoi2.py) 3584 3585  3586 """ 3587 pts = self.coordinates 3588 3589 if method == "scipy": 3590 from scipy.spatial import Voronoi as scipy_voronoi 3591 3592 pts = np.asarray(pts)[:, (0, 1)] 3593 vor = scipy_voronoi(pts) 3594 regs = [] # filter out invalid indices 3595 for r in vor.regions: 3596 flag = True 3597 for x in r: 3598 if x < 0: 3599 flag = False 3600 break 3601 if flag and len(r) > 0: 3602 regs.append(r) 3603 3604 m = vedo.Mesh([vor.vertices, regs]) 3605 m.celldata["VoronoiID"] = np.array(list(range(len(regs)))).astype(int) 3606 3607 elif method == "vtk": 3608 vor = vtki.new("Voronoi2D") 3609 if isinstance(pts, Points): 3610 vor.SetInputData(pts) 3611 else: 3612 pts = np.asarray(pts) 3613 if pts.shape[1] == 2: 3614 pts = np.c_[pts, np.zeros(len(pts))] 3615 pd = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3616 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 3617 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(pts, dtype=np.float32)) 3618 pd.SetPoints(vpts) 3619 vor.SetInputData(pd) 3620 vor.SetPadding(padding) 3621 vor.SetGenerateScalarsToPointIds() 3622 if fit: 3623 vor.SetProjectionPlaneModeToBestFittingPlane() 3624 else: 3625 vor.SetProjectionPlaneModeToXYPlane() 3626 vor.Update() 3627 poly = vor.GetOutput() 3628 arr = poly.GetCellData().GetArray(0) 3629 if arr: 3630 arr.SetName("VoronoiID") 3631 m = vedo.Mesh(poly, c="orange5") 3632 3633 else: 3634 vedo.logger.error(f"Unknown method {method} in voronoi()") 3635 raise RuntimeError 3636 3637 m.lw(2).lighting("off").wireframe() 3638 m.name = "Voronoi" 3639 return m 3640 3641 ########################################################################## 3642 def generate_delaunay3d(self, radius=0, tol=None) -> "vedo.TetMesh": 3643 """ 3644 Create 3D Delaunay triangulation of input points. 3645 3646 Arguments: 3647 radius : (float) 3648 specify distance (or "alpha") value to control output. 3649 For a non-zero values, only tetra contained within the circumsphere 3650 will be output. 3651 tol : (float) 3652 Specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. 3653 This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of 3654 the bounding box of the points. 3655 """ 3656 deln = vtki.new("Delaunay3D") 3657 deln.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3658 deln.SetAlpha(radius) 3659 deln.AlphaTetsOn() 3660 deln.AlphaTrisOff() 3661 deln.AlphaLinesOff() 3662 deln.AlphaVertsOff() 3663 deln.BoundingTriangulationOff() 3664 if tol: 3665 deln.SetTolerance(tol) 3666 deln.Update() 3667 m = vedo.TetMesh(deln.GetOutput()) 3668 m.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3669 "generate_delaunay3d", c="#e9c46a:#edabab", parents=[self], 3670 ) 3671 m.name = "Delaunay3D" 3672 return m 3673 3674 #################################################### 3675 def visible_points(self, area=(), tol=None, invert=False) -> Union[Self, None]: 3676 """ 3677 Extract points based on whether they are visible or not. 3678 Visibility is determined by accessing the z-buffer of a rendering window. 3679 The position of each input point is converted into display coordinates, 3680 and then the z-value at that point is obtained. 3681 If within the user-specified tolerance, the point is considered visible. 3682 Associated data attributes are passed to the output as well. 3683 3684 This filter also allows you to specify a rectangular window in display (pixel) 3685 coordinates in which the visible points must lie. 3686 3687 Arguments: 3688 area : (list) 3689 specify a rectangular region as (xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax) 3690 tol : (float) 3691 a tolerance in normalized display coordinate system 3692 invert : (bool) 3693 select invisible points instead. 3694 3695 Example: 3696 ```python 3697 from vedo import Ellipsoid, show 3698 s = Ellipsoid().rotate_y(30) 3699 3700 # Camera options: pos, focal_point, viewup, distance 3701 camopts = dict(pos=(0,0,25), focal_point=(0,0,0)) 3702 show(s, camera=camopts, offscreen=True) 3703 3704 m = s.visible_points() 3705 # print('visible pts:', m.vertices) # numpy array 3706 show(m, new=True, axes=1).close() # optionally draw result in a new window 3707 ``` 3708  3709 """ 3710 svp = vtki.new("SelectVisiblePoints") 3711 svp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3712 3713 ren = None 3714 if vedo.plotter_instance: 3715 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 3716 ren = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer 3717 svp.SetRenderer(ren) 3718 if not ren: 3719 vedo.logger.warning( 3720 "visible_points() can only be used after a rendering step" 3721 ) 3722 return None 3723 3724 if len(area) == 2: 3725 area = utils.flatten(area) 3726 if len(area) == 4: 3727 # specify a rectangular region 3728 svp.SetSelection(area[0], area[1], area[2], area[3]) 3729 if tol is not None: 3730 svp.SetTolerance(tol) 3731 if invert: 3732 svp.SelectInvisibleOn() 3733 svp.Update() 3734 3735 m = Points(svp.GetOutput()) 3736 m.name = "VisiblePoints" 3737 return m
Work with point clouds.
458 def __init__(self, inputobj=None, r=4, c=(0.2, 0.2, 0.2), alpha=1): 459 """ 460 Build an object made of only vertex points for a list of 2D/3D points. 461 Both shapes (N, 3) or (3, N) are accepted as input, if N>3. 462 463 Arguments: 464 inputobj : (list, tuple) 465 r : (int) 466 Point radius in units of pixels. 467 c : (str, list) 468 Color name or rgb tuple. 469 alpha : (float) 470 Transparency in range [0,1]. 471 472 Example: 473 ```python 474 from vedo import * 475 476 def fibonacci_sphere(n): 477 s = np.linspace(0, n, num=n, endpoint=False) 478 theta = s * 2.399963229728653 479 y = 1 - s * (2/(n-1)) 480 r = np.sqrt(1 - y * y) 481 x = np.cos(theta) * r 482 z = np.sin(theta) * r 483 return np._c[x,y,z] 484 485 Points(fibonacci_sphere(1000)).show(axes=1).close() 486 ``` 487  488 """ 489 # print("INIT POINTS") 490 super().__init__() 491 492 self.name = "" 493 self.filename = "" 494 self.file_size = "" 495 496 self.info = {} 497 self.time = time.time() 498 499 self.transform = LinearTransform() 500 501 self.point_locator = None 502 self.cell_locator = None 503 self.line_locator = None 504 505 self.actor = vtki.vtkActor() 506 self.properties = self.actor.GetProperty() 507 self.properties_backface = self.actor.GetBackfaceProperty() 508 self.mapper = vtki.new("PolyDataMapper") 509 self.dataset = vtki.vtkPolyData() 510 511 # Create weakref so actor can access this object (eg to pick/remove): 512 self.actor.retrieve_object = weak_ref_to(self) 513 514 try: 515 self.properties.RenderPointsAsSpheresOn() 516 except AttributeError: 517 pass 518 519 if inputobj is None: #################### 520 return 521 ########################################## 522 523 self.name = "Points" 524 525 ###### 526 if isinstance(inputobj, vtki.vtkActor): 527 self.dataset.DeepCopy(inputobj.GetMapper().GetInput()) 528 pr = vtki.vtkProperty() 529 pr.DeepCopy(inputobj.GetProperty()) 530 self.actor.SetProperty(pr) 531 self.properties = pr 532 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(inputobj.GetMapper().GetScalarVisibility()) 533 534 elif isinstance(inputobj, vtki.vtkPolyData): 535 self.dataset = inputobj 536 if self.dataset.GetNumberOfCells() == 0: 537 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 538 for i in range(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()): 539 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 540 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 541 self.dataset.SetVerts(carr) 542 543 elif isinstance(inputobj, Points): 544 self.dataset = inputobj.dataset 545 self.copy_properties_from(inputobj) 546 547 elif utils.is_sequence(inputobj): # passing point coords 548 self.dataset = utils.buildPolyData(utils.make3d(inputobj)) 549 550 elif isinstance(inputobj, str) or "PosixPath" in str(type(inputobj)): 551 verts = vedo.file_io.load(inputobj) 552 self.filename = str(inputobj) 553 self.dataset = verts.dataset 554 555 elif "meshlib" in str(type(inputobj)): 556 from meshlib import mrmeshnumpy as mn 557 self.dataset = utils.buildPolyData(mn.toNumpyArray(inputobj.points)) 558 559 else: 560 # try to extract the points from a generic VTK input data object 561 if hasattr(inputobj, "dataset"): 562 inputobj = inputobj.dataset 563 try: 564 vvpts = inputobj.GetPoints() 565 self.dataset = vtki.vtkPolyData() 566 self.dataset.SetPoints(vvpts) 567 for i in range(inputobj.GetPointData().GetNumberOfArrays()): 568 arr = inputobj.GetPointData().GetArray(i) 569 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(arr) 570 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 571 for i in range(self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()): 572 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 573 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 574 self.dataset.SetVerts(carr) 575 except: 576 vedo.logger.error(f"cannot build Points from type {type(inputobj)}") 577 raise RuntimeError() 578 579 self.actor.SetMapper(self.mapper) 580 self.mapper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 581 582 self.properties.SetColor(colors.get_color(c)) 583 self.properties.SetOpacity(alpha) 584 self.properties.SetRepresentationToPoints() 585 self.properties.SetPointSize(r) 586 self.properties.LightingOff() 587 588 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 589 self, parents=[], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 590 )
Build an object made of only vertex points for a list of 2D/3D points. Both shapes (N, 3) or (3, N) are accepted as input, if N>3.
Arguments:
- inputobj : (list, tuple)
- r : (int) Point radius in units of pixels.
- c : (str, list) Color name or rgb tuple.
- alpha : (float) Transparency in range [0,1].
Example:
from vedo import * def fibonacci_sphere(n): s = np.linspace(0, n, num=n, endpoint=False) theta = s * 2.399963229728653 y = 1 - s * (2/(n-1)) r = np.sqrt(1 - y * y) x = np.cos(theta) * r z = np.sin(theta) * r return np._c[x,y,z] Points(fibonacci_sphere(1000)).show(axes=1).close()
812 def polydata(self): 813 """ 814 Obsolete. Use property `.dataset` instead. 815 Returns the underlying `vtkPolyData` object. 816 """ 817 colors.printc( 818 "WARNING: call to .polydata() is obsolete, use property .dataset instead.", 819 c="y") 820 return self.dataset
Obsolete. Use property .dataset instead.
Returns the underlying vtkPolyData object.
828 def copy(self, deep=True) -> Self: 829 """Return a copy of the object. Alias of `clone()`.""" 830 return self.clone(deep=deep)
Return a copy of the object. Alias of clone().
832 def clone(self, deep=True) -> Self: 833 """ 834 Clone a `PointCloud` or `Mesh` object to make an exact copy of it. 835 Alias of `copy()`. 836 837 Arguments: 838 deep : (bool) 839 if False return a shallow copy of the mesh without copying the points array. 840 841 Examples: 842 - [mirror.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mirror.py) 843 844  845 """ 846 poly = vtki.vtkPolyData() 847 if deep or isinstance(deep, dict): # if a memo object is passed this checks as True 848 poly.DeepCopy(self.dataset) 849 else: 850 poly.ShallowCopy(self.dataset) 851 852 if isinstance(self, vedo.Mesh): 853 cloned = vedo.Mesh(poly) 854 else: 855 cloned = Points(poly) 856 # print([self], self.__class__) 857 # cloned = self.__class__(poly) 858 859 cloned.transform = self.transform.clone() 860 861 cloned.copy_properties_from(self) 862 863 cloned.name = str(self.name) 864 cloned.filename = str(self.filename) 865 cloned.info = dict(self.info) 866 cloned.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("clone", parents=[self], shape="diamond", c="#edede9") 867 868 if isinstance(deep, dict): 869 deep[id(self)] = cloned 870 871 return cloned
873 def compute_normals_with_pca(self, n=20, orientation_point=None, invert=False) -> Self: 874 """ 875 Generate point normals using PCA (principal component analysis). 876 This algorithm estimates a local tangent plane around each sample point p 877 by considering a small neighborhood of points around p, and fitting a plane 878 to the neighborhood (via PCA). 879 880 Arguments: 881 n : (int) 882 neighborhood size to calculate the normal 883 orientation_point : (list) 884 adjust the +/- sign of the normals so that 885 the normals all point towards a specified point. If None, perform a traversal 886 of the point cloud and flip neighboring normals so that they are mutually consistent. 887 invert : (bool) 888 flip all normals 889 """ 890 poly = self.dataset 891 pcan = vtki.new("PCANormalEstimation") 892 pcan.SetInputData(poly) 893 pcan.SetSampleSize(n) 894 895 if orientation_point is not None: 896 pcan.SetNormalOrientationToPoint() 897 pcan.SetOrientationPoint(orientation_point) 898 else: 899 pcan.SetNormalOrientationToGraphTraversal() 900 901 if invert: 902 pcan.FlipNormalsOn() 903 pcan.Update() 904 905 varr = pcan.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetNormals() 906 varr.SetName("Normals") 907 self.dataset.GetPointData().SetNormals(varr) 908 self.dataset.GetPointData().Modified() 909 return self
Generate point normals using PCA (principal component analysis). This algorithm estimates a local tangent plane around each sample point p by considering a small neighborhood of points around p, and fitting a plane to the neighborhood (via PCA).
Arguments:
- n : (int) neighborhood size to calculate the normal
- orientation_point : (list) adjust the +/- sign of the normals so that the normals all point towards a specified point. If None, perform a traversal of the point cloud and flip neighboring normals so that they are mutually consistent.
- invert : (bool) flip all normals
911 def compute_acoplanarity(self, n=25, radius=None, on="points") -> Self: 912 """ 913 Compute acoplanarity which is a measure of how much a local region of the mesh 914 differs from a plane. 915 916 The information is stored in a `pointdata` or `celldata` array with name 'Acoplanarity'. 917 918 Either `n` (number of neighbour points) or `radius` (radius of local search) can be specified. 919 If a radius value is given and not enough points fall inside it, then a -1 is stored. 920 921 Example: 922 ```python 923 from vedo import * 924 msh = ParametricShape('RandomHills') 925 msh.compute_acoplanarity(radius=0.1, on='cells') 926 msh.cmap("coolwarm", on='cells').add_scalarbar() 927 msh.show(axes=1).close() 928 ``` 929  930 """ 931 acoplanarities = [] 932 if "point" in on: 933 pts = self.coordinates 934 elif "cell" in on: 935 pts = self.cell_centers().coordinates 936 else: 937 raise ValueError(f"In compute_acoplanarity() set on to either 'cells' or 'points', not {on}") 938 939 for p in utils.progressbar(pts, delay=5, width=15, title=f"{on} acoplanarity"): 940 if n: 941 data = self.closest_point(p, n=n) 942 npts = n 943 elif radius: 944 data = self.closest_point(p, radius=radius) 945 npts = len(data) 946 947 try: 948 center = data.mean(axis=0) 949 res = np.linalg.svd(data - center) 950 acoplanarities.append(res[1][2] / npts) 951 except: 952 acoplanarities.append(-1.0) 953 954 if "point" in on: 955 self.pointdata["Acoplanarity"] = np.array(acoplanarities, dtype=float) 956 else: 957 self.celldata["Acoplanarity"] = np.array(acoplanarities, dtype=float) 958 return self
Compute acoplanarity which is a measure of how much a local region of the mesh differs from a plane.
The information is stored in a pointdata or celldata array with name 'Acoplanarity'.
Either n (number of neighbour points) or radius (radius of local search) can be specified.
If a radius value is given and not enough points fall inside it, then a -1 is stored.
Example:
from vedo import * msh = ParametricShape('RandomHills') msh.compute_acoplanarity(radius=0.1, on='cells') msh.cmap("coolwarm", on='cells').add_scalarbar() msh.show(axes=1).close()
960 def distance_to(self, pcloud, signed=False, invert=False, name="Distance") -> np.ndarray: 961 """ 962 Computes the distance from one point cloud or mesh to another point cloud or mesh. 963 This new `pointdata` array is saved with default name "Distance". 964 965 Keywords `signed` and `invert` are used to compute signed distance, 966 but the mesh in that case must have polygonal faces (not a simple point cloud), 967 and normals must also be computed. 968 969 Examples: 970 - [distance2mesh.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/distance2mesh.py) 971 972  973 """ 974 if pcloud.dataset.GetNumberOfPolys(): 975 976 poly1 = self.dataset 977 poly2 = pcloud.dataset 978 df = vtki.new("DistancePolyDataFilter") 979 df.ComputeSecondDistanceOff() 980 df.SetInputData(0, poly1) 981 df.SetInputData(1, poly2) 982 df.SetSignedDistance(signed) 983 df.SetNegateDistance(invert) 984 df.Update() 985 scals = df.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetScalars() 986 dists = utils.vtk2numpy(scals) 987 988 else: # has no polygons 989 990 if signed: 991 vedo.logger.warning("distance_to() called with signed=True but input object has no polygons") 992 993 if not pcloud.point_locator: 994 pcloud.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 995 pcloud.point_locator.SetDataSet(pcloud.dataset) 996 pcloud.point_locator.BuildLocator() 997 998 ids = [] 999 ps1 = self.coordinates 1000 ps2 = pcloud.coordinates 1001 for p in ps1: 1002 pid = pcloud.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1003 ids.append(pid) 1004 1005 deltas = ps2[ids] - ps1 1006 dists = np.linalg.norm(deltas, axis=1).astype(np.float32) 1007 scals = utils.numpy2vtk(dists) 1008 1009 scals.SetName(name) 1010 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(scals) 1011 self.dataset.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(scals.GetName()) 1012 rng = scals.GetRange() 1013 self.mapper.SetScalarRange(rng[0], rng[1]) 1014 self.mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn() 1015 1016 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1017 "distance_to", 1018 parents=[self, pcloud], 1019 shape="cylinder", 1020 comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 1021 ) 1022 return dists
Computes the distance from one point cloud or mesh to another point cloud or mesh.
This new pointdata array is saved with default name "Distance".
Keywords signed and invert are used to compute signed distance,
but the mesh in that case must have polygonal faces (not a simple point cloud),
and normals must also be computed.
Examples:
1024 def clean(self) -> Self: 1025 """Clean pointcloud or mesh by removing coincident points.""" 1026 cpd = vtki.new("CleanPolyData") 1027 cpd.PointMergingOn() 1028 cpd.ConvertLinesToPointsOff() 1029 cpd.ConvertPolysToLinesOff() 1030 cpd.ConvertStripsToPolysOff() 1031 cpd.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1032 cpd.Update() 1033 self._update(cpd.GetOutput()) 1034 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1035 "clean", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 1036 ) 1037 return self
Clean pointcloud or mesh by removing coincident points.
1039 def subsample(self, fraction: float, absolute=False) -> Self: 1040 """ 1041 Subsample a point cloud by requiring that the points 1042 or vertices are far apart at least by the specified fraction of the object size. 1043 If a Mesh is passed the polygonal faces are not removed 1044 but holes can appear as their vertices are removed. 1045 1046 Examples: 1047 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 1048 1049  1050 1051 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 1052 1053  1054 """ 1055 if not absolute: 1056 if fraction > 1: 1057 vedo.logger.warning( 1058 f"subsample(fraction=...), fraction must be < 1, but is {fraction}" 1059 ) 1060 if fraction <= 0: 1061 return self 1062 1063 cpd = vtki.new("CleanPolyData") 1064 cpd.PointMergingOn() 1065 cpd.ConvertLinesToPointsOn() 1066 cpd.ConvertPolysToLinesOn() 1067 cpd.ConvertStripsToPolysOn() 1068 cpd.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1069 if absolute: 1070 cpd.SetTolerance(fraction / self.diagonal_size()) 1071 # cpd.SetToleranceIsAbsolute(absolute) 1072 else: 1073 cpd.SetTolerance(fraction) 1074 cpd.Update() 1075 1076 ps = 2 1077 if self.properties.GetRepresentation() == 0: 1078 ps = self.properties.GetPointSize() 1079 1080 self._update(cpd.GetOutput()) 1081 self.ps(ps) 1082 1083 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1084 "subsample", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 1085 ) 1086 return self
Subsample a point cloud by requiring that the points or vertices are far apart at least by the specified fraction of the object size. If a Mesh is passed the polygonal faces are not removed but holes can appear as their vertices are removed.
Examples:
1088 def threshold(self, scalars: str, above=None, below=None, on="points") -> Self: 1089 """ 1090 Extracts cells where scalar value satisfies threshold criterion. 1091 1092 Arguments: 1093 scalars : (str) 1094 name of the scalars array. 1095 above : (float) 1096 minimum value of the scalar 1097 below : (float) 1098 maximum value of the scalar 1099 on : (str) 1100 if 'cells' assume array of scalars refers to cell data. 1101 1102 Examples: 1103 - [mesh_threshold.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mesh_threshold.py) 1104 """ 1105 thres = vtki.new("Threshold") 1106 thres.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1107 1108 if on.startswith("c"): 1109 asso = vtki.vtkDataObject.FIELD_ASSOCIATION_CELLS 1110 else: 1111 asso = vtki.vtkDataObject.FIELD_ASSOCIATION_POINTS 1112 1113 thres.SetInputArrayToProcess(0, 0, 0, asso, scalars) 1114 1115 if above is None and below is not None: 1116 try: # vtk 9.2 1117 thres.ThresholdByLower(below) 1118 except AttributeError: # vtk 9.3 1119 thres.SetUpperThreshold(below) 1120 1121 elif below is None and above is not None: 1122 try: 1123 thres.ThresholdByUpper(above) 1124 except AttributeError: 1125 thres.SetLowerThreshold(above) 1126 else: 1127 try: 1128 thres.ThresholdBetween(above, below) 1129 except AttributeError: 1130 thres.SetUpperThreshold(below) 1131 thres.SetLowerThreshold(above) 1132 1133 thres.Update() 1134 1135 gf = vtki.new("GeometryFilter") 1136 gf.SetInputData(thres.GetOutput()) 1137 gf.Update() 1138 self._update(gf.GetOutput()) 1139 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("threshold", parents=[self]) 1140 return self
Extracts cells where scalar value satisfies threshold criterion.
Arguments:
- scalars : (str) name of the scalars array.
- above : (float) minimum value of the scalar
- below : (float) maximum value of the scalar
- on : (str) if 'cells' assume array of scalars refers to cell data.
Examples:
1142 def quantize(self, value: float) -> Self: 1143 """ 1144 The user should input a value and all {x,y,z} coordinates 1145 will be quantized to that absolute grain size. 1146 """ 1147 qp = vtki.new("QuantizePolyDataPoints") 1148 qp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1149 qp.SetQFactor(value) 1150 qp.Update() 1151 self._update(qp.GetOutput()) 1152 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("quantize", parents=[self]) 1153 return self
The user should input a value and all {x,y,z} coordinates will be quantized to that absolute grain size.
1155 @property 1156 def vertex_normals(self) -> np.ndarray: 1157 """ 1158 Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as `point_normals`. 1159 If needed, normals are computed via `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1160 Check out also `compute_normals()` and `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1161 """ 1162 vtknormals = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetNormals() 1163 if vtknormals is None: 1164 self.compute_normals_with_pca() 1165 vtknormals = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetNormals() 1166 return utils.vtk2numpy(vtknormals)
Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as point_normals.
If needed, normals are computed via compute_normals_with_pca().
Check out also compute_normals() and compute_normals_with_pca().
1168 @property 1169 def point_normals(self) -> np.ndarray: 1170 """ 1171 Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as `vertex_normals`. 1172 Check out also `compute_normals()` and `compute_normals_with_pca()`. 1173 """ 1174 return self.vertex_normals
Retrieve vertex normals as a numpy array. Same as vertex_normals.
Check out also compute_normals() and compute_normals_with_pca().
1176 def align_to(self, target, iters=100, rigid=False, invert=False, use_centroids=False) -> Self: 1177 """ 1178 Aligned to target mesh through the `Iterative Closest Point` algorithm. 1179 1180 The core of the algorithm is to match each vertex in one surface with 1181 the closest surface point on the other, then apply the transformation 1182 that modify one surface to best match the other (in the least-square sense). 1183 1184 Arguments: 1185 rigid : (bool) 1186 if True do not allow scaling 1187 invert : (bool) 1188 if True start by aligning the target to the source but 1189 invert the transformation finally. Useful when the target is smaller 1190 than the source. 1191 use_centroids : (bool) 1192 start by matching the centroids of the two objects. 1193 1194 Examples: 1195 - [align1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align1.py) 1196 1197  1198 1199 - [align2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align2.py) 1200 1201  1202 """ 1203 icp = vtki.new("IterativeClosestPointTransform") 1204 icp.SetSource(self.dataset) 1205 icp.SetTarget(target.dataset) 1206 if invert: 1207 icp.Inverse() 1208 icp.SetMaximumNumberOfIterations(iters) 1209 if rigid: 1210 icp.GetLandmarkTransform().SetModeToRigidBody() 1211 icp.SetStartByMatchingCentroids(use_centroids) 1212 icp.Update() 1213 1214 self.apply_transform(icp.GetMatrix()) 1215 1216 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1217 "align_to", parents=[self, target], comment=f"rigid = {rigid}" 1218 ) 1219 return self
Aligned to target mesh through the Iterative Closest Point algorithm.
The core of the algorithm is to match each vertex in one surface with the closest surface point on the other, then apply the transformation that modify one surface to best match the other (in the least-square sense).
Arguments:
- rigid : (bool) if True do not allow scaling
- invert : (bool) if True start by aligning the target to the source but invert the transformation finally. Useful when the target is smaller than the source.
- use_centroids : (bool) start by matching the centroids of the two objects.
Examples:
1221 def align_to_bounding_box(self, msh, rigid=False) -> Self: 1222 """ 1223 Align the current object's bounding box to the bounding box 1224 of the input object. 1225 1226 Use `rigid=True` to disable scaling. 1227 1228 Example: 1229 [align6.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align6.py) 1230 """ 1231 lmt = vtki.vtkLandmarkTransform() 1232 ss = vtki.vtkPoints() 1233 xss0, xss1, yss0, yss1, zss0, zss1 = self.bounds() 1234 for p in [ 1235 [xss0, yss0, zss0], 1236 [xss1, yss0, zss0], 1237 [xss1, yss1, zss0], 1238 [xss0, yss1, zss0], 1239 [xss0, yss0, zss1], 1240 [xss1, yss0, zss1], 1241 [xss1, yss1, zss1], 1242 [xss0, yss1, zss1], 1243 ]: 1244 ss.InsertNextPoint(p) 1245 st = vtki.vtkPoints() 1246 xst0, xst1, yst0, yst1, zst0, zst1 = msh.bounds() 1247 for p in [ 1248 [xst0, yst0, zst0], 1249 [xst1, yst0, zst0], 1250 [xst1, yst1, zst0], 1251 [xst0, yst1, zst0], 1252 [xst0, yst0, zst1], 1253 [xst1, yst0, zst1], 1254 [xst1, yst1, zst1], 1255 [xst0, yst1, zst1], 1256 ]: 1257 st.InsertNextPoint(p) 1258 1259 lmt.SetSourceLandmarks(ss) 1260 lmt.SetTargetLandmarks(st) 1261 lmt.SetModeToAffine() 1262 if rigid: 1263 lmt.SetModeToRigidBody() 1264 lmt.Update() 1265 1266 LT = LinearTransform(lmt) 1267 self.apply_transform(LT) 1268 return self
Align the current object's bounding box to the bounding box of the input object.
Use rigid=True to disable scaling.
Example:
1270 def align_with_landmarks( 1271 self, 1272 source_landmarks, 1273 target_landmarks, 1274 rigid=False, 1275 affine=False, 1276 least_squares=False, 1277 ) -> Self: 1278 """ 1279 Transform mesh orientation and position based on a set of landmarks points. 1280 The algorithm finds the best matching of source points to target points 1281 in the mean least square sense, in one single step. 1282 1283 If `affine` is True the x, y and z axes can scale independently but stay collinear. 1284 With least_squares they can vary orientation. 1285 1286 Examples: 1287 - [align5.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align5.py) 1288 1289  1290 """ 1291 1292 if utils.is_sequence(source_landmarks): 1293 ss = vtki.vtkPoints() 1294 for p in source_landmarks: 1295 ss.InsertNextPoint(p) 1296 else: 1297 ss = source_landmarks.dataset.GetPoints() 1298 if least_squares: 1299 source_landmarks = source_landmarks.coordinates 1300 1301 if utils.is_sequence(target_landmarks): 1302 st = vtki.vtkPoints() 1303 for p in target_landmarks: 1304 st.InsertNextPoint(p) 1305 else: 1306 st = target_landmarks.GetPoints() 1307 if least_squares: 1308 target_landmarks = target_landmarks.coordinates 1309 1310 if ss.GetNumberOfPoints() != st.GetNumberOfPoints(): 1311 n1 = ss.GetNumberOfPoints() 1312 n2 = st.GetNumberOfPoints() 1313 vedo.logger.error(f"source and target have different nr of points {n1} vs {n2}") 1314 raise RuntimeError() 1315 1316 if int(rigid) + int(affine) + int(least_squares) > 1: 1317 vedo.logger.error( 1318 "only one of rigid, affine, least_squares can be True at a time" 1319 ) 1320 raise RuntimeError() 1321 1322 lmt = vtki.vtkLandmarkTransform() 1323 lmt.SetSourceLandmarks(ss) 1324 lmt.SetTargetLandmarks(st) 1325 lmt.SetModeToSimilarity() 1326 1327 if rigid: 1328 lmt.SetModeToRigidBody() 1329 lmt.Update() 1330 1331 elif affine: 1332 lmt.SetModeToAffine() 1333 lmt.Update() 1334 1335 elif least_squares: 1336 cms = source_landmarks.mean(axis=0) 1337 cmt = target_landmarks.mean(axis=0) 1338 m = np.linalg.lstsq(source_landmarks - cms, target_landmarks - cmt, rcond=None)[0] 1339 M = vtki.vtkMatrix4x4() 1340 for i in range(3): 1341 for j in range(3): 1342 M.SetElement(j, i, m[i][j]) 1343 lmt = vtki.vtkTransform() 1344 lmt.Translate(cmt) 1345 lmt.Concatenate(M) 1346 lmt.Translate(-cms) 1347 1348 else: 1349 lmt.Update() 1350 1351 self.apply_transform(lmt) 1352 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("transform_with_landmarks", parents=[self]) 1353 return self
Transform mesh orientation and position based on a set of landmarks points. The algorithm finds the best matching of source points to target points in the mean least square sense, in one single step.
If affine is True the x, y and z axes can scale independently but stay collinear.
With least_squares they can vary orientation.
Examples:
1355 def normalize(self) -> Self: 1356 """Scale average size to unit. The scaling is performed around the center of mass.""" 1357 coords = self.coordinates 1358 if not coords.shape[0]: 1359 return self 1360 cm = np.mean(coords, axis=0) 1361 pts = coords - cm 1362 xyz2 = np.sum(pts * pts, axis=0) 1363 scale = 1 / np.sqrt(np.sum(xyz2) / len(pts)) 1364 self.scale(scale, origin=cm) 1365 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("normalize", parents=[self]) 1366 return self
Scale average size to unit. The scaling is performed around the center of mass.
1368 def mirror(self, axis="x", origin=True) -> Self: 1369 """ 1370 Mirror reflect along one of the cartesian axes 1371 1372 Arguments: 1373 axis : (str) 1374 axis to use for mirroring, must be set to `x, y, z`. 1375 Or any combination of those. 1376 origin : (list) 1377 use this point as the origin of the mirroring transformation. 1378 1379 Examples: 1380 - [mirror.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/mirror.py) 1381 1382  1383 """ 1384 sx, sy, sz = 1, 1, 1 1385 if "x" in axis.lower(): sx = -1 1386 if "y" in axis.lower(): sy = -1 1387 if "z" in axis.lower(): sz = -1 1388 1389 self.scale([sx, sy, sz], origin=origin) 1390 1391 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1392 "mirror", comment=f"axis = {axis}", parents=[self]) 1393 1394 if sx * sy * sz < 0: 1395 if hasattr(self, "reverse"): 1396 self.reverse() 1397 return self
Mirror reflect along one of the cartesian axes
Arguments:
- axis : (str)
axis to use for mirroring, must be set to
x, y, z. Or any combination of those. - origin : (list) use this point as the origin of the mirroring transformation.
Examples:
1399 def flip_normals(self) -> Self: 1400 """Flip all normals orientation.""" 1401 rs = vtki.new("ReverseSense") 1402 rs.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1403 rs.ReverseCellsOff() 1404 rs.ReverseNormalsOn() 1405 rs.Update() 1406 self._update(rs.GetOutput()) 1407 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("flip_normals", parents=[self]) 1408 return self
Flip all normals orientation.
1410 def add_gaussian_noise(self, sigma=1.0) -> Self: 1411 """ 1412 Add gaussian noise to point positions. 1413 An extra array is added named "GaussianNoise" with the displacements. 1414 1415 Arguments: 1416 sigma : (float) 1417 nr. of standard deviations, expressed in percent of the diagonal size of mesh. 1418 Can also be a list `[sigma_x, sigma_y, sigma_z]`. 1419 1420 Example: 1421 ```python 1422 from vedo import Sphere 1423 Sphere().add_gaussian_noise(1.0).point_size(8).show().close() 1424 ``` 1425 """ 1426 sz = self.diagonal_size() 1427 pts = self.coordinates 1428 n = len(pts) 1429 ns = (np.random.randn(n, 3) * sigma) * (sz / 100) 1430 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 1431 vpts.SetNumberOfPoints(n) 1432 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(pts + ns, dtype=np.float32)) 1433 self.dataset.SetPoints(vpts) 1434 self.dataset.GetPoints().Modified() 1435 self.pointdata["GaussianNoise"] = -ns 1436 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 1437 "gaussian_noise", parents=[self], shape="egg", comment=f"sigma = {sigma}" 1438 ) 1439 return self
Add gaussian noise to point positions. An extra array is added named "GaussianNoise" with the displacements.
Arguments:
- sigma : (float)
nr. of standard deviations, expressed in percent of the diagonal size of mesh.
Can also be a list
[sigma_x, sigma_y, sigma_z].
Example:
from vedo import Sphere Sphere().add_gaussian_noise(1.0).point_size(8).show().close()
1441 def closest_point( 1442 self, pt, n=1, radius=None, return_point_id=False, return_cell_id=False 1443 ) -> Union[List[int], int, np.ndarray]: 1444 """ 1445 Find the closest point(s) on a mesh given from the input point `pt`. 1446 1447 Arguments: 1448 n : (int) 1449 if greater than 1, return a list of n ordered closest points 1450 radius : (float) 1451 if given, get all points within that radius. Then n is ignored. 1452 return_point_id : (bool) 1453 return point ID instead of coordinates 1454 return_cell_id : (bool) 1455 return cell ID in which the closest point sits 1456 1457 Examples: 1458 - [align1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/align1.py) 1459 - [fitplanes.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/fitplanes.py) 1460 - [quadratic_morphing.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/quadratic_morphing.py) 1461 1462 .. note:: 1463 The appropriate tree search locator is built on the fly and cached for speed. 1464 1465 If you want to reset it use `mymesh.point_locator=None` 1466 and / or `mymesh.cell_locator=None`. 1467 """ 1468 if len(pt) != 3: 1469 pt = [pt[0], pt[1], 0] 1470 1471 # NB: every time the mesh moves or is warped the locators are set to None 1472 if ((n > 1 or radius) or (n == 1 and return_point_id)) and not return_cell_id: 1473 poly = None 1474 if not self.point_locator: 1475 poly = self.dataset 1476 self.point_locator = vtki.new("StaticPointLocator") 1477 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 1478 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1479 1480 ########## 1481 if radius: 1482 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1483 self.point_locator.FindPointsWithinRadius(radius, pt, vtklist) 1484 elif n > 1: 1485 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1486 self.point_locator.FindClosestNPoints(n, pt, vtklist) 1487 else: # n==1 hence return_point_id==True 1488 ######## 1489 return self.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(pt) 1490 ######## 1491 1492 if return_point_id: 1493 ######## 1494 return utils.vtk2numpy(vtklist) 1495 ######## 1496 1497 if not poly: 1498 poly = self.dataset 1499 trgp = [] 1500 for i in range(vtklist.GetNumberOfIds()): 1501 trgp_ = [0, 0, 0] 1502 vi = vtklist.GetId(i) 1503 poly.GetPoints().GetPoint(vi, trgp_) 1504 trgp.append(trgp_) 1505 ######## 1506 return np.array(trgp) 1507 ######## 1508 1509 else: 1510 1511 if not self.cell_locator: 1512 poly = self.dataset 1513 1514 # As per Miquel example with limbs the vtkStaticCellLocator doesnt work !! 1515 # https://discourse.vtk.org/t/vtkstaticcelllocator-problem-vtk9-0-3/7854/4 1516 if vedo.vtk_version[0] >= 9 and vedo.vtk_version[1] > 0: 1517 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("StaticCellLocator") 1518 else: 1519 self.cell_locator = vtki.new("CellLocator") 1520 1521 self.cell_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 1522 self.cell_locator.BuildLocator() 1523 1524 if radius is not None: 1525 vedo.printc("Warning: closest_point() with radius is not implemented for cells.", c='r') 1526 1527 if n != 1: 1528 vedo.printc("Warning: closest_point() with n>1 is not implemented for cells.", c='r') 1529 1530 trgp = [0, 0, 0] 1531 cid = vtki.mutable(0) 1532 dist2 = vtki.mutable(0) 1533 subid = vtki.mutable(0) 1534 self.cell_locator.FindClosestPoint(pt, trgp, cid, subid, dist2) 1535 1536 if return_cell_id: 1537 return int(cid) 1538 1539 return np.array(trgp)
Find the closest point(s) on a mesh given from the input point pt.
Arguments:
- n : (int) if greater than 1, return a list of n ordered closest points
- radius : (float) if given, get all points within that radius. Then n is ignored.
- return_point_id : (bool) return point ID instead of coordinates
- return_cell_id : (bool) return cell ID in which the closest point sits
Examples:
The appropriate tree search locator is built on the fly and cached for speed.
If you want to reset it use mymesh.point_locator=None
and / or mymesh.cell_locator=None.
1541 def auto_distance(self) -> np.ndarray: 1542 """ 1543 Calculate the distance to the closest point in the same cloud of points. 1544 The output is stored in a new pointdata array called "AutoDistance", 1545 and it is also returned by the function. 1546 """ 1547 points = self.coordinates 1548 if not self.point_locator: 1549 self.point_locator = vtki.new("StaticPointLocator") 1550 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(self.dataset) 1551 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1552 qs = [] 1553 vtklist = vtki.vtkIdList() 1554 vtkpoints = self.dataset.GetPoints() 1555 for p in points: 1556 self.point_locator.FindClosestNPoints(2, p, vtklist) 1557 q = [0, 0, 0] 1558 pid = vtklist.GetId(1) 1559 vtkpoints.GetPoint(pid, q) 1560 qs.append(q) 1561 dists = np.linalg.norm(points - np.array(qs), axis=1) 1562 self.pointdata["AutoDistance"] = dists 1563 return dists
Calculate the distance to the closest point in the same cloud of points. The output is stored in a new pointdata array called "AutoDistance", and it is also returned by the function.
1565 def hausdorff_distance(self, points) -> float: 1566 """ 1567 Compute the Hausdorff distance to the input point set. 1568 Returns a single `float`. 1569 1570 Example: 1571 ```python 1572 from vedo import * 1573 t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) 1574 x = 4/3 * sin(t)**3 1575 y = cos(t) - cos(2*t)/3 - cos(3*t)/6 - cos(4*t)/12 1576 pol1 = Line(np.c_[x,y], closed=True).triangulate() 1577 pol2 = Polygon(nsides=5).pos(2,2) 1578 d12 = pol1.distance_to(pol2) 1579 d21 = pol2.distance_to(pol1) 1580 pol1.lw(0).cmap("viridis") 1581 pol2.lw(0).cmap("viridis") 1582 print("distance d12, d21 :", min(d12), min(d21)) 1583 print("hausdorff distance:", pol1.hausdorff_distance(pol2)) 1584 print("chamfer distance :", pol1.chamfer_distance(pol2)) 1585 show(pol1, pol2, axes=1) 1586 ``` 1587  1588 """ 1589 hp = vtki.new("HausdorffDistancePointSetFilter") 1590 hp.SetInputData(0, self.dataset) 1591 hp.SetInputData(1, points.dataset) 1592 hp.SetTargetDistanceMethodToPointToCell() 1593 hp.Update() 1594 return hp.GetHausdorffDistance()
Compute the Hausdorff distance to the input point set.
Returns a single float.
Example:
from vedo import * t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) x = 4/3 * sin(t)**3 y = cos(t) - cos(2*t)/3 - cos(3*t)/6 - cos(4*t)/12 pol1 = Line(np.c_[x,y], closed=True).triangulate() pol2 = Polygon(nsides=5).pos(2,2) d12 = pol1.distance_to(pol2) d21 = pol2.distance_to(pol1) pol1.lw(0).cmap("viridis") pol2.lw(0).cmap("viridis") print("distance d12, d21 :", min(d12), min(d21)) print("hausdorff distance:", pol1.hausdorff_distance(pol2)) print("chamfer distance :", pol1.chamfer_distance(pol2)) show(pol1, pol2, axes=1)
1596 def chamfer_distance(self, pcloud) -> float: 1597 """ 1598 Compute the Chamfer distance to the input point set. 1599 1600 Example: 1601 ```python 1602 from vedo import * 1603 cloud1 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) 1604 cloud2 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) + [1, 2, 3] 1605 c1 = Points(cloud1, r=5, c="red") 1606 c2 = Points(cloud2, r=5, c="green") 1607 d = c1.chamfer_distance(c2) 1608 show(f"Chamfer distance = {d}", c1, c2, axes=1).close() 1609 ``` 1610 """ 1611 # Definition of Chamfer distance may vary, here we use the average 1612 if not pcloud.point_locator: 1613 pcloud.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 1614 pcloud.point_locator.SetDataSet(pcloud.dataset) 1615 pcloud.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1616 if not self.point_locator: 1617 self.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 1618 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(self.dataset) 1619 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 1620 1621 ps1 = self.coordinates 1622 ps2 = pcloud.coordinates 1623 1624 ids12 = [] 1625 for p in ps1: 1626 pid12 = pcloud.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1627 ids12.append(pid12) 1628 deltav = ps2[ids12] - ps1 1629 da = np.mean(np.linalg.norm(deltav, axis=1)) 1630 1631 ids21 = [] 1632 for p in ps2: 1633 pid21 = self.point_locator.FindClosestPoint(p) 1634 ids21.append(pid21) 1635 deltav = ps1[ids21] - ps2 1636 db = np.mean(np.linalg.norm(deltav, axis=1)) 1637 return (da + db) / 2
Compute the Chamfer distance to the input point set.
Example:
from vedo import * cloud1 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) cloud2 = np.random.randn(1000, 3) + [1, 2, 3] c1 = Points(cloud1, r=5, c="red") c2 = Points(cloud2, r=5, c="green") d = c1.chamfer_distance(c2) show(f"Chamfer distance = {d}", c1, c2, axes=1).close()
1639 def remove_outliers(self, radius: float, neighbors=5) -> Self: 1640 """ 1641 Remove outliers from a cloud of points within the specified `radius` search. 1642 1643 Arguments: 1644 radius : (float) 1645 Specify the local search radius. 1646 neighbors : (int) 1647 Specify the number of neighbors that a point must have, 1648 within the specified radius, for the point to not be considered isolated. 1649 1650 Examples: 1651 - [clustering.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/clustering.py) 1652 1653  1654 """ 1655 removal = vtki.new("RadiusOutlierRemoval") 1656 removal.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1657 removal.SetRadius(radius) 1658 removal.SetNumberOfNeighbors(neighbors) 1659 removal.GenerateOutliersOff() 1660 removal.Update() 1661 inputobj = removal.GetOutput() 1662 if inputobj.GetNumberOfCells() == 0: 1663 carr = vtki.vtkCellArray() 1664 for i in range(inputobj.GetNumberOfPoints()): 1665 carr.InsertNextCell(1) 1666 carr.InsertCellPoint(i) 1667 inputobj.SetVerts(carr) 1668 self._update(removal.GetOutput()) 1669 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("remove_outliers", parents=[self]) 1670 return self
Remove outliers from a cloud of points within the specified radius search.
Arguments:
- radius : (float) Specify the local search radius.
- neighbors : (int) Specify the number of neighbors that a point must have, within the specified radius, for the point to not be considered isolated.
Examples:
1672 def relax_point_positions( 1673 self, 1674 n=10, 1675 iters=10, 1676 sub_iters=10, 1677 packing_factor=1, 1678 max_step=0, 1679 constraints=(), 1680 ) -> Self: 1681 """ 1682 Smooth mesh or points with a 1683 [Laplacian algorithm](https://vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkPointSmoothingFilter.html) 1684 variant. This modifies the coordinates of the input points by adjusting their positions 1685 to create a smooth distribution (and thereby form a pleasing packing of the points). 1686 Smoothing is performed by considering the effects of neighboring points on one another 1687 it uses a cubic cutoff function to produce repulsive forces between close points 1688 and attractive forces that are a little further away. 1689 1690 In general, the larger the neighborhood size, the greater the reduction in high frequency 1691 information. The memory and computational requirements of the algorithm may also 1692 significantly increase. 1693 1694 The algorithm incrementally adjusts the point positions through an iterative process. 1695 Basically points are moved due to the influence of neighboring points. 1696 1697 As points move, both the local connectivity and data attributes associated with each point 1698 must be updated. Rather than performing these expensive operations after every iteration, 1699 a number of sub-iterations can be specified. If so, then the neighborhood and attribute 1700 value updates occur only every sub iteration, which can improve performance significantly. 1701 1702 Arguments: 1703 n : (int) 1704 neighborhood size to calculate the Laplacian. 1705 iters : (int) 1706 number of iterations. 1707 sub_iters : (int) 1708 number of sub-iterations, i.e. the number of times the neighborhood and attribute 1709 value updates occur during each iteration. 1710 packing_factor : (float) 1711 adjust convergence speed. 1712 max_step : (float) 1713 Specify the maximum smoothing step size for each smoothing iteration. 1714 This limits the the distance over which a point can move in each iteration. 1715 As in all iterative methods, the stability of the process is sensitive to this parameter. 1716 In general, small step size and large numbers of iterations are more stable than a larger 1717 step size and a smaller numbers of iterations. 1718 constraints : (dict) 1719 dictionary of constraints. 1720 Point constraints are used to prevent points from moving, 1721 or to move only on a plane. This can prevent shrinking or growing point clouds. 1722 If enabled, a local topological analysis is performed to determine whether a point 1723 should be marked as fixed" i.e., never moves, or the point only moves on a plane, 1724 or the point can move freely. 1725 If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined by 1726 `fixed_angle`, then the point is classified as fixed. 1727 If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined by 1728 `boundary_angle`, then the point is classified as lying on a plane. 1729 Angles are expressed in degrees. 1730 1731 Example: 1732 ```py 1733 import numpy as np 1734 from vedo import Points, show 1735 from vedo.pyplot import histogram 1736 1737 vpts1 = Points(np.random.rand(10_000, 3)) 1738 dists = vpts1.auto_distance() 1739 h1 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() 1740 1741 vpts2 = vpts1.clone().relax_point_positions(n=100, iters=20, sub_iters=10) 1742 dists = vpts2.auto_distance() 1743 h2 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() 1744 1745 show([[vpts1, h1], [vpts2, h2]], N=2).close() 1746 ``` 1747 """ 1748 smooth = vtki.new("PointSmoothingFilter") 1749 smooth.SetInputData(self.dataset) 1750 smooth.SetSmoothingModeToUniform() 1751 smooth.SetNumberOfIterations(iters) 1752 smooth.SetNumberOfSubIterations(sub_iters) 1753 smooth.SetPackingFactor(packing_factor) 1754 if self.point_locator: 1755 smooth.SetLocator(self.point_locator) 1756 if not max_step: 1757 max_step = self.diagonal_size() / 100 1758 smooth.SetMaximumStepSize(max_step) 1759 smooth.SetNeighborhoodSize(n) 1760 if constraints: 1761 fixed_angle = constraints.get("fixed_angle", 45) 1762 boundary_angle = constraints.get("boundary_angle", 110) 1763 smooth.EnableConstraintsOn() 1764 smooth.SetFixedAngle(fixed_angle) 1765 smooth.SetBoundaryAngle(boundary_angle) 1766 smooth.GenerateConstraintScalarsOn() 1767 smooth.GenerateConstraintNormalsOn() 1768 smooth.Update() 1769 self._update(smooth.GetOutput()) 1770 self.metadata["PackingRadius"] = smooth.GetPackingRadius() 1771 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("relax_point_positions", parents=[self]) 1772 return self
Smooth mesh or points with a Laplacian algorithm variant. This modifies the coordinates of the input points by adjusting their positions to create a smooth distribution (and thereby form a pleasing packing of the points). Smoothing is performed by considering the effects of neighboring points on one another it uses a cubic cutoff function to produce repulsive forces between close points and attractive forces that are a little further away.
In general, the larger the neighborhood size, the greater the reduction in high frequency information. The memory and computational requirements of the algorithm may also significantly increase.
The algorithm incrementally adjusts the point positions through an iterative process. Basically points are moved due to the influence of neighboring points.
As points move, both the local connectivity and data attributes associated with each point must be updated. Rather than performing these expensive operations after every iteration, a number of sub-iterations can be specified. If so, then the neighborhood and attribute value updates occur only every sub iteration, which can improve performance significantly.
Arguments:
- n : (int) neighborhood size to calculate the Laplacian.
- iters : (int) number of iterations.
- sub_iters : (int) number of sub-iterations, i.e. the number of times the neighborhood and attribute value updates occur during each iteration.
- packing_factor : (float) adjust convergence speed.
- max_step : (float) Specify the maximum smoothing step size for each smoothing iteration. This limits the the distance over which a point can move in each iteration. As in all iterative methods, the stability of the process is sensitive to this parameter. In general, small step size and large numbers of iterations are more stable than a larger step size and a smaller numbers of iterations.
- constraints : (dict)
dictionary of constraints.
Point constraints are used to prevent points from moving,
or to move only on a plane. This can prevent shrinking or growing point clouds.
If enabled, a local topological analysis is performed to determine whether a point
should be marked as fixed" i.e., never moves, or the point only moves on a plane,
or the point can move freely.
If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined by
fixed_angle, then the point is classified as fixed. If all points in the neighborhood surrounding a point are in the cone defined byboundary_angle, then the point is classified as lying on a plane. Angles are expressed in degrees.
Example:
import numpy as np from vedo import Points, show from vedo.pyplot import histogram vpts1 = Points(np.random.rand(10_000, 3)) dists = vpts1.auto_distance() h1 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() vpts2 = vpts1.clone().relax_point_positions(n=100, iters=20, sub_iters=10) dists = vpts2.auto_distance() h2 = histogram(dists, xlim=(0,0.08)).clone2d() show([[vpts1, h1], [vpts2, h2]], N=2).close()
1774 def smooth_mls_1d(self, f=0.2, radius=None, n=0) -> Self: 1775 """ 1776 Smooth mesh or points with a `Moving Least Squares` variant. 1777 The point data array "Variances" will contain the residue calculated for each point. 1778 1779 Arguments: 1780 f : (float) 1781 smoothing factor - typical range is [0,2]. 1782 radius : (float) 1783 radius search in absolute units. 1784 If set then `f` is ignored. 1785 n : (int) 1786 number of neighbours to be used for the fit. 1787 If set then `f` and `radius` are ignored. 1788 1789 Examples: 1790 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 1791 - [skeletonize.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/skeletonize.py) 1792 1793  1794 """ 1795 coords = self.coordinates 1796 ncoords = len(coords) 1797 1798 if n: 1799 Ncp = n 1800 elif radius: 1801 Ncp = 1 1802 else: 1803 Ncp = int(ncoords * f / 10) 1804 if Ncp < 5: 1805 vedo.logger.warning(f"Please choose a fraction higher than {f}") 1806 Ncp = 5 1807 1808 variances, newline = [], [] 1809 for p in coords: 1810 points = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius) 1811 if len(points) < 4: 1812 continue 1813 1814 points = np.array(points) 1815 pointsmean = points.mean(axis=0) # plane center 1816 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(points - pointsmean) 1817 newp = np.dot(p - pointsmean, vv[0]) * vv[0] + pointsmean 1818 variances.append(dd[1] + dd[2]) 1819 newline.append(newp) 1820 1821 self.pointdata["Variances"] = np.array(variances).astype(np.float32) 1822 self.coordinates = newline 1823 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_mls_1d", parents=[self]) 1824 return self
Smooth mesh or points with a Moving Least Squares variant.
The point data array "Variances" will contain the residue calculated for each point.
Arguments:
- f : (float) smoothing factor - typical range is [0,2].
- radius : (float)
radius search in absolute units.
If set then
fis ignored. - n : (int)
number of neighbours to be used for the fit.
If set then
fandradiusare ignored.
Examples:
1826 def smooth_mls_2d(self, f=0.2, radius=None, n=0) -> Self: 1827 """ 1828 Smooth mesh or points with a `Moving Least Squares` algorithm variant. 1829 1830 The `mesh.pointdata['MLSVariance']` array will contain the residue calculated for each point. 1831 When a radius is specified, points that are isolated will not be moved and will get 1832 a 0 entry in array `mesh.pointdata['MLSValidPoint']`. 1833 1834 Arguments: 1835 f : (float) 1836 smoothing factor - typical range is [0, 2]. 1837 radius : (float | array) 1838 radius search in absolute units. Can be single value (float) or sequence 1839 for adaptive smoothing. If set then `f` is ignored. 1840 n : (int) 1841 number of neighbours to be used for the fit. 1842 If set then `f` and `radius` are ignored. 1843 1844 Examples: 1845 - [moving_least_squares2D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares2D.py) 1846 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 1847 1848  1849 """ 1850 coords = self.coordinates 1851 ncoords = len(coords) 1852 1853 if n: 1854 Ncp = n 1855 radius = None 1856 elif radius is not None: 1857 Ncp = 1 1858 else: 1859 Ncp = int(ncoords * f / 100) 1860 if Ncp < 4: 1861 vedo.logger.error(f"please choose a f-value higher than {f}") 1862 Ncp = 4 1863 1864 variances, newpts, valid = [], [], [] 1865 radius_is_sequence = utils.is_sequence(radius) 1866 1867 pb = None 1868 if ncoords > 10000: 1869 pb = utils.ProgressBar(0, ncoords, delay=3) 1870 1871 for i, p in enumerate(coords): 1872 if pb: 1873 pb.print("smooth_mls_2d working ...") 1874 1875 # if a radius was provided for each point 1876 if radius_is_sequence: 1877 pts = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius[i]) 1878 else: 1879 pts = self.closest_point(p, n=Ncp, radius=radius) 1880 1881 if len(pts) > 3: 1882 ptsmean = pts.mean(axis=0) # plane center 1883 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(pts - ptsmean) 1884 cv = np.cross(vv[0], vv[1]) 1885 t = (np.dot(cv, ptsmean) - np.dot(cv, p)) / np.dot(cv, cv) 1886 newpts.append(p + cv * t) 1887 variances.append(dd[2]) 1888 if radius is not None: 1889 valid.append(1) 1890 else: 1891 newpts.append(p) 1892 variances.append(0) 1893 if radius is not None: 1894 valid.append(0) 1895 1896 if radius is not None: 1897 self.pointdata["MLSValidPoint"] = np.array(valid).astype(np.uint8) 1898 self.pointdata["MLSVariance"] = np.array(variances).astype(np.float32) 1899 1900 self.coordinates = newpts 1901 1902 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_mls_2d", parents=[self]) 1903 return self
Smooth mesh or points with a Moving Least Squares algorithm variant.
The mesh.pointdata['MLSVariance'] array will contain the residue calculated for each point.
When a radius is specified, points that are isolated will not be moved and will get
a 0 entry in array mesh.pointdata['MLSValidPoint'].
Arguments:
- f : (float) smoothing factor - typical range is [0, 2].
- radius : (float | array)
radius search in absolute units. Can be single value (float) or sequence
for adaptive smoothing. If set then
fis ignored. - n : (int)
number of neighbours to be used for the fit.
If set then
fandradiusare ignored.
Examples:
1905 def smooth_lloyd_2d(self, iterations=2, bounds=None, options="Qbb Qc Qx") -> Self: 1906 """ 1907 Lloyd relaxation of a 2D pointcloud. 1908 1909 Arguments: 1910 iterations : (int) 1911 number of iterations. 1912 bounds : (list) 1913 bounding box of the domain. 1914 options : (str) 1915 options for the Qhull algorithm. 1916 """ 1917 # Credits: https://hatarilabs.com/ih-en/ 1918 # tutorial-to-create-a-geospatial-voronoi-sh-mesh-with-python-scipy-and-geopandas 1919 from scipy.spatial import Voronoi as scipy_voronoi 1920 1921 def _constrain_points(points): 1922 # Update any points that have drifted beyond the boundaries of this space 1923 if bounds is not None: 1924 for point in points: 1925 if point[0] < bounds[0]: point[0] = bounds[0] 1926 if point[0] > bounds[1]: point[0] = bounds[1] 1927 if point[1] < bounds[2]: point[1] = bounds[2] 1928 if point[1] > bounds[3]: point[1] = bounds[3] 1929 return points 1930 1931 def _find_centroid(vertices): 1932 # The equation for the method used here to find the centroid of a 1933 # 2D polygon is given here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centroid#Of_a_polygon 1934 area = 0 1935 centroid_x = 0 1936 centroid_y = 0 1937 for i in range(len(vertices) - 1): 1938 step = (vertices[i, 0] * vertices[i + 1, 1]) - (vertices[i + 1, 0] * vertices[i, 1]) 1939 centroid_x += (vertices[i, 0] + vertices[i + 1, 0]) * step 1940 centroid_y += (vertices[i, 1] + vertices[i + 1, 1]) * step 1941 area += step 1942 if area: 1943 centroid_x = (1.0 / (3.0 * area)) * centroid_x 1944 centroid_y = (1.0 / (3.0 * area)) * centroid_y 1945 # prevent centroids from escaping bounding box 1946 return _constrain_points([[centroid_x, centroid_y]])[0] 1947 1948 def _relax(voron): 1949 # Moves each point to the centroid of its cell in the voronoi 1950 # map to "relax" the points (i.e. jitter the points so as 1951 # to spread them out within the space). 1952 centroids = [] 1953 for idx in voron.point_region: 1954 # the region is a series of indices into voronoi.vertices 1955 # remove point at infinity, designated by index -1 1956 region = [i for i in voron.regions[idx] if i != -1] 1957 # enclose the polygon 1958 region = region + [region[0]] 1959 verts = voron.vertices[region] 1960 # find the centroid of those vertices 1961 centroids.append(_find_centroid(verts)) 1962 return _constrain_points(centroids) 1963 1964 if bounds is None: 1965 bounds = self.bounds() 1966 1967 pts = self.vertices[:, (0, 1)] 1968 for i in range(iterations): 1969 vor = scipy_voronoi(pts, qhull_options=options) 1970 _constrain_points(vor.vertices) 1971 pts = _relax(vor) 1972 out = Points(pts) 1973 out.name = "MeshSmoothLloyd2D" 1974 out.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("smooth_lloyd", parents=[self]) 1975 return out
Lloyd relaxation of a 2D pointcloud.
Arguments:
- iterations : (int) number of iterations.
- bounds : (list) bounding box of the domain.
- options : (str) options for the Qhull algorithm.
1977 def project_on_plane(self, plane="z", point=None, direction=None) -> Self: 1978 """ 1979 Project the mesh on one of the Cartesian planes. 1980 1981 Arguments: 1982 plane : (str, Plane) 1983 if plane is `str`, plane can be one of ['x', 'y', 'z'], 1984 represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. 1985 Otherwise, plane should be an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane`. 1986 point : (float, array) 1987 if plane is `str`, point should be a float represents the intercept. 1988 Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection 1989 direction : (array) 1990 direction of oblique projection 1991 1992 Note: 1993 Parameters `point` and `direction` are only used if the given plane 1994 is an instance of `vedo.shapes.Plane`. And one of these two params 1995 should be left as `None` to specify the projection type. 1996 1997 Example: 1998 ```python 1999 s.project_on_plane(plane='z') # project to z-plane 2000 plane = Plane(pos=(4, 8, -4), normal=(-1, 0, 1), s=(5,5)) 2001 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane) # orthogonal projection 2002 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, point=(6, 6, 6)) # perspective projection 2003 s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, direction=(1, 2, -1)) # oblique projection 2004 ``` 2005 2006 Examples: 2007 - [silhouette2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/silhouette2.py) 2008 2009  2010 """ 2011 coords = self.coordinates 2012 2013 if plane == "x": 2014 coords[:, 0] = self.transform.position[0] 2015 intercept = self.xbounds()[0] if point is None else point 2016 self.x(intercept) 2017 elif plane == "y": 2018 coords[:, 1] = self.transform.position[1] 2019 intercept = self.ybounds()[0] if point is None else point 2020 self.y(intercept) 2021 elif plane == "z": 2022 coords[:, 2] = self.transform.position[2] 2023 intercept = self.zbounds()[0] if point is None else point 2024 self.z(intercept) 2025 2026 elif isinstance(plane, vedo.shapes.Plane): 2027 normal = plane.normal / np.linalg.norm(plane.normal) 2028 pl = np.hstack((normal, -np.dot(plane.pos(), normal))).reshape(4, 1) 2029 if direction is None and point is None: 2030 # orthogonal projection 2031 pt = np.hstack((normal, [0])).reshape(4, 1) 2032 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T # python3 only 2033 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2034 2035 elif direction is None: 2036 # perspective projection 2037 pt = np.hstack((np.array(point), [1])).reshape(4, 1) 2038 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T 2039 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2040 2041 elif point is None: 2042 # oblique projection 2043 pt = np.hstack((np.array(direction), [0])).reshape(4, 1) 2044 # proj_mat = pt.T @ pl * np.eye(4) - pt @ pl.T 2045 proj_mat = np.matmul(pt.T, pl) * np.eye(4) - np.matmul(pt, pl.T) 2046 2047 coords = np.concatenate([coords, np.ones((coords.shape[:-1] + (1,)))], axis=-1) 2048 # coords = coords @ proj_mat.T 2049 coords = np.matmul(coords, proj_mat.T) 2050 coords = coords[:, :3] / coords[:, 3:] 2051 2052 else: 2053 vedo.logger.error(f"unknown plane {plane}") 2054 raise RuntimeError() 2055 2056 self.alpha(0.1) 2057 self.coordinates = coords 2058 return self
Project the mesh on one of the Cartesian planes.
Arguments:
- plane : (str, Plane)
if plane is
str, plane can be one of ['x', 'y', 'z'], represents x-plane, y-plane and z-plane, respectively. Otherwise, plane should be an instance ofvedo.shapes.Plane. - point : (float, array)
if plane is
str, point should be a float represents the intercept. Otherwise, point is the camera point of perspective projection - direction : (array) direction of oblique projection
Note:
Parameters
pointanddirectionare only used if the given plane is an instance ofvedo.shapes.Plane. And one of these two params should be left asNoneto specify the projection type.
Example:
s.project_on_plane(plane='z') # project to z-plane plane = Plane(pos=(4, 8, -4), normal=(-1, 0, 1), s=(5,5)) s.project_on_plane(plane=plane) # orthogonal projection s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, point=(6, 6, 6)) # perspective projection s.project_on_plane(plane=plane, direction=(1, 2, -1)) # oblique projection
Examples:
2060 def warp(self, source, target, sigma=1.0, mode="3d") -> Self: 2061 """ 2062 "Thin Plate Spline" transformations describe a nonlinear warp transform defined by a set 2063 of source and target landmarks. Any point on the mesh close to a source landmark will 2064 be moved to a place close to the corresponding target landmark. 2065 The points in between are interpolated smoothly using 2066 Bookstein's Thin Plate Spline algorithm. 2067 2068 Transformation object can be accessed with `mesh.transform`. 2069 2070 Arguments: 2071 sigma : (float) 2072 specify the 'stiffness' of the spline. 2073 mode : (str) 2074 set the basis function to either abs(R) (for 3d) or R2LogR (for 2d meshes) 2075 2076 Examples: 2077 - [interpolate_field.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/interpolate_field.py) 2078 - [warp1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp1.py) 2079 - [warp2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp2.py) 2080 - [warp3.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp3.py) 2081 - [warp4a.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp4a.py) 2082 - [warp4b.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp4b.py) 2083 - [warp6.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp6.py) 2084 2085  2086 """ 2087 parents = [self] 2088 2089 try: 2090 source = source.coordinates 2091 parents.append(source) 2092 except AttributeError: 2093 source = utils.make3d(source) 2094 2095 try: 2096 target = target.coordinates 2097 parents.append(target) 2098 except AttributeError: 2099 target = utils.make3d(target) 2100 2101 ns = len(source) 2102 nt = len(target) 2103 if ns != nt: 2104 vedo.logger.error(f"#source {ns} != {nt} #target points") 2105 raise RuntimeError() 2106 2107 NLT = NonLinearTransform(sigma=sigma, mode=mode) 2108 NLT.source_points = source 2109 NLT.target_points = target 2110 self.apply_transform(NLT) 2111 2112 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("warp", parents=parents) 2113 return self
"Thin Plate Spline" transformations describe a nonlinear warp transform defined by a set of source and target landmarks. Any point on the mesh close to a source landmark will be moved to a place close to the corresponding target landmark. The points in between are interpolated smoothly using Bookstein's Thin Plate Spline algorithm.
Transformation object can be accessed with mesh.transform.
Arguments:
- sigma : (float) specify the 'stiffness' of the spline.
- mode : (str) set the basis function to either abs(R) (for 3d) or R2LogR (for 2d meshes)
Examples:
2115 def cut_with_plane( 2116 self, 2117 origin=(0, 0, 0), 2118 normal=(1, 0, 0), 2119 invert=False, 2120 # generate_ids=False, 2121 ) -> Self: 2122 """ 2123 Cut the mesh with the plane defined by a point and a normal. 2124 2125 Arguments: 2126 origin : (array) 2127 the cutting plane goes through this point 2128 normal : (array) 2129 normal of the cutting plane 2130 invert : (bool) 2131 select which side of the plane to keep 2132 2133 Example: 2134 ```python 2135 from vedo import Cube 2136 cube = Cube().cut_with_plane(normal=(1,1,1)) 2137 cube.back_color('pink').show().close() 2138 ``` 2139  2140 2141 Examples: 2142 - [trail.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/simulations/trail.py) 2143 2144  2145 2146 Check out also: 2147 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_cylinder()`, `cut_with_sphere()`. 2148 """ 2149 s = str(normal) 2150 if "x" in s: 2151 normal = (1, 0, 0) 2152 if "-" in s: 2153 normal = -np.array(normal) 2154 elif "y" in s: 2155 normal = (0, 1, 0) 2156 if "-" in s: 2157 normal = -np.array(normal) 2158 elif "z" in s: 2159 normal = (0, 0, 1) 2160 if "-" in s: 2161 normal = -np.array(normal) 2162 plane = vtki.vtkPlane() 2163 plane.SetOrigin(origin) 2164 plane.SetNormal(normal) 2165 2166 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2167 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2168 clipper.SetClipFunction(plane) 2169 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2170 clipper.SetGenerateClipScalars(0) 2171 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2172 clipper.SetValue(0) 2173 clipper.Update() 2174 2175 # if generate_ids: 2176 # saved_scalars = None # otherwise the scalars are lost 2177 # if self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars(): 2178 # saved_scalars = self.dataset.GetPointData().GetScalars() 2179 # varr = clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetScalars() 2180 # if varr.GetName() is None: 2181 # varr.SetName("DistanceToCut") 2182 # arr = utils.vtk2numpy(varr) 2183 # # array of original ids 2184 # ids = np.arange(arr.shape[0]).astype(int) 2185 # ids[arr == 0] = -1 2186 # ids_arr = utils.numpy2vtk(ids, dtype=int) 2187 # ids_arr.SetName("OriginalIds") 2188 # clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().AddArray(ids_arr) 2189 # if saved_scalars: 2190 # clipper.GetOutput().GetPointData().AddArray(saved_scalars) 2191 2192 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2193 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_plane", parents=[self]) 2194 return self
Cut the mesh with the plane defined by a point and a normal.
Arguments:
- origin : (array) the cutting plane goes through this point
- normal : (array) normal of the cutting plane
- invert : (bool) select which side of the plane to keep
Example:
from vedo import Cube cube = Cube().cut_with_plane(normal=(1,1,1)) cube.back_color('pink').show().close()
Examples:
Check out also:
2196 def cut_with_planes(self, origins, normals, invert=False) -> Self: 2197 """ 2198 Cut the mesh with a convex set of planes defined by points and normals. 2199 2200 Arguments: 2201 origins : (array) 2202 each cutting plane goes through this point 2203 normals : (array) 2204 normal of each of the cutting planes 2205 invert : (bool) 2206 if True, cut outside instead of inside 2207 2208 Check out also: 2209 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_cylinder()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2210 """ 2211 2212 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 2213 for p in utils.make3d(origins): 2214 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 2215 normals = utils.make3d(normals) 2216 2217 planes = vtki.vtkPlanes() 2218 planes.SetPoints(vpoints) 2219 planes.SetNormals(utils.numpy2vtk(normals, dtype=float)) 2220 2221 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2222 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2223 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2224 clipper.SetClipFunction(planes) 2225 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2226 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2227 clipper.SetValue(0) 2228 clipper.Update() 2229 2230 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2231 2232 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_planes", parents=[self]) 2233 return self
Cut the mesh with a convex set of planes defined by points and normals.
Arguments:
- origins : (array) each cutting plane goes through this point
- normals : (array) normal of each of the cutting planes
- invert : (bool) if True, cut outside instead of inside
Check out also:
2235 def cut_with_box(self, bounds, invert=False) -> Self: 2236 """ 2237 Cut the current mesh with a box or a set of boxes. 2238 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2239 2240 Input `bounds` can be either: 2241 - a Mesh or Points object 2242 - a list of 6 number representing a bounding box `[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax]` 2243 - a list of bounding boxes like the above: `[[xmin1,...], [xmin2,...], ...]` 2244 2245 Example: 2246 ```python 2247 from vedo import Sphere, Cube, show 2248 mesh = Sphere(r=1, res=50) 2249 box = Cube(side=1.5).wireframe() 2250 mesh.cut_with_box(box) 2251 show(mesh, box, axes=1).close() 2252 ``` 2253  2254 2255 Check out also: 2256 `cut_with_line()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2257 """ 2258 if isinstance(bounds, Points): 2259 bounds = bounds.bounds() 2260 2261 box = vtki.new("Box") 2262 if utils.is_sequence(bounds[0]): 2263 for bs in bounds: 2264 box.AddBounds(bs) 2265 else: 2266 box.SetBounds(bounds) 2267 2268 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2269 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2270 clipper.SetClipFunction(box) 2271 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2272 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2273 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2274 clipper.SetValue(0) 2275 clipper.Update() 2276 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2277 2278 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_box", parents=[self]) 2279 return self
Cut the current mesh with a box or a set of boxes.
This is much faster than cut_with_mesh().
Input bounds can be either:
- a Mesh or Points object
- a list of 6 number representing a bounding box
[xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zmin,zmax] - a list of bounding boxes like the above:
[[xmin1,...], [xmin2,...], ...]
Example:
from vedo import Sphere, Cube, show mesh = Sphere(r=1, res=50) box = Cube(side=1.5).wireframe() mesh.cut_with_box(box) show(mesh, box, axes=1).close()
Check out also:
2281 def cut_with_line(self, points, invert=False, closed=True) -> Self: 2282 """ 2283 Cut the current mesh with a line vertically in the z-axis direction like a cookie cutter. 2284 The polyline is defined by a set of points (z-coordinates are ignored). 2285 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2286 2287 Check out also: 2288 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2289 """ 2290 pplane = vtki.new("PolyPlane") 2291 if isinstance(points, Points): 2292 points = points.coordinates.tolist() 2293 2294 if closed: 2295 if isinstance(points, np.ndarray): 2296 points = points.tolist() 2297 points.append(points[0]) 2298 2299 vpoints = vtki.vtkPoints() 2300 for p in points: 2301 if len(p) == 2: 2302 p = [p[0], p[1], 0.0] 2303 vpoints.InsertNextPoint(p) 2304 2305 n = len(points) 2306 polyline = vtki.new("PolyLine") 2307 polyline.Initialize(n, vpoints) 2308 polyline.GetPointIds().SetNumberOfIds(n) 2309 for i in range(n): 2310 polyline.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i) 2311 pplane.SetPolyLine(polyline) 2312 2313 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2314 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2315 clipper.SetClipFunction(pplane) 2316 clipper.SetInsideOut(invert) 2317 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2318 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2319 clipper.SetValue(0) 2320 clipper.Update() 2321 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2322 2323 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_line", parents=[self]) 2324 return self
Cut the current mesh with a line vertically in the z-axis direction like a cookie cutter.
The polyline is defined by a set of points (z-coordinates are ignored).
This is much faster than cut_with_mesh().
Check out also:
2402 def cut_with_cylinder(self, center=(0, 0, 0), axis=(0, 0, 1), r=1, invert=False) -> Self: 2403 """ 2404 Cut the current mesh with an infinite cylinder. 2405 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2406 2407 Arguments: 2408 center : (array) 2409 the center of the cylinder 2410 normal : (array) 2411 direction of the cylinder axis 2412 r : (float) 2413 radius of the cylinder 2414 2415 Example: 2416 ```python 2417 from vedo import Disc, show 2418 disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) 2419 mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) 2420 mesh.cut_with_cylinder([0,0,2], r=0.4, axis='y', invert=True) 2421 show(mesh, axes=1).close() 2422 ``` 2423  2424 2425 Examples: 2426 - [optics_main1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/simulations/optics_main1.py) 2427 2428 Check out also: 2429 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_sphere()` 2430 """ 2431 s = str(axis) 2432 if "x" in s: 2433 axis = (1, 0, 0) 2434 elif "y" in s: 2435 axis = (0, 1, 0) 2436 elif "z" in s: 2437 axis = (0, 0, 1) 2438 cyl = vtki.new("Cylinder") 2439 cyl.SetCenter(center) 2440 cyl.SetAxis(axis[0], axis[1], axis[2]) 2441 cyl.SetRadius(r) 2442 2443 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2444 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2445 clipper.SetClipFunction(cyl) 2446 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2447 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2448 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2449 clipper.SetValue(0) 2450 clipper.Update() 2451 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2452 2453 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_cylinder", parents=[self]) 2454 return self
Cut the current mesh with an infinite cylinder.
This is much faster than cut_with_mesh().
Arguments:
- center : (array) the center of the cylinder
- normal : (array) direction of the cylinder axis
- r : (float) radius of the cylinder
Example:
from vedo import Disc, show disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) mesh.cut_with_cylinder([0,0,2], r=0.4, axis='y', invert=True) show(mesh, axes=1).close()
Examples:
Check out also:
2456 def cut_with_sphere(self, center=(0, 0, 0), r=1.0, invert=False) -> Self: 2457 """ 2458 Cut the current mesh with an sphere. 2459 This is much faster than `cut_with_mesh()`. 2460 2461 Arguments: 2462 center : (array) 2463 the center of the sphere 2464 r : (float) 2465 radius of the sphere 2466 2467 Example: 2468 ```python 2469 from vedo import Disc, show 2470 disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) 2471 mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) 2472 mesh.cut_with_sphere([1,-0.7,2], r=1.5, invert=True) 2473 show(mesh, axes=1).close() 2474 ``` 2475  2476 2477 Check out also: 2478 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2479 """ 2480 sph = vtki.new("Sphere") 2481 sph.SetCenter(center) 2482 sph.SetRadius(r) 2483 2484 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2485 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2486 clipper.SetClipFunction(sph) 2487 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2488 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2489 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2490 clipper.SetValue(0) 2491 clipper.Update() 2492 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2493 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_sphere", parents=[self]) 2494 return self
Cut the current mesh with an sphere.
This is much faster than cut_with_mesh().
Arguments:
- center : (array) the center of the sphere
- r : (float) radius of the sphere
Example:
from vedo import Disc, show disc = Disc(r1=1, r2=1.2) mesh = disc.extrude(3, res=50).linewidth(1) mesh.cut_with_sphere([1,-0.7,2], r=1.5, invert=True) show(mesh, axes=1).close()
Check out also:
2496 def cut_with_mesh(self, mesh, invert=False, keep=False) -> Union[Self, "vedo.Assembly"]: 2497 """ 2498 Cut an `Mesh` mesh with another `Mesh`. 2499 2500 Use `invert` to invert the selection. 2501 2502 Use `keep` to keep the cutoff part, in this case an `Assembly` is returned: 2503 the "cut" object and the "discarded" part of the original object. 2504 You can access both via `assembly.unpack()` method. 2505 2506 Example: 2507 ```python 2508 from vedo import * 2509 arr = np.random.randn(100000, 3)/2 2510 pts = Points(arr).c('red3').pos(5,0,0) 2511 cube = Cube().pos(4,0.5,0) 2512 assem = pts.cut_with_mesh(cube, keep=True) 2513 show(assem.unpack(), axes=1).close() 2514 ``` 2515  2516 2517 Check out also: 2518 `cut_with_box()`, `cut_with_plane()`, `cut_with_cylinder()` 2519 """ 2520 polymesh = mesh.dataset 2521 poly = self.dataset 2522 2523 # Create an array to hold distance information 2524 signed_distances = vtki.vtkFloatArray() 2525 signed_distances.SetNumberOfComponents(1) 2526 signed_distances.SetName("SignedDistances") 2527 2528 # implicit function that will be used to slice the mesh 2529 ippd = vtki.new("ImplicitPolyDataDistance") 2530 ippd.SetInput(polymesh) 2531 2532 # Evaluate the signed distance function at all of the grid points 2533 for pointId in range(poly.GetNumberOfPoints()): 2534 p = poly.GetPoint(pointId) 2535 signed_distance = ippd.EvaluateFunction(p) 2536 signed_distances.InsertNextValue(signed_distance) 2537 2538 currentscals = poly.GetPointData().GetScalars() 2539 if currentscals: 2540 currentscals = currentscals.GetName() 2541 2542 poly.GetPointData().AddArray(signed_distances) 2543 poly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars("SignedDistances") 2544 2545 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2546 clipper.SetInputData(poly) 2547 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2548 clipper.SetGenerateClippedOutput(keep) 2549 clipper.SetValue(0.0) 2550 clipper.Update() 2551 cpoly = clipper.GetOutput() 2552 2553 if keep: 2554 kpoly = clipper.GetOutput(1) 2555 2556 vis = False 2557 if currentscals: 2558 cpoly.GetPointData().SetActiveScalars(currentscals) 2559 vis = self.mapper.GetScalarVisibility() 2560 2561 self._update(cpoly) 2562 2563 self.pointdata.remove("SignedDistances") 2564 self.mapper.SetScalarVisibility(vis) 2565 if keep: 2566 if isinstance(self, vedo.Mesh): 2567 cutoff = vedo.Mesh(kpoly) 2568 else: 2569 cutoff = vedo.Points(kpoly) 2570 # cutoff = self.__class__(kpoly) # this does not work properly 2571 cutoff.properties = vtki.vtkProperty() 2572 cutoff.properties.DeepCopy(self.properties) 2573 cutoff.actor.SetProperty(cutoff.properties) 2574 cutoff.c("k5").alpha(0.2) 2575 return vedo.Assembly([self, cutoff]) 2576 2577 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_mesh", parents=[self, mesh]) 2578 return self
Cut an Mesh mesh with another Mesh.
Use invert to invert the selection.
Use keep to keep the cutoff part, in this case an Assembly is returned:
the "cut" object and the "discarded" part of the original object.
You can access both via assembly.unpack() method.
Example:
from vedo import *
arr = np.random.randn(100000, 3)/2
pts = Points(arr).c('red3').pos(5,0,0)
cube = Cube().pos(4,0.5,0)
assem = pts.cut_with_mesh(cube, keep=True)
show(assem.unpack(), axes=1).close()

Check out also:
2580 def cut_with_point_loop( 2581 self, points, invert=False, on="points", include_boundary=False 2582 ) -> Self: 2583 """ 2584 Cut an `Mesh` object with a set of points forming a closed loop. 2585 2586 Arguments: 2587 invert : (bool) 2588 invert selection (inside-out) 2589 on : (str) 2590 if 'cells' will extract the whole cells lying inside (or outside) the point loop 2591 include_boundary : (bool) 2592 include cells lying exactly on the boundary line. Only relevant on 'cells' mode 2593 2594 Examples: 2595 - [cut_with_points1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/cut_with_points1.py) 2596 2597  2598 2599 - [cut_with_points2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/cut_with_points2.py) 2600 2601  2602 """ 2603 if isinstance(points, Points): 2604 parents = [points] 2605 vpts = points.dataset.GetPoints() 2606 points = points.coordinates 2607 else: 2608 parents = [self] 2609 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 2610 points = utils.make3d(points) 2611 for p in points: 2612 vpts.InsertNextPoint(p) 2613 2614 if "cell" in on: 2615 ippd = vtki.new("ImplicitSelectionLoop") 2616 ippd.SetLoop(vpts) 2617 ippd.AutomaticNormalGenerationOn() 2618 clipper = vtki.new("ExtractPolyDataGeometry") 2619 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2620 clipper.SetImplicitFunction(ippd) 2621 clipper.SetExtractInside(not invert) 2622 clipper.SetExtractBoundaryCells(include_boundary) 2623 else: 2624 spol = vtki.new("SelectPolyData") 2625 spol.SetLoop(vpts) 2626 spol.GenerateSelectionScalarsOn() 2627 spol.GenerateUnselectedOutputOff() 2628 spol.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2629 spol.Update() 2630 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2631 clipper.SetInputData(spol.GetOutput()) 2632 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2633 clipper.SetValue(0.0) 2634 clipper.Update() 2635 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2636 2637 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_pointloop", parents=parents) 2638 return self
Cut an Mesh object with a set of points forming a closed loop.
Arguments:
- invert : (bool) invert selection (inside-out)
- on : (str) if 'cells' will extract the whole cells lying inside (or outside) the point loop
- include_boundary : (bool) include cells lying exactly on the boundary line. Only relevant on 'cells' mode
Examples:
2640 def cut_with_scalar(self, value: float, name="", invert=False) -> Self: 2641 """ 2642 Cut a mesh or point cloud with some input scalar point-data. 2643 2644 Arguments: 2645 value : (float) 2646 cutting value 2647 name : (str) 2648 array name of the scalars to be used 2649 invert : (bool) 2650 flip selection 2651 2652 Example: 2653 ```python 2654 from vedo import * 2655 s = Sphere().lw(1) 2656 pts = s.points 2657 scalars = np.sin(3*pts[:,2]) + pts[:,0] 2658 s.pointdata["somevalues"] = scalars 2659 s.cut_with_scalar(0.3) 2660 s.cmap("Spectral", "somevalues").add_scalarbar() 2661 s.show(axes=1).close() 2662 ``` 2663  2664 """ 2665 if name: 2666 self.pointdata.select(name) 2667 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2668 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2669 clipper.SetValue(value) 2670 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2671 clipper.SetInsideOut(not invert) 2672 clipper.Update() 2673 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2674 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("cut_with_scalar", parents=[self]) 2675 return self
Cut a mesh or point cloud with some input scalar point-data.
Arguments:
- value : (float) cutting value
- name : (str) array name of the scalars to be used
- invert : (bool) flip selection
Example:
from vedo import * s = Sphere().lw(1) pts = s.points scalars = np.sin(3*pts[:,2]) + pts[:,0] s.pointdata["somevalues"] = scalars s.cut_with_scalar(0.3) s.cmap("Spectral", "somevalues").add_scalarbar() s.show(axes=1).close()
2677 def crop(self, 2678 top=None, bottom=None, right=None, left=None, front=None, back=None, 2679 bounds=()) -> Self: 2680 """ 2681 Crop an `Mesh` object. 2682 2683 Arguments: 2684 top : (float) 2685 fraction to crop from the top plane (positive z) 2686 bottom : (float) 2687 fraction to crop from the bottom plane (negative z) 2688 front : (float) 2689 fraction to crop from the front plane (positive y) 2690 back : (float) 2691 fraction to crop from the back plane (negative y) 2692 right : (float) 2693 fraction to crop from the right plane (positive x) 2694 left : (float) 2695 fraction to crop from the left plane (negative x) 2696 bounds : (list) 2697 bounding box of the crop region as `[x0,x1, y0,y1, z0,z1]` 2698 2699 Example: 2700 ```python 2701 from vedo import Sphere 2702 Sphere().crop(right=0.3, left=0.1).show() 2703 ``` 2704  2705 """ 2706 if len(bounds) == 0: 2707 pos = np.array(self.pos()) 2708 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2709 x0, y0, z0 = [x0, y0, z0] - pos 2710 x1, y1, z1 = [x1, y1, z1] - pos 2711 2712 dx, dy, dz = x1 - x0, y1 - y0, z1 - z0 2713 if top: 2714 z1 = z1 - top * dz 2715 if bottom: 2716 z0 = z0 + bottom * dz 2717 if front: 2718 y1 = y1 - front * dy 2719 if back: 2720 y0 = y0 + back * dy 2721 if right: 2722 x1 = x1 - right * dx 2723 if left: 2724 x0 = x0 + left * dx 2725 bounds = (x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1) 2726 2727 cu = vtki.new("Box") 2728 cu.SetBounds(bounds) 2729 2730 clipper = vtki.new("ClipPolyData") 2731 clipper.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2732 clipper.SetClipFunction(cu) 2733 clipper.InsideOutOn() 2734 clipper.GenerateClippedOutputOff() 2735 clipper.GenerateClipScalarsOff() 2736 clipper.SetValue(0) 2737 clipper.Update() 2738 self._update(clipper.GetOutput()) 2739 2740 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2741 "crop", parents=[self], comment=f"#pts {self.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 2742 ) 2743 return self
Crop an Mesh object.
Arguments:
- top : (float) fraction to crop from the top plane (positive z)
- bottom : (float) fraction to crop from the bottom plane (negative z)
- front : (float) fraction to crop from the front plane (positive y)
- back : (float) fraction to crop from the back plane (negative y)
- right : (float) fraction to crop from the right plane (positive x)
- left : (float) fraction to crop from the left plane (negative x)
- bounds : (list)
bounding box of the crop region as
[x0,x1, y0,y1, z0,z1]
Example:
from vedo import Sphere Sphere().crop(right=0.3, left=0.1).show()
2745 def generate_surface_halo( 2746 self, 2747 distance=0.05, 2748 res=(50, 50, 50), 2749 bounds=(), 2750 maxdist=None, 2751 ) -> "vedo.Mesh": 2752 """ 2753 Generate the surface halo which sits at the specified distance from the input one. 2754 2755 Arguments: 2756 distance : (float) 2757 distance from the input surface 2758 res : (int) 2759 resolution of the surface 2760 bounds : (list) 2761 bounding box of the surface 2762 maxdist : (float) 2763 maximum distance to generate the surface 2764 """ 2765 if not bounds: 2766 bounds = self.bounds() 2767 2768 if not maxdist: 2769 maxdist = self.diagonal_size() / 2 2770 2771 imp = vtki.new("ImplicitModeller") 2772 imp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 2773 imp.SetSampleDimensions(res) 2774 if maxdist: 2775 imp.SetMaximumDistance(maxdist) 2776 if len(bounds) == 6: 2777 imp.SetModelBounds(bounds) 2778 contour = vtki.new("ContourFilter") 2779 contour.SetInputConnection(imp.GetOutputPort()) 2780 contour.SetValue(0, distance) 2781 contour.Update() 2782 out = vedo.Mesh(contour.GetOutput()) 2783 out.c("lightblue").alpha(0.25).lighting("off") 2784 out.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("generate_surface_halo", parents=[self]) 2785 return out
Generate the surface halo which sits at the specified distance from the input one.
Arguments:
- distance : (float) distance from the input surface
- res : (int) resolution of the surface
- bounds : (list) bounding box of the surface
- maxdist : (float) maximum distance to generate the surface
2787 def generate_mesh( 2788 self, 2789 line_resolution=None, 2790 mesh_resolution=None, 2791 smooth=0.0, 2792 jitter=0.001, 2793 grid=None, 2794 quads=False, 2795 invert=False, 2796 ) -> Self: 2797 """ 2798 Generate a polygonal Mesh from a closed contour line. 2799 If line is not closed it will be closed with a straight segment. 2800 2801 Check also `generate_delaunay2d()`. 2802 2803 Arguments: 2804 line_resolution : (int) 2805 resolution of the contour line. The default is None, in this case 2806 the contour is not resampled. 2807 mesh_resolution : (int) 2808 resolution of the internal triangles not touching the boundary. 2809 smooth : (float) 2810 smoothing of the contour before meshing. 2811 jitter : (float) 2812 add a small noise to the internal points. 2813 grid : (Grid) 2814 manually pass a Grid object. The default is True. 2815 quads : (bool) 2816 generate a mesh of quads instead of triangles. 2817 invert : (bool) 2818 flip the line orientation. The default is False. 2819 2820 Examples: 2821 - [line2mesh_tri.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/line2mesh_tri.py) 2822 2823  2824 2825 - [line2mesh_quads.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/line2mesh_quads.py) 2826 2827  2828 """ 2829 if line_resolution is None: 2830 contour = vedo.shapes.Line(self.coordinates) 2831 else: 2832 contour = vedo.shapes.Spline(self.coordinates, smooth=smooth, res=line_resolution) 2833 contour.clean() 2834 2835 length = contour.length() 2836 density = length / contour.npoints 2837 # print(f"tomesh():\n\tline length = {length}") 2838 # print(f"\tdensity = {density} length/pt_separation") 2839 2840 x0, x1 = contour.xbounds() 2841 y0, y1 = contour.ybounds() 2842 2843 if grid is None: 2844 if mesh_resolution is None: 2845 resx = int((x1 - x0) / density + 0.5) 2846 resy = int((y1 - y0) / density + 0.5) 2847 # print(f"tmesh_resolution = {[resx, resy]}") 2848 else: 2849 if utils.is_sequence(mesh_resolution): 2850 resx, resy = mesh_resolution 2851 else: 2852 resx, resy = mesh_resolution, mesh_resolution 2853 grid = vedo.shapes.Grid( 2854 [(x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, 0], 2855 s=((x1 - x0) * 1.025, (y1 - y0) * 1.025), 2856 res=(resx, resy), 2857 ) 2858 else: 2859 grid = grid.clone() 2860 2861 cpts = contour.coordinates 2862 2863 # make sure it's closed 2864 p0, p1 = cpts[0], cpts[-1] 2865 nj = max(2, int(utils.mag(p1 - p0) / density + 0.5)) 2866 joinline = vedo.shapes.Line(p1, p0, res=nj) 2867 contour = vedo.merge(contour, joinline).subsample(0.0001) 2868 2869 ####################################### quads 2870 if quads: 2871 cmesh = grid.clone().cut_with_point_loop(contour, on="cells", invert=invert) 2872 cmesh.wireframe(False).lw(0.5) 2873 cmesh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2874 "generate_mesh", 2875 parents=[self, contour], 2876 comment=f"#quads {cmesh.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 2877 ) 2878 return cmesh 2879 ############################################# 2880 2881 grid_tmp = grid.coordinates.copy() 2882 2883 if jitter: 2884 np.random.seed(0) 2885 sigma = 1.0 / np.sqrt(grid.npoints) * grid.diagonal_size() * jitter 2886 # print(f"\tsigma jittering = {sigma}") 2887 grid_tmp += np.random.rand(grid.npoints, 3) * sigma 2888 grid_tmp[:, 2] = 0.0 2889 2890 todel = [] 2891 density /= np.sqrt(3) 2892 vgrid_tmp = Points(grid_tmp) 2893 2894 for p in contour.coordinates: 2895 out = vgrid_tmp.closest_point(p, radius=density, return_point_id=True) 2896 todel += out.tolist() 2897 2898 grid_tmp = grid_tmp.tolist() 2899 for index in sorted(list(set(todel)), reverse=True): 2900 del grid_tmp[index] 2901 2902 points = contour.coordinates.tolist() + grid_tmp 2903 if invert: 2904 boundary = list(reversed(range(contour.npoints))) 2905 else: 2906 boundary = list(range(contour.npoints)) 2907 2908 dln = Points(points).generate_delaunay2d(mode="xy", boundaries=[boundary]) 2909 dln.compute_normals(points=False) # fixes reversd faces 2910 dln.lw(1) 2911 2912 dln.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 2913 "generate_mesh", 2914 parents=[self, contour], 2915 comment=f"#cells {dln.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 2916 ) 2917 return dln
Generate a polygonal Mesh from a closed contour line. If line is not closed it will be closed with a straight segment.
Check also generate_delaunay2d().
Arguments:
- line_resolution : (int) resolution of the contour line. The default is None, in this case the contour is not resampled.
- mesh_resolution : (int) resolution of the internal triangles not touching the boundary.
- smooth : (float) smoothing of the contour before meshing.
- jitter : (float) add a small noise to the internal points.
- grid : (Grid) manually pass a Grid object. The default is True.
- quads : (bool) generate a mesh of quads instead of triangles.
- invert : (bool) flip the line orientation. The default is False.
Examples:
2919 def reconstruct_surface( 2920 self, 2921 dims=(100, 100, 100), 2922 radius=None, 2923 sample_size=None, 2924 hole_filling=True, 2925 bounds=(), 2926 padding=0.05, 2927 ) -> "vedo.Mesh": 2928 """ 2929 Surface reconstruction from a scattered cloud of points. 2930 2931 Arguments: 2932 dims : (int) 2933 number of voxels in x, y and z to control precision. 2934 radius : (float) 2935 radius of influence of each point. 2936 Smaller values generally improve performance markedly. 2937 Note that after the signed distance function is computed, 2938 any voxel taking on the value >= radius 2939 is presumed to be "unseen" or uninitialized. 2940 sample_size : (int) 2941 if normals are not present 2942 they will be calculated using this sample size per point. 2943 hole_filling : (bool) 2944 enables hole filling, this generates 2945 separating surfaces between the empty and unseen portions of the volume. 2946 bounds : (list) 2947 region in space in which to perform the sampling 2948 in format (xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zim, zmax) 2949 padding : (float) 2950 increase by this fraction the bounding box 2951 2952 Examples: 2953 - [recosurface.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/advanced/recosurface.py) 2954 2955  2956 """ 2957 if not utils.is_sequence(dims): 2958 dims = (dims, dims, dims) 2959 2960 sdf = vtki.new("SignedDistance") 2961 2962 if len(bounds) == 6: 2963 sdf.SetBounds(bounds) 2964 else: 2965 x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1 = self.bounds() 2966 sdf.SetBounds( 2967 x0 - (x1 - x0) * padding, 2968 x1 + (x1 - x0) * padding, 2969 y0 - (y1 - y0) * padding, 2970 y1 + (y1 - y0) * padding, 2971 z0 - (z1 - z0) * padding, 2972 z1 + (z1 - z0) * padding, 2973 ) 2974 2975 bb = sdf.GetBounds() 2976 if bb[0]==bb[1]: 2977 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero x-range") 2978 if bb[2]==bb[3]: 2979 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero y-range") 2980 if bb[4]==bb[5]: 2981 vedo.logger.warning("reconstruct_surface(): zero z-range") 2982 2983 pd = self.dataset 2984 2985 if pd.GetPointData().GetNormals(): 2986 sdf.SetInputData(pd) 2987 else: 2988 normals = vtki.new("PCANormalEstimation") 2989 normals.SetInputData(pd) 2990 if not sample_size: 2991 sample_size = int(pd.GetNumberOfPoints() / 50) 2992 normals.SetSampleSize(sample_size) 2993 normals.SetNormalOrientationToGraphTraversal() 2994 sdf.SetInputConnection(normals.GetOutputPort()) 2995 # print("Recalculating normals with sample size =", sample_size) 2996 2997 if radius is None: 2998 radius = self.diagonal_size() / (sum(dims) / 3) * 5 2999 # print("Calculating mesh from points with radius =", radius) 3000 3001 sdf.SetRadius(radius) 3002 sdf.SetDimensions(dims) 3003 sdf.Update() 3004 3005 surface = vtki.new("ExtractSurface") 3006 surface.SetRadius(radius * 0.99) 3007 surface.SetHoleFilling(hole_filling) 3008 surface.ComputeNormalsOff() 3009 surface.ComputeGradientsOff() 3010 surface.SetInputConnection(sdf.GetOutputPort()) 3011 surface.Update() 3012 m = vedo.mesh.Mesh(surface.GetOutput(), c=self.color()) 3013 3014 m.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3015 "reconstruct_surface", 3016 parents=[self], 3017 comment=f"#pts {m.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 3018 ) 3019 return m
Surface reconstruction from a scattered cloud of points.
Arguments:
- dims : (int) number of voxels in x, y and z to control precision.
- radius : (float) radius of influence of each point. Smaller values generally improve performance markedly. Note that after the signed distance function is computed, any voxel taking on the value >= radius is presumed to be "unseen" or uninitialized.
- sample_size : (int) if normals are not present they will be calculated using this sample size per point.
- hole_filling : (bool) enables hole filling, this generates separating surfaces between the empty and unseen portions of the volume.
- bounds : (list) region in space in which to perform the sampling in format (xmin,xmax, ymin,ymax, zim, zmax)
- padding : (float) increase by this fraction the bounding box
Examples:
3021 def compute_clustering(self, radius: float) -> Self: 3022 """ 3023 Cluster points in space. The `radius` is the radius of local search. 3024 3025 An array named "ClusterId" is added to `pointdata`. 3026 3027 Examples: 3028 - [clustering.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/basic/clustering.py) 3029 3030  3031 """ 3032 cluster = vtki.new("EuclideanClusterExtraction") 3033 cluster.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3034 cluster.SetExtractionModeToAllClusters() 3035 cluster.SetRadius(radius) 3036 cluster.ColorClustersOn() 3037 cluster.Update() 3038 idsarr = cluster.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetArray("ClusterId") 3039 self.dataset.GetPointData().AddArray(idsarr) 3040 self.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3041 "compute_clustering", parents=[self], comment=f"radius = {radius}" 3042 ) 3043 return self
Cluster points in space. The radius is the radius of local search.
An array named "ClusterId" is added to pointdata.
Examples:
3045 def compute_connections(self, radius, mode=0, regions=(), vrange=(0, 1), seeds=(), angle=0.0) -> Self: 3046 """ 3047 Extracts and/or segments points from a point cloud based on geometric distance measures 3048 (e.g., proximity, normal alignments, etc.) and optional measures such as scalar range. 3049 The default operation is to segment the points into "connected" regions where the connection 3050 is determined by an appropriate distance measure. Each region is given a region id. 3051 3052 Optionally, the filter can output the largest connected region of points; a particular region 3053 (via id specification); those regions that are seeded using a list of input point ids; 3054 or the region of points closest to a specified position. 3055 3056 The key parameter of this filter is the radius defining a sphere around each point which defines 3057 a local neighborhood: any other points in the local neighborhood are assumed connected to the point. 3058 Note that the radius is defined in absolute terms. 3059 3060 Other parameters are used to further qualify what it means to be a neighboring point. 3061 For example, scalar range and/or point normals can be used to further constrain the neighborhood. 3062 Also the extraction mode defines how the filter operates. 3063 By default, all regions are extracted but it is possible to extract particular regions; 3064 the region closest to a seed point; seeded regions; or the largest region found while processing. 3065 By default, all regions are extracted. 3066 3067 On output, all points are labeled with a region number. 3068 However note that the number of input and output points may not be the same: 3069 if not extracting all regions then the output size may be less than the input size. 3070 3071 Arguments: 3072 radius : (float) 3073 variable specifying a local sphere used to define local point neighborhood 3074 mode : (int) 3075 - 0, Extract all regions 3076 - 1, Extract point seeded regions 3077 - 2, Extract largest region 3078 - 3, Test specified regions 3079 - 4, Extract all regions with scalar connectivity 3080 - 5, Extract point seeded regions 3081 regions : (list) 3082 a list of non-negative regions id to extract 3083 vrange : (list) 3084 scalar range to use to extract points based on scalar connectivity 3085 seeds : (list) 3086 a list of non-negative point seed ids 3087 angle : (list) 3088 points are connected if the angle between their normals is 3089 within this angle threshold (expressed in degrees). 3090 """ 3091 # https://vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkConnectedPointsFilter.html 3092 cpf = vtki.new("ConnectedPointsFilter") 3093 cpf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3094 cpf.SetRadius(radius) 3095 if mode == 0: # Extract all regions 3096 pass 3097 3098 elif mode == 1: # Extract point seeded regions 3099 cpf.SetExtractionModeToPointSeededRegions() 3100 for s in seeds: 3101 cpf.AddSeed(s) 3102 3103 elif mode == 2: # Test largest region 3104 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3105 3106 elif mode == 3: # Test specified regions 3107 cpf.SetExtractionModeToSpecifiedRegions() 3108 for r in regions: 3109 cpf.AddSpecifiedRegion(r) 3110 3111 elif mode == 4: # Extract all regions with scalar connectivity 3112 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3113 cpf.ScalarConnectivityOn() 3114 cpf.SetScalarRange(vrange[0], vrange[1]) 3115 3116 elif mode == 5: # Extract point seeded regions 3117 cpf.SetExtractionModeToLargestRegion() 3118 cpf.ScalarConnectivityOn() 3119 cpf.SetScalarRange(vrange[0], vrange[1]) 3120 cpf.AlignedNormalsOn() 3121 cpf.SetNormalAngle(angle) 3122 3123 cpf.Update() 3124 self._update(cpf.GetOutput(), reset_locators=False) 3125 return self
Extracts and/or segments points from a point cloud based on geometric distance measures (e.g., proximity, normal alignments, etc.) and optional measures such as scalar range. The default operation is to segment the points into "connected" regions where the connection is determined by an appropriate distance measure. Each region is given a region id.
Optionally, the filter can output the largest connected region of points; a particular region (via id specification); those regions that are seeded using a list of input point ids; or the region of points closest to a specified position.
The key parameter of this filter is the radius defining a sphere around each point which defines a local neighborhood: any other points in the local neighborhood are assumed connected to the point. Note that the radius is defined in absolute terms.
Other parameters are used to further qualify what it means to be a neighboring point. For example, scalar range and/or point normals can be used to further constrain the neighborhood. Also the extraction mode defines how the filter operates. By default, all regions are extracted but it is possible to extract particular regions; the region closest to a seed point; seeded regions; or the largest region found while processing. By default, all regions are extracted.
On output, all points are labeled with a region number. However note that the number of input and output points may not be the same: if not extracting all regions then the output size may be less than the input size.
Arguments:
- radius : (float) variable specifying a local sphere used to define local point neighborhood
- mode : (int)
- 0, Extract all regions
- 1, Extract point seeded regions
- 2, Extract largest region
- 3, Test specified regions
- 4, Extract all regions with scalar connectivity
- 5, Extract point seeded regions
- regions : (list) a list of non-negative regions id to extract
- vrange : (list) scalar range to use to extract points based on scalar connectivity
- seeds : (list) a list of non-negative point seed ids
- angle : (list) points are connected if the angle between their normals is within this angle threshold (expressed in degrees).
3127 def compute_camera_distance(self) -> np.ndarray: 3128 """ 3129 Calculate the distance from points to the camera. 3130 3131 A pointdata array is created with name 'DistanceToCamera' and returned. 3132 """ 3133 if vedo.plotter_instance and vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 3134 poly = self.dataset 3135 dc = vtki.new("DistanceToCamera") 3136 dc.SetInputData(poly) 3137 dc.SetRenderer(vedo.plotter_instance.renderer) 3138 dc.Update() 3139 self._update(dc.GetOutput(), reset_locators=False) 3140 return self.pointdata["DistanceToCamera"] 3141 return np.array([])
Calculate the distance from points to the camera.
A pointdata array is created with name 'DistanceToCamera' and returned.
3143 def densify(self, target_distance=0.1, nclosest=6, radius=None, niter=1, nmax=None) -> Self: 3144 """ 3145 Return a copy of the cloud with new added points. 3146 The new points are created in such a way that all points in any local neighborhood are 3147 within a target distance of one another. 3148 3149 For each input point, the distance to all points in its neighborhood is computed. 3150 If any of its neighbors is further than the target distance, 3151 the edge connecting the point and its neighbor is bisected and 3152 a new point is inserted at the bisection point. 3153 A single pass is completed once all the input points are visited. 3154 Then the process repeats to the number of iterations. 3155 3156 Examples: 3157 - [densifycloud.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/densifycloud.py) 3158 3159  3160 3161 .. note:: 3162 Points will be created in an iterative fashion until all points in their 3163 local neighborhood are the target distance apart or less. 3164 Note that the process may terminate early due to the 3165 number of iterations. By default the target distance is set to 0.5. 3166 Note that the target_distance should be less than the radius 3167 or nothing will change on output. 3168 3169 .. warning:: 3170 This class can generate a lot of points very quickly. 3171 The maximum number of iterations is by default set to =1.0 for this reason. 3172 Increase the number of iterations very carefully. 3173 Also, `nmax` can be set to limit the explosion of points. 3174 It is also recommended that a N closest neighborhood is used. 3175 3176 """ 3177 src = vtki.new("ProgrammableSource") 3178 opts = self.coordinates 3179 # zeros = np.zeros(3) 3180 3181 def _read_points(): 3182 output = src.GetPolyDataOutput() 3183 points = vtki.vtkPoints() 3184 for p in opts: 3185 # print(p) 3186 # if not np.array_equal(p, zeros): 3187 points.InsertNextPoint(p) 3188 output.SetPoints(points) 3189 3190 src.SetExecuteMethod(_read_points) 3191 3192 dens = vtki.new("DensifyPointCloudFilter") 3193 dens.SetInputConnection(src.GetOutputPort()) 3194 # dens.SetInputData(self.dataset) # this does not work 3195 dens.InterpolateAttributeDataOn() 3196 dens.SetTargetDistance(target_distance) 3197 dens.SetMaximumNumberOfIterations(niter) 3198 if nmax: 3199 dens.SetMaximumNumberOfPoints(nmax) 3200 3201 if radius: 3202 dens.SetNeighborhoodTypeToRadius() 3203 dens.SetRadius(radius) 3204 elif nclosest: 3205 dens.SetNeighborhoodTypeToNClosest() 3206 dens.SetNumberOfClosestPoints(nclosest) 3207 else: 3208 vedo.logger.error("set either radius or nclosest") 3209 raise RuntimeError() 3210 dens.Update() 3211 3212 cld = Points(dens.GetOutput()) 3213 cld.copy_properties_from(self) 3214 cld.interpolate_data_from(self, n=nclosest, radius=radius) 3215 cld.name = "DensifiedCloud" 3216 cld.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3217 "densify", 3218 parents=[self], 3219 c="#e9c46a:", 3220 comment=f"#pts {cld.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}", 3221 ) 3222 return cld
Return a copy of the cloud with new added points. The new points are created in such a way that all points in any local neighborhood are within a target distance of one another.
For each input point, the distance to all points in its neighborhood is computed. If any of its neighbors is further than the target distance, the edge connecting the point and its neighbor is bisected and a new point is inserted at the bisection point. A single pass is completed once all the input points are visited. Then the process repeats to the number of iterations.
Examples:
Points will be created in an iterative fashion until all points in their local neighborhood are the target distance apart or less. Note that the process may terminate early due to the number of iterations. By default the target distance is set to 0.5. Note that the target_distance should be less than the radius or nothing will change on output.
This class can generate a lot of points very quickly.
The maximum number of iterations is by default set to =1.0 for this reason.
Increase the number of iterations very carefully.
Also, nmax can be set to limit the explosion of points.
It is also recommended that a N closest neighborhood is used.
3228 def density( 3229 self, dims=(40, 40, 40), bounds=None, radius=None, compute_gradient=False, locator=None 3230 ) -> "vedo.Volume": 3231 """ 3232 Generate a density field from a point cloud. Input can also be a set of 3D coordinates. 3233 Output is a `Volume`. 3234 3235 The local neighborhood is specified as the `radius` around each sample position (each voxel). 3236 If left to None, the radius is automatically computed as the diagonal of the bounding box 3237 and can be accessed via `vol.metadata["radius"]`. 3238 The density is expressed as the number of counts in the radius search. 3239 3240 Arguments: 3241 dims : (int, list) 3242 number of voxels in x, y and z of the output Volume. 3243 compute_gradient : (bool) 3244 Turn on/off the generation of the gradient vector, 3245 gradient magnitude scalar, and function classification scalar. 3246 By default this is off. Note that this will increase execution time 3247 and the size of the output. (The names of these point data arrays are: 3248 "Gradient", "Gradient Magnitude", and "Classification") 3249 locator : (vtkPointLocator) 3250 can be assigned from a previous call for speed (access it via `object.point_locator`). 3251 3252 Examples: 3253 - [plot_density3d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/pyplot/plot_density3d.py) 3254 3255  3256 """ 3257 pdf = vtki.new("PointDensityFilter") 3258 pdf.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3259 3260 if not utils.is_sequence(dims): 3261 dims = [dims, dims, dims] 3262 3263 if bounds is None: 3264 bounds = list(self.bounds()) 3265 elif len(bounds) == 4: 3266 bounds = [*bounds, 0, 0] 3267 3268 if bounds[5] - bounds[4] == 0 or len(dims) == 2: # its 2D 3269 dims = list(dims) 3270 dims = [dims[0], dims[1], 2] 3271 diag = self.diagonal_size() 3272 bounds[5] = bounds[4] + diag / 1000 3273 pdf.SetModelBounds(bounds) 3274 3275 pdf.SetSampleDimensions(dims) 3276 3277 if locator: 3278 pdf.SetLocator(locator) 3279 3280 pdf.SetDensityEstimateToFixedRadius() 3281 if radius is None: 3282 radius = self.diagonal_size() / 20 3283 pdf.SetRadius(radius) 3284 pdf.SetComputeGradient(compute_gradient) 3285 pdf.Update() 3286 3287 vol = vedo.Volume(pdf.GetOutput()).mode(1) 3288 vol.name = "PointDensity" 3289 vol.metadata["radius"] = radius 3290 vol.locator = pdf.GetLocator() 3291 vol.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3292 "density", parents=[self], comment=f"dims={tuple(vol.dimensions())}" 3293 ) 3294 return vol
Generate a density field from a point cloud. Input can also be a set of 3D coordinates.
Output is a Volume.
The local neighborhood is specified as the radius around each sample position (each voxel).
If left to None, the radius is automatically computed as the diagonal of the bounding box
and can be accessed via vol.metadata["radius"].
The density is expressed as the number of counts in the radius search.
Arguments:
- dims : (int, list) number of voxels in x, y and z of the output Volume.
- compute_gradient : (bool) Turn on/off the generation of the gradient vector, gradient magnitude scalar, and function classification scalar. By default this is off. Note that this will increase execution time and the size of the output. (The names of these point data arrays are: "Gradient", "Gradient Magnitude", and "Classification")
- locator : (vtkPointLocator)
can be assigned from a previous call for speed (access it via
object.point_locator).
Examples:
3297 def tovolume( 3298 self, 3299 kernel="shepard", 3300 radius=None, 3301 n=None, 3302 bounds=None, 3303 null_value=None, 3304 dims=(25, 25, 25), 3305 ) -> "vedo.Volume": 3306 """ 3307 Generate a `Volume` by interpolating a scalar 3308 or vector field which is only known on a scattered set of points or mesh. 3309 Available interpolation kernels are: shepard, gaussian, or linear. 3310 3311 Arguments: 3312 kernel : (str) 3313 interpolation kernel type [shepard] 3314 radius : (float) 3315 radius of the local search 3316 n : (int) 3317 number of point to use for interpolation 3318 bounds : (list) 3319 bounding box of the output Volume object 3320 dims : (list) 3321 dimensions of the output Volume object 3322 null_value : (float) 3323 value to be assigned to invalid points 3324 3325 Examples: 3326 - [interpolate_volume.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/interpolate_volume.py) 3327 3328  3329 """ 3330 if radius is None and not n: 3331 vedo.logger.error("please set either radius or n") 3332 raise RuntimeError 3333 3334 poly = self.dataset 3335 3336 # Create a probe volume 3337 probe = vtki.vtkImageData() 3338 probe.SetDimensions(dims) 3339 if bounds is None: 3340 bounds = self.bounds() 3341 probe.SetOrigin(bounds[0], bounds[2], bounds[4]) 3342 probe.SetSpacing( 3343 (bounds[1] - bounds[0]) / dims[0], 3344 (bounds[3] - bounds[2]) / dims[1], 3345 (bounds[5] - bounds[4]) / dims[2], 3346 ) 3347 3348 if not self.point_locator: 3349 self.point_locator = vtki.new("PointLocator") 3350 self.point_locator.SetDataSet(poly) 3351 self.point_locator.BuildLocator() 3352 3353 if kernel == "shepard": 3354 kern = vtki.new("ShepardKernel") 3355 kern.SetPowerParameter(2) 3356 elif kernel == "gaussian": 3357 kern = vtki.new("GaussianKernel") 3358 elif kernel == "linear": 3359 kern = vtki.new("LinearKernel") 3360 else: 3361 vedo.logger.error("Error in tovolume(), available kernels are:") 3362 vedo.logger.error(" [shepard, gaussian, linear]") 3363 raise RuntimeError() 3364 3365 if radius: 3366 kern.SetRadius(radius) 3367 3368 interpolator = vtki.new("PointInterpolator") 3369 interpolator.SetInputData(probe) 3370 interpolator.SetSourceData(poly) 3371 interpolator.SetKernel(kern) 3372 interpolator.SetLocator(self.point_locator) 3373 3374 if n: 3375 kern.SetNumberOfPoints(n) 3376 kern.SetKernelFootprintToNClosest() 3377 else: 3378 kern.SetRadius(radius) 3379 3380 if null_value is not None: 3381 interpolator.SetNullValue(null_value) 3382 else: 3383 interpolator.SetNullPointsStrategyToClosestPoint() 3384 interpolator.Update() 3385 3386 vol = vedo.Volume(interpolator.GetOutput()) 3387 3388 vol.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3389 "signed_distance", 3390 parents=[self], 3391 comment=f"dims={tuple(vol.dimensions())}", 3392 c="#e9c46a:#0096c7", 3393 ) 3394 return vol
Generate a Volume by interpolating a scalar
or vector field which is only known on a scattered set of points or mesh.
Available interpolation kernels are: shepard, gaussian, or linear.
Arguments:
- kernel : (str) interpolation kernel type [shepard]
- radius : (float) radius of the local search
- n : (int) number of point to use for interpolation
- bounds : (list) bounding box of the output Volume object
- dims : (list) dimensions of the output Volume object
- null_value : (float) value to be assigned to invalid points
Examples:
3397 def generate_segments(self, istart=0, rmax=1e30, niter=3) -> "vedo.shapes.Lines": 3398 """ 3399 Generate a line segments from a set of points. 3400 The algorithm is based on the closest point search. 3401 3402 Returns a `Line` object. 3403 This object contains the a metadata array of used vertex counts in "UsedVertexCount" 3404 and the sum of the length of the segments in "SegmentsLengthSum". 3405 3406 Arguments: 3407 istart : (int) 3408 index of the starting point 3409 rmax : (float) 3410 maximum length of a segment 3411 niter : (int) 3412 number of iterations or passes through the points 3413 3414 Examples: 3415 - [moving_least_squares1D.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/moving_least_squares1D.py) 3416 """ 3417 points = self.coordinates 3418 segments = [] 3419 dists = [] 3420 n = len(points) 3421 used = np.zeros(n, dtype=int) 3422 for _ in range(niter): 3423 i = istart 3424 for _ in range(n): 3425 p = points[i] 3426 ids = self.closest_point(p, n=4, return_point_id=True) 3427 j = ids[1] 3428 if used[j] > 1 or [j, i] in segments: 3429 j = ids[2] 3430 if used[j] > 1: 3431 j = ids[3] 3432 d = np.linalg.norm(p - points[j]) 3433 if used[j] > 1 or used[i] > 1 or d > rmax: 3434 i += 1 3435 if i >= n: 3436 i = 0 3437 continue 3438 used[i] += 1 3439 used[j] += 1 3440 segments.append([i, j]) 3441 dists.append(d) 3442 i = j 3443 segments = np.array(segments, dtype=int) 3444 3445 lines = vedo.shapes.Lines(points[segments], c="k", lw=3) 3446 lines.metadata["UsedVertexCount"] = used 3447 lines.metadata["SegmentsLengthSum"] = np.sum(dists) 3448 lines.pipeline = utils.OperationNode("generate_segments", parents=[self]) 3449 lines.name = "Segments" 3450 return lines
Generate a line segments from a set of points. The algorithm is based on the closest point search.
Returns a Line object.
This object contains the a metadata array of used vertex counts in "UsedVertexCount"
and the sum of the length of the segments in "SegmentsLengthSum".
Arguments:
- istart : (int) index of the starting point
- rmax : (float) maximum length of a segment
- niter : (int) number of iterations or passes through the points
Examples:
3452 def generate_delaunay2d( 3453 self, 3454 mode="scipy", 3455 boundaries=(), 3456 tol=None, 3457 alpha=0.0, 3458 offset=0.0, 3459 transform=None, 3460 ) -> "vedo.mesh.Mesh": 3461 """ 3462 Create a mesh from points in the XY plane. 3463 If `mode='fit'` then the filter computes a best fitting 3464 plane and projects the points onto it. 3465 3466 Check also `generate_mesh()`. 3467 3468 Arguments: 3469 tol : (float) 3470 specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. 3471 This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of the bounding box of the points. 3472 alpha : (float) 3473 for a non-zero alpha value, only edges or triangles contained 3474 within a sphere centered at mesh vertices will be output. 3475 Otherwise, only triangles will be output. 3476 offset : (float) 3477 multiplier to control the size of the initial, bounding Delaunay triangulation. 3478 transform: (LinearTransform, NonLinearTransform) 3479 a transformation which is applied to points to generate a 2D problem. 3480 This maps a 3D dataset into a 2D dataset where triangulation can be done on the XY plane. 3481 The points are transformed and triangulated. 3482 The topology of triangulated points is used as the output topology. 3483 3484 Examples: 3485 - [delaunay2d.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/delaunay2d.py) 3486 3487  3488 """ 3489 plist = self.coordinates.copy() 3490 3491 ######################################################### 3492 if mode == "scipy": 3493 from scipy.spatial import Delaunay as scipy_delaunay 3494 3495 tri = scipy_delaunay(plist[:, 0:2]) 3496 return vedo.mesh.Mesh([plist, tri.simplices]) 3497 ########################################################## 3498 3499 pd = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3500 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 3501 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(plist, dtype=np.float32)) 3502 pd.SetPoints(vpts) 3503 3504 delny = vtki.new("Delaunay2D") 3505 delny.SetInputData(pd) 3506 if tol: 3507 delny.SetTolerance(tol) 3508 delny.SetAlpha(alpha) 3509 delny.SetOffset(offset) 3510 3511 if transform: 3512 delny.SetTransform(transform.T) 3513 elif mode == "fit": 3514 delny.SetProjectionPlaneMode(vtki.get_class("VTK_BEST_FITTING_PLANE")) 3515 elif mode == "xy" and boundaries: 3516 boundary = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3517 boundary.SetPoints(vpts) 3518 cell_array = vtki.vtkCellArray() 3519 for b in boundaries: 3520 cpolygon = vtki.vtkPolygon() 3521 for idd in b: 3522 cpolygon.GetPointIds().InsertNextId(idd) 3523 cell_array.InsertNextCell(cpolygon) 3524 boundary.SetPolys(cell_array) 3525 delny.SetSourceData(boundary) 3526 3527 delny.Update() 3528 3529 msh = vedo.mesh.Mesh(delny.GetOutput()) 3530 msh.name = "Delaunay2D" 3531 msh.clean().lighting("off") 3532 msh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3533 "delaunay2d", 3534 parents=[self], 3535 comment=f"#cells {msh.dataset.GetNumberOfCells()}", 3536 ) 3537 return msh
Create a mesh from points in the XY plane.
If mode='fit' then the filter computes a best fitting
plane and projects the points onto it.
Check also generate_mesh().
Arguments:
- tol : (float) specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of the bounding box of the points.
- alpha : (float) for a non-zero alpha value, only edges or triangles contained within a sphere centered at mesh vertices will be output. Otherwise, only triangles will be output.
- offset : (float) multiplier to control the size of the initial, bounding Delaunay triangulation.
- transform: (LinearTransform, NonLinearTransform) a transformation which is applied to points to generate a 2D problem. This maps a 3D dataset into a 2D dataset where triangulation can be done on the XY plane. The points are transformed and triangulated. The topology of triangulated points is used as the output topology.
Examples:
3539 def generate_voronoi(self, padding=0.0, fit=False, method="vtk") -> "vedo.Mesh": 3540 """ 3541 Generate the 2D Voronoi convex tiling of the input points (z is ignored). 3542 The points are assumed to lie in a plane. The output is a Mesh. Each output cell is a convex polygon. 3543 3544 A cell array named "VoronoiID" is added to the output Mesh. 3545 3546 The 2D Voronoi tessellation is a tiling of space, where each Voronoi tile represents the region nearest 3547 to one of the input points. Voronoi tessellations are important in computational geometry 3548 (and many other fields), and are the dual of Delaunay triangulations. 3549 3550 Thus the triangulation is constructed in the x-y plane, and the z coordinate is ignored 3551 (although carried through to the output). 3552 If you desire to triangulate in a different plane, you can use fit=True. 3553 3554 A brief summary is as follows. Each (generating) input point is associated with 3555 an initial Voronoi tile, which is simply the bounding box of the point set. 3556 A locator is then used to identify nearby points: each neighbor in turn generates a 3557 clipping line positioned halfway between the generating point and the neighboring point, 3558 and orthogonal to the line connecting them. Clips are readily performed by evaluationg the 3559 vertices of the convex Voronoi tile as being on either side (inside,outside) of the clip line. 3560 If two intersections of the Voronoi tile are found, the portion of the tile "outside" the clip 3561 line is discarded, resulting in a new convex, Voronoi tile. As each clip occurs, 3562 the Voronoi "Flower" error metric (the union of error spheres) is compared to the extent of the region 3563 containing the neighboring clip points. The clip region (along with the points contained in it) is grown 3564 by careful expansion (e.g., outward spiraling iterator over all candidate clip points). 3565 When the Voronoi Flower is contained within the clip region, the algorithm terminates and the Voronoi 3566 tile is output. Once complete, it is possible to construct the Delaunay triangulation from the Voronoi 3567 tessellation. Note that topological and geometric information is used to generate a valid triangulation 3568 (e.g., merging points and validating topology). 3569 3570 Arguments: 3571 pts : (list) 3572 list of input points. 3573 padding : (float) 3574 padding distance. The default is 0. 3575 fit : (bool) 3576 detect automatically the best fitting plane. The default is False. 3577 3578 Examples: 3579 - [voronoi1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/voronoi1.py) 3580 3581  3582 3583 - [voronoi2.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/voronoi2.py) 3584 3585  3586 """ 3587 pts = self.coordinates 3588 3589 if method == "scipy": 3590 from scipy.spatial import Voronoi as scipy_voronoi 3591 3592 pts = np.asarray(pts)[:, (0, 1)] 3593 vor = scipy_voronoi(pts) 3594 regs = [] # filter out invalid indices 3595 for r in vor.regions: 3596 flag = True 3597 for x in r: 3598 if x < 0: 3599 flag = False 3600 break 3601 if flag and len(r) > 0: 3602 regs.append(r) 3603 3604 m = vedo.Mesh([vor.vertices, regs]) 3605 m.celldata["VoronoiID"] = np.array(list(range(len(regs)))).astype(int) 3606 3607 elif method == "vtk": 3608 vor = vtki.new("Voronoi2D") 3609 if isinstance(pts, Points): 3610 vor.SetInputData(pts) 3611 else: 3612 pts = np.asarray(pts) 3613 if pts.shape[1] == 2: 3614 pts = np.c_[pts, np.zeros(len(pts))] 3615 pd = vtki.vtkPolyData() 3616 vpts = vtki.vtkPoints() 3617 vpts.SetData(utils.numpy2vtk(pts, dtype=np.float32)) 3618 pd.SetPoints(vpts) 3619 vor.SetInputData(pd) 3620 vor.SetPadding(padding) 3621 vor.SetGenerateScalarsToPointIds() 3622 if fit: 3623 vor.SetProjectionPlaneModeToBestFittingPlane() 3624 else: 3625 vor.SetProjectionPlaneModeToXYPlane() 3626 vor.Update() 3627 poly = vor.GetOutput() 3628 arr = poly.GetCellData().GetArray(0) 3629 if arr: 3630 arr.SetName("VoronoiID") 3631 m = vedo.Mesh(poly, c="orange5") 3632 3633 else: 3634 vedo.logger.error(f"Unknown method {method} in voronoi()") 3635 raise RuntimeError 3636 3637 m.lw(2).lighting("off").wireframe() 3638 m.name = "Voronoi" 3639 return m
Generate the 2D Voronoi convex tiling of the input points (z is ignored). The points are assumed to lie in a plane. The output is a Mesh. Each output cell is a convex polygon.
A cell array named "VoronoiID" is added to the output Mesh.
The 2D Voronoi tessellation is a tiling of space, where each Voronoi tile represents the region nearest to one of the input points. Voronoi tessellations are important in computational geometry (and many other fields), and are the dual of Delaunay triangulations.
Thus the triangulation is constructed in the x-y plane, and the z coordinate is ignored (although carried through to the output). If you desire to triangulate in a different plane, you can use fit=True.
A brief summary is as follows. Each (generating) input point is associated with an initial Voronoi tile, which is simply the bounding box of the point set. A locator is then used to identify nearby points: each neighbor in turn generates a clipping line positioned halfway between the generating point and the neighboring point, and orthogonal to the line connecting them. Clips are readily performed by evaluationg the vertices of the convex Voronoi tile as being on either side (inside,outside) of the clip line. If two intersections of the Voronoi tile are found, the portion of the tile "outside" the clip line is discarded, resulting in a new convex, Voronoi tile. As each clip occurs, the Voronoi "Flower" error metric (the union of error spheres) is compared to the extent of the region containing the neighboring clip points. The clip region (along with the points contained in it) is grown by careful expansion (e.g., outward spiraling iterator over all candidate clip points). When the Voronoi Flower is contained within the clip region, the algorithm terminates and the Voronoi tile is output. Once complete, it is possible to construct the Delaunay triangulation from the Voronoi tessellation. Note that topological and geometric information is used to generate a valid triangulation (e.g., merging points and validating topology).
Arguments:
- pts : (list) list of input points.
- padding : (float) padding distance. The default is 0.
- fit : (bool) detect automatically the best fitting plane. The default is False.
Examples:
3642 def generate_delaunay3d(self, radius=0, tol=None) -> "vedo.TetMesh": 3643 """ 3644 Create 3D Delaunay triangulation of input points. 3645 3646 Arguments: 3647 radius : (float) 3648 specify distance (or "alpha") value to control output. 3649 For a non-zero values, only tetra contained within the circumsphere 3650 will be output. 3651 tol : (float) 3652 Specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. 3653 This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of 3654 the bounding box of the points. 3655 """ 3656 deln = vtki.new("Delaunay3D") 3657 deln.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3658 deln.SetAlpha(radius) 3659 deln.AlphaTetsOn() 3660 deln.AlphaTrisOff() 3661 deln.AlphaLinesOff() 3662 deln.AlphaVertsOff() 3663 deln.BoundingTriangulationOff() 3664 if tol: 3665 deln.SetTolerance(tol) 3666 deln.Update() 3667 m = vedo.TetMesh(deln.GetOutput()) 3668 m.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 3669 "generate_delaunay3d", c="#e9c46a:#edabab", parents=[self], 3670 ) 3671 m.name = "Delaunay3D" 3672 return m
Create 3D Delaunay triangulation of input points.
Arguments:
- radius : (float) specify distance (or "alpha") value to control output. For a non-zero values, only tetra contained within the circumsphere will be output.
- tol : (float) Specify a tolerance to control discarding of closely spaced points. This tolerance is specified as a fraction of the diagonal length of the bounding box of the points.
3675 def visible_points(self, area=(), tol=None, invert=False) -> Union[Self, None]: 3676 """ 3677 Extract points based on whether they are visible or not. 3678 Visibility is determined by accessing the z-buffer of a rendering window. 3679 The position of each input point is converted into display coordinates, 3680 and then the z-value at that point is obtained. 3681 If within the user-specified tolerance, the point is considered visible. 3682 Associated data attributes are passed to the output as well. 3683 3684 This filter also allows you to specify a rectangular window in display (pixel) 3685 coordinates in which the visible points must lie. 3686 3687 Arguments: 3688 area : (list) 3689 specify a rectangular region as (xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax) 3690 tol : (float) 3691 a tolerance in normalized display coordinate system 3692 invert : (bool) 3693 select invisible points instead. 3694 3695 Example: 3696 ```python 3697 from vedo import Ellipsoid, show 3698 s = Ellipsoid().rotate_y(30) 3699 3700 # Camera options: pos, focal_point, viewup, distance 3701 camopts = dict(pos=(0,0,25), focal_point=(0,0,0)) 3702 show(s, camera=camopts, offscreen=True) 3703 3704 m = s.visible_points() 3705 # print('visible pts:', m.vertices) # numpy array 3706 show(m, new=True, axes=1).close() # optionally draw result in a new window 3707 ``` 3708  3709 """ 3710 svp = vtki.new("SelectVisiblePoints") 3711 svp.SetInputData(self.dataset) 3712 3713 ren = None 3714 if vedo.plotter_instance: 3715 if vedo.plotter_instance.renderer: 3716 ren = vedo.plotter_instance.renderer 3717 svp.SetRenderer(ren) 3718 if not ren: 3719 vedo.logger.warning( 3720 "visible_points() can only be used after a rendering step" 3721 ) 3722 return None 3723 3724 if len(area) == 2: 3725 area = utils.flatten(area) 3726 if len(area) == 4: 3727 # specify a rectangular region 3728 svp.SetSelection(area[0], area[1], area[2], area[3]) 3729 if tol is not None: 3730 svp.SetTolerance(tol) 3731 if invert: 3732 svp.SelectInvisibleOn() 3733 svp.Update() 3734 3735 m = Points(svp.GetOutput()) 3736 m.name = "VisiblePoints" 3737 return m
Extract points based on whether they are visible or not. Visibility is determined by accessing the z-buffer of a rendering window. The position of each input point is converted into display coordinates, and then the z-value at that point is obtained. If within the user-specified tolerance, the point is considered visible. Associated data attributes are passed to the output as well.
This filter also allows you to specify a rectangular window in display (pixel) coordinates in which the visible points must lie.
Arguments:
- area : (list) specify a rectangular region as (xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax)
- tol : (float) a tolerance in normalized display coordinate system
- invert : (bool) select invisible points instead.
Example:
from vedo import Ellipsoid, show s = Ellipsoid().rotate_y(30) # Camera options: pos, focal_point, viewup, distance camopts = dict(pos=(0,0,25), focal_point=(0,0,0)) show(s, camera=camopts, offscreen=True) m = s.visible_points() # print('visible pts:', m.vertices) # numpy array show(m, new=True, axes=1).close() # optionally draw result in a new window
Inherited Members
- vedo.visual.PointsVisual
- clone2d
- copy_properties_from
- color
- c
- alpha
- lut_color_at
- opacity
- force_opaque
- force_translucent
- point_size
- ps
- render_points_as_spheres
- lighting
- point_blurring
- cellcolors
- pointcolors
- cmap
- add_trail
- update_trail
- add_shadow
- update_shadows
- labels
- labels2d
- legend
- flagpole
- flagpost
- caption
- vedo.visual.CommonVisual
- LUT
- scalar_range
- add_observer
- invoke_event
- show
- thumbnail
- pickable
- use_bounds
- draggable
- on
- off
- toggle
- add_scalarbar
- add_scalarbar3d
- vedo.core.PointAlgorithms
- apply_transform
- apply_transform_from_actor
- pos
- shift
- x
- y
- z
- rotate
- rotate_x
- rotate_y
- rotate_z
- reorient
- scale
- vedo.core.CommonAlgorithms
- pointdata
- celldata
- metadata
- rename
- memory_address
- memory_size
- modified
- box
- update_dataset
- bounds
- xbounds
- ybounds
- zbounds
- diagonal_size
- average_size
- center_of_mass
- copy_data_from
- inputdata
- npoints
- nvertices
- ncells
- cell_centers
- lines
- lines_as_flat_array
- mark_boundaries
- find_cells_in_bounds
- find_cells_along_line
- find_cells_along_plane
- keep_cell_types
- map_cells_to_points
- vertices
- points
- coordinates
- cells_as_flat_array
- cells
- cell_edge_neighbors
- map_points_to_cells
- resample_data_from
- interpolate_data_from
- add_ids
- gradient
- divergence
- vorticity
- probe
- compute_cell_size
- generate_random_data
- integrate_data
- write
- tomesh
- signed_distance
- unsigned_distance
- smooth_data
- compute_streamlines
443def Point(pos=(0, 0, 0), r=12, c="red", alpha=1.0) -> Self: 444 """ 445 Create a simple point in space. 446 447 .. note:: if you are creating many points you should use class `Points` instead! 448 """ 449 pt = Points([[0,0,0]], r, c, alpha).pos(pos) 450 pt.name = "Point" 451 return pt
Create a simple point in space.
if you are creating many points you should use class Points instead!
43def merge(*meshs, flag=False) -> Union["vedo.Mesh", "vedo.Points", None]: 44 """ 45 Build a new Mesh (or Points) formed by the fusion of the inputs. 46 47 Similar to Assembly, but in this case the input objects become a single entity. 48 49 To keep track of the original identities of the inputs you can set `flag=True`. 50 In this case a `pointdata` array of ids is added to the output with name "OriginalMeshID". 51 52 Examples: 53 - [warp1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/warp1.py) 54 55  56 57 - [value_iteration.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/value_iteration.py) 58 59 """ 60 objs = [a for a in utils.flatten(meshs) if a] 61 62 if not objs: 63 return None 64 65 idarr = [] 66 polyapp = vtki.new("AppendPolyData") 67 for i, ob in enumerate(objs): 68 polyapp.AddInputData(ob.dataset) 69 if flag: 70 idarr += [i] * ob.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints() 71 polyapp.Update() 72 mpoly = polyapp.GetOutput() 73 74 if flag: 75 varr = utils.numpy2vtk(idarr, dtype=np.uint16, name="OriginalMeshID") 76 mpoly.GetPointData().AddArray(varr) 77 78 has_mesh = False 79 for ob in objs: 80 if isinstance(ob, vedo.Mesh): 81 has_mesh = True 82 break 83 84 if has_mesh: 85 msh = vedo.Mesh(mpoly) 86 else: 87 msh = Points(mpoly) # type: ignore 88 89 msh.copy_properties_from(objs[0]) 90 91 msh.pipeline = utils.OperationNode( 92 "merge", parents=objs, comment=f"#pts {msh.dataset.GetNumberOfPoints()}" 93 ) 94 return msh
Build a new Mesh (or Points) formed by the fusion of the inputs.
Similar to Assembly, but in this case the input objects become a single entity.
To keep track of the original identities of the inputs you can set flag=True.
In this case a pointdata array of ids is added to the output with name "OriginalMeshID".
Examples:
137def fit_line(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"]) -> "vedo.shapes.Line": 138 """ 139 Fits a line through points. 140 141 Extra info is stored in `Line.slope`, `Line.center`, `Line.variances`. 142 143 Examples: 144 - [fitline.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/fitline.py) 145 146  147 """ 148 if isinstance(points, Points): 149 points = points.coordinates 150 data = np.asarray(points) 151 datamean = data.mean(axis=0) 152 _, dd, vv = np.linalg.svd(data - datamean) 153 vv = vv[0] / np.linalg.norm(vv[0]) 154 # vv contains the first principal component, i.e. the direction 155 # vector of the best fit line in the least squares sense. 156 xyz_min = data.min(axis=0) 157 xyz_max = data.max(axis=0) 158 a = np.linalg.norm(xyz_min - datamean) 159 b = np.linalg.norm(xyz_max - datamean) 160 p1 = datamean - a * vv 161 p2 = datamean + b * vv 162 line = vedo.shapes.Line(p1, p2, lw=1) 163 line.slope = vv 164 line.center = datamean 165 line.variances = dd 166 return line
Fits a line through points.
Extra info is stored in Line.slope, Line.center, Line.variances.
Examples:
169def fit_circle(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"]) -> tuple: 170 """ 171 Fits a circle through a set of 3D points, with a very fast non-iterative method. 172 173 Returns the tuple `(center, radius, normal_to_circle)`. 174 175 .. warning:: 176 trying to fit s-shaped points will inevitably lead to instabilities and 177 circles of small radius. 178 179 References: 180 *J.F. Crawford, Nucl. Instr. Meth. 211, 1983, 223-225.* 181 """ 182 if isinstance(points, Points): 183 points = points.coordinates 184 data = np.asarray(points) 185 186 offs = data.mean(axis=0) 187 data, n0 = _rotate_points(data - offs) 188 189 xi = data[:, 0] 190 yi = data[:, 1] 191 192 x = sum(xi) 193 xi2 = xi * xi 194 xx = sum(xi2) 195 xxx = sum(xi2 * xi) 196 197 y = sum(yi) 198 yi2 = yi * yi 199 yy = sum(yi2) 200 yyy = sum(yi2 * yi) 201 202 xiyi = xi * yi 203 xy = sum(xiyi) 204 xyy = sum(xiyi * yi) 205 xxy = sum(xi * xiyi) 206 207 N = len(xi) 208 k = (xx + yy) / N 209 210 a1 = xx - x * x / N 211 b1 = xy - x * y / N 212 c1 = 0.5 * (xxx + xyy - x * k) 213 214 a2 = xy - x * y / N 215 b2 = yy - y * y / N 216 c2 = 0.5 * (xxy + yyy - y * k) 217 218 d = a2 * b1 - a1 * b2 219 if not d: 220 return offs, 0, n0 221 x0 = (b1 * c2 - b2 * c1) / d 222 y0 = (c1 - a1 * x0) / b1 223 224 R = np.sqrt(x0 * x0 + y0 * y0 - 1 / N * (2 * x0 * x + 2 * y0 * y - xx - yy)) 225 226 c, _ = _rotate_points([x0, y0, 0], (0, 0, 1), n0) 227 228 return c[0] + offs, R, n0
Fits a circle through a set of 3D points, with a very fast non-iterative method.
Returns the tuple (center, radius, normal_to_circle).
trying to fit s-shaped points will inevitably lead to instabilities and circles of small radius.
References:
J.F. Crawford, Nucl. Instr. Meth. 211, 1983, 223-225.
231def fit_plane(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"], signed=False) -> "vedo.shapes.Plane": 232 """ 233 Fits a plane to a set of points. 234 235 Extra info is stored in `Plane.normal`, `Plane.center`, `Plane.variance`. 236 237 Arguments: 238 signed : (bool) 239 if True flip sign of the normal based on the ordering of the points 240 241 Examples: 242 - [fitline.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/advanced/fitline.py) 243 244  245 """ 246 if isinstance(points, Points): 247 points = points.coordinates 248 data = np.asarray(points) 249 datamean = data.mean(axis=0) 250 pts = data - datamean 251 res = np.linalg.svd(pts) 252 dd, vv = res[1], res[2] 253 n = np.cross(vv[0], vv[1]) 254 if signed: 255 v = np.zeros_like(pts) 256 for i in range(len(pts) - 1): 257 vi = np.cross(pts[i], pts[i + 1]) 258 v[i] = vi / np.linalg.norm(vi) 259 ns = np.mean(v, axis=0) # normal to the points plane 260 if np.dot(n, ns) < 0: 261 n = -n 262 xyz_min = data.min(axis=0) 263 xyz_max = data.max(axis=0) 264 s = np.linalg.norm(xyz_max - xyz_min) 265 pla = vedo.shapes.Plane(datamean, n, s=[s, s]) 266 pla.variance = dd[2] 267 pla.name = "FitPlane" 268 return pla
Fits a plane to a set of points.
Extra info is stored in Plane.normal, Plane.center, Plane.variance.
Arguments:
- signed : (bool) if True flip sign of the normal based on the ordering of the points
Examples:
271def fit_sphere(coords: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"]) -> "vedo.shapes.Sphere": 272 """ 273 Fits a sphere to a set of points. 274 275 Extra info is stored in `Sphere.radius`, `Sphere.center`, `Sphere.residue`. 276 277 Examples: 278 - [fitspheres1.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/fitspheres1.py) 279 280  281 """ 282 if isinstance(coords, Points): 283 coords = coords.coordinates 284 coords = np.array(coords) 285 n = len(coords) 286 A = np.zeros((n, 4)) 287 A[:, :-1] = coords * 2 288 A[:, 3] = 1 289 f = np.zeros((n, 1)) 290 x = coords[:, 0] 291 y = coords[:, 1] 292 z = coords[:, 2] 293 f[:, 0] = x * x + y * y + z * z 294 try: 295 C, residue, rank, _ = np.linalg.lstsq(A, f, rcond=-1) # solve AC=f 296 except: 297 C, residue, rank, _ = np.linalg.lstsq(A, f) # solve AC=f 298 if rank < 4: 299 return None 300 t = (C[0] * C[0]) + (C[1] * C[1]) + (C[2] * C[2]) + C[3] 301 radius = np.sqrt(t)[0] 302 center = np.array([C[0][0], C[1][0], C[2][0]]) 303 if len(residue) > 0: 304 residue = np.sqrt(residue[0]) / n 305 else: 306 residue = 0 307 sph = vedo.shapes.Sphere(center, radius, c=(1, 0, 0)).wireframe(1) 308 sph.radius = radius 309 sph.center = center 310 sph.residue = residue 311 sph.name = "FitSphere" 312 return sph
Fits a sphere to a set of points.
Extra info is stored in Sphere.radius, Sphere.center, Sphere.residue.
Examples:
315def pca_ellipse(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"], pvalue=0.673, res=60) -> Union["vedo.shapes.Circle", None]: 316 """ 317 Create the oriented 2D ellipse that contains the fraction `pvalue` of points. 318 PCA (Principal Component Analysis) is used to compute the ellipse orientation. 319 320 Parameter `pvalue` sets the specified fraction of points inside the ellipse. 321 Normalized directions are stored in `ellipse.axis1`, `ellipse.axis2`. 322 Axes sizes are stored in `ellipse.va`, `ellipse.vb` 323 324 Arguments: 325 pvalue : (float) 326 ellipse will include this fraction of points 327 res : (int) 328 resolution of the ellipse 329 330 Examples: 331 - [pca_ellipse.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/pca_ellipse.py) 332 - [histo_pca.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/pyplot/histo_pca.py) 333 334  335 """ 336 from scipy.stats import f 337 338 if isinstance(points, Points): 339 coords = points.coordinates 340 else: 341 coords = points 342 if len(coords) < 4: 343 vedo.logger.warning("in pca_ellipse(), there are not enough points!") 344 return None 345 346 P = np.array(coords, dtype=float)[:, (0, 1)] 347 cov = np.cov(P, rowvar=0) # type: ignore 348 _, s, R = np.linalg.svd(cov) # singular value decomposition 349 p, n = s.size, P.shape[0] 350 fppf = f.ppf(pvalue, p, n - p) # f % point function 351 u = np.sqrt(s * fppf / 2) * 2 # semi-axes (largest first) 352 ua, ub = u 353 center = utils.make3d(np.mean(P, axis=0)) # centroid of the ellipse 354 355 t = LinearTransform(R.T * u).translate(center) 356 elli = vedo.shapes.Circle(alpha=0.75, res=res) 357 elli.apply_transform(t) 358 elli.properties.LightingOff() 359 360 elli.pvalue = pvalue 361 elli.center = np.array([center[0], center[1], 0]) 362 elli.nr_of_points = n 363 elli.va = ua 364 elli.vb = ub 365 366 # we subtract center because it's in t 367 elli.axis1 = t.move([1, 0, 0]) - center 368 elli.axis2 = t.move([0, 1, 0]) - center 369 370 elli.axis1 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis1) 371 elli.axis2 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis2) 372 elli.name = "PCAEllipse" 373 return elli
Create the oriented 2D ellipse that contains the fraction pvalue of points.
PCA (Principal Component Analysis) is used to compute the ellipse orientation.
Parameter pvalue sets the specified fraction of points inside the ellipse.
Normalized directions are stored in ellipse.axis1, ellipse.axis2.
Axes sizes are stored in ellipse.va, ellipse.vb
Arguments:
- pvalue : (float) ellipse will include this fraction of points
- res : (int) resolution of the ellipse
Examples:
376def pca_ellipsoid(points: Union[np.ndarray, "vedo.Points"], pvalue=0.673, res=24) -> Union["vedo.shapes.Ellipsoid", None]: 377 """ 378 Create the oriented ellipsoid that contains the fraction `pvalue` of points. 379 PCA (Principal Component Analysis) is used to compute the ellipsoid orientation. 380 381 Axes sizes can be accessed in `ellips.va`, `ellips.vb`, `ellips.vc`, 382 normalized directions are stored in `ellips.axis1`, `ellips.axis2` and `ellips.axis3`. 383 Center of mass is stored in `ellips.center`. 384 385 Asphericity can be accessed in `ellips.asphericity()` and ellips.asphericity_error(). 386 A value of 0 means a perfect sphere. 387 388 Arguments: 389 pvalue : (float) 390 ellipsoid will include this fraction of points 391 392 Examples: 393 [pca_ellipsoid.py](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/basic/pca_ellipsoid.py) 394 395  396 397 See also: 398 `pca_ellipse()` for a 2D ellipse. 399 """ 400 from scipy.stats import f 401 402 if isinstance(points, Points): 403 coords = points.coordinates 404 else: 405 coords = points 406 if len(coords) < 4: 407 vedo.logger.warning("in pca_ellipsoid(), not enough input points!") 408 return None 409 410 P = np.array(coords, ndmin=2, dtype=float) 411 cov = np.cov(P, rowvar=0) # type: ignore 412 _, s, R = np.linalg.svd(cov) # singular value decomposition 413 p, n = s.size, P.shape[0] 414 fppf = f.ppf(pvalue, p, n-p)*(n-1)*p*(n+1)/n/(n-p) # f % point function 415 u = np.sqrt(s*fppf) 416 ua, ub, uc = u # semi-axes (largest first) 417 center = np.mean(P, axis=0) # centroid of the hyperellipsoid 418 419 t = LinearTransform(R.T * u).translate(center) 420 elli = vedo.shapes.Ellipsoid((0,0,0), (1,0,0), (0,1,0), (0,0,1), res=res) 421 elli.apply_transform(t) 422 elli.alpha(0.25) 423 elli.properties.LightingOff() 424 425 elli.pvalue = pvalue 426 elli.nr_of_points = n 427 elli.center = center 428 elli.va = ua 429 elli.vb = ub 430 elli.vc = uc 431 # we subtract center because it's in t 432 elli.axis1 = np.array(t.move([1, 0, 0])) - center 433 elli.axis2 = np.array(t.move([0, 1, 0])) - center 434 elli.axis3 = np.array(t.move([0, 0, 1])) - center 435 elli.axis1 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis1) 436 elli.axis2 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis2) 437 elli.axis3 /= np.linalg.norm(elli.axis3) 438 elli.name = "PCAEllipsoid" 439 return elli
Create the oriented ellipsoid that contains the fraction pvalue of points.
PCA (Principal Component Analysis) is used to compute the ellipsoid orientation.
Axes sizes can be accessed in ellips.va, ellips.vb, ellips.vc,
normalized directions are stored in ellips.axis1, ellips.axis2 and ellips.axis3.
Center of mass is stored in ellips.center.
Asphericity can be accessed in ellips.asphericity() and ellips.asphericity_error().
A value of 0 means a perfect sphere.
Arguments:
- pvalue : (float) ellipsoid will include this fraction of points
Examples:

See also:
pca_ellipse()for a 2D ellipse.



































